Deck 2: Perspectives in Sociological Social Psychology
ملء الشاشة (f)
سؤال
Match the term to its definition by filling in the letter before the term in the appropriate blank.
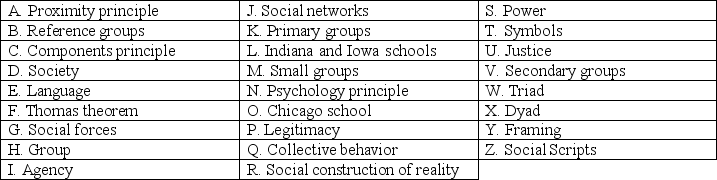 ____ Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how individuals internalize proximal experiences.
____ Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how individuals internalize proximal experiences.
____ A perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on understanding the social processes involved in a given situation rather than on trying to quantify and predict people's thoughts,feelings,and behavior.
____ The action or behavior of people in groups or crowds.
____ Within the social structure and personality perspective,the ability to identify the elements or components of society most likely to affect a given attitude or behavior.
____ A two-person group.
____ Interactions that involve more than one person.
____ Perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on the quantitative study of social interaction processes because of the stable nature of social life.
____ The process by which individuals transform the meaning of a situation using basic cognitive structures provided by society.
____ Perceptions that a social arrangement or distribution is fair.
____ Theorem stating that when people define situations as real,the consequences of those situations become real.
____ A series of symbols that can be combined in various ways to create new meanings.
____ The perception that a social arrangement or position is the way that things should be.
____ The ability to obtain what we desire in a group despite resistance.
____ People we are close to and interact with regularly.
____ Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how people are affected by social structure through their immediate social environments.
____ People we look to as a source of standards and identity.
____ People we affiliate with to achieve common goals or meet common needs.
____ Two or more persons (generally,not more than 20)engaged in or capable of face-to-face interaction.
____ Any way in which society compels individuals to act in accordance with an external norm,rule,or demand.
____ A series of relationships between individuals and groups.[
____ In symbolic interactionism,the network of interaction between people.
_____ The appropriate thoughts,feelings,and behaviors that should be displayed in a particular social frame.
____ Anything that has a similar meaning for two or more individuals.
____ A three-person group.
____ The ability to act and think independent of the constraints imposed by social conditions.
____ The process by which we use symbols and language to give meaning and value to objects and people.
 ____ Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how individuals internalize proximal experiences.
____ Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how individuals internalize proximal experiences.____ A perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on understanding the social processes involved in a given situation rather than on trying to quantify and predict people's thoughts,feelings,and behavior.
____ The action or behavior of people in groups or crowds.
____ Within the social structure and personality perspective,the ability to identify the elements or components of society most likely to affect a given attitude or behavior.
____ A two-person group.
____ Interactions that involve more than one person.
____ Perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on the quantitative study of social interaction processes because of the stable nature of social life.
____ The process by which individuals transform the meaning of a situation using basic cognitive structures provided by society.
____ Perceptions that a social arrangement or distribution is fair.
____ Theorem stating that when people define situations as real,the consequences of those situations become real.
____ A series of symbols that can be combined in various ways to create new meanings.
____ The perception that a social arrangement or position is the way that things should be.
____ The ability to obtain what we desire in a group despite resistance.
____ People we are close to and interact with regularly.
____ Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how people are affected by social structure through their immediate social environments.
____ People we look to as a source of standards and identity.
____ People we affiliate with to achieve common goals or meet common needs.
____ Two or more persons (generally,not more than 20)engaged in or capable of face-to-face interaction.
____ Any way in which society compels individuals to act in accordance with an external norm,rule,or demand.
____ A series of relationships between individuals and groups.[
____ In symbolic interactionism,the network of interaction between people.
_____ The appropriate thoughts,feelings,and behaviors that should be displayed in a particular social frame.
____ Anything that has a similar meaning for two or more individuals.
____ A three-person group.
____ The ability to act and think independent of the constraints imposed by social conditions.
____ The process by which we use symbols and language to give meaning and value to objects and people.
استخدم زر المسافة أو 
 لقلب البطاقة.
لقلب البطاقة.
سؤال
Which social psychologist is most associated with the concepts of dyads and triads?
A)Emile Durkheim
B)Auguste Comte
C)Herbert Blumer
D)Georg Simmel
A)Emile Durkheim
B)Auguste Comte
C)Herbert Blumer
D)Georg Simmel
سؤال
The development of symbolic interactionism stems from which philosophical tradition or traditions?
A)French philosophy
B)German economic analysis
C)American pragmatism
D)Austrian theory
A)French philosophy
B)German economic analysis
C)American pragmatism
D)Austrian theory
سؤال
Terence has started to believe that a friend at work is really a spy from another company,leading him to avoid interactions with this person as much as possible.He treats all interactions with her as suspect and is reluctant to share any work-related information with her.Which of the following principles,theorems,or concepts best explains Terence's behavior?
A)the components principle of the social structure and personality perspective
B)the Thomas theorem
C)the Peter principle
D)the group processes concept of legitimacy
A)the components principle of the social structure and personality perspective
B)the Thomas theorem
C)the Peter principle
D)the group processes concept of legitimacy
سؤال
Read the vignette and answer the questions that follow.
When Malcolm started working at the local print shop,he got along with everyone.He was a supervisor but always tried to stay friends with the people who worked for him.Soon after joining the shop,a new supervisor,Ginny,was hired to manage the shipping department.One day Malcolm heard Ginny use a racial slur.Then Malcolm started noticing other things about her behavior.He noticed that Ginny would eat only with people of her own race and gender,for that matter.He heard her make another racist remark.He ignored her as best he could,sharing his concerns with coworkers and questioning whether a racist should be managing other people.Malcolm discussed Ginny's behavior with his supervisor but she did not see enough evidence of racism to do anything about it.
What type of group is depicted in the vignette?
A)primary
B)secondary
C)tertiary
D)reference
When Malcolm started working at the local print shop,he got along with everyone.He was a supervisor but always tried to stay friends with the people who worked for him.Soon after joining the shop,a new supervisor,Ginny,was hired to manage the shipping department.One day Malcolm heard Ginny use a racial slur.Then Malcolm started noticing other things about her behavior.He noticed that Ginny would eat only with people of her own race and gender,for that matter.He heard her make another racist remark.He ignored her as best he could,sharing his concerns with coworkers and questioning whether a racist should be managing other people.Malcolm discussed Ginny's behavior with his supervisor but she did not see enough evidence of racism to do anything about it.
What type of group is depicted in the vignette?
A)primary
B)secondary
C)tertiary
D)reference
سؤال
After Donna cheated on her most recent exam,she started to feel a sense of guilt,making her reconsider whether she will cheat again.Donna's feelings of guilt can be considered a __________,according to the social structure and personality perspective,leading her to rethink her future behaviors.
A)social more
B)social norm
C)social force
D)social fear
A)social more
B)social norm
C)social force
D)social fear
سؤال
Professor Swanson is studying the meaning of "goodness" using a survey of public attitudes toward the topic.Which school,or schools,of symbolic interaction is she most likely using in her research?
A)the Chicago school
B)the Indiana and Iowa schools
C)the Swanson school
D)the sociological social psychology school
A)the Chicago school
B)the Indiana and Iowa schools
C)the Swanson school
D)the sociological social psychology school
سؤال
Networks are important to the study of the effects of society on individuals' thoughts,feelings,and behaviors because __________.
A)they provide important links between people
B)they give people more friends
C)they provide ways of managing life's problems
D)they give people more prestigious jobs
A)they provide important links between people
B)they give people more friends
C)they provide ways of managing life's problems
D)they give people more prestigious jobs
سؤال
Read the vignette and answer the questions that follow.
When Malcolm started working at the local print shop,he got along with everyone.He was a supervisor but always tried to stay friends with the people who worked for him.Soon after joining the shop,a new supervisor,Ginny,was hired to manage the shipping department.One day Malcolm heard Ginny use a racial slur.Then Malcolm started noticing other things about her behavior.He noticed that Ginny would eat only with people of her own race and gender,for that matter.He heard her make another racist remark.He ignored her as best he could,sharing his concerns with coworkers and questioning whether a racist should be managing other people.Malcolm discussed Ginny's behavior with his supervisor but she did not see enough evidence of racism to do anything about it.
What component of the group processes perspective is most evident in Malcolm's belief that Ginny should not be a supervisor?
A)power
B)status
C)justice
D)legitimacy
When Malcolm started working at the local print shop,he got along with everyone.He was a supervisor but always tried to stay friends with the people who worked for him.Soon after joining the shop,a new supervisor,Ginny,was hired to manage the shipping department.One day Malcolm heard Ginny use a racial slur.Then Malcolm started noticing other things about her behavior.He noticed that Ginny would eat only with people of her own race and gender,for that matter.He heard her make another racist remark.He ignored her as best he could,sharing his concerns with coworkers and questioning whether a racist should be managing other people.Malcolm discussed Ginny's behavior with his supervisor but she did not see enough evidence of racism to do anything about it.
What component of the group processes perspective is most evident in Malcolm's belief that Ginny should not be a supervisor?
A)power
B)status
C)justice
D)legitimacy
سؤال
Which of the following are considered major dimensions of group processes?
A)power and justice
B)justice and legitimacy
C)legitimacy and power
D)power,justice,and legitimacy
A)power and justice
B)justice and legitimacy
C)legitimacy and power
D)power,justice,and legitimacy
سؤال
Who coined the expression "symbolic interaction"?
A)Emile Durkheim
B)Herbert Blumer
C)Auguste Comte
D)George Herbert Mead
A)Emile Durkheim
B)Herbert Blumer
C)Auguste Comte
D)George Herbert Mead
سؤال
Socioeconomic status (social class),race or ethnicity,gender,age,and sexuality all relate to which principle of the social structure and personality perspective?
A)the components principle
B)the proximity principle
C)the psychology principle
D)the Peter principle
A)the components principle
B)the proximity principle
C)the psychology principle
D)the Peter principle
سؤال
Which social theorists are most associated with the concept of the social construction of reality?
A)Marx and Engels
B)Thomas and Thomas
C)Berger and Luckmann
D)Blumer and Mead
A)Marx and Engels
B)Thomas and Thomas
C)Berger and Luckmann
D)Blumer and Mead
سؤال
Read the vignette and answer the questions that follow.
When Malcolm started working at the local print shop,he got along with everyone.He was a supervisor but always tried to stay friends with the people who worked for him.Soon after joining the shop,a new supervisor,Ginny,was hired to manage the shipping department.One day Malcolm heard Ginny use a racial slur.Then Malcolm started noticing other things about her behavior.He noticed that Ginny would eat only with people of her own race and gender,for that matter.He heard her make another racist remark.He ignored her as best he could,sharing his concerns with coworkers and questioning whether a racist should be managing other people.Malcolm discussed Ginny's behavior with his supervisor but she did not see enough evidence of racism to do anything about it.
Which symbolic interaction principle helps to explain Malcolm's behavior toward Ginny?
A)Meanings arise through social interaction among individuals.
B)People use the meanings they derive from their first impressions only to guide their own behavior.
C)People employ a biological process regarding interactions.
D)The size of Malcolm's group influences his relationships with members.
When Malcolm started working at the local print shop,he got along with everyone.He was a supervisor but always tried to stay friends with the people who worked for him.Soon after joining the shop,a new supervisor,Ginny,was hired to manage the shipping department.One day Malcolm heard Ginny use a racial slur.Then Malcolm started noticing other things about her behavior.He noticed that Ginny would eat only with people of her own race and gender,for that matter.He heard her make another racist remark.He ignored her as best he could,sharing his concerns with coworkers and questioning whether a racist should be managing other people.Malcolm discussed Ginny's behavior with his supervisor but she did not see enough evidence of racism to do anything about it.
Which symbolic interaction principle helps to explain Malcolm's behavior toward Ginny?
A)Meanings arise through social interaction among individuals.
B)People use the meanings they derive from their first impressions only to guide their own behavior.
C)People employ a biological process regarding interactions.
D)The size of Malcolm's group influences his relationships with members.
سؤال
The difference between dyads and triads is important because __________.
A)moving from a dyad to a triad exponentially increases the number of relationships available in an interaction
B)moving from a dyad to a triad exponentially increases the amount of intimacy possible in a group
C)moving from a dyad to a triad exponentially decreases the number of relationships available in an interaction
D)moving from a dyad to a triad does not impact the amount of intimacy possible in a group
A)moving from a dyad to a triad exponentially increases the number of relationships available in an interaction
B)moving from a dyad to a triad exponentially increases the amount of intimacy possible in a group
C)moving from a dyad to a triad exponentially decreases the number of relationships available in an interaction
D)moving from a dyad to a triad does not impact the amount of intimacy possible in a group
سؤال
A local fraternity developed a special hand signal whenever members see each other on the university quad.In symbolic interactionist terms,this signal has become a(n)__________ for this group.
A)cultural exchange
B)important source of pride
C)language
D)symbol
A)cultural exchange
B)important source of pride
C)language
D)symbol
سؤال
Franklin did not think much about how the economy or society affects his life until he lost his job.Franklin's change in attitude about the impact of the economy on his life best reflects which principle from the social structure and personality perspective?
A)the components principle
B)the proximity principle
C)the propinquity principle
D)the psychology principle
A)the components principle
B)the proximity principle
C)the propinquity principle
D)the psychology principle
سؤال
Role theory is associated with which perspective in sociological social psychology?
A)conflict theory
B)social structure and personality
C)group processes
D)structural functionalism
A)conflict theory
B)social structure and personality
C)group processes
D)structural functionalism
سؤال
A group of friends getting together for dinner represents a __________ group,whereas a group of people at work represents a __________ group?
A)reference;primary
B)primary;reference
C)primary;secondary
D)secondary;reference
A)reference;primary
B)primary;reference
C)primary;secondary
D)secondary;reference
سؤال
Janelle wants to study how and why some people are able to tell other people what to do,whereas others are not.What aspect of group processes is she studying?
A)power
B)status
C)justice
D)legitimacy
A)power
B)status
C)justice
D)legitimacy
سؤال
In the previous question,Franklin's internal processesing of his job loss best represents which principle from the social structure and personality perspective?
A)the components principle
B)the proximity principle
C)the propinquity principle
D)the psychology principle
A)the components principle
B)the proximity principle
C)the propinquity principle
D)the psychology principle
سؤال
Match between columns
الفرضيات:
الردود:
The perception that a social arrangement or position is the way that things should be.
Psychology principle
The perception that a social arrangement or position is the way that things should be.
Chicago school
The perception that a social arrangement or position is the way that things should be.
Collective behavior
The perception that a social arrangement or position is the way that things should be.
Components principle
The perception that a social arrangement or position is the way that things should be.
Dyad
The perception that a social arrangement or position is the way that things should be.
Group
The perception that a social arrangement or position is the way that things should be.
Indiana and Iowa schools
The perception that a social arrangement or position is the way that things should be.
Framing
The perception that a social arrangement or position is the way that things should be.
Justice
The perception that a social arrangement or position is the way that things should be.
Thomas theorem
The perception that a social arrangement or position is the way that things should be.
Language
The perception that a social arrangement or position is the way that things should be.
Legitimacy
The perception that a social arrangement or position is the way that things should be.
Power
The perception that a social arrangement or position is the way that things should be.
Primary groups
The perception that a social arrangement or position is the way that things should be.
Proximity principle
The perception that a social arrangement or position is the way that things should be.
Reference groups
The perception that a social arrangement or position is the way that things should be.
Secondary groups
The perception that a social arrangement or position is the way that things should be.
Small groups
The perception that a social arrangement or position is the way that things should be.
Social forces
The perception that a social arrangement or position is the way that things should be.
Social networks
The perception that a social arrangement or position is the way that things should be.
Society
The perception that a social arrangement or position is the way that things should be.
Social Scripts
The perception that a social arrangement or position is the way that things should be.
Symbols
The perception that a social arrangement or position is the way that things should be.
Triad
The perception that a social arrangement or position is the way that things should be.
Agency
The perception that a social arrangement or position is the way that things should be.
Social construction of reality
Perceptions that a social arrangement or distribution is fair.
Psychology principle
Perceptions that a social arrangement or distribution is fair.
Chicago school
Perceptions that a social arrangement or distribution is fair.
Collective behavior
Perceptions that a social arrangement or distribution is fair.
Components principle
Perceptions that a social arrangement or distribution is fair.
Dyad
Perceptions that a social arrangement or distribution is fair.
Group
Perceptions that a social arrangement or distribution is fair.
Indiana and Iowa schools
Perceptions that a social arrangement or distribution is fair.
Framing
Perceptions that a social arrangement or distribution is fair.
Justice
Perceptions that a social arrangement or distribution is fair.
Thomas theorem
Perceptions that a social arrangement or distribution is fair.
Language
Perceptions that a social arrangement or distribution is fair.
Legitimacy
Perceptions that a social arrangement or distribution is fair.
Power
Perceptions that a social arrangement or distribution is fair.
Primary groups
Perceptions that a social arrangement or distribution is fair.
Proximity principle
Perceptions that a social arrangement or distribution is fair.
Reference groups
Perceptions that a social arrangement or distribution is fair.
Secondary groups
Perceptions that a social arrangement or distribution is fair.
Small groups
Perceptions that a social arrangement or distribution is fair.
Social forces
Perceptions that a social arrangement or distribution is fair.
Social networks
Perceptions that a social arrangement or distribution is fair.
Society
Perceptions that a social arrangement or distribution is fair.
Social Scripts
Perceptions that a social arrangement or distribution is fair.
Symbols
Perceptions that a social arrangement or distribution is fair.
Triad
Perceptions that a social arrangement or distribution is fair.
Agency
Perceptions that a social arrangement or distribution is fair.
Social construction of reality
Interactions that involve more than one person.
Psychology principle
Interactions that involve more than one person.
Chicago school
Interactions that involve more than one person.
Collective behavior
Interactions that involve more than one person.
Components principle
Interactions that involve more than one person.
Dyad
Interactions that involve more than one person.
Group
Interactions that involve more than one person.
Indiana and Iowa schools
Interactions that involve more than one person.
Framing
Interactions that involve more than one person.
Justice
Interactions that involve more than one person.
Thomas theorem
Interactions that involve more than one person.
Language
Interactions that involve more than one person.
Legitimacy
Interactions that involve more than one person.
Power
Interactions that involve more than one person.
Primary groups
Interactions that involve more than one person.
Proximity principle
Interactions that involve more than one person.
Reference groups
Interactions that involve more than one person.
Secondary groups
Interactions that involve more than one person.
Small groups
Interactions that involve more than one person.
Social forces
Interactions that involve more than one person.
Social networks
Interactions that involve more than one person.
Society
Interactions that involve more than one person.
Social Scripts
Interactions that involve more than one person.
Symbols
Interactions that involve more than one person.
Triad
Interactions that involve more than one person.
Agency
Interactions that involve more than one person.
Social construction of reality
The process by which we use symbols and language to give meaning and value to objects and people.
Psychology principle
The process by which we use symbols and language to give meaning and value to objects and people.
Chicago school
The process by which we use symbols and language to give meaning and value to objects and people.
Collective behavior
The process by which we use symbols and language to give meaning and value to objects and people.
Components principle
The process by which we use symbols and language to give meaning and value to objects and people.
Dyad
The process by which we use symbols and language to give meaning and value to objects and people.
Group
The process by which we use symbols and language to give meaning and value to objects and people.
Indiana and Iowa schools
The process by which we use symbols and language to give meaning and value to objects and people.
Framing
The process by which we use symbols and language to give meaning and value to objects and people.
Justice
The process by which we use symbols and language to give meaning and value to objects and people.
Thomas theorem
The process by which we use symbols and language to give meaning and value to objects and people.
Language
The process by which we use symbols and language to give meaning and value to objects and people.
Legitimacy
The process by which we use symbols and language to give meaning and value to objects and people.
Power
The process by which we use symbols and language to give meaning and value to objects and people.
Primary groups
The process by which we use symbols and language to give meaning and value to objects and people.
Proximity principle
The process by which we use symbols and language to give meaning and value to objects and people.
Reference groups
The process by which we use symbols and language to give meaning and value to objects and people.
Secondary groups
The process by which we use symbols and language to give meaning and value to objects and people.
Small groups
The process by which we use symbols and language to give meaning and value to objects and people.
Social forces
The process by which we use symbols and language to give meaning and value to objects and people.
Social networks
The process by which we use symbols and language to give meaning and value to objects and people.
Society
The process by which we use symbols and language to give meaning and value to objects and people.
Social Scripts
The process by which we use symbols and language to give meaning and value to objects and people.
Symbols
The process by which we use symbols and language to give meaning and value to objects and people.
Triad
The process by which we use symbols and language to give meaning and value to objects and people.
Agency
The process by which we use symbols and language to give meaning and value to objects and people.
Social construction of reality
Anything that has a similar meaning for two or more individuals.
Psychology principle
Anything that has a similar meaning for two or more individuals.
Chicago school
Anything that has a similar meaning for two or more individuals.
Collective behavior
Anything that has a similar meaning for two or more individuals.
Components principle
Anything that has a similar meaning for two or more individuals.
Dyad
Anything that has a similar meaning for two or more individuals.
Group
Anything that has a similar meaning for two or more individuals.
Indiana and Iowa schools
Anything that has a similar meaning for two or more individuals.
Framing
Anything that has a similar meaning for two or more individuals.
Justice
Anything that has a similar meaning for two or more individuals.
Thomas theorem
Anything that has a similar meaning for two or more individuals.
Language
Anything that has a similar meaning for two or more individuals.
Legitimacy
Anything that has a similar meaning for two or more individuals.
Power
Anything that has a similar meaning for two or more individuals.
Primary groups
Anything that has a similar meaning for two or more individuals.
Proximity principle
Anything that has a similar meaning for two or more individuals.
Reference groups
Anything that has a similar meaning for two or more individuals.
Secondary groups
Anything that has a similar meaning for two or more individuals.
Small groups
Anything that has a similar meaning for two or more individuals.
Social forces
Anything that has a similar meaning for two or more individuals.
Social networks
Anything that has a similar meaning for two or more individuals.
Society
Anything that has a similar meaning for two or more individuals.
Social Scripts
Anything that has a similar meaning for two or more individuals.
Symbols
Anything that has a similar meaning for two or more individuals.
Triad
Anything that has a similar meaning for two or more individuals.
Agency
Anything that has a similar meaning for two or more individuals.
Social construction of reality
Any way in which society compels individuals to act in accordance with an external norm, rule, or demand.
Psychology principle
Any way in which society compels individuals to act in accordance with an external norm, rule, or demand.
Chicago school
Any way in which society compels individuals to act in accordance with an external norm, rule, or demand.
Collective behavior
Any way in which society compels individuals to act in accordance with an external norm, rule, or demand.
Components principle
Any way in which society compels individuals to act in accordance with an external norm, rule, or demand.
Dyad
Any way in which society compels individuals to act in accordance with an external norm, rule, or demand.
Group
Any way in which society compels individuals to act in accordance with an external norm, rule, or demand.
Indiana and Iowa schools
Any way in which society compels individuals to act in accordance with an external norm, rule, or demand.
Framing
Any way in which society compels individuals to act in accordance with an external norm, rule, or demand.
Justice
Any way in which society compels individuals to act in accordance with an external norm, rule, or demand.
Thomas theorem
Any way in which society compels individuals to act in accordance with an external norm, rule, or demand.
Language
Any way in which society compels individuals to act in accordance with an external norm, rule, or demand.
Legitimacy
Any way in which society compels individuals to act in accordance with an external norm, rule, or demand.
Power
Any way in which society compels individuals to act in accordance with an external norm, rule, or demand.
Primary groups
Any way in which society compels individuals to act in accordance with an external norm, rule, or demand.
Proximity principle
Any way in which society compels individuals to act in accordance with an external norm, rule, or demand.
Reference groups
Any way in which society compels individuals to act in accordance with an external norm, rule, or demand.
Secondary groups
Any way in which society compels individuals to act in accordance with an external norm, rule, or demand.
Small groups
Any way in which society compels individuals to act in accordance with an external norm, rule, or demand.
Social forces
Any way in which society compels individuals to act in accordance with an external norm, rule, or demand.
Social networks
Any way in which society compels individuals to act in accordance with an external norm, rule, or demand.
Society
Any way in which society compels individuals to act in accordance with an external norm, rule, or demand.
Social Scripts
Any way in which society compels individuals to act in accordance with an external norm, rule, or demand.
Symbols
Any way in which society compels individuals to act in accordance with an external norm, rule, or demand.
Triad
Any way in which society compels individuals to act in accordance with an external norm, rule, or demand.
Agency
Any way in which society compels individuals to act in accordance with an external norm, rule, or demand.
Social construction of reality
Perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on the quantitative study of social interaction processes because of the stable nature of social life.
Psychology principle
Perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on the quantitative study of social interaction processes because of the stable nature of social life.
Chicago school
Perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on the quantitative study of social interaction processes because of the stable nature of social life.
Collective behavior
Perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on the quantitative study of social interaction processes because of the stable nature of social life.
Components principle
Perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on the quantitative study of social interaction processes because of the stable nature of social life.
Dyad
Perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on the quantitative study of social interaction processes because of the stable nature of social life.
Group
Perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on the quantitative study of social interaction processes because of the stable nature of social life.
Indiana and Iowa schools
Perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on the quantitative study of social interaction processes because of the stable nature of social life.
Framing
Perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on the quantitative study of social interaction processes because of the stable nature of social life.
Justice
Perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on the quantitative study of social interaction processes because of the stable nature of social life.
Thomas theorem
Perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on the quantitative study of social interaction processes because of the stable nature of social life.
Language
Perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on the quantitative study of social interaction processes because of the stable nature of social life.
Legitimacy
Perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on the quantitative study of social interaction processes because of the stable nature of social life.
Power
Perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on the quantitative study of social interaction processes because of the stable nature of social life.
Primary groups
Perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on the quantitative study of social interaction processes because of the stable nature of social life.
Proximity principle
Perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on the quantitative study of social interaction processes because of the stable nature of social life.
Reference groups
Perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on the quantitative study of social interaction processes because of the stable nature of social life.
Secondary groups
Perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on the quantitative study of social interaction processes because of the stable nature of social life.
Small groups
Perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on the quantitative study of social interaction processes because of the stable nature of social life.
Social forces
Perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on the quantitative study of social interaction processes because of the stable nature of social life.
Social networks
Perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on the quantitative study of social interaction processes because of the stable nature of social life.
Society
Perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on the quantitative study of social interaction processes because of the stable nature of social life.
Social Scripts
Perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on the quantitative study of social interaction processes because of the stable nature of social life.
Symbols
Perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on the quantitative study of social interaction processes because of the stable nature of social life.
Triad
Perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on the quantitative study of social interaction processes because of the stable nature of social life.
Agency
Perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on the quantitative study of social interaction processes because of the stable nature of social life.
Social construction of reality
People we are close to and interact with regularly.
Psychology principle
People we are close to and interact with regularly.
Chicago school
People we are close to and interact with regularly.
Collective behavior
People we are close to and interact with regularly.
Components principle
People we are close to and interact with regularly.
Dyad
People we are close to and interact with regularly.
Group
People we are close to and interact with regularly.
Indiana and Iowa schools
People we are close to and interact with regularly.
Framing
People we are close to and interact with regularly.
Justice
People we are close to and interact with regularly.
Thomas theorem
People we are close to and interact with regularly.
Language
People we are close to and interact with regularly.
Legitimacy
People we are close to and interact with regularly.
Power
People we are close to and interact with regularly.
Primary groups
People we are close to and interact with regularly.
Proximity principle
People we are close to and interact with regularly.
Reference groups
People we are close to and interact with regularly.
Secondary groups
People we are close to and interact with regularly.
Small groups
People we are close to and interact with regularly.
Social forces
People we are close to and interact with regularly.
Social networks
People we are close to and interact with regularly.
Society
People we are close to and interact with regularly.
Social Scripts
People we are close to and interact with regularly.
Symbols
People we are close to and interact with regularly.
Triad
People we are close to and interact with regularly.
Agency
People we are close to and interact with regularly.
Social construction of reality
Two or more persons (generally, not more than 20) engaged in or capable of face-to-face interaction.
Psychology principle
Two or more persons (generally, not more than 20) engaged in or capable of face-to-face interaction.
Chicago school
Two or more persons (generally, not more than 20) engaged in or capable of face-to-face interaction.
Collective behavior
Two or more persons (generally, not more than 20) engaged in or capable of face-to-face interaction.
Components principle
Two or more persons (generally, not more than 20) engaged in or capable of face-to-face interaction.
Dyad
Two or more persons (generally, not more than 20) engaged in or capable of face-to-face interaction.
Group
Two or more persons (generally, not more than 20) engaged in or capable of face-to-face interaction.
Indiana and Iowa schools
Two or more persons (generally, not more than 20) engaged in or capable of face-to-face interaction.
Framing
Two or more persons (generally, not more than 20) engaged in or capable of face-to-face interaction.
Justice
Two or more persons (generally, not more than 20) engaged in or capable of face-to-face interaction.
Thomas theorem
Two or more persons (generally, not more than 20) engaged in or capable of face-to-face interaction.
Language
Two or more persons (generally, not more than 20) engaged in or capable of face-to-face interaction.
Legitimacy
Two or more persons (generally, not more than 20) engaged in or capable of face-to-face interaction.
Power
Two or more persons (generally, not more than 20) engaged in or capable of face-to-face interaction.
Primary groups
Two or more persons (generally, not more than 20) engaged in or capable of face-to-face interaction.
Proximity principle
Two or more persons (generally, not more than 20) engaged in or capable of face-to-face interaction.
Reference groups
Two or more persons (generally, not more than 20) engaged in or capable of face-to-face interaction.
Secondary groups
Two or more persons (generally, not more than 20) engaged in or capable of face-to-face interaction.
Small groups
Two or more persons (generally, not more than 20) engaged in or capable of face-to-face interaction.
Social forces
Two or more persons (generally, not more than 20) engaged in or capable of face-to-face interaction.
Social networks
Two or more persons (generally, not more than 20) engaged in or capable of face-to-face interaction.
Society
Two or more persons (generally, not more than 20) engaged in or capable of face-to-face interaction.
Social Scripts
Two or more persons (generally, not more than 20) engaged in or capable of face-to-face interaction.
Symbols
Two or more persons (generally, not more than 20) engaged in or capable of face-to-face interaction.
Triad
Two or more persons (generally, not more than 20) engaged in or capable of face-to-face interaction.
Agency
Two or more persons (generally, not more than 20) engaged in or capable of face-to-face interaction.
Social construction of reality
Within the social structure and personality perspective, the ability to identify the elements or components of society most likely to affect a given attitude or behavior.
Psychology principle
Within the social structure and personality perspective, the ability to identify the elements or components of society most likely to affect a given attitude or behavior.
Chicago school
Within the social structure and personality perspective, the ability to identify the elements or components of society most likely to affect a given attitude or behavior.
Collective behavior
Within the social structure and personality perspective, the ability to identify the elements or components of society most likely to affect a given attitude or behavior.
Components principle
Within the social structure and personality perspective, the ability to identify the elements or components of society most likely to affect a given attitude or behavior.
Dyad
Within the social structure and personality perspective, the ability to identify the elements or components of society most likely to affect a given attitude or behavior.
Group
Within the social structure and personality perspective, the ability to identify the elements or components of society most likely to affect a given attitude or behavior.
Indiana and Iowa schools
Within the social structure and personality perspective, the ability to identify the elements or components of society most likely to affect a given attitude or behavior.
Framing
Within the social structure and personality perspective, the ability to identify the elements or components of society most likely to affect a given attitude or behavior.
Justice
Within the social structure and personality perspective, the ability to identify the elements or components of society most likely to affect a given attitude or behavior.
Thomas theorem
Within the social structure and personality perspective, the ability to identify the elements or components of society most likely to affect a given attitude or behavior.
Language
Within the social structure and personality perspective, the ability to identify the elements or components of society most likely to affect a given attitude or behavior.
Legitimacy
Within the social structure and personality perspective, the ability to identify the elements or components of society most likely to affect a given attitude or behavior.
Power
Within the social structure and personality perspective, the ability to identify the elements or components of society most likely to affect a given attitude or behavior.
Primary groups
Within the social structure and personality perspective, the ability to identify the elements or components of society most likely to affect a given attitude or behavior.
Proximity principle
Within the social structure and personality perspective, the ability to identify the elements or components of society most likely to affect a given attitude or behavior.
Reference groups
Within the social structure and personality perspective, the ability to identify the elements or components of society most likely to affect a given attitude or behavior.
Secondary groups
Within the social structure and personality perspective, the ability to identify the elements or components of society most likely to affect a given attitude or behavior.
Small groups
Within the social structure and personality perspective, the ability to identify the elements or components of society most likely to affect a given attitude or behavior.
Social forces
Within the social structure and personality perspective, the ability to identify the elements or components of society most likely to affect a given attitude or behavior.
Social networks
Within the social structure and personality perspective, the ability to identify the elements or components of society most likely to affect a given attitude or behavior.
Society
Within the social structure and personality perspective, the ability to identify the elements or components of society most likely to affect a given attitude or behavior.
Social Scripts
Within the social structure and personality perspective, the ability to identify the elements or components of society most likely to affect a given attitude or behavior.
Symbols
Within the social structure and personality perspective, the ability to identify the elements or components of society most likely to affect a given attitude or behavior.
Triad
Within the social structure and personality perspective, the ability to identify the elements or components of society most likely to affect a given attitude or behavior.
Agency
Within the social structure and personality perspective, the ability to identify the elements or components of society most likely to affect a given attitude or behavior.
Social construction of reality
In symbolic interactionism, the network of interaction between people.
Psychology principle
In symbolic interactionism, the network of interaction between people.
Chicago school
In symbolic interactionism, the network of interaction between people.
Collective behavior
In symbolic interactionism, the network of interaction between people.
Components principle
In symbolic interactionism, the network of interaction between people.
Dyad
In symbolic interactionism, the network of interaction between people.
Group
In symbolic interactionism, the network of interaction between people.
Indiana and Iowa schools
In symbolic interactionism, the network of interaction between people.
Framing
In symbolic interactionism, the network of interaction between people.
Justice
In symbolic interactionism, the network of interaction between people.
Thomas theorem
In symbolic interactionism, the network of interaction between people.
Language
In symbolic interactionism, the network of interaction between people.
Legitimacy
In symbolic interactionism, the network of interaction between people.
Power
In symbolic interactionism, the network of interaction between people.
Primary groups
In symbolic interactionism, the network of interaction between people.
Proximity principle
In symbolic interactionism, the network of interaction between people.
Reference groups
In symbolic interactionism, the network of interaction between people.
Secondary groups
In symbolic interactionism, the network of interaction between people.
Small groups
In symbolic interactionism, the network of interaction between people.
Social forces
In symbolic interactionism, the network of interaction between people.
Social networks
In symbolic interactionism, the network of interaction between people.
Society
In symbolic interactionism, the network of interaction between people.
Social Scripts
In symbolic interactionism, the network of interaction between people.
Symbols
In symbolic interactionism, the network of interaction between people.
Triad
In symbolic interactionism, the network of interaction between people.
Agency
In symbolic interactionism, the network of interaction between people.
Social construction of reality
A three-person group.
Psychology principle
A three-person group.
Chicago school
A three-person group.
Collective behavior
A three-person group.
Components principle
A three-person group.
Dyad
A three-person group.
Group
A three-person group.
Indiana and Iowa schools
A three-person group.
Framing
A three-person group.
Justice
A three-person group.
Thomas theorem
A three-person group.
Language
A three-person group.
Legitimacy
A three-person group.
Power
A three-person group.
Primary groups
A three-person group.
Proximity principle
A three-person group.
Reference groups
A three-person group.
Secondary groups
A three-person group.
Small groups
A three-person group.
Social forces
A three-person group.
Social networks
A three-person group.
Society
A three-person group.
Social Scripts
A three-person group.
Symbols
A three-person group.
Triad
A three-person group.
Agency
A three-person group.
Social construction of reality
The ability to act and think independent of the constraints imposed by social conditions.
Psychology principle
The ability to act and think independent of the constraints imposed by social conditions.
Chicago school
The ability to act and think independent of the constraints imposed by social conditions.
Collective behavior
The ability to act and think independent of the constraints imposed by social conditions.
Components principle
The ability to act and think independent of the constraints imposed by social conditions.
Dyad
The ability to act and think independent of the constraints imposed by social conditions.
Group
The ability to act and think independent of the constraints imposed by social conditions.
Indiana and Iowa schools
The ability to act and think independent of the constraints imposed by social conditions.
Framing
The ability to act and think independent of the constraints imposed by social conditions.
Justice
The ability to act and think independent of the constraints imposed by social conditions.
Thomas theorem
The ability to act and think independent of the constraints imposed by social conditions.
Language
The ability to act and think independent of the constraints imposed by social conditions.
Legitimacy
The ability to act and think independent of the constraints imposed by social conditions.
Power
The ability to act and think independent of the constraints imposed by social conditions.
Primary groups
The ability to act and think independent of the constraints imposed by social conditions.
Proximity principle
The ability to act and think independent of the constraints imposed by social conditions.
Reference groups
The ability to act and think independent of the constraints imposed by social conditions.
Secondary groups
The ability to act and think independent of the constraints imposed by social conditions.
Small groups
The ability to act and think independent of the constraints imposed by social conditions.
Social forces
The ability to act and think independent of the constraints imposed by social conditions.
Social networks
The ability to act and think independent of the constraints imposed by social conditions.
Society
The ability to act and think independent of the constraints imposed by social conditions.
Social Scripts
The ability to act and think independent of the constraints imposed by social conditions.
Symbols
The ability to act and think independent of the constraints imposed by social conditions.
Triad
The ability to act and think independent of the constraints imposed by social conditions.
Agency
The ability to act and think independent of the constraints imposed by social conditions.
Social construction of reality
The ability to obtain what we desire in a group despite resistance.
Psychology principle
The ability to obtain what we desire in a group despite resistance.
Chicago school
The ability to obtain what we desire in a group despite resistance.
Collective behavior
The ability to obtain what we desire in a group despite resistance.
Components principle
The ability to obtain what we desire in a group despite resistance.
Dyad
The ability to obtain what we desire in a group despite resistance.
Group
The ability to obtain what we desire in a group despite resistance.
Indiana and Iowa schools
The ability to obtain what we desire in a group despite resistance.
Framing
The ability to obtain what we desire in a group despite resistance.
Justice
The ability to obtain what we desire in a group despite resistance.
Thomas theorem
The ability to obtain what we desire in a group despite resistance.
Language
The ability to obtain what we desire in a group despite resistance.
Legitimacy
The ability to obtain what we desire in a group despite resistance.
Power
The ability to obtain what we desire in a group despite resistance.
Primary groups
The ability to obtain what we desire in a group despite resistance.
Proximity principle
The ability to obtain what we desire in a group despite resistance.
Reference groups
The ability to obtain what we desire in a group despite resistance.
Secondary groups
The ability to obtain what we desire in a group despite resistance.
Small groups
The ability to obtain what we desire in a group despite resistance.
Social forces
The ability to obtain what we desire in a group despite resistance.
Social networks
The ability to obtain what we desire in a group despite resistance.
Society
The ability to obtain what we desire in a group despite resistance.
Social Scripts
The ability to obtain what we desire in a group despite resistance.
Symbols
The ability to obtain what we desire in a group despite resistance.
Triad
The ability to obtain what we desire in a group despite resistance.
Agency
The ability to obtain what we desire in a group despite resistance.
Social construction of reality
A two-person group.
Psychology principle
A two-person group.
Chicago school
A two-person group.
Collective behavior
A two-person group.
Components principle
A two-person group.
Dyad
A two-person group.
Group
A two-person group.
Indiana and Iowa schools
A two-person group.
Framing
A two-person group.
Justice
A two-person group.
Thomas theorem
A two-person group.
Language
A two-person group.
Legitimacy
A two-person group.
Power
A two-person group.
Primary groups
A two-person group.
Proximity principle
A two-person group.
Reference groups
A two-person group.
Secondary groups
A two-person group.
Small groups
A two-person group.
Social forces
A two-person group.
Social networks
A two-person group.
Society
A two-person group.
Social Scripts
A two-person group.
Symbols
A two-person group.
Triad
A two-person group.
Agency
A two-person group.
Social construction of reality
People we affiliate with to achieve common goals or meet common needs.
Psychology principle
People we affiliate with to achieve common goals or meet common needs.
Chicago school
People we affiliate with to achieve common goals or meet common needs.
Collective behavior
People we affiliate with to achieve common goals or meet common needs.
Components principle
People we affiliate with to achieve common goals or meet common needs.
Dyad
People we affiliate with to achieve common goals or meet common needs.
Group
People we affiliate with to achieve common goals or meet common needs.
Indiana and Iowa schools
People we affiliate with to achieve common goals or meet common needs.
Framing
People we affiliate with to achieve common goals or meet common needs.
Justice
People we affiliate with to achieve common goals or meet common needs.
Thomas theorem
People we affiliate with to achieve common goals or meet common needs.
Language
People we affiliate with to achieve common goals or meet common needs.
Legitimacy
People we affiliate with to achieve common goals or meet common needs.
Power
People we affiliate with to achieve common goals or meet common needs.
Primary groups
People we affiliate with to achieve common goals or meet common needs.
Proximity principle
People we affiliate with to achieve common goals or meet common needs.
Reference groups
People we affiliate with to achieve common goals or meet common needs.
Secondary groups
People we affiliate with to achieve common goals or meet common needs.
Small groups
People we affiliate with to achieve common goals or meet common needs.
Social forces
People we affiliate with to achieve common goals or meet common needs.
Social networks
People we affiliate with to achieve common goals or meet common needs.
Society
People we affiliate with to achieve common goals or meet common needs.
Social Scripts
People we affiliate with to achieve common goals or meet common needs.
Symbols
People we affiliate with to achieve common goals or meet common needs.
Triad
People we affiliate with to achieve common goals or meet common needs.
Agency
People we affiliate with to achieve common goals or meet common needs.
Social construction of reality
People we look to as a source of standards and identity.
Psychology principle
People we look to as a source of standards and identity.
Chicago school
People we look to as a source of standards and identity.
Collective behavior
People we look to as a source of standards and identity.
Components principle
People we look to as a source of standards and identity.
Dyad
People we look to as a source of standards and identity.
Group
People we look to as a source of standards and identity.
Indiana and Iowa schools
People we look to as a source of standards and identity.
Framing
People we look to as a source of standards and identity.
Justice
People we look to as a source of standards and identity.
Thomas theorem
People we look to as a source of standards and identity.
Language
People we look to as a source of standards and identity.
Legitimacy
People we look to as a source of standards and identity.
Power
People we look to as a source of standards and identity.
Primary groups
People we look to as a source of standards and identity.
Proximity principle
People we look to as a source of standards and identity.
Reference groups
People we look to as a source of standards and identity.
Secondary groups
People we look to as a source of standards and identity.
Small groups
People we look to as a source of standards and identity.
Social forces
People we look to as a source of standards and identity.
Social networks
People we look to as a source of standards and identity.
Society
People we look to as a source of standards and identity.
Social Scripts
People we look to as a source of standards and identity.
Symbols
People we look to as a source of standards and identity.
Triad
People we look to as a source of standards and identity.
Agency
People we look to as a source of standards and identity.
Social construction of reality
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how individuals internalize proximal experiences.
Psychology principle
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how individuals internalize proximal experiences.
Chicago school
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how individuals internalize proximal experiences.
Collective behavior
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how individuals internalize proximal experiences.
Components principle
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how individuals internalize proximal experiences.
Dyad
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how individuals internalize proximal experiences.
Group
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how individuals internalize proximal experiences.
Indiana and Iowa schools
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how individuals internalize proximal experiences.
Framing
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how individuals internalize proximal experiences.
Justice
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how individuals internalize proximal experiences.
Thomas theorem
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how individuals internalize proximal experiences.
Language
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how individuals internalize proximal experiences.
Legitimacy
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how individuals internalize proximal experiences.
Power
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how individuals internalize proximal experiences.
Primary groups
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how individuals internalize proximal experiences.
Proximity principle
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how individuals internalize proximal experiences.
Reference groups
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how individuals internalize proximal experiences.
Secondary groups
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how individuals internalize proximal experiences.
Small groups
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how individuals internalize proximal experiences.
Social forces
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how individuals internalize proximal experiences.
Social networks
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how individuals internalize proximal experiences.
Society
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how individuals internalize proximal experiences.
Social Scripts
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how individuals internalize proximal experiences.
Symbols
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how individuals internalize proximal experiences.
Triad
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how individuals internalize proximal experiences.
Agency
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how individuals internalize proximal experiences.
Social construction of reality
The appropriate thoughts, feelings, and behaviors that should be displayed in a particular social frame.
Psychology principle
The appropriate thoughts, feelings, and behaviors that should be displayed in a particular social frame.
Chicago school
The appropriate thoughts, feelings, and behaviors that should be displayed in a particular social frame.
Collective behavior
The appropriate thoughts, feelings, and behaviors that should be displayed in a particular social frame.
Components principle
The appropriate thoughts, feelings, and behaviors that should be displayed in a particular social frame.
Dyad
The appropriate thoughts, feelings, and behaviors that should be displayed in a particular social frame.
Group
The appropriate thoughts, feelings, and behaviors that should be displayed in a particular social frame.
Indiana and Iowa schools
The appropriate thoughts, feelings, and behaviors that should be displayed in a particular social frame.
Framing
The appropriate thoughts, feelings, and behaviors that should be displayed in a particular social frame.
Justice
The appropriate thoughts, feelings, and behaviors that should be displayed in a particular social frame.
Thomas theorem
The appropriate thoughts, feelings, and behaviors that should be displayed in a particular social frame.
Language
The appropriate thoughts, feelings, and behaviors that should be displayed in a particular social frame.
Legitimacy
The appropriate thoughts, feelings, and behaviors that should be displayed in a particular social frame.
Power
The appropriate thoughts, feelings, and behaviors that should be displayed in a particular social frame.
Primary groups
The appropriate thoughts, feelings, and behaviors that should be displayed in a particular social frame.
Proximity principle
The appropriate thoughts, feelings, and behaviors that should be displayed in a particular social frame.
Reference groups
The appropriate thoughts, feelings, and behaviors that should be displayed in a particular social frame.
Secondary groups
The appropriate thoughts, feelings, and behaviors that should be displayed in a particular social frame.
Small groups
The appropriate thoughts, feelings, and behaviors that should be displayed in a particular social frame.
Social forces
The appropriate thoughts, feelings, and behaviors that should be displayed in a particular social frame.
Social networks
The appropriate thoughts, feelings, and behaviors that should be displayed in a particular social frame.
Society
The appropriate thoughts, feelings, and behaviors that should be displayed in a particular social frame.
Social Scripts
The appropriate thoughts, feelings, and behaviors that should be displayed in a particular social frame.
Symbols
The appropriate thoughts, feelings, and behaviors that should be displayed in a particular social frame.
Triad
The appropriate thoughts, feelings, and behaviors that should be displayed in a particular social frame.
Agency
The appropriate thoughts, feelings, and behaviors that should be displayed in a particular social frame.
Social construction of reality
A series of relationships between individuals and groups.
Psychology principle
A series of relationships between individuals and groups.
Chicago school
A series of relationships between individuals and groups.
Collective behavior
A series of relationships between individuals and groups.
Components principle
A series of relationships between individuals and groups.
Dyad
A series of relationships between individuals and groups.
Group
A series of relationships between individuals and groups.
Indiana and Iowa schools
A series of relationships between individuals and groups.
Framing
A series of relationships between individuals and groups.
Justice
A series of relationships between individuals and groups.
Thomas theorem
A series of relationships between individuals and groups.
Language
A series of relationships between individuals and groups.
Legitimacy
A series of relationships between individuals and groups.
Power
A series of relationships between individuals and groups.
Primary groups
A series of relationships between individuals and groups.
Proximity principle
A series of relationships between individuals and groups.
Reference groups
A series of relationships between individuals and groups.
Secondary groups
A series of relationships between individuals and groups.
Small groups
A series of relationships between individuals and groups.
Social forces
A series of relationships between individuals and groups.
Social networks
A series of relationships between individuals and groups.
Society
A series of relationships between individuals and groups.
Social Scripts
A series of relationships between individuals and groups.
Symbols
A series of relationships between individuals and groups.
Triad
A series of relationships between individuals and groups.
Agency
A series of relationships between individuals and groups.
Social construction of reality
Theorem stating that when people define situations as real, the consequences of those situations become real.
Psychology principle
Theorem stating that when people define situations as real, the consequences of those situations become real.
Chicago school
Theorem stating that when people define situations as real, the consequences of those situations become real.
Collective behavior
Theorem stating that when people define situations as real, the consequences of those situations become real.
Components principle
Theorem stating that when people define situations as real, the consequences of those situations become real.
Dyad
Theorem stating that when people define situations as real, the consequences of those situations become real.
Group
Theorem stating that when people define situations as real, the consequences of those situations become real.
Indiana and Iowa schools
Theorem stating that when people define situations as real, the consequences of those situations become real.
Framing
Theorem stating that when people define situations as real, the consequences of those situations become real.
Justice
Theorem stating that when people define situations as real, the consequences of those situations become real.
Thomas theorem
Theorem stating that when people define situations as real, the consequences of those situations become real.
Language
Theorem stating that when people define situations as real, the consequences of those situations become real.
Legitimacy
Theorem stating that when people define situations as real, the consequences of those situations become real.
Power
Theorem stating that when people define situations as real, the consequences of those situations become real.
Primary groups
Theorem stating that when people define situations as real, the consequences of those situations become real.
Proximity principle
Theorem stating that when people define situations as real, the consequences of those situations become real.
Reference groups
Theorem stating that when people define situations as real, the consequences of those situations become real.
Secondary groups
Theorem stating that when people define situations as real, the consequences of those situations become real.
Small groups
Theorem stating that when people define situations as real, the consequences of those situations become real.
Social forces
Theorem stating that when people define situations as real, the consequences of those situations become real.
Social networks
Theorem stating that when people define situations as real, the consequences of those situations become real.
Society
Theorem stating that when people define situations as real, the consequences of those situations become real.
Social Scripts
Theorem stating that when people define situations as real, the consequences of those situations become real.
Symbols
Theorem stating that when people define situations as real, the consequences of those situations become real.
Triad
Theorem stating that when people define situations as real, the consequences of those situations become real.
Agency
Theorem stating that when people define situations as real, the consequences of those situations become real.
Social construction of reality
The process by which individuals transform the meaning of a situation using basic cognitive structures provided by society.
Psychology principle
The process by which individuals transform the meaning of a situation using basic cognitive structures provided by society.
Chicago school
The process by which individuals transform the meaning of a situation using basic cognitive structures provided by society.
Collective behavior
The process by which individuals transform the meaning of a situation using basic cognitive structures provided by society.
Components principle
The process by which individuals transform the meaning of a situation using basic cognitive structures provided by society.
Dyad
The process by which individuals transform the meaning of a situation using basic cognitive structures provided by society.
Group
The process by which individuals transform the meaning of a situation using basic cognitive structures provided by society.
Indiana and Iowa schools
The process by which individuals transform the meaning of a situation using basic cognitive structures provided by society.
Framing
The process by which individuals transform the meaning of a situation using basic cognitive structures provided by society.
Justice
The process by which individuals transform the meaning of a situation using basic cognitive structures provided by society.
Thomas theorem
The process by which individuals transform the meaning of a situation using basic cognitive structures provided by society.
Language
The process by which individuals transform the meaning of a situation using basic cognitive structures provided by society.
Legitimacy
The process by which individuals transform the meaning of a situation using basic cognitive structures provided by society.
Power
The process by which individuals transform the meaning of a situation using basic cognitive structures provided by society.
Primary groups
The process by which individuals transform the meaning of a situation using basic cognitive structures provided by society.
Proximity principle
The process by which individuals transform the meaning of a situation using basic cognitive structures provided by society.
Reference groups
The process by which individuals transform the meaning of a situation using basic cognitive structures provided by society.
Secondary groups
The process by which individuals transform the meaning of a situation using basic cognitive structures provided by society.
Small groups
The process by which individuals transform the meaning of a situation using basic cognitive structures provided by society.
Social forces
The process by which individuals transform the meaning of a situation using basic cognitive structures provided by society.
Social networks
The process by which individuals transform the meaning of a situation using basic cognitive structures provided by society.
Society
The process by which individuals transform the meaning of a situation using basic cognitive structures provided by society.
Social Scripts
The process by which individuals transform the meaning of a situation using basic cognitive structures provided by society.
Symbols
The process by which individuals transform the meaning of a situation using basic cognitive structures provided by society.
Triad
The process by which individuals transform the meaning of a situation using basic cognitive structures provided by society.
Agency
The process by which individuals transform the meaning of a situation using basic cognitive structures provided by society.
Social construction of reality
The action or behavior of people in groups or crowds.
Psychology principle
The action or behavior of people in groups or crowds.
Chicago school
The action or behavior of people in groups or crowds.
Collective behavior
The action or behavior of people in groups or crowds.
Components principle
The action or behavior of people in groups or crowds.
Dyad
The action or behavior of people in groups or crowds.
Group
The action or behavior of people in groups or crowds.
Indiana and Iowa schools
The action or behavior of people in groups or crowds.
Framing
The action or behavior of people in groups or crowds.
Justice
The action or behavior of people in groups or crowds.
Thomas theorem
The action or behavior of people in groups or crowds.
Language
The action or behavior of people in groups or crowds.
Legitimacy
The action or behavior of people in groups or crowds.
Power
The action or behavior of people in groups or crowds.
Primary groups
The action or behavior of people in groups or crowds.
Proximity principle
The action or behavior of people in groups or crowds.
Reference groups
The action or behavior of people in groups or crowds.
Secondary groups
The action or behavior of people in groups or crowds.
Small groups
The action or behavior of people in groups or crowds.
Social forces
The action or behavior of people in groups or crowds.
Social networks
The action or behavior of people in groups or crowds.
Society
The action or behavior of people in groups or crowds.
Social Scripts
The action or behavior of people in groups or crowds.
Symbols
The action or behavior of people in groups or crowds.
Triad
The action or behavior of people in groups or crowds.
Agency
The action or behavior of people in groups or crowds.
Social construction of reality
A perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on understanding the social processes involved in a given situation rather than on trying to quantify and predict people’s thoughts, feelings, and behavior.
Psychology principle
A perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on understanding the social processes involved in a given situation rather than on trying to quantify and predict people’s thoughts, feelings, and behavior.
Chicago school
A perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on understanding the social processes involved in a given situation rather than on trying to quantify and predict people’s thoughts, feelings, and behavior.
Collective behavior
A perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on understanding the social processes involved in a given situation rather than on trying to quantify and predict people’s thoughts, feelings, and behavior.
Components principle
A perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on understanding the social processes involved in a given situation rather than on trying to quantify and predict people’s thoughts, feelings, and behavior.
Dyad
A perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on understanding the social processes involved in a given situation rather than on trying to quantify and predict people’s thoughts, feelings, and behavior.
Group
A perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on understanding the social processes involved in a given situation rather than on trying to quantify and predict people’s thoughts, feelings, and behavior.
Indiana and Iowa schools
A perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on understanding the social processes involved in a given situation rather than on trying to quantify and predict people’s thoughts, feelings, and behavior.
Framing
A perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on understanding the social processes involved in a given situation rather than on trying to quantify and predict people’s thoughts, feelings, and behavior.
Justice
A perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on understanding the social processes involved in a given situation rather than on trying to quantify and predict people’s thoughts, feelings, and behavior.
Thomas theorem
A perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on understanding the social processes involved in a given situation rather than on trying to quantify and predict people’s thoughts, feelings, and behavior.
Language
A perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on understanding the social processes involved in a given situation rather than on trying to quantify and predict people’s thoughts, feelings, and behavior.
Legitimacy
A perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on understanding the social processes involved in a given situation rather than on trying to quantify and predict people’s thoughts, feelings, and behavior.
Power
A perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on understanding the social processes involved in a given situation rather than on trying to quantify and predict people’s thoughts, feelings, and behavior.
Primary groups
A perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on understanding the social processes involved in a given situation rather than on trying to quantify and predict people’s thoughts, feelings, and behavior.
Proximity principle
A perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on understanding the social processes involved in a given situation rather than on trying to quantify and predict people’s thoughts, feelings, and behavior.
Reference groups
A perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on understanding the social processes involved in a given situation rather than on trying to quantify and predict people’s thoughts, feelings, and behavior.
Secondary groups
A perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on understanding the social processes involved in a given situation rather than on trying to quantify and predict people’s thoughts, feelings, and behavior.
Small groups
A perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on understanding the social processes involved in a given situation rather than on trying to quantify and predict people’s thoughts, feelings, and behavior.
Social forces
A perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on understanding the social processes involved in a given situation rather than on trying to quantify and predict people’s thoughts, feelings, and behavior.
Social networks
A perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on understanding the social processes involved in a given situation rather than on trying to quantify and predict people’s thoughts, feelings, and behavior.
Society
A perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on understanding the social processes involved in a given situation rather than on trying to quantify and predict people’s thoughts, feelings, and behavior.
Social Scripts
A perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on understanding the social processes involved in a given situation rather than on trying to quantify and predict people’s thoughts, feelings, and behavior.
Symbols
A perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on understanding the social processes involved in a given situation rather than on trying to quantify and predict people’s thoughts, feelings, and behavior.
Triad
A perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on understanding the social processes involved in a given situation rather than on trying to quantify and predict people’s thoughts, feelings, and behavior.
Agency
A perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on understanding the social processes involved in a given situation rather than on trying to quantify and predict people’s thoughts, feelings, and behavior.
Social construction of reality
A series of symbols that can be combined in various ways to create new meanings.
Psychology principle
A series of symbols that can be combined in various ways to create new meanings.
Chicago school
A series of symbols that can be combined in various ways to create new meanings.
Collective behavior
A series of symbols that can be combined in various ways to create new meanings.
Components principle
A series of symbols that can be combined in various ways to create new meanings.
Dyad
A series of symbols that can be combined in various ways to create new meanings.
Group
A series of symbols that can be combined in various ways to create new meanings.
Indiana and Iowa schools
A series of symbols that can be combined in various ways to create new meanings.
Framing
A series of symbols that can be combined in various ways to create new meanings.
Justice
A series of symbols that can be combined in various ways to create new meanings.
Thomas theorem
A series of symbols that can be combined in various ways to create new meanings.
Language
A series of symbols that can be combined in various ways to create new meanings.
Legitimacy
A series of symbols that can be combined in various ways to create new meanings.
Power
A series of symbols that can be combined in various ways to create new meanings.
Primary groups
A series of symbols that can be combined in various ways to create new meanings.
Proximity principle
A series of symbols that can be combined in various ways to create new meanings.
Reference groups
A series of symbols that can be combined in various ways to create new meanings.
Secondary groups
A series of symbols that can be combined in various ways to create new meanings.
Small groups
A series of symbols that can be combined in various ways to create new meanings.
Social forces
A series of symbols that can be combined in various ways to create new meanings.
Social networks
A series of symbols that can be combined in various ways to create new meanings.
Society
A series of symbols that can be combined in various ways to create new meanings.
Social Scripts
A series of symbols that can be combined in various ways to create new meanings.
Symbols
A series of symbols that can be combined in various ways to create new meanings.
Triad
A series of symbols that can be combined in various ways to create new meanings.
Agency
A series of symbols that can be combined in various ways to create new meanings.
Social construction of reality
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how people are affected by social structure through their immediate social environments.
Psychology principle
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how people are affected by social structure through their immediate social environments.
Chicago school
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how people are affected by social structure through their immediate social environments.
Collective behavior
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how people are affected by social structure through their immediate social environments.
Components principle
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how people are affected by social structure through their immediate social environments.
Dyad
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how people are affected by social structure through their immediate social environments.
Group
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how people are affected by social structure through their immediate social environments.
Indiana and Iowa schools
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how people are affected by social structure through their immediate social environments.
Framing
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how people are affected by social structure through their immediate social environments.
Justice
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how people are affected by social structure through their immediate social environments.
Thomas theorem
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how people are affected by social structure through their immediate social environments.
Language
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how people are affected by social structure through their immediate social environments.
Legitimacy
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how people are affected by social structure through their immediate social environments.
Power
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how people are affected by social structure through their immediate social environments.
Primary groups
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how people are affected by social structure through their immediate social environments.
Proximity principle
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how people are affected by social structure through their immediate social environments.
Reference groups
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how people are affected by social structure through their immediate social environments.
Secondary groups
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how people are affected by social structure through their immediate social environments.
Small groups
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how people are affected by social structure through their immediate social environments.
Social forces
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how people are affected by social structure through their immediate social environments.
Social networks
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how people are affected by social structure through their immediate social environments.
Society
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how people are affected by social structure through their immediate social environments.
Social Scripts
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how people are affected by social structure through their immediate social environments.
Symbols
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how people are affected by social structure through their immediate social environments.
Triad
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how people are affected by social structure through their immediate social environments.
Agency
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how people are affected by social structure through their immediate social environments.
Social construction of reality

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/22
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 2: Perspectives in Sociological Social Psychology
1
Match the term to its definition by filling in the letter before the term in the appropriate blank.
 ____ Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how individuals internalize proximal experiences.
____ Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how individuals internalize proximal experiences.
____ A perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on understanding the social processes involved in a given situation rather than on trying to quantify and predict people's thoughts,feelings,and behavior.
____ The action or behavior of people in groups or crowds.
____ Within the social structure and personality perspective,the ability to identify the elements or components of society most likely to affect a given attitude or behavior.
____ A two-person group.
____ Interactions that involve more than one person.
____ Perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on the quantitative study of social interaction processes because of the stable nature of social life.
____ The process by which individuals transform the meaning of a situation using basic cognitive structures provided by society.
____ Perceptions that a social arrangement or distribution is fair.
____ Theorem stating that when people define situations as real,the consequences of those situations become real.
____ A series of symbols that can be combined in various ways to create new meanings.
____ The perception that a social arrangement or position is the way that things should be.
____ The ability to obtain what we desire in a group despite resistance.
____ People we are close to and interact with regularly.
____ Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how people are affected by social structure through their immediate social environments.
____ People we look to as a source of standards and identity.
____ People we affiliate with to achieve common goals or meet common needs.
____ Two or more persons (generally,not more than 20)engaged in or capable of face-to-face interaction.
____ Any way in which society compels individuals to act in accordance with an external norm,rule,or demand.
____ A series of relationships between individuals and groups.[
____ In symbolic interactionism,the network of interaction between people.
_____ The appropriate thoughts,feelings,and behaviors that should be displayed in a particular social frame.
____ Anything that has a similar meaning for two or more individuals.
____ A three-person group.
____ The ability to act and think independent of the constraints imposed by social conditions.
____ The process by which we use symbols and language to give meaning and value to objects and people.
 ____ Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how individuals internalize proximal experiences.
____ Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how individuals internalize proximal experiences.____ A perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on understanding the social processes involved in a given situation rather than on trying to quantify and predict people's thoughts,feelings,and behavior.
____ The action or behavior of people in groups or crowds.
____ Within the social structure and personality perspective,the ability to identify the elements or components of society most likely to affect a given attitude or behavior.
____ A two-person group.
____ Interactions that involve more than one person.
____ Perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on the quantitative study of social interaction processes because of the stable nature of social life.
____ The process by which individuals transform the meaning of a situation using basic cognitive structures provided by society.
____ Perceptions that a social arrangement or distribution is fair.
____ Theorem stating that when people define situations as real,the consequences of those situations become real.
____ A series of symbols that can be combined in various ways to create new meanings.
____ The perception that a social arrangement or position is the way that things should be.
____ The ability to obtain what we desire in a group despite resistance.
____ People we are close to and interact with regularly.
____ Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how people are affected by social structure through their immediate social environments.
____ People we look to as a source of standards and identity.
____ People we affiliate with to achieve common goals or meet common needs.
____ Two or more persons (generally,not more than 20)engaged in or capable of face-to-face interaction.
____ Any way in which society compels individuals to act in accordance with an external norm,rule,or demand.
____ A series of relationships between individuals and groups.[
____ In symbolic interactionism,the network of interaction between people.
_____ The appropriate thoughts,feelings,and behaviors that should be displayed in a particular social frame.
____ Anything that has a similar meaning for two or more individuals.
____ A three-person group.
____ The ability to act and think independent of the constraints imposed by social conditions.
____ The process by which we use symbols and language to give meaning and value to objects and people.
____ Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how individuals internalize proximal experiences.[Answer:N]
____ A perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on understanding the social processes involved in a given situation rather than on trying to quantify and predict people's thoughts,feelings,and behavior.[Answer:O]
____ The action or behavior of people in groups or crowds.[Answer:Q]
____ Within the social structure and personality perspective,the ability to identify the elements or components of society most likely to affect a given attitude or behavior.[Answer:C]
____ A two-person group.[Answer:X]
____ Interactions that involve more than one person.[Answer:H]
____ Perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on the quantitative study of social interaction processes because of the stable nature of social life.[Answer:L]
____ The process by which individuals transform the meaning of a situation using basic cognitive structures provided by society.[Answer:Y]
____ Perceptions that a social arrangement or distribution is fair.[Answer:U]
____ Theorem stating that when people define situations as real,the consequences of those situations become real.[Answer:F]
____ A series of symbols that can be combined in various ways to create new meanings.[Answer:E]
____ The perception that a social arrangement or position is the way that things should be.[Answer:P]
____ The ability to obtain what we desire in a group despite resistance.[Answer:S]
____ People we are close to and interact with regularly.[Answer:K]
____ Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how people are affected by social structure through their immediate social environments.[Answer:A]
____ People we look to as a source of standards and identity.[Answer:B]
____ People we affiliate with to achieve common goals or meet common needs.[Answer:V]
____ Two or more persons (generally,not more than 20)engaged in or capable of face-to-face interaction.[Answer:M]
____ Any way in which society compels individuals to act in accordance with an external norm,rule,or demand.[Answer:G]
____ A series of relationships between individuals and groups.[Answer:J]
____ In symbolic interactionism,the network of interaction between people.[Answer:D]
_____ The appropriate thoughts,feelings,and behaviors that should be displayed in a particular social frame.[Answer:Z]
____ Anything that has a similar meaning for two or more individuals.[Answer:T]
____ A three-person group.[Answer:W]
____ The ability to act and think independent of the constraints imposed by social conditions.[Answer:I]
____ The process by which we use symbols and language to give meaning and value to objects and people.[Answer:R]
____ A perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on understanding the social processes involved in a given situation rather than on trying to quantify and predict people's thoughts,feelings,and behavior.[Answer:O]
____ The action or behavior of people in groups or crowds.[Answer:Q]
____ Within the social structure and personality perspective,the ability to identify the elements or components of society most likely to affect a given attitude or behavior.[Answer:C]
____ A two-person group.[Answer:X]
____ Interactions that involve more than one person.[Answer:H]
____ Perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on the quantitative study of social interaction processes because of the stable nature of social life.[Answer:L]
____ The process by which individuals transform the meaning of a situation using basic cognitive structures provided by society.[Answer:Y]
____ Perceptions that a social arrangement or distribution is fair.[Answer:U]
____ Theorem stating that when people define situations as real,the consequences of those situations become real.[Answer:F]
____ A series of symbols that can be combined in various ways to create new meanings.[Answer:E]
____ The perception that a social arrangement or position is the way that things should be.[Answer:P]
____ The ability to obtain what we desire in a group despite resistance.[Answer:S]
____ People we are close to and interact with regularly.[Answer:K]
____ Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how people are affected by social structure through their immediate social environments.[Answer:A]
____ People we look to as a source of standards and identity.[Answer:B]
____ People we affiliate with to achieve common goals or meet common needs.[Answer:V]
____ Two or more persons (generally,not more than 20)engaged in or capable of face-to-face interaction.[Answer:M]
____ Any way in which society compels individuals to act in accordance with an external norm,rule,or demand.[Answer:G]
____ A series of relationships between individuals and groups.[Answer:J]
____ In symbolic interactionism,the network of interaction between people.[Answer:D]
_____ The appropriate thoughts,feelings,and behaviors that should be displayed in a particular social frame.[Answer:Z]
____ Anything that has a similar meaning for two or more individuals.[Answer:T]
____ A three-person group.[Answer:W]
____ The ability to act and think independent of the constraints imposed by social conditions.[Answer:I]
____ The process by which we use symbols and language to give meaning and value to objects and people.[Answer:R]
1
Which social psychologist is most associated with the concepts of dyads and triads?
A)Emile Durkheim
B)Auguste Comte
C)Herbert Blumer
D)Georg Simmel
A)Emile Durkheim
B)Auguste Comte
C)Herbert Blumer
D)Georg Simmel
Georg Simmel
2
The development of symbolic interactionism stems from which philosophical tradition or traditions?
A)French philosophy
B)German economic analysis
C)American pragmatism
D)Austrian theory
A)French philosophy
B)German economic analysis
C)American pragmatism
D)Austrian theory
American pragmatism
3
Terence has started to believe that a friend at work is really a spy from another company,leading him to avoid interactions with this person as much as possible.He treats all interactions with her as suspect and is reluctant to share any work-related information with her.Which of the following principles,theorems,or concepts best explains Terence's behavior?
A)the components principle of the social structure and personality perspective
B)the Thomas theorem
C)the Peter principle
D)the group processes concept of legitimacy
A)the components principle of the social structure and personality perspective
B)the Thomas theorem
C)the Peter principle
D)the group processes concept of legitimacy
the Thomas theorem
4
Read the vignette and answer the questions that follow.
When Malcolm started working at the local print shop,he got along with everyone.He was a supervisor but always tried to stay friends with the people who worked for him.Soon after joining the shop,a new supervisor,Ginny,was hired to manage the shipping department.One day Malcolm heard Ginny use a racial slur.Then Malcolm started noticing other things about her behavior.He noticed that Ginny would eat only with people of her own race and gender,for that matter.He heard her make another racist remark.He ignored her as best he could,sharing his concerns with coworkers and questioning whether a racist should be managing other people.Malcolm discussed Ginny's behavior with his supervisor but she did not see enough evidence of racism to do anything about it.
What type of group is depicted in the vignette?
A)primary
B)secondary
C)tertiary
D)reference
When Malcolm started working at the local print shop,he got along with everyone.He was a supervisor but always tried to stay friends with the people who worked for him.Soon after joining the shop,a new supervisor,Ginny,was hired to manage the shipping department.One day Malcolm heard Ginny use a racial slur.Then Malcolm started noticing other things about her behavior.He noticed that Ginny would eat only with people of her own race and gender,for that matter.He heard her make another racist remark.He ignored her as best he could,sharing his concerns with coworkers and questioning whether a racist should be managing other people.Malcolm discussed Ginny's behavior with his supervisor but she did not see enough evidence of racism to do anything about it.
What type of group is depicted in the vignette?
A)primary
B)secondary
C)tertiary
D)reference

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 22 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
After Donna cheated on her most recent exam,she started to feel a sense of guilt,making her reconsider whether she will cheat again.Donna's feelings of guilt can be considered a __________,according to the social structure and personality perspective,leading her to rethink her future behaviors.
A)social more
B)social norm
C)social force
D)social fear
A)social more
B)social norm
C)social force
D)social fear

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 22 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Professor Swanson is studying the meaning of "goodness" using a survey of public attitudes toward the topic.Which school,or schools,of symbolic interaction is she most likely using in her research?
A)the Chicago school
B)the Indiana and Iowa schools
C)the Swanson school
D)the sociological social psychology school
A)the Chicago school
B)the Indiana and Iowa schools
C)the Swanson school
D)the sociological social psychology school

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 22 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Networks are important to the study of the effects of society on individuals' thoughts,feelings,and behaviors because __________.
A)they provide important links between people
B)they give people more friends
C)they provide ways of managing life's problems
D)they give people more prestigious jobs
A)they provide important links between people
B)they give people more friends
C)they provide ways of managing life's problems
D)they give people more prestigious jobs

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 22 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Read the vignette and answer the questions that follow.
When Malcolm started working at the local print shop,he got along with everyone.He was a supervisor but always tried to stay friends with the people who worked for him.Soon after joining the shop,a new supervisor,Ginny,was hired to manage the shipping department.One day Malcolm heard Ginny use a racial slur.Then Malcolm started noticing other things about her behavior.He noticed that Ginny would eat only with people of her own race and gender,for that matter.He heard her make another racist remark.He ignored her as best he could,sharing his concerns with coworkers and questioning whether a racist should be managing other people.Malcolm discussed Ginny's behavior with his supervisor but she did not see enough evidence of racism to do anything about it.
What component of the group processes perspective is most evident in Malcolm's belief that Ginny should not be a supervisor?
A)power
B)status
C)justice
D)legitimacy
When Malcolm started working at the local print shop,he got along with everyone.He was a supervisor but always tried to stay friends with the people who worked for him.Soon after joining the shop,a new supervisor,Ginny,was hired to manage the shipping department.One day Malcolm heard Ginny use a racial slur.Then Malcolm started noticing other things about her behavior.He noticed that Ginny would eat only with people of her own race and gender,for that matter.He heard her make another racist remark.He ignored her as best he could,sharing his concerns with coworkers and questioning whether a racist should be managing other people.Malcolm discussed Ginny's behavior with his supervisor but she did not see enough evidence of racism to do anything about it.
What component of the group processes perspective is most evident in Malcolm's belief that Ginny should not be a supervisor?
A)power
B)status
C)justice
D)legitimacy

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 22 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Which of the following are considered major dimensions of group processes?
A)power and justice
B)justice and legitimacy
C)legitimacy and power
D)power,justice,and legitimacy
A)power and justice
B)justice and legitimacy
C)legitimacy and power
D)power,justice,and legitimacy

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 22 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Who coined the expression "symbolic interaction"?
A)Emile Durkheim
B)Herbert Blumer
C)Auguste Comte
D)George Herbert Mead
A)Emile Durkheim
B)Herbert Blumer
C)Auguste Comte
D)George Herbert Mead

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 22 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Socioeconomic status (social class),race or ethnicity,gender,age,and sexuality all relate to which principle of the social structure and personality perspective?
A)the components principle
B)the proximity principle
C)the psychology principle
D)the Peter principle
A)the components principle
B)the proximity principle
C)the psychology principle
D)the Peter principle

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 22 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Which social theorists are most associated with the concept of the social construction of reality?
A)Marx and Engels
B)Thomas and Thomas
C)Berger and Luckmann
D)Blumer and Mead
A)Marx and Engels
B)Thomas and Thomas
C)Berger and Luckmann
D)Blumer and Mead

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 22 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Read the vignette and answer the questions that follow.
When Malcolm started working at the local print shop,he got along with everyone.He was a supervisor but always tried to stay friends with the people who worked for him.Soon after joining the shop,a new supervisor,Ginny,was hired to manage the shipping department.One day Malcolm heard Ginny use a racial slur.Then Malcolm started noticing other things about her behavior.He noticed that Ginny would eat only with people of her own race and gender,for that matter.He heard her make another racist remark.He ignored her as best he could,sharing his concerns with coworkers and questioning whether a racist should be managing other people.Malcolm discussed Ginny's behavior with his supervisor but she did not see enough evidence of racism to do anything about it.
Which symbolic interaction principle helps to explain Malcolm's behavior toward Ginny?
A)Meanings arise through social interaction among individuals.
B)People use the meanings they derive from their first impressions only to guide their own behavior.
C)People employ a biological process regarding interactions.
D)The size of Malcolm's group influences his relationships with members.
When Malcolm started working at the local print shop,he got along with everyone.He was a supervisor but always tried to stay friends with the people who worked for him.Soon after joining the shop,a new supervisor,Ginny,was hired to manage the shipping department.One day Malcolm heard Ginny use a racial slur.Then Malcolm started noticing other things about her behavior.He noticed that Ginny would eat only with people of her own race and gender,for that matter.He heard her make another racist remark.He ignored her as best he could,sharing his concerns with coworkers and questioning whether a racist should be managing other people.Malcolm discussed Ginny's behavior with his supervisor but she did not see enough evidence of racism to do anything about it.
Which symbolic interaction principle helps to explain Malcolm's behavior toward Ginny?
A)Meanings arise through social interaction among individuals.
B)People use the meanings they derive from their first impressions only to guide their own behavior.
C)People employ a biological process regarding interactions.
D)The size of Malcolm's group influences his relationships with members.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 22 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
The difference between dyads and triads is important because __________.
A)moving from a dyad to a triad exponentially increases the number of relationships available in an interaction
B)moving from a dyad to a triad exponentially increases the amount of intimacy possible in a group
C)moving from a dyad to a triad exponentially decreases the number of relationships available in an interaction
D)moving from a dyad to a triad does not impact the amount of intimacy possible in a group
A)moving from a dyad to a triad exponentially increases the number of relationships available in an interaction
B)moving from a dyad to a triad exponentially increases the amount of intimacy possible in a group
C)moving from a dyad to a triad exponentially decreases the number of relationships available in an interaction
D)moving from a dyad to a triad does not impact the amount of intimacy possible in a group

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 22 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
A local fraternity developed a special hand signal whenever members see each other on the university quad.In symbolic interactionist terms,this signal has become a(n)__________ for this group.
A)cultural exchange
B)important source of pride
C)language
D)symbol
A)cultural exchange
B)important source of pride
C)language
D)symbol

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 22 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Franklin did not think much about how the economy or society affects his life until he lost his job.Franklin's change in attitude about the impact of the economy on his life best reflects which principle from the social structure and personality perspective?
A)the components principle
B)the proximity principle
C)the propinquity principle
D)the psychology principle
A)the components principle
B)the proximity principle
C)the propinquity principle
D)the psychology principle

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 22 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Role theory is associated with which perspective in sociological social psychology?
A)conflict theory
B)social structure and personality
C)group processes
D)structural functionalism
A)conflict theory
B)social structure and personality
C)group processes
D)structural functionalism

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 22 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
A group of friends getting together for dinner represents a __________ group,whereas a group of people at work represents a __________ group?
A)reference;primary
B)primary;reference
C)primary;secondary
D)secondary;reference
A)reference;primary
B)primary;reference
C)primary;secondary
D)secondary;reference

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 22 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Janelle wants to study how and why some people are able to tell other people what to do,whereas others are not.What aspect of group processes is she studying?
A)power
B)status
C)justice
D)legitimacy
A)power
B)status
C)justice
D)legitimacy

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 22 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
In the previous question,Franklin's internal processesing of his job loss best represents which principle from the social structure and personality perspective?
A)the components principle
B)the proximity principle
C)the propinquity principle
D)the psychology principle
A)the components principle
B)the proximity principle
C)the propinquity principle
D)the psychology principle

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 22 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Match between columns
الفرضيات:
الردود:
The perception that a social arrangement or position is the way that things should be.
Psychology principle
The perception that a social arrangement or position is the way that things should be.
Chicago school
The perception that a social arrangement or position is the way that things should be.
Collective behavior
The perception that a social arrangement or position is the way that things should be.
Components principle
The perception that a social arrangement or position is the way that things should be.
Dyad
The perception that a social arrangement or position is the way that things should be.
Group
The perception that a social arrangement or position is the way that things should be.
Indiana and Iowa schools
The perception that a social arrangement or position is the way that things should be.
Framing
The perception that a social arrangement or position is the way that things should be.
Justice
The perception that a social arrangement or position is the way that things should be.
Thomas theorem
The perception that a social arrangement or position is the way that things should be.
Language
The perception that a social arrangement or position is the way that things should be.
Legitimacy
The perception that a social arrangement or position is the way that things should be.
Power
The perception that a social arrangement or position is the way that things should be.
Primary groups
The perception that a social arrangement or position is the way that things should be.
Proximity principle
The perception that a social arrangement or position is the way that things should be.
Reference groups
The perception that a social arrangement or position is the way that things should be.
Secondary groups
The perception that a social arrangement or position is the way that things should be.
Small groups
The perception that a social arrangement or position is the way that things should be.
Social forces
The perception that a social arrangement or position is the way that things should be.
Social networks
The perception that a social arrangement or position is the way that things should be.
Society
The perception that a social arrangement or position is the way that things should be.
Social Scripts
The perception that a social arrangement or position is the way that things should be.
Symbols
The perception that a social arrangement or position is the way that things should be.
Triad
The perception that a social arrangement or position is the way that things should be.
Agency
The perception that a social arrangement or position is the way that things should be.
Social construction of reality
Perceptions that a social arrangement or distribution is fair.
Psychology principle
Perceptions that a social arrangement or distribution is fair.
Chicago school
Perceptions that a social arrangement or distribution is fair.
Collective behavior
Perceptions that a social arrangement or distribution is fair.
Components principle
Perceptions that a social arrangement or distribution is fair.
Dyad
Perceptions that a social arrangement or distribution is fair.
Group
Perceptions that a social arrangement or distribution is fair.
Indiana and Iowa schools
Perceptions that a social arrangement or distribution is fair.
Framing
Perceptions that a social arrangement or distribution is fair.
Justice
Perceptions that a social arrangement or distribution is fair.
Thomas theorem
Perceptions that a social arrangement or distribution is fair.
Language
Perceptions that a social arrangement or distribution is fair.
Legitimacy
Perceptions that a social arrangement or distribution is fair.
Power
Perceptions that a social arrangement or distribution is fair.
Primary groups
Perceptions that a social arrangement or distribution is fair.
Proximity principle
Perceptions that a social arrangement or distribution is fair.
Reference groups
Perceptions that a social arrangement or distribution is fair.
Secondary groups
Perceptions that a social arrangement or distribution is fair.
Small groups
Perceptions that a social arrangement or distribution is fair.
Social forces
Perceptions that a social arrangement or distribution is fair.
Social networks
Perceptions that a social arrangement or distribution is fair.
Society
Perceptions that a social arrangement or distribution is fair.
Social Scripts
Perceptions that a social arrangement or distribution is fair.
Symbols
Perceptions that a social arrangement or distribution is fair.
Triad
Perceptions that a social arrangement or distribution is fair.
Agency
Perceptions that a social arrangement or distribution is fair.
Social construction of reality
Interactions that involve more than one person.
Psychology principle
Interactions that involve more than one person.
Chicago school
Interactions that involve more than one person.
Collective behavior
Interactions that involve more than one person.
Components principle
Interactions that involve more than one person.
Dyad
Interactions that involve more than one person.
Group
Interactions that involve more than one person.
Indiana and Iowa schools
Interactions that involve more than one person.
Framing
Interactions that involve more than one person.
Justice
Interactions that involve more than one person.
Thomas theorem
Interactions that involve more than one person.
Language
Interactions that involve more than one person.
Legitimacy
Interactions that involve more than one person.
Power
Interactions that involve more than one person.
Primary groups
Interactions that involve more than one person.
Proximity principle
Interactions that involve more than one person.
Reference groups
Interactions that involve more than one person.
Secondary groups
Interactions that involve more than one person.
Small groups
Interactions that involve more than one person.
Social forces
Interactions that involve more than one person.
Social networks
Interactions that involve more than one person.
Society
Interactions that involve more than one person.
Social Scripts
Interactions that involve more than one person.
Symbols
Interactions that involve more than one person.
Triad
Interactions that involve more than one person.
Agency
Interactions that involve more than one person.
Social construction of reality
The process by which we use symbols and language to give meaning and value to objects and people.
Psychology principle
The process by which we use symbols and language to give meaning and value to objects and people.
Chicago school
The process by which we use symbols and language to give meaning and value to objects and people.
Collective behavior
The process by which we use symbols and language to give meaning and value to objects and people.
Components principle
The process by which we use symbols and language to give meaning and value to objects and people.
Dyad
The process by which we use symbols and language to give meaning and value to objects and people.
Group
The process by which we use symbols and language to give meaning and value to objects and people.
Indiana and Iowa schools
The process by which we use symbols and language to give meaning and value to objects and people.
Framing
The process by which we use symbols and language to give meaning and value to objects and people.
Justice
The process by which we use symbols and language to give meaning and value to objects and people.
Thomas theorem
The process by which we use symbols and language to give meaning and value to objects and people.
Language
The process by which we use symbols and language to give meaning and value to objects and people.
Legitimacy
The process by which we use symbols and language to give meaning and value to objects and people.
Power
The process by which we use symbols and language to give meaning and value to objects and people.
Primary groups
The process by which we use symbols and language to give meaning and value to objects and people.
Proximity principle
The process by which we use symbols and language to give meaning and value to objects and people.
Reference groups
The process by which we use symbols and language to give meaning and value to objects and people.
Secondary groups
The process by which we use symbols and language to give meaning and value to objects and people.
Small groups
The process by which we use symbols and language to give meaning and value to objects and people.
Social forces
The process by which we use symbols and language to give meaning and value to objects and people.
Social networks
The process by which we use symbols and language to give meaning and value to objects and people.
Society
The process by which we use symbols and language to give meaning and value to objects and people.
Social Scripts
The process by which we use symbols and language to give meaning and value to objects and people.
Symbols
The process by which we use symbols and language to give meaning and value to objects and people.
Triad
The process by which we use symbols and language to give meaning and value to objects and people.
Agency
The process by which we use symbols and language to give meaning and value to objects and people.
Social construction of reality
Anything that has a similar meaning for two or more individuals.
Psychology principle
Anything that has a similar meaning for two or more individuals.
Chicago school
Anything that has a similar meaning for two or more individuals.
Collective behavior
Anything that has a similar meaning for two or more individuals.
Components principle
Anything that has a similar meaning for two or more individuals.
Dyad
Anything that has a similar meaning for two or more individuals.
Group
Anything that has a similar meaning for two or more individuals.
Indiana and Iowa schools
Anything that has a similar meaning for two or more individuals.
Framing
Anything that has a similar meaning for two or more individuals.
Justice
Anything that has a similar meaning for two or more individuals.
Thomas theorem
Anything that has a similar meaning for two or more individuals.
Language
Anything that has a similar meaning for two or more individuals.
Legitimacy
Anything that has a similar meaning for two or more individuals.
Power
Anything that has a similar meaning for two or more individuals.
Primary groups
Anything that has a similar meaning for two or more individuals.
Proximity principle
Anything that has a similar meaning for two or more individuals.
Reference groups
Anything that has a similar meaning for two or more individuals.
Secondary groups
Anything that has a similar meaning for two or more individuals.
Small groups
Anything that has a similar meaning for two or more individuals.
Social forces
Anything that has a similar meaning for two or more individuals.
Social networks
Anything that has a similar meaning for two or more individuals.
Society
Anything that has a similar meaning for two or more individuals.
Social Scripts
Anything that has a similar meaning for two or more individuals.
Symbols
Anything that has a similar meaning for two or more individuals.
Triad
Anything that has a similar meaning for two or more individuals.
Agency
Anything that has a similar meaning for two or more individuals.
Social construction of reality
Any way in which society compels individuals to act in accordance with an external norm, rule, or demand.
Psychology principle
Any way in which society compels individuals to act in accordance with an external norm, rule, or demand.
Chicago school
Any way in which society compels individuals to act in accordance with an external norm, rule, or demand.
Collective behavior
Any way in which society compels individuals to act in accordance with an external norm, rule, or demand.
Components principle
Any way in which society compels individuals to act in accordance with an external norm, rule, or demand.
Dyad
Any way in which society compels individuals to act in accordance with an external norm, rule, or demand.
Group
Any way in which society compels individuals to act in accordance with an external norm, rule, or demand.
Indiana and Iowa schools
Any way in which society compels individuals to act in accordance with an external norm, rule, or demand.
Framing
Any way in which society compels individuals to act in accordance with an external norm, rule, or demand.
Justice
Any way in which society compels individuals to act in accordance with an external norm, rule, or demand.
Thomas theorem
Any way in which society compels individuals to act in accordance with an external norm, rule, or demand.
Language
Any way in which society compels individuals to act in accordance with an external norm, rule, or demand.
Legitimacy
Any way in which society compels individuals to act in accordance with an external norm, rule, or demand.
Power
Any way in which society compels individuals to act in accordance with an external norm, rule, or demand.
Primary groups
Any way in which society compels individuals to act in accordance with an external norm, rule, or demand.
Proximity principle
Any way in which society compels individuals to act in accordance with an external norm, rule, or demand.
Reference groups
Any way in which society compels individuals to act in accordance with an external norm, rule, or demand.
Secondary groups
Any way in which society compels individuals to act in accordance with an external norm, rule, or demand.
Small groups
Any way in which society compels individuals to act in accordance with an external norm, rule, or demand.
Social forces
Any way in which society compels individuals to act in accordance with an external norm, rule, or demand.
Social networks
Any way in which society compels individuals to act in accordance with an external norm, rule, or demand.
Society
Any way in which society compels individuals to act in accordance with an external norm, rule, or demand.
Social Scripts
Any way in which society compels individuals to act in accordance with an external norm, rule, or demand.
Symbols
Any way in which society compels individuals to act in accordance with an external norm, rule, or demand.
Triad
Any way in which society compels individuals to act in accordance with an external norm, rule, or demand.
Agency
Any way in which society compels individuals to act in accordance with an external norm, rule, or demand.
Social construction of reality
Perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on the quantitative study of social interaction processes because of the stable nature of social life.
Psychology principle
Perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on the quantitative study of social interaction processes because of the stable nature of social life.
Chicago school
Perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on the quantitative study of social interaction processes because of the stable nature of social life.
Collective behavior
Perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on the quantitative study of social interaction processes because of the stable nature of social life.
Components principle
Perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on the quantitative study of social interaction processes because of the stable nature of social life.
Dyad
Perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on the quantitative study of social interaction processes because of the stable nature of social life.
Group
Perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on the quantitative study of social interaction processes because of the stable nature of social life.
Indiana and Iowa schools
Perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on the quantitative study of social interaction processes because of the stable nature of social life.
Framing
Perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on the quantitative study of social interaction processes because of the stable nature of social life.
Justice
Perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on the quantitative study of social interaction processes because of the stable nature of social life.
Thomas theorem
Perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on the quantitative study of social interaction processes because of the stable nature of social life.
Language
Perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on the quantitative study of social interaction processes because of the stable nature of social life.
Legitimacy
Perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on the quantitative study of social interaction processes because of the stable nature of social life.
Power
Perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on the quantitative study of social interaction processes because of the stable nature of social life.
Primary groups
Perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on the quantitative study of social interaction processes because of the stable nature of social life.
Proximity principle
Perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on the quantitative study of social interaction processes because of the stable nature of social life.
Reference groups
Perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on the quantitative study of social interaction processes because of the stable nature of social life.
Secondary groups
Perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on the quantitative study of social interaction processes because of the stable nature of social life.
Small groups
Perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on the quantitative study of social interaction processes because of the stable nature of social life.
Social forces
Perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on the quantitative study of social interaction processes because of the stable nature of social life.
Social networks
Perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on the quantitative study of social interaction processes because of the stable nature of social life.
Society
Perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on the quantitative study of social interaction processes because of the stable nature of social life.
Social Scripts
Perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on the quantitative study of social interaction processes because of the stable nature of social life.
Symbols
Perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on the quantitative study of social interaction processes because of the stable nature of social life.
Triad
Perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on the quantitative study of social interaction processes because of the stable nature of social life.
Agency
Perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on the quantitative study of social interaction processes because of the stable nature of social life.
Social construction of reality
People we are close to and interact with regularly.
Psychology principle
People we are close to and interact with regularly.
Chicago school
People we are close to and interact with regularly.
Collective behavior
People we are close to and interact with regularly.
Components principle
People we are close to and interact with regularly.
Dyad
People we are close to and interact with regularly.
Group
People we are close to and interact with regularly.
Indiana and Iowa schools
People we are close to and interact with regularly.
Framing
People we are close to and interact with regularly.
Justice
People we are close to and interact with regularly.
Thomas theorem
People we are close to and interact with regularly.
Language
People we are close to and interact with regularly.
Legitimacy
People we are close to and interact with regularly.
Power
People we are close to and interact with regularly.
Primary groups
People we are close to and interact with regularly.
Proximity principle
People we are close to and interact with regularly.
Reference groups
People we are close to and interact with regularly.
Secondary groups
People we are close to and interact with regularly.
Small groups
People we are close to and interact with regularly.
Social forces
People we are close to and interact with regularly.
Social networks
People we are close to and interact with regularly.
Society
People we are close to and interact with regularly.
Social Scripts
People we are close to and interact with regularly.
Symbols
People we are close to and interact with regularly.
Triad
People we are close to and interact with regularly.
Agency
People we are close to and interact with regularly.
Social construction of reality
Two or more persons (generally, not more than 20) engaged in or capable of face-to-face interaction.
Psychology principle
Two or more persons (generally, not more than 20) engaged in or capable of face-to-face interaction.
Chicago school
Two or more persons (generally, not more than 20) engaged in or capable of face-to-face interaction.
Collective behavior
Two or more persons (generally, not more than 20) engaged in or capable of face-to-face interaction.
Components principle
Two or more persons (generally, not more than 20) engaged in or capable of face-to-face interaction.
Dyad
Two or more persons (generally, not more than 20) engaged in or capable of face-to-face interaction.
Group
Two or more persons (generally, not more than 20) engaged in or capable of face-to-face interaction.
Indiana and Iowa schools
Two or more persons (generally, not more than 20) engaged in or capable of face-to-face interaction.
Framing
Two or more persons (generally, not more than 20) engaged in or capable of face-to-face interaction.
Justice
Two or more persons (generally, not more than 20) engaged in or capable of face-to-face interaction.
Thomas theorem
Two or more persons (generally, not more than 20) engaged in or capable of face-to-face interaction.
Language
Two or more persons (generally, not more than 20) engaged in or capable of face-to-face interaction.
Legitimacy
Two or more persons (generally, not more than 20) engaged in or capable of face-to-face interaction.
Power
Two or more persons (generally, not more than 20) engaged in or capable of face-to-face interaction.
Primary groups
Two or more persons (generally, not more than 20) engaged in or capable of face-to-face interaction.
Proximity principle
Two or more persons (generally, not more than 20) engaged in or capable of face-to-face interaction.
Reference groups
Two or more persons (generally, not more than 20) engaged in or capable of face-to-face interaction.
Secondary groups
Two or more persons (generally, not more than 20) engaged in or capable of face-to-face interaction.
Small groups
Two or more persons (generally, not more than 20) engaged in or capable of face-to-face interaction.
Social forces
Two or more persons (generally, not more than 20) engaged in or capable of face-to-face interaction.
Social networks
Two or more persons (generally, not more than 20) engaged in or capable of face-to-face interaction.
Society
Two or more persons (generally, not more than 20) engaged in or capable of face-to-face interaction.
Social Scripts
Two or more persons (generally, not more than 20) engaged in or capable of face-to-face interaction.
Symbols
Two or more persons (generally, not more than 20) engaged in or capable of face-to-face interaction.
Triad
Two or more persons (generally, not more than 20) engaged in or capable of face-to-face interaction.
Agency
Two or more persons (generally, not more than 20) engaged in or capable of face-to-face interaction.
Social construction of reality
Within the social structure and personality perspective, the ability to identify the elements or components of society most likely to affect a given attitude or behavior.
Psychology principle
Within the social structure and personality perspective, the ability to identify the elements or components of society most likely to affect a given attitude or behavior.
Chicago school
Within the social structure and personality perspective, the ability to identify the elements or components of society most likely to affect a given attitude or behavior.
Collective behavior
Within the social structure and personality perspective, the ability to identify the elements or components of society most likely to affect a given attitude or behavior.
Components principle
Within the social structure and personality perspective, the ability to identify the elements or components of society most likely to affect a given attitude or behavior.
Dyad
Within the social structure and personality perspective, the ability to identify the elements or components of society most likely to affect a given attitude or behavior.
Group
Within the social structure and personality perspective, the ability to identify the elements or components of society most likely to affect a given attitude or behavior.
Indiana and Iowa schools
Within the social structure and personality perspective, the ability to identify the elements or components of society most likely to affect a given attitude or behavior.
Framing
Within the social structure and personality perspective, the ability to identify the elements or components of society most likely to affect a given attitude or behavior.
Justice
Within the social structure and personality perspective, the ability to identify the elements or components of society most likely to affect a given attitude or behavior.
Thomas theorem
Within the social structure and personality perspective, the ability to identify the elements or components of society most likely to affect a given attitude or behavior.
Language
Within the social structure and personality perspective, the ability to identify the elements or components of society most likely to affect a given attitude or behavior.
Legitimacy
Within the social structure and personality perspective, the ability to identify the elements or components of society most likely to affect a given attitude or behavior.
Power
Within the social structure and personality perspective, the ability to identify the elements or components of society most likely to affect a given attitude or behavior.
Primary groups
Within the social structure and personality perspective, the ability to identify the elements or components of society most likely to affect a given attitude or behavior.
Proximity principle
Within the social structure and personality perspective, the ability to identify the elements or components of society most likely to affect a given attitude or behavior.
Reference groups
Within the social structure and personality perspective, the ability to identify the elements or components of society most likely to affect a given attitude or behavior.
Secondary groups
Within the social structure and personality perspective, the ability to identify the elements or components of society most likely to affect a given attitude or behavior.
Small groups
Within the social structure and personality perspective, the ability to identify the elements or components of society most likely to affect a given attitude or behavior.
Social forces
Within the social structure and personality perspective, the ability to identify the elements or components of society most likely to affect a given attitude or behavior.
Social networks
Within the social structure and personality perspective, the ability to identify the elements or components of society most likely to affect a given attitude or behavior.
Society
Within the social structure and personality perspective, the ability to identify the elements or components of society most likely to affect a given attitude or behavior.
Social Scripts
Within the social structure and personality perspective, the ability to identify the elements or components of society most likely to affect a given attitude or behavior.
Symbols
Within the social structure and personality perspective, the ability to identify the elements or components of society most likely to affect a given attitude or behavior.
Triad
Within the social structure and personality perspective, the ability to identify the elements or components of society most likely to affect a given attitude or behavior.
Agency
Within the social structure and personality perspective, the ability to identify the elements or components of society most likely to affect a given attitude or behavior.
Social construction of reality
In symbolic interactionism, the network of interaction between people.
Psychology principle
In symbolic interactionism, the network of interaction between people.
Chicago school
In symbolic interactionism, the network of interaction between people.
Collective behavior
In symbolic interactionism, the network of interaction between people.
Components principle
In symbolic interactionism, the network of interaction between people.
Dyad
In symbolic interactionism, the network of interaction between people.
Group
In symbolic interactionism, the network of interaction between people.
Indiana and Iowa schools
In symbolic interactionism, the network of interaction between people.
Framing
In symbolic interactionism, the network of interaction between people.
Justice
In symbolic interactionism, the network of interaction between people.
Thomas theorem
In symbolic interactionism, the network of interaction between people.
Language
In symbolic interactionism, the network of interaction between people.
Legitimacy
In symbolic interactionism, the network of interaction between people.
Power
In symbolic interactionism, the network of interaction between people.
Primary groups
In symbolic interactionism, the network of interaction between people.
Proximity principle
In symbolic interactionism, the network of interaction between people.
Reference groups
In symbolic interactionism, the network of interaction between people.
Secondary groups
In symbolic interactionism, the network of interaction between people.
Small groups
In symbolic interactionism, the network of interaction between people.
Social forces
In symbolic interactionism, the network of interaction between people.
Social networks
In symbolic interactionism, the network of interaction between people.
Society
In symbolic interactionism, the network of interaction between people.
Social Scripts
In symbolic interactionism, the network of interaction between people.
Symbols
In symbolic interactionism, the network of interaction between people.
Triad
In symbolic interactionism, the network of interaction between people.
Agency
In symbolic interactionism, the network of interaction between people.
Social construction of reality
A three-person group.
Psychology principle
A three-person group.
Chicago school
A three-person group.
Collective behavior
A three-person group.
Components principle
A three-person group.
Dyad
A three-person group.
Group
A three-person group.
Indiana and Iowa schools
A three-person group.
Framing
A three-person group.
Justice
A three-person group.
Thomas theorem
A three-person group.
Language
A three-person group.
Legitimacy
A three-person group.
Power
A three-person group.
Primary groups
A three-person group.
Proximity principle
A three-person group.
Reference groups
A three-person group.
Secondary groups
A three-person group.
Small groups
A three-person group.
Social forces
A three-person group.
Social networks
A three-person group.
Society
A three-person group.
Social Scripts
A three-person group.
Symbols
A three-person group.
Triad
A three-person group.
Agency
A three-person group.
Social construction of reality
The ability to act and think independent of the constraints imposed by social conditions.
Psychology principle
The ability to act and think independent of the constraints imposed by social conditions.
Chicago school
The ability to act and think independent of the constraints imposed by social conditions.
Collective behavior
The ability to act and think independent of the constraints imposed by social conditions.
Components principle
The ability to act and think independent of the constraints imposed by social conditions.
Dyad
The ability to act and think independent of the constraints imposed by social conditions.
Group
The ability to act and think independent of the constraints imposed by social conditions.
Indiana and Iowa schools
The ability to act and think independent of the constraints imposed by social conditions.
Framing
The ability to act and think independent of the constraints imposed by social conditions.
Justice
The ability to act and think independent of the constraints imposed by social conditions.
Thomas theorem
The ability to act and think independent of the constraints imposed by social conditions.
Language
The ability to act and think independent of the constraints imposed by social conditions.
Legitimacy
The ability to act and think independent of the constraints imposed by social conditions.
Power
The ability to act and think independent of the constraints imposed by social conditions.
Primary groups
The ability to act and think independent of the constraints imposed by social conditions.
Proximity principle
The ability to act and think independent of the constraints imposed by social conditions.
Reference groups
The ability to act and think independent of the constraints imposed by social conditions.
Secondary groups
The ability to act and think independent of the constraints imposed by social conditions.
Small groups
The ability to act and think independent of the constraints imposed by social conditions.
Social forces
The ability to act and think independent of the constraints imposed by social conditions.
Social networks
The ability to act and think independent of the constraints imposed by social conditions.
Society
The ability to act and think independent of the constraints imposed by social conditions.
Social Scripts
The ability to act and think independent of the constraints imposed by social conditions.
Symbols
The ability to act and think independent of the constraints imposed by social conditions.
Triad
The ability to act and think independent of the constraints imposed by social conditions.
Agency
The ability to act and think independent of the constraints imposed by social conditions.
Social construction of reality
The ability to obtain what we desire in a group despite resistance.
Psychology principle
The ability to obtain what we desire in a group despite resistance.
Chicago school
The ability to obtain what we desire in a group despite resistance.
Collective behavior
The ability to obtain what we desire in a group despite resistance.
Components principle
The ability to obtain what we desire in a group despite resistance.
Dyad
The ability to obtain what we desire in a group despite resistance.
Group
The ability to obtain what we desire in a group despite resistance.
Indiana and Iowa schools
The ability to obtain what we desire in a group despite resistance.
Framing
The ability to obtain what we desire in a group despite resistance.
Justice
The ability to obtain what we desire in a group despite resistance.
Thomas theorem
The ability to obtain what we desire in a group despite resistance.
Language
The ability to obtain what we desire in a group despite resistance.
Legitimacy
The ability to obtain what we desire in a group despite resistance.
Power
The ability to obtain what we desire in a group despite resistance.
Primary groups
The ability to obtain what we desire in a group despite resistance.
Proximity principle
The ability to obtain what we desire in a group despite resistance.
Reference groups
The ability to obtain what we desire in a group despite resistance.
Secondary groups
The ability to obtain what we desire in a group despite resistance.
Small groups
The ability to obtain what we desire in a group despite resistance.
Social forces
The ability to obtain what we desire in a group despite resistance.
Social networks
The ability to obtain what we desire in a group despite resistance.
Society
The ability to obtain what we desire in a group despite resistance.
Social Scripts
The ability to obtain what we desire in a group despite resistance.
Symbols
The ability to obtain what we desire in a group despite resistance.
Triad
The ability to obtain what we desire in a group despite resistance.
Agency
The ability to obtain what we desire in a group despite resistance.
Social construction of reality
A two-person group.
Psychology principle
A two-person group.
Chicago school
A two-person group.
Collective behavior
A two-person group.
Components principle
A two-person group.
Dyad
A two-person group.
Group
A two-person group.
Indiana and Iowa schools
A two-person group.
Framing
A two-person group.
Justice
A two-person group.
Thomas theorem
A two-person group.
Language
A two-person group.
Legitimacy
A two-person group.
Power
A two-person group.
Primary groups
A two-person group.
Proximity principle
A two-person group.
Reference groups
A two-person group.
Secondary groups
A two-person group.
Small groups
A two-person group.
Social forces
A two-person group.
Social networks
A two-person group.
Society
A two-person group.
Social Scripts
A two-person group.
Symbols
A two-person group.
Triad
A two-person group.
Agency
A two-person group.
Social construction of reality
People we affiliate with to achieve common goals or meet common needs.
Psychology principle
People we affiliate with to achieve common goals or meet common needs.
Chicago school
People we affiliate with to achieve common goals or meet common needs.
Collective behavior
People we affiliate with to achieve common goals or meet common needs.
Components principle
People we affiliate with to achieve common goals or meet common needs.
Dyad
People we affiliate with to achieve common goals or meet common needs.
Group
People we affiliate with to achieve common goals or meet common needs.
Indiana and Iowa schools
People we affiliate with to achieve common goals or meet common needs.
Framing
People we affiliate with to achieve common goals or meet common needs.
Justice
People we affiliate with to achieve common goals or meet common needs.
Thomas theorem
People we affiliate with to achieve common goals or meet common needs.
Language
People we affiliate with to achieve common goals or meet common needs.
Legitimacy
People we affiliate with to achieve common goals or meet common needs.
Power
People we affiliate with to achieve common goals or meet common needs.
Primary groups
People we affiliate with to achieve common goals or meet common needs.
Proximity principle
People we affiliate with to achieve common goals or meet common needs.
Reference groups
People we affiliate with to achieve common goals or meet common needs.
Secondary groups
People we affiliate with to achieve common goals or meet common needs.
Small groups
People we affiliate with to achieve common goals or meet common needs.
Social forces
People we affiliate with to achieve common goals or meet common needs.
Social networks
People we affiliate with to achieve common goals or meet common needs.
Society
People we affiliate with to achieve common goals or meet common needs.
Social Scripts
People we affiliate with to achieve common goals or meet common needs.
Symbols
People we affiliate with to achieve common goals or meet common needs.
Triad
People we affiliate with to achieve common goals or meet common needs.
Agency
People we affiliate with to achieve common goals or meet common needs.
Social construction of reality
People we look to as a source of standards and identity.
Psychology principle
People we look to as a source of standards and identity.
Chicago school
People we look to as a source of standards and identity.
Collective behavior
People we look to as a source of standards and identity.
Components principle
People we look to as a source of standards and identity.
Dyad
People we look to as a source of standards and identity.
Group
People we look to as a source of standards and identity.
Indiana and Iowa schools
People we look to as a source of standards and identity.
Framing
People we look to as a source of standards and identity.
Justice
People we look to as a source of standards and identity.
Thomas theorem
People we look to as a source of standards and identity.
Language
People we look to as a source of standards and identity.
Legitimacy
People we look to as a source of standards and identity.
Power
People we look to as a source of standards and identity.
Primary groups
People we look to as a source of standards and identity.
Proximity principle
People we look to as a source of standards and identity.
Reference groups
People we look to as a source of standards and identity.
Secondary groups
People we look to as a source of standards and identity.
Small groups
People we look to as a source of standards and identity.
Social forces
People we look to as a source of standards and identity.
Social networks
People we look to as a source of standards and identity.
Society
People we look to as a source of standards and identity.
Social Scripts
People we look to as a source of standards and identity.
Symbols
People we look to as a source of standards and identity.
Triad
People we look to as a source of standards and identity.
Agency
People we look to as a source of standards and identity.
Social construction of reality
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how individuals internalize proximal experiences.
Psychology principle
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how individuals internalize proximal experiences.
Chicago school
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how individuals internalize proximal experiences.
Collective behavior
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how individuals internalize proximal experiences.
Components principle
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how individuals internalize proximal experiences.
Dyad
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how individuals internalize proximal experiences.
Group
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how individuals internalize proximal experiences.
Indiana and Iowa schools
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how individuals internalize proximal experiences.
Framing
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how individuals internalize proximal experiences.
Justice
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how individuals internalize proximal experiences.
Thomas theorem
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how individuals internalize proximal experiences.
Language
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how individuals internalize proximal experiences.
Legitimacy
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how individuals internalize proximal experiences.
Power
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how individuals internalize proximal experiences.
Primary groups
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how individuals internalize proximal experiences.
Proximity principle
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how individuals internalize proximal experiences.
Reference groups
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how individuals internalize proximal experiences.
Secondary groups
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how individuals internalize proximal experiences.
Small groups
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how individuals internalize proximal experiences.
Social forces
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how individuals internalize proximal experiences.
Social networks
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how individuals internalize proximal experiences.
Society
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how individuals internalize proximal experiences.
Social Scripts
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how individuals internalize proximal experiences.
Symbols
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how individuals internalize proximal experiences.
Triad
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how individuals internalize proximal experiences.
Agency
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how individuals internalize proximal experiences.
Social construction of reality
The appropriate thoughts, feelings, and behaviors that should be displayed in a particular social frame.
Psychology principle
The appropriate thoughts, feelings, and behaviors that should be displayed in a particular social frame.
Chicago school
The appropriate thoughts, feelings, and behaviors that should be displayed in a particular social frame.
Collective behavior
The appropriate thoughts, feelings, and behaviors that should be displayed in a particular social frame.
Components principle
The appropriate thoughts, feelings, and behaviors that should be displayed in a particular social frame.
Dyad
The appropriate thoughts, feelings, and behaviors that should be displayed in a particular social frame.
Group
The appropriate thoughts, feelings, and behaviors that should be displayed in a particular social frame.
Indiana and Iowa schools
The appropriate thoughts, feelings, and behaviors that should be displayed in a particular social frame.
Framing
The appropriate thoughts, feelings, and behaviors that should be displayed in a particular social frame.
Justice
The appropriate thoughts, feelings, and behaviors that should be displayed in a particular social frame.
Thomas theorem
The appropriate thoughts, feelings, and behaviors that should be displayed in a particular social frame.
Language
The appropriate thoughts, feelings, and behaviors that should be displayed in a particular social frame.
Legitimacy
The appropriate thoughts, feelings, and behaviors that should be displayed in a particular social frame.
Power
The appropriate thoughts, feelings, and behaviors that should be displayed in a particular social frame.
Primary groups
The appropriate thoughts, feelings, and behaviors that should be displayed in a particular social frame.
Proximity principle
The appropriate thoughts, feelings, and behaviors that should be displayed in a particular social frame.
Reference groups
The appropriate thoughts, feelings, and behaviors that should be displayed in a particular social frame.
Secondary groups
The appropriate thoughts, feelings, and behaviors that should be displayed in a particular social frame.
Small groups
The appropriate thoughts, feelings, and behaviors that should be displayed in a particular social frame.
Social forces
The appropriate thoughts, feelings, and behaviors that should be displayed in a particular social frame.
Social networks
The appropriate thoughts, feelings, and behaviors that should be displayed in a particular social frame.
Society
The appropriate thoughts, feelings, and behaviors that should be displayed in a particular social frame.
Social Scripts
The appropriate thoughts, feelings, and behaviors that should be displayed in a particular social frame.
Symbols
The appropriate thoughts, feelings, and behaviors that should be displayed in a particular social frame.
Triad
The appropriate thoughts, feelings, and behaviors that should be displayed in a particular social frame.
Agency
The appropriate thoughts, feelings, and behaviors that should be displayed in a particular social frame.
Social construction of reality
A series of relationships between individuals and groups.
Psychology principle
A series of relationships between individuals and groups.
Chicago school
A series of relationships between individuals and groups.
Collective behavior
A series of relationships between individuals and groups.
Components principle
A series of relationships between individuals and groups.
Dyad
A series of relationships between individuals and groups.
Group
A series of relationships between individuals and groups.
Indiana and Iowa schools
A series of relationships between individuals and groups.
Framing
A series of relationships between individuals and groups.
Justice
A series of relationships between individuals and groups.
Thomas theorem
A series of relationships between individuals and groups.
Language
A series of relationships between individuals and groups.
Legitimacy
A series of relationships between individuals and groups.
Power
A series of relationships between individuals and groups.
Primary groups
A series of relationships between individuals and groups.
Proximity principle
A series of relationships between individuals and groups.
Reference groups
A series of relationships between individuals and groups.
Secondary groups
A series of relationships between individuals and groups.
Small groups
A series of relationships between individuals and groups.
Social forces
A series of relationships between individuals and groups.
Social networks
A series of relationships between individuals and groups.
Society
A series of relationships between individuals and groups.
Social Scripts
A series of relationships between individuals and groups.
Symbols
A series of relationships between individuals and groups.
Triad
A series of relationships between individuals and groups.
Agency
A series of relationships between individuals and groups.
Social construction of reality
Theorem stating that when people define situations as real, the consequences of those situations become real.
Psychology principle
Theorem stating that when people define situations as real, the consequences of those situations become real.
Chicago school
Theorem stating that when people define situations as real, the consequences of those situations become real.
Collective behavior
Theorem stating that when people define situations as real, the consequences of those situations become real.
Components principle
Theorem stating that when people define situations as real, the consequences of those situations become real.
Dyad
Theorem stating that when people define situations as real, the consequences of those situations become real.
Group
Theorem stating that when people define situations as real, the consequences of those situations become real.
Indiana and Iowa schools
Theorem stating that when people define situations as real, the consequences of those situations become real.
Framing
Theorem stating that when people define situations as real, the consequences of those situations become real.
Justice
Theorem stating that when people define situations as real, the consequences of those situations become real.
Thomas theorem
Theorem stating that when people define situations as real, the consequences of those situations become real.
Language
Theorem stating that when people define situations as real, the consequences of those situations become real.
Legitimacy
Theorem stating that when people define situations as real, the consequences of those situations become real.
Power
Theorem stating that when people define situations as real, the consequences of those situations become real.
Primary groups
Theorem stating that when people define situations as real, the consequences of those situations become real.
Proximity principle
Theorem stating that when people define situations as real, the consequences of those situations become real.
Reference groups
Theorem stating that when people define situations as real, the consequences of those situations become real.
Secondary groups
Theorem stating that when people define situations as real, the consequences of those situations become real.
Small groups
Theorem stating that when people define situations as real, the consequences of those situations become real.
Social forces
Theorem stating that when people define situations as real, the consequences of those situations become real.
Social networks
Theorem stating that when people define situations as real, the consequences of those situations become real.
Society
Theorem stating that when people define situations as real, the consequences of those situations become real.
Social Scripts
Theorem stating that when people define situations as real, the consequences of those situations become real.
Symbols
Theorem stating that when people define situations as real, the consequences of those situations become real.
Triad
Theorem stating that when people define situations as real, the consequences of those situations become real.
Agency
Theorem stating that when people define situations as real, the consequences of those situations become real.
Social construction of reality
The process by which individuals transform the meaning of a situation using basic cognitive structures provided by society.
Psychology principle
The process by which individuals transform the meaning of a situation using basic cognitive structures provided by society.
Chicago school
The process by which individuals transform the meaning of a situation using basic cognitive structures provided by society.
Collective behavior
The process by which individuals transform the meaning of a situation using basic cognitive structures provided by society.
Components principle
The process by which individuals transform the meaning of a situation using basic cognitive structures provided by society.
Dyad
The process by which individuals transform the meaning of a situation using basic cognitive structures provided by society.
Group
The process by which individuals transform the meaning of a situation using basic cognitive structures provided by society.
Indiana and Iowa schools
The process by which individuals transform the meaning of a situation using basic cognitive structures provided by society.
Framing
The process by which individuals transform the meaning of a situation using basic cognitive structures provided by society.
Justice
The process by which individuals transform the meaning of a situation using basic cognitive structures provided by society.
Thomas theorem
The process by which individuals transform the meaning of a situation using basic cognitive structures provided by society.
Language
The process by which individuals transform the meaning of a situation using basic cognitive structures provided by society.
Legitimacy
The process by which individuals transform the meaning of a situation using basic cognitive structures provided by society.
Power
The process by which individuals transform the meaning of a situation using basic cognitive structures provided by society.
Primary groups
The process by which individuals transform the meaning of a situation using basic cognitive structures provided by society.
Proximity principle
The process by which individuals transform the meaning of a situation using basic cognitive structures provided by society.
Reference groups
The process by which individuals transform the meaning of a situation using basic cognitive structures provided by society.
Secondary groups
The process by which individuals transform the meaning of a situation using basic cognitive structures provided by society.
Small groups
The process by which individuals transform the meaning of a situation using basic cognitive structures provided by society.
Social forces
The process by which individuals transform the meaning of a situation using basic cognitive structures provided by society.
Social networks
The process by which individuals transform the meaning of a situation using basic cognitive structures provided by society.
Society
The process by which individuals transform the meaning of a situation using basic cognitive structures provided by society.
Social Scripts
The process by which individuals transform the meaning of a situation using basic cognitive structures provided by society.
Symbols
The process by which individuals transform the meaning of a situation using basic cognitive structures provided by society.
Triad
The process by which individuals transform the meaning of a situation using basic cognitive structures provided by society.
Agency
The process by which individuals transform the meaning of a situation using basic cognitive structures provided by society.
Social construction of reality
The action or behavior of people in groups or crowds.
Psychology principle
The action or behavior of people in groups or crowds.
Chicago school
The action or behavior of people in groups or crowds.
Collective behavior
The action or behavior of people in groups or crowds.
Components principle
The action or behavior of people in groups or crowds.
Dyad
The action or behavior of people in groups or crowds.
Group
The action or behavior of people in groups or crowds.
Indiana and Iowa schools
The action or behavior of people in groups or crowds.
Framing
The action or behavior of people in groups or crowds.
Justice
The action or behavior of people in groups or crowds.
Thomas theorem
The action or behavior of people in groups or crowds.
Language
The action or behavior of people in groups or crowds.
Legitimacy
The action or behavior of people in groups or crowds.
Power
The action or behavior of people in groups or crowds.
Primary groups
The action or behavior of people in groups or crowds.
Proximity principle
The action or behavior of people in groups or crowds.
Reference groups
The action or behavior of people in groups or crowds.
Secondary groups
The action or behavior of people in groups or crowds.
Small groups
The action or behavior of people in groups or crowds.
Social forces
The action or behavior of people in groups or crowds.
Social networks
The action or behavior of people in groups or crowds.
Society
The action or behavior of people in groups or crowds.
Social Scripts
The action or behavior of people in groups or crowds.
Symbols
The action or behavior of people in groups or crowds.
Triad
The action or behavior of people in groups or crowds.
Agency
The action or behavior of people in groups or crowds.
Social construction of reality
A perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on understanding the social processes involved in a given situation rather than on trying to quantify and predict people’s thoughts, feelings, and behavior.
Psychology principle
A perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on understanding the social processes involved in a given situation rather than on trying to quantify and predict people’s thoughts, feelings, and behavior.
Chicago school
A perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on understanding the social processes involved in a given situation rather than on trying to quantify and predict people’s thoughts, feelings, and behavior.
Collective behavior
A perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on understanding the social processes involved in a given situation rather than on trying to quantify and predict people’s thoughts, feelings, and behavior.
Components principle
A perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on understanding the social processes involved in a given situation rather than on trying to quantify and predict people’s thoughts, feelings, and behavior.
Dyad
A perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on understanding the social processes involved in a given situation rather than on trying to quantify and predict people’s thoughts, feelings, and behavior.
Group
A perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on understanding the social processes involved in a given situation rather than on trying to quantify and predict people’s thoughts, feelings, and behavior.
Indiana and Iowa schools
A perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on understanding the social processes involved in a given situation rather than on trying to quantify and predict people’s thoughts, feelings, and behavior.
Framing
A perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on understanding the social processes involved in a given situation rather than on trying to quantify and predict people’s thoughts, feelings, and behavior.
Justice
A perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on understanding the social processes involved in a given situation rather than on trying to quantify and predict people’s thoughts, feelings, and behavior.
Thomas theorem
A perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on understanding the social processes involved in a given situation rather than on trying to quantify and predict people’s thoughts, feelings, and behavior.
Language
A perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on understanding the social processes involved in a given situation rather than on trying to quantify and predict people’s thoughts, feelings, and behavior.
Legitimacy
A perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on understanding the social processes involved in a given situation rather than on trying to quantify and predict people’s thoughts, feelings, and behavior.
Power
A perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on understanding the social processes involved in a given situation rather than on trying to quantify and predict people’s thoughts, feelings, and behavior.
Primary groups
A perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on understanding the social processes involved in a given situation rather than on trying to quantify and predict people’s thoughts, feelings, and behavior.
Proximity principle
A perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on understanding the social processes involved in a given situation rather than on trying to quantify and predict people’s thoughts, feelings, and behavior.
Reference groups
A perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on understanding the social processes involved in a given situation rather than on trying to quantify and predict people’s thoughts, feelings, and behavior.
Secondary groups
A perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on understanding the social processes involved in a given situation rather than on trying to quantify and predict people’s thoughts, feelings, and behavior.
Small groups
A perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on understanding the social processes involved in a given situation rather than on trying to quantify and predict people’s thoughts, feelings, and behavior.
Social forces
A perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on understanding the social processes involved in a given situation rather than on trying to quantify and predict people’s thoughts, feelings, and behavior.
Social networks
A perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on understanding the social processes involved in a given situation rather than on trying to quantify and predict people’s thoughts, feelings, and behavior.
Society
A perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on understanding the social processes involved in a given situation rather than on trying to quantify and predict people’s thoughts, feelings, and behavior.
Social Scripts
A perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on understanding the social processes involved in a given situation rather than on trying to quantify and predict people’s thoughts, feelings, and behavior.
Symbols
A perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on understanding the social processes involved in a given situation rather than on trying to quantify and predict people’s thoughts, feelings, and behavior.
Triad
A perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on understanding the social processes involved in a given situation rather than on trying to quantify and predict people’s thoughts, feelings, and behavior.
Agency
A perspective within symbolic interactionism that focuses on understanding the social processes involved in a given situation rather than on trying to quantify and predict people’s thoughts, feelings, and behavior.
Social construction of reality
A series of symbols that can be combined in various ways to create new meanings.
Psychology principle
A series of symbols that can be combined in various ways to create new meanings.
Chicago school
A series of symbols that can be combined in various ways to create new meanings.
Collective behavior
A series of symbols that can be combined in various ways to create new meanings.
Components principle
A series of symbols that can be combined in various ways to create new meanings.
Dyad
A series of symbols that can be combined in various ways to create new meanings.
Group
A series of symbols that can be combined in various ways to create new meanings.
Indiana and Iowa schools
A series of symbols that can be combined in various ways to create new meanings.
Framing
A series of symbols that can be combined in various ways to create new meanings.
Justice
A series of symbols that can be combined in various ways to create new meanings.
Thomas theorem
A series of symbols that can be combined in various ways to create new meanings.
Language
A series of symbols that can be combined in various ways to create new meanings.
Legitimacy
A series of symbols that can be combined in various ways to create new meanings.
Power
A series of symbols that can be combined in various ways to create new meanings.
Primary groups
A series of symbols that can be combined in various ways to create new meanings.
Proximity principle
A series of symbols that can be combined in various ways to create new meanings.
Reference groups
A series of symbols that can be combined in various ways to create new meanings.
Secondary groups
A series of symbols that can be combined in various ways to create new meanings.
Small groups
A series of symbols that can be combined in various ways to create new meanings.
Social forces
A series of symbols that can be combined in various ways to create new meanings.
Social networks
A series of symbols that can be combined in various ways to create new meanings.
Society
A series of symbols that can be combined in various ways to create new meanings.
Social Scripts
A series of symbols that can be combined in various ways to create new meanings.
Symbols
A series of symbols that can be combined in various ways to create new meanings.
Triad
A series of symbols that can be combined in various ways to create new meanings.
Agency
A series of symbols that can be combined in various ways to create new meanings.
Social construction of reality
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how people are affected by social structure through their immediate social environments.
Psychology principle
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how people are affected by social structure through their immediate social environments.
Chicago school
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how people are affected by social structure through their immediate social environments.
Collective behavior
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how people are affected by social structure through their immediate social environments.
Components principle
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how people are affected by social structure through their immediate social environments.
Dyad
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how people are affected by social structure through their immediate social environments.
Group
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how people are affected by social structure through their immediate social environments.
Indiana and Iowa schools
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how people are affected by social structure through their immediate social environments.
Framing
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how people are affected by social structure through their immediate social environments.
Justice
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how people are affected by social structure through their immediate social environments.
Thomas theorem
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how people are affected by social structure through their immediate social environments.
Language
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how people are affected by social structure through their immediate social environments.
Legitimacy
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how people are affected by social structure through their immediate social environments.
Power
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how people are affected by social structure through their immediate social environments.
Primary groups
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how people are affected by social structure through their immediate social environments.
Proximity principle
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how people are affected by social structure through their immediate social environments.
Reference groups
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how people are affected by social structure through their immediate social environments.
Secondary groups
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how people are affected by social structure through their immediate social environments.
Small groups
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how people are affected by social structure through their immediate social environments.
Social forces
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how people are affected by social structure through their immediate social environments.
Social networks
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how people are affected by social structure through their immediate social environments.
Society
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how people are affected by social structure through their immediate social environments.
Social Scripts
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how people are affected by social structure through their immediate social environments.
Symbols
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how people are affected by social structure through their immediate social environments.
Triad
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how people are affected by social structure through their immediate social environments.
Agency
Element of the social structure and personality perspective referring to how people are affected by social structure through their immediate social environments.
Social construction of reality

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 22 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 22 في هذه المجموعة.








