Deck 3: Techniques of Differentiation
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/69
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 3: Techniques of Differentiation
1
Find the slope of the tangent line to f(x) = 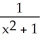 at (-1, f(-1)).
at (-1, f(-1)).
Enter a reduced fraction.
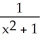 at (-1, f(-1)).
at (-1, f(-1)).Enter a reduced fraction.
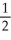
2
Differentiate
y =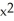 + 4x(
+ 4x( 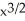 )
)
A) 2x + 10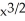
B)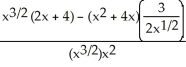
C) (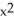 + 4x)
+ 4x) 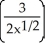 + (
+ ( 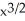 )(2x + 4)
)(2x + 4)
D) 6x(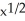 ) + 4
) + 4 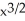
y =
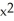 + 4x(
+ 4x( 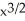 )
)A) 2x + 10
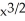
B)
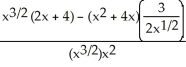
C) (
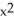 + 4x)
+ 4x) 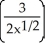 + (
+ ( 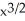 )(2x + 4)
)(2x + 4)D) 6x(
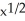 ) + 4
) + 4 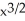
2x + 10 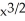
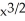
3
Differentiate
f(x) =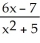 at x = -1
at x = -1
Enter just a reduced fraction.
f(x) =
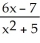 at x = -1
at x = -1Enter just a reduced fraction.
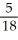
4
Find the slope of the tangent line to f(x) = 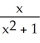 at (2, f(2)).
at (2, f(2)).
Enter just a reduced fraction.
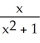 at (2, f(2)).
at (2, f(2)).Enter just a reduced fraction.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
Differentiate
f(x) =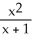 at x = 2
at x = 2
Enter just a reduced fraction.
f(x) =
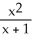 at x = 2
at x = 2Enter just a reduced fraction.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Differentiate
y =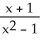
A)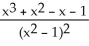
B)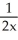
C) -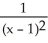
D) none of these
y =
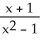
A)
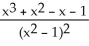
B)
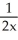
C) -
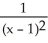
D) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Differentiate
f(x) =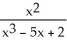 at x = -1
at x = -1
Enter a reduced fraction only.
f(x) =
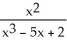 at x = -1
at x = -1Enter a reduced fraction only.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Find the slope of the tangent line to f(x) = 4( 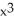 + 1)(2
+ 1)(2 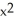 + 2x + 1
+ 2x + 1 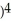 at (-1, f(-1)).
at (-1, f(-1)).
Enter just an integer.
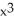 + 1)(2
+ 1)(2 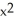 + 2x + 1
+ 2x + 1 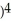 at (-1, f(-1)).
at (-1, f(-1)).Enter just an integer.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Differentiate
f(x) =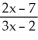
A) -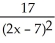
B)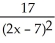
C) -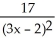
D)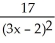
f(x) =
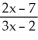
A) -
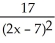
B)
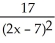
C) -
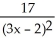
D)
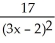

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Find the slope of the tangent line to f(x) = 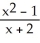 at (-1, f(-1)).
at (-1, f(-1)).
Enter just an integer.
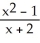 at (-1, f(-1)).
at (-1, f(-1)).Enter just an integer.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Differentiate
f(x) = (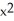 + 1
+ 1 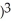 (
( 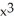 - 1
- 1 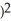 at x = -1
at x = -1
Enter just an integer.
f(x) = (
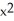 + 1
+ 1 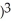 (
( 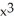 - 1
- 1 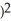 at x = -1
at x = -1Enter just an integer.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Differentiate
f(x) = (2x + 1)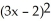 at x = 1
at x = 1
Enter just an integer.
f(x) = (2x + 1)
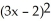 at x = 1
at x = 1Enter just an integer.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Differentiate
f(x) = (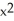 + x)(3
+ x)(3 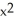 + 4x - 1) at x = 1
+ 4x - 1) at x = 1
Enter just an integer.
f(x) = (
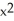 + x)(3
+ x)(3 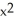 + 4x - 1) at x = 1
+ 4x - 1) at x = 1Enter just an integer.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Differentiate
f(x) = (4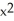 + 4)(2
+ 4)(2 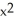 + 2x) at x = 1
+ 2x) at x = 1
Enter just an integer.
f(x) = (4
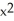 + 4)(2
+ 4)(2 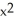 + 2x) at x = 1
+ 2x) at x = 1Enter just an integer.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Differentiate
f(x) = (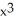 - 2
- 2 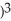 (
( 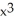 + 2
+ 2 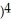 at x = -1
at x = -1
Enter just an integer.
f(x) = (
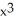 - 2
- 2 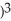 (
( 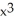 + 2
+ 2 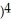 at x = -1
at x = -1Enter just an integer.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Differentiate
-f(x) = (-3 - )(2 - 5x + 3)
A) -84 - 105 + 16 + 20
B) -84 + 105 - 16 + 20
C) -54 + 120 - 63 - 12 + 25 - 12
D) 30 - 90 + 63 + 4 - 15 + 12
-f(x) = (-3 - )(2 - 5x + 3)
A) -84 - 105 + 16 + 20
B) -84 + 105 - 16 + 20
C) -54 + 120 - 63 - 12 + 25 - 12
D) 30 - 90 + 63 + 4 - 15 + 12

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Differentiate
g(x) = (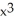 + 1)(3
+ 1)(3 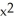 - 1)
- 1)
A) -3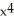 + 3
+ 3 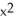 + 6x
+ 6x
B) 15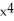 - 3
- 3 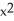 + 6x
+ 6x
C) -3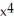 - 3
- 3 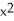 + 6x
+ 6x
D) 3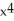 - 3
- 3 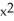 - 6x
- 6x
g(x) = (
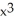 + 1)(3
+ 1)(3 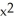 - 1)
- 1)A) -3
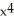 + 3
+ 3 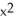 + 6x
+ 6xB) 15
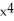 - 3
- 3 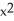 + 6x
+ 6xC) -3
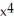 - 3
- 3 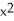 + 6x
+ 6xD) 3
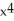 - 3
- 3 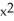 - 6x
- 6x
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Differentiate
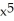 ∙
∙ 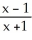 at x = 1
at x = 1
Enter just a reduced fraction.
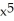 ∙
∙ 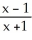 at x = 1
at x = 1Enter just a reduced fraction.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Differentiate
f(x) = (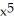 - 8
- 8 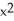 + 5)(
+ 5)( 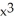 +
+ 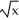 - 1) at x = 1
- 1) at x = 1
Enter just an integer.
f(x) = (
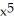 - 8
- 8 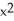 + 5)(
+ 5)( 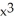 +
+ 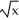 - 1) at x = 1
- 1) at x = 1Enter just an integer.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Differentiate
F(r) =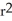 (r - 1)(r + 1
(r - 1)(r + 1 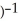
A) (2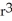 + 2
+ 2 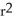 - 2r)(r + 1
- 2r)(r + 1 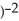
B) 2r(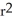 + r -1)
+ r -1)
C)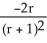
D) 4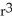 - 2r
- 2r
F(r) =
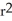 (r - 1)(r + 1
(r - 1)(r + 1 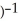
A) (2
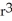 + 2
+ 2 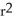 - 2r)(r + 1
- 2r)(r + 1 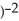
B) 2r(
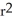 + r -1)
+ r -1)C)
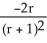
D) 4
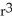 - 2r
- 2r
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
The following function may be viewed as a composite function f(g(x)). Find f(x) and g(x). 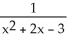
A) f(x) = x, G(x) =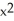 + 2x - 3
+ 2x - 3
B) f(x) = , G(x) =
, G(x) = 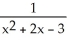
C) f(x) = , G(x) =
, G(x) = 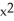 + 2x - 3
+ 2x - 3
D) f(x) =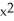 + 2x - 3, G(x) =
+ 2x - 3, G(x) = 
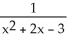
A) f(x) = x, G(x) =
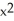 + 2x - 3
+ 2x - 3B) f(x) =
 , G(x) =
, G(x) = 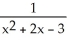
C) f(x) =
 , G(x) =
, G(x) = 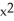 + 2x - 3
+ 2x - 3D) f(x) =
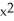 + 2x - 3, G(x) =
+ 2x - 3, G(x) = 

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
If f(x) = 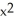 - 9 and g(x) =
- 9 and g(x) = 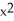 - 16, find
- 16, find 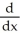 g(f(x)).
g(f(x)).
A) (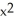 - 9
- 9 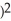 - 16
- 16
B)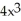 - 36x
- 36x
C) ((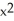 - 9
- 9 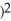 - 16)(2x)
- 16)(2x)
D) 4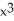 - 50
- 50 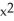
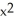 - 9 and g(x) =
- 9 and g(x) = 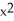 - 16, find
- 16, find 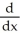 g(f(x)).
g(f(x)).A) (
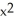 - 9
- 9 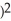 - 16
- 16B)
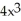 - 36x
- 36xC) ((
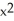 - 9
- 9 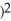 - 16)(2x)
- 16)(2x)D) 4
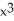 - 50
- 50 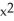

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Let f(x) = ![<strong>Let f(x) = . Using the chain rule, find an expression for the derivative of [f(g(x))].</strong> A) 3 g'(x B) 3[g(x) C) g'(x D) 3[g(x) g'(x) E) none of these](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3874/11ea9846_68d3_9214_b1f1_f5dad4332bb4_TB3874_11.jpg) . Using the chain rule, find an expression for the derivative of [f(g(x))].
. Using the chain rule, find an expression for the derivative of [f(g(x))].
A) 3![<strong>Let f(x) = . Using the chain rule, find an expression for the derivative of [f(g(x))].</strong> A) 3 g'(x B) 3[g(x) C) g'(x D) 3[g(x) g'(x) E) none of these](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3874/11ea9846_68d3_b925_b1f1_5f5171d8493a_TB3874_11.jpg) g'(x
g'(x ![<strong>Let f(x) = . Using the chain rule, find an expression for the derivative of [f(g(x))].</strong> A) 3 g'(x B) 3[g(x) C) g'(x D) 3[g(x) g'(x) E) none of these](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3874/11ea9846_68d3_e036_b1f1_b90ccc15f73e_TB3874_11.jpg)
B) 3[g(x)![<strong>Let f(x) = . Using the chain rule, find an expression for the derivative of [f(g(x))].</strong> A) 3 g'(x B) 3[g(x) C) g'(x D) 3[g(x) g'(x) E) none of these](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3874/11ea9846_68d4_0747_b1f1_1d752125c238_TB3874_11.jpg)
C) g'(x![<strong>Let f(x) = . Using the chain rule, find an expression for the derivative of [f(g(x))].</strong> A) 3 g'(x B) 3[g(x) C) g'(x D) 3[g(x) g'(x) E) none of these](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3874/11ea9846_68d4_2e58_b1f1_67b20296c0ea_TB3874_11.jpg)
D) 3[g(x)![<strong>Let f(x) = . Using the chain rule, find an expression for the derivative of [f(g(x))].</strong> A) 3 g'(x B) 3[g(x) C) g'(x D) 3[g(x) g'(x) E) none of these](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3874/11ea9846_68d4_5569_b1f1_7363c170367c_TB3874_11.jpg) g'(x)
g'(x)
E) none of these
![<strong>Let f(x) = . Using the chain rule, find an expression for the derivative of [f(g(x))].</strong> A) 3 g'(x B) 3[g(x) C) g'(x D) 3[g(x) g'(x) E) none of these](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3874/11ea9846_68d3_9214_b1f1_f5dad4332bb4_TB3874_11.jpg) . Using the chain rule, find an expression for the derivative of [f(g(x))].
. Using the chain rule, find an expression for the derivative of [f(g(x))].A) 3
![<strong>Let f(x) = . Using the chain rule, find an expression for the derivative of [f(g(x))].</strong> A) 3 g'(x B) 3[g(x) C) g'(x D) 3[g(x) g'(x) E) none of these](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3874/11ea9846_68d3_b925_b1f1_5f5171d8493a_TB3874_11.jpg) g'(x
g'(x ![<strong>Let f(x) = . Using the chain rule, find an expression for the derivative of [f(g(x))].</strong> A) 3 g'(x B) 3[g(x) C) g'(x D) 3[g(x) g'(x) E) none of these](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3874/11ea9846_68d3_e036_b1f1_b90ccc15f73e_TB3874_11.jpg)
B) 3[g(x)
![<strong>Let f(x) = . Using the chain rule, find an expression for the derivative of [f(g(x))].</strong> A) 3 g'(x B) 3[g(x) C) g'(x D) 3[g(x) g'(x) E) none of these](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3874/11ea9846_68d4_0747_b1f1_1d752125c238_TB3874_11.jpg)
C) g'(x
![<strong>Let f(x) = . Using the chain rule, find an expression for the derivative of [f(g(x))].</strong> A) 3 g'(x B) 3[g(x) C) g'(x D) 3[g(x) g'(x) E) none of these](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3874/11ea9846_68d4_2e58_b1f1_67b20296c0ea_TB3874_11.jpg)
D) 3[g(x)
![<strong>Let f(x) = . Using the chain rule, find an expression for the derivative of [f(g(x))].</strong> A) 3 g'(x B) 3[g(x) C) g'(x D) 3[g(x) g'(x) E) none of these](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3874/11ea9846_68d4_5569_b1f1_7363c170367c_TB3874_11.jpg) g'(x)
g'(x)E) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
One hour after x milligrams of a particular drug are given to a person, the change in body temperature T(x), in degrees Celsius, is given approximately by: T(x) = 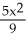
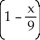 -
- 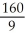 , 0 ≤ x ≤ 6. Find the sensitivity, T'(x), of the body to a dosage of three milligrams.
, 0 ≤ x ≤ 6. Find the sensitivity, T'(x), of the body to a dosage of three milligrams.
A) degrees per milligram
degrees per milligram
B) -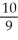 degrees per milligram
degrees per milligram
C) - degrees per milligram
degrees per milligram
D) -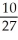 degree per milligram
degree per milligram
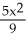
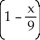 -
- 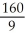 , 0 ≤ x ≤ 6. Find the sensitivity, T'(x), of the body to a dosage of three milligrams.
, 0 ≤ x ≤ 6. Find the sensitivity, T'(x), of the body to a dosage of three milligrams.A)
 degrees per milligram
degrees per milligramB) -
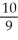 degrees per milligram
degrees per milligramC) -
 degrees per milligram
degrees per milligramD) -
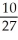 degree per milligram
degree per milligram
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
A publishing company has published a new magazine for young adults. The monthly sales S (in thousands) is given by 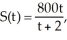 where t is the number of months since the first issue was published. Find S(3) and S'(3) and interpret the results.
where t is the number of months since the first issue was published. Find S(3) and S'(3) and interpret the results.
A) At three months, the monthly sales are $480,000 and increasing at 64,000 magazines per month.
B) At three months, the monthly sales are $2, 400,000 and increasing at 64,000 magazines per month.
C) At three months, the monthly sales are $2,400,000 and increasing at 800,000 magazines per month.
D) At three months, the monthly sales are $480,000 and decreasing at 64,000 magazines per month.
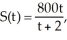 where t is the number of months since the first issue was published. Find S(3) and S'(3) and interpret the results.
where t is the number of months since the first issue was published. Find S(3) and S'(3) and interpret the results.A) At three months, the monthly sales are $480,000 and increasing at 64,000 magazines per month.
B) At three months, the monthly sales are $2, 400,000 and increasing at 64,000 magazines per month.
C) At three months, the monthly sales are $2,400,000 and increasing at 800,000 magazines per month.
D) At three months, the monthly sales are $480,000 and decreasing at 64,000 magazines per month.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Find the values of x where the tangent line is horizontal for the graph of 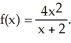
A) x = 0, x = -4
B) x = 0, x = -2
C) x = -2
D) x = -2, x = 0, x = -4
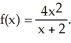
A) x = 0, x = -4
B) x = 0, x = -2
C) x = -2
D) x = -2, x = 0, x = -4

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Find the equation of the tangent line to the graph of the function 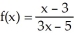 at
at 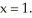
A) y = x
B) y =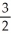 x -
x - 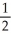
C) y = -3x + 4
D) y = 3x - 2
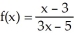 at
at 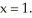
A) y = x
B) y =
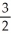 x -
x - 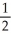
C) y = -3x + 4
D) y = 3x - 2

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
The following function may be viewed as a composite function f(g(x)). Find f(x) and g(x). 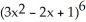
A) f(x) = x, G(x) = 3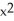 - 2x + 1
- 2x + 1
B) f(x) =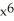 , G(x) = 3
, G(x) = 3 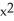 - 2x + 1
- 2x + 1
C) f(x) = 3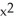 - 2x + 1, G(x) =
- 2x + 1, G(x) = 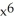
D) f(x) =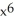 , G(x) =
, G(x) = 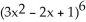
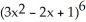
A) f(x) = x, G(x) = 3
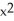 - 2x + 1
- 2x + 1B) f(x) =
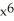 , G(x) = 3
, G(x) = 3 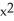 - 2x + 1
- 2x + 1C) f(x) = 3
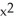 - 2x + 1, G(x) =
- 2x + 1, G(x) = 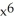
D) f(x) =
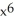 , G(x) =
, G(x) = 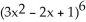

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Use the chain rule to compute the derivative of 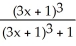 at x = -1.
at x = -1.
Enter just a reduced fraction.
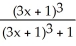 at x = -1.
at x = -1.Enter just a reduced fraction.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
If y = ( 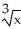 + 1
+ 1 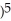 , find
, find 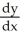 .
.
A) (
( 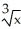 + 1
+ 1 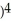
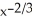
B) (
( 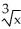 + 1
+ 1 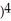
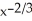
C) 5(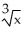 + 1
+ 1 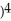
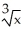
D) 5(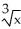 + 1
+ 1 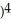
E) none of these
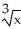 + 1
+ 1 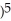 , find
, find 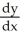 .
.A)
 (
( 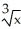 + 1
+ 1 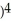
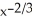
B)
 (
( 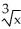 + 1
+ 1 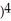
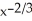
C) 5(
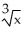 + 1
+ 1 
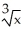
D) 5(
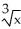 + 1
+ 1 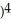
E) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Let g(x) = ![<strong>Let g(x) = . Using the chain rule, find an expression for the derivative of [g(f(x))].</strong> A) f'(x) B) f'( ) C) f'(x) + f(x) D) f( ) E) none of these](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3874/11ea9846_68d4_a38a_b1f1_ed459fc56463_TB3874_11.jpg) . Using the chain rule, find an expression for the derivative of [g(f(x))].
. Using the chain rule, find an expression for the derivative of [g(f(x))].
A)![<strong>Let g(x) = . Using the chain rule, find an expression for the derivative of [g(f(x))].</strong> A) f'(x) B) f'( ) C) f'(x) + f(x) D) f( ) E) none of these](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3874/11ea9846_68d4_ca9b_b1f1_47f8558327c9_TB3874_11.jpg) f'(x)
f'(x)
B)![<strong>Let g(x) = . Using the chain rule, find an expression for the derivative of [g(f(x))].</strong> A) f'(x) B) f'( ) C) f'(x) + f(x) D) f( ) E) none of these](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3874/11ea9846_68d4_f1ac_b1f1_5d68b887c0cb_TB3874_11.jpg) f'(
f'( ![<strong>Let g(x) = . Using the chain rule, find an expression for the derivative of [g(f(x))].</strong> A) f'(x) B) f'( ) C) f'(x) + f(x) D) f( ) E) none of these](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3874/11ea9846_68d4_f1ad_b1f1_4928ffc7b424_TB3874_11.jpg) )
)
C)![<strong>Let g(x) = . Using the chain rule, find an expression for the derivative of [g(f(x))].</strong> A) f'(x) B) f'( ) C) f'(x) + f(x) D) f( ) E) none of these](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3874/11ea9846_68d5_3fce_b1f1_471246d1be7c_TB3874_11.jpg) f'(x) +
f'(x) + ![<strong>Let g(x) = . Using the chain rule, find an expression for the derivative of [g(f(x))].</strong> A) f'(x) B) f'( ) C) f'(x) + f(x) D) f( ) E) none of these](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3874/11ea9846_68d5_3fcf_b1f1_6fab200d75c9_TB3874_11.jpg)
![<strong>Let g(x) = . Using the chain rule, find an expression for the derivative of [g(f(x))].</strong> A) f'(x) B) f'( ) C) f'(x) + f(x) D) f( ) E) none of these](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3874/11ea9846_68d5_66e0_b1f1_7dfe191e6ef0_TB3874_11.jpg) f(x)
f(x)
D)![<strong>Let g(x) = . Using the chain rule, find an expression for the derivative of [g(f(x))].</strong> A) f'(x) B) f'( ) C) f'(x) + f(x) D) f( ) E) none of these](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3874/11ea9846_68d5_8df1_b1f1_3b75742cd46b_TB3874_11.jpg) f(
f( ![<strong>Let g(x) = . Using the chain rule, find an expression for the derivative of [g(f(x))].</strong> A) f'(x) B) f'( ) C) f'(x) + f(x) D) f( ) E) none of these](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3874/11ea9846_68d5_b502_b1f1_07737212c2a4_TB3874_11.jpg) )
)
E) none of these
![<strong>Let g(x) = . Using the chain rule, find an expression for the derivative of [g(f(x))].</strong> A) f'(x) B) f'( ) C) f'(x) + f(x) D) f( ) E) none of these](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3874/11ea9846_68d4_a38a_b1f1_ed459fc56463_TB3874_11.jpg) . Using the chain rule, find an expression for the derivative of [g(f(x))].
. Using the chain rule, find an expression for the derivative of [g(f(x))].A)
![<strong>Let g(x) = . Using the chain rule, find an expression for the derivative of [g(f(x))].</strong> A) f'(x) B) f'( ) C) f'(x) + f(x) D) f( ) E) none of these](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3874/11ea9846_68d4_ca9b_b1f1_47f8558327c9_TB3874_11.jpg) f'(x)
f'(x)B)
![<strong>Let g(x) = . Using the chain rule, find an expression for the derivative of [g(f(x))].</strong> A) f'(x) B) f'( ) C) f'(x) + f(x) D) f( ) E) none of these](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3874/11ea9846_68d4_f1ac_b1f1_5d68b887c0cb_TB3874_11.jpg) f'(
f'( ![<strong>Let g(x) = . Using the chain rule, find an expression for the derivative of [g(f(x))].</strong> A) f'(x) B) f'( ) C) f'(x) + f(x) D) f( ) E) none of these](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3874/11ea9846_68d4_f1ad_b1f1_4928ffc7b424_TB3874_11.jpg) )
)C)
![<strong>Let g(x) = . Using the chain rule, find an expression for the derivative of [g(f(x))].</strong> A) f'(x) B) f'( ) C) f'(x) + f(x) D) f( ) E) none of these](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3874/11ea9846_68d5_3fce_b1f1_471246d1be7c_TB3874_11.jpg) f'(x) +
f'(x) + ![<strong>Let g(x) = . Using the chain rule, find an expression for the derivative of [g(f(x))].</strong> A) f'(x) B) f'( ) C) f'(x) + f(x) D) f( ) E) none of these](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3874/11ea9846_68d5_3fcf_b1f1_6fab200d75c9_TB3874_11.jpg)
![<strong>Let g(x) = . Using the chain rule, find an expression for the derivative of [g(f(x))].</strong> A) f'(x) B) f'( ) C) f'(x) + f(x) D) f( ) E) none of these](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3874/11ea9846_68d5_66e0_b1f1_7dfe191e6ef0_TB3874_11.jpg) f(x)
f(x)D)
![<strong>Let g(x) = . Using the chain rule, find an expression for the derivative of [g(f(x))].</strong> A) f'(x) B) f'( ) C) f'(x) + f(x) D) f( ) E) none of these](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3874/11ea9846_68d5_8df1_b1f1_3b75742cd46b_TB3874_11.jpg) f(
f( ![<strong>Let g(x) = . Using the chain rule, find an expression for the derivative of [g(f(x))].</strong> A) f'(x) B) f'( ) C) f'(x) + f(x) D) f( ) E) none of these](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3874/11ea9846_68d5_b502_b1f1_07737212c2a4_TB3874_11.jpg) )
)E) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Let f(x) = 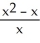 , g(x) =
, g(x) = 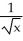 . Compute f(g(x)) at x= 4.
. Compute f(g(x)) at x= 4.
Enter just a reduced fraction.
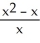 , g(x) =
, g(x) = 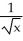 . Compute f(g(x)) at x= 4.
. Compute f(g(x)) at x= 4.Enter just a reduced fraction.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
Find all x-coordinates of points (x, y) on the graph of Q(x) = 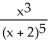 where the tangent line is horizontal. Enter your answer as just a, or a, b where these are integers and
where the tangent line is horizontal. Enter your answer as just a, or a, b where these are integers and  < b.
< b.
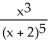 where the tangent line is horizontal. Enter your answer as just a, or a, b where these are integers and
where the tangent line is horizontal. Enter your answer as just a, or a, b where these are integers and  < b.
< b.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
The radius, r, of a sphere is increasing. For what value of r is 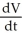 equal to 64π times the rate of increase of r. Enter just an integer.
equal to 64π times the rate of increase of r. Enter just an integer.
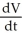 equal to 64π times the rate of increase of r. Enter just an integer.
equal to 64π times the rate of increase of r. Enter just an integer.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Find the slope of the tangent line to f(x) = 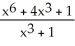 at (1, f(1)).
at (1, f(1)).
Enter just a reduced fraction of form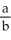 .
.
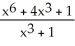 at (1, f(1)).
at (1, f(1)).Enter just a reduced fraction of form
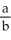 .
.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
If f(x) =  +
+ 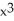 and g(x) = 1 -
and g(x) = 1 - 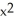 , find
, find 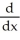 f(g(x)).
f(g(x)).
A)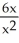 - 6
- 6 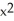
B) - + 3
+ 3 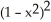
C)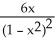 - 6x
- 6x 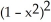
D)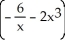
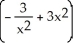
 +
+ 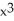 and g(x) = 1 -
and g(x) = 1 - 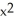 , find
, find 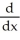 f(g(x)).
f(g(x)).A)
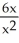 - 6
- 6 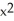
B) -
 + 3
+ 3 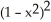
C)
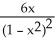 - 6x
- 6x 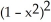
D)
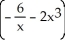
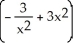

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Use the chain rule to find the derivative of 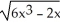 at x = 1.
at x = 1.
Enter just an integer.
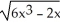 at x = 1.
at x = 1.Enter just an integer.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
Differentiate: f(x) = (( 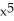 + 2
+ 2 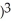 + 1
+ 1 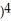 at x = -1.
at x = -1.
Enter just an integer.
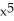 + 2
+ 2 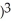 + 1
+ 1 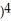 at x = -1.
at x = -1.Enter just an integer.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
If f(x) = 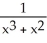 , find
, find 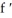 (x).
(x).
A)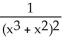
B)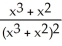
C)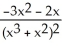
D) -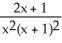
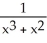 , find
, find 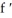 (x).
(x).A)
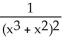
B)
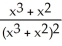
C)
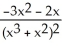
D) -
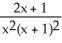

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Find the slope of the tangent line to the graph of y = 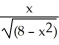 at the point (2, 1).
at the point (2, 1).
Enter just an integer.
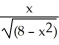 at the point (2, 1).
at the point (2, 1).Enter just an integer.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
If y = 3u + 2 and u = 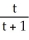 , find
, find 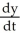 .
.
A)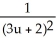
B)
C)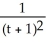
D)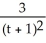
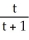 , find
, find 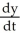 .
.A)
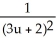
B)

C)
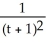
D)
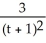

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
Use implicit differentiation to determine the slope of the graph of 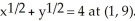 Enter just an integer.
Enter just an integer.
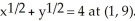 Enter just an integer.
Enter just an integer.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
Suppose that x and y are related by the equation 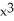 +
+ 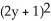 =
= 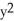 . Use implicit differentiation to determine
. Use implicit differentiation to determine 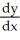 .
.
A)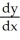 =
= 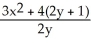
B)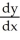 = 3
= 3 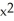 + 2(y + 1)
+ 2(y + 1)
C)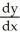 =
= 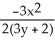
D)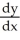 =
= 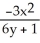
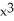 +
+ 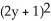 =
= 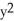 . Use implicit differentiation to determine
. Use implicit differentiation to determine 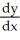 .
.A)
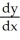 =
= 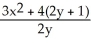
B)
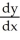 = 3
= 3 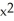 + 2(y + 1)
+ 2(y + 1)C)
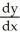 =
= 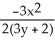
D)
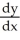 =
= 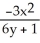

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
Use implicit differentiation to determine 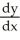 where 4
where 4 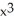 + 4xy + y = 8. Is
+ 4xy + y = 8. Is 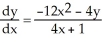 correct?
correct?
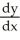 where 4
where 4 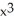 + 4xy + y = 8. Is
+ 4xy + y = 8. Is 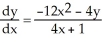 correct?
correct?
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
If y = 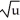 and u =
and u = 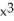 - 5
- 5 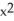 + 1, find
+ 1, find 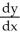 .
.
A)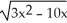
B)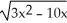
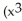 -
- 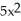 + 1)
+ 1)
C)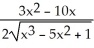
D)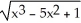
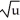 and u =
and u = 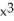 - 5
- 5 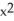 + 1, find
+ 1, find 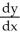 .
.A)
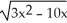
B)
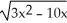
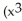 -
- 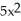 + 1)
+ 1)C)
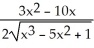
D)
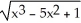

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
Use implicit differentiation to determine the slope of the graph of 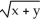 = x at (2, 2).
= x at (2, 2).
Enter just an integer.
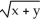 = x at (2, 2).
= x at (2, 2).Enter just an integer.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
Use implicit differentiation to determine 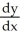 where
where 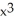 +
+ 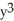 = 2xy. Is
= 2xy. Is 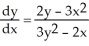 correct?
correct?
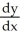 where
where 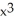 +
+ 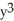 = 2xy. Is
= 2xy. Is 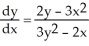 correct?
correct?
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
Use implicit differentiation to determine 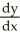 where
where 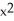 +
+ 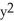 = 4. Is
= 4. Is 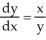 correct?
correct?
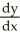 where
where 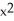 +
+ 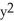 = 4. Is
= 4. Is 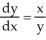 correct?
correct?
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
Suppose that the cost of manufacturing x units of a product is C(x) = 6x - 2 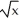 + 1 dollars and that the production level t weeks from the present is x = 4
+ 1 dollars and that the production level t weeks from the present is x = 4 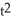 . Find the rate of change in cost with respect to time. Enter your answer as a polynomial in t in standard form (not labeled).
. Find the rate of change in cost with respect to time. Enter your answer as a polynomial in t in standard form (not labeled).
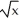 + 1 dollars and that the production level t weeks from the present is x = 4
+ 1 dollars and that the production level t weeks from the present is x = 4 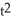 . Find the rate of change in cost with respect to time. Enter your answer as a polynomial in t in standard form (not labeled).
. Find the rate of change in cost with respect to time. Enter your answer as a polynomial in t in standard form (not labeled).
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
Compute 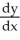 using the chain rule where
using the chain rule where 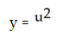 and u = 3x + 4.
and u = 3x + 4.
Enter your answer as just a polynomial in x in standard form (no label).
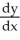 using the chain rule where
using the chain rule where 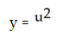 and u = 3x + 4.
and u = 3x + 4.Enter your answer as just a polynomial in x in standard form (no label).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
Compute 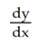 y = 4
y = 4 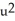 + 8u + 4 and u = 3x + 1.
+ 8u + 4 and u = 3x + 1.
Enter your answer as just a polynomial in x in standard form (no label).
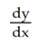 y = 4
y = 4 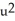 + 8u + 4 and u = 3x + 1.
+ 8u + 4 and u = 3x + 1.Enter your answer as just a polynomial in x in standard form (no label).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
Use implicit differentiation to determine 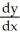 where
where 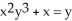 . Is
. Is 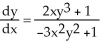 correct?
correct?
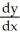 where
where 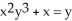 . Is
. Is 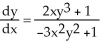 correct?
correct?
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
Suppose that x and y are related by the equation 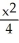 +
+ 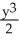 = 4. Use implicit differentiation to determine
= 4. Use implicit differentiation to determine 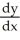 .
.
A)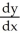 = -
= - 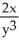
B)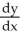 =
= 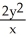
C)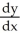 =
= 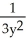 , y ≠ 0
, y ≠ 0
D)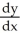 = -
= - 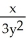 , y ≠ 0
, y ≠ 0
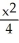 +
+ 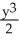 = 4. Use implicit differentiation to determine
= 4. Use implicit differentiation to determine 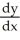 .
.A)
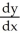 = -
= - 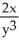
B)
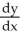 =
= 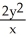
C)
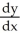 =
= 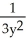 , y ≠ 0
, y ≠ 0D)
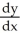 = -
= - 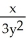 , y ≠ 0
, y ≠ 0
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
Compute 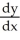 using the chain rule where y =
using the chain rule where y = 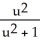 and u =
and u = 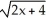 at x = 1.
at x = 1.
Enter just a reduced fraction.
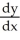 using the chain rule where y =
using the chain rule where y = 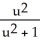 and u =
and u = 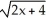 at x = 1.
at x = 1.Enter just a reduced fraction.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
If y = u + 1 - 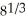 and u =
and u =  + 1, find
+ 1, find 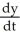 .
.
A)
B) -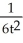 ∙
∙ 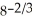
C) -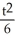
D) -2 ∙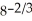
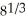 and u =
and u =  + 1, find
+ 1, find 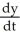 .
.A)

B) -
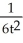 ∙
∙ 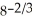
C) -
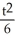
D) -2 ∙
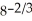

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
If f(x) = x 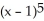 and g(x) =
and g(x) = 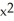 , find
, find 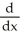 f(g(x)).
f(g(x)).
A) 2x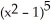 + 10
+ 10 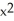
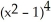
B)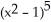 + 5
+ 5 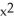
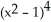
C) 2x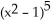 + 10
+ 10 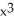 (
( 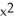 - 1)
- 1)
D) 2x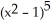 + 10
+ 10 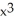
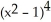
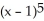 and g(x) =
and g(x) = 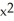 , find
, find 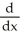 f(g(x)).
f(g(x)).A) 2x
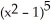 + 10
+ 10 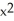
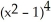
B)
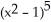 + 5
+ 5 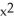
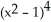
C) 2x
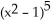 + 10
+ 10 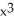 (
( 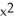 - 1)
- 1)D) 2x
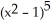 + 10
+ 10 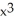

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
Use implicit differentiation to determine 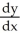 where xy + 10 =
where xy + 10 =  . Is
. Is 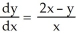 correct?
correct?
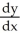 where xy + 10 =
where xy + 10 = 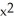 . Is
. Is 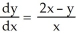 correct?
correct?
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
Assume 4 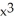 + 2xy -
+ 2xy - 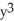 =
= 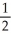 . What is the slope of the graph at the point
. What is the slope of the graph at the point 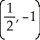 ?
?
A) -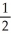
B) 8
C)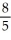
D) 1
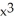 + 2xy -
+ 2xy - 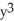 =
= 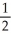 . What is the slope of the graph at the point
. What is the slope of the graph at the point 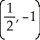 ?
?A) -
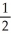
B) 8
C)
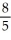
D) 1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
The cost of manufacturing x units is C dollars, where C = 4x + 6 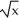 + 5. Weekly production at t weeks from the present is estimated to be x = 2800 + 100t units when t = 8. Find the time rate of change of cost,
+ 5. Weekly production at t weeks from the present is estimated to be x = 2800 + 100t units when t = 8. Find the time rate of change of cost, 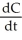 . Enter just an integer.
. Enter just an integer.
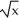 + 5. Weekly production at t weeks from the present is estimated to be x = 2800 + 100t units when t = 8. Find the time rate of change of cost,
+ 5. Weekly production at t weeks from the present is estimated to be x = 2800 + 100t units when t = 8. Find the time rate of change of cost, 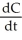 . Enter just an integer.
. Enter just an integer.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
When a manufacturer produces and sells x units per week, its weekly profit is P dollars, where 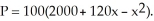 Production level t weeks from the present will be
Production level t weeks from the present will be 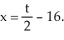 Find the rate of change in profit with respect to x. Enter your answer as a polynomial in x in standard form (not labeled).
Find the rate of change in profit with respect to x. Enter your answer as a polynomial in x in standard form (not labeled).
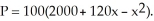 Production level t weeks from the present will be
Production level t weeks from the present will be 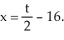 Find the rate of change in profit with respect to x. Enter your answer as a polynomial in x in standard form (not labeled).
Find the rate of change in profit with respect to x. Enter your answer as a polynomial in x in standard form (not labeled).
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
Suppose 2 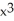 - 3
- 3 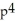 = 6, where x and p are differentiable functions of t. Find
= 6, where x and p are differentiable functions of t. Find 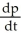 .
.
A) 6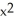
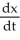 - 12
- 12 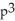
B)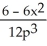
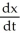
C) 6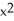 - 12
- 12 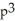
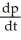
D)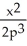
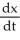
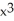 - 3
- 3 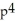 = 6, where x and p are differentiable functions of t. Find
= 6, where x and p are differentiable functions of t. Find 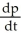 .
.A) 6
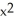
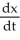 - 12
- 12 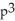
B)
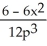
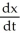
C) 6
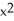 - 12
- 12 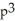
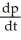
D)
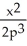
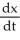

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
Suppose that 15 = 50, where x and y are both differentiable functions of t. Find .
A)
B)
C)
D)
A)
B)
C)
D)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
Mr. Smith is 6 ft tall and walks at a constant rate of 2 ft/sec toward a street light that is 10 ft above the ground. At what rate is the length of his shadow changing when he is 6 ft from the base of the pole that supports the light? Enter just an integer (no units).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
The radius of a spherical balloon increases at a rate of 1 mm/sec. How fast is the surface area increasing when the radius is 10mm? (Note: The surface area S of a sphere of radius r is S = 4π 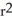 .) Enter just a real number (no approximations, no units or words).
.) Enter just a real number (no approximations, no units or words).
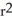 .) Enter just a real number (no approximations, no units or words).
.) Enter just a real number (no approximations, no units or words).
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
Assume  +
+ 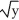 = x. What is the slope of the graph at the point (-1, 9)?
= x. What is the slope of the graph at the point (-1, 9)?
A) 30
B) 4 +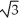
C) 3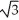
D) 18
 +
+ 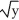 = x. What is the slope of the graph at the point (-1, 9)?
= x. What is the slope of the graph at the point (-1, 9)?A) 30
B) 4 +
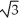
C) 3
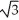
D) 18

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
Find the equation of the tangent line to the graph of 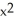 +
+ 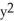 = 1 at the point
= 1 at the point 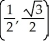 .
.
Is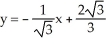 correct?
correct?
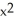 +
+ 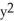 = 1 at the point
= 1 at the point 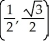 .
.Is
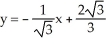 correct?
correct?
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
Find the equation of the line tangent to the graph of 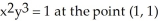 Enter your answer in slope-intercept form.
Enter your answer in slope-intercept form.
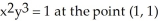 Enter your answer in slope-intercept form.
Enter your answer in slope-intercept form.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
Find the equation of the line tangent to the graph of 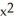
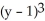 = 8 at the point (1, 3).
= 8 at the point (1, 3).
Enter your answer in slope-intercept form.
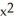
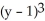 = 8 at the point (1, 3).
= 8 at the point (1, 3).Enter your answer in slope-intercept form.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
Determine the rate of change of 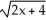 with respect to x at x = 1.
with respect to x at x = 1.
Enter just a reduced quotient of form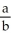 .
.
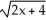 with respect to x at x = 1.
with respect to x at x = 1.Enter just a reduced quotient of form
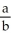 .
.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 69 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








