Deck 8: Variable Costing and the Costs of Quality and Sustainability
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/64
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 8: Variable Costing and the Costs of Quality and Sustainability
1
Roma Corporation has computed the following unit costs for the year just ended: Under variable costing, each unit of the company's inventory would be carried at:
A) $49.
B) $54.
C) $72.
D) $104.
E) None of the other answers are correct.
A) $49.
B) $54.
C) $72.
D) $104.
E) None of the other answers are correct.
$49.
2
Roma Corporation has computed the following unit costs for the year just ended: Under absorption costing, each unit of the company's inventory would be carried at:
A) $49.
B) $54.
C) $72.
D) $104.
E) None of the other answers are correct.
A) $49.
B) $54.
C) $72.
D) $104.
E) None of the other answers are correct.
$72.
3
Lone Star has computed the following unit costs for the year just ended: Under variable costing, each unit of the company's inventory would be carried at:
A) $35.
B) $55.
C) $65.
D) $84.
E) None of the other answers are correct.
A) $35.
B) $55.
C) $65.
D) $84.
E) None of the other answers are correct.
$55.
4
All of the following are inventoried under absorption costing except:
A) direct labor.
B) raw materials used in production.
C) utilities cost consumed in manufacturing.
D) sales commissions.
E) machine lubricant used in production.
A) direct labor.
B) raw materials used in production.
C) utilities cost consumed in manufacturing.
D) sales commissions.
E) machine lubricant used in production.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
All of the following costs are inventoried under absorption costing except:
A) direct materials.
B) direct labor.
C) variable manufacturing overhead.
D) fixed manufacturing overhead.
E) fixed administrative salaries.
A) direct materials.
B) direct labor.
C) variable manufacturing overhead.
D) fixed manufacturing overhead.
E) fixed administrative salaries.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Fixed manufacturing overhead is not inventoried under absorption costing.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Under variable costing, fixed manufacturing overhead is:
A) expensed immediately when incurred.
B) never expensed.
C) applied directly to Finished-Goods Inventory.
D) applied directly to Work-in-Process Inventory.
E) treated in the same manner as variable manufacturing overhead.
A) expensed immediately when incurred.
B) never expensed.
C) applied directly to Finished-Goods Inventory.
D) applied directly to Work-in-Process Inventory.
E) treated in the same manner as variable manufacturing overhead.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
All of the following are inventoried under variable costing except:
A) direct materials.
B) direct labor.
C) variable manufacturing overhead.
D) fixed manufacturing overhead.
E) variable manufacturing overhead and fixed manufacturing overhead.
A) direct materials.
B) direct labor.
C) variable manufacturing overhead.
D) fixed manufacturing overhead.
E) variable manufacturing overhead and fixed manufacturing overhead.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Indiana Company incurred the following costs during the past year when planned production and actual production each totaled 20,000 units: If Indiana uses absorption costing, the total inventoriable costs for the year would be:
A) $400,000.
B) $460,000.
C) $560,000.
D) $620,000.
E) $660,000.
A) $400,000.
B) $460,000.
C) $560,000.
D) $620,000.
E) $660,000.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Indiana Company incurred the following costs during the past year when planned production and actual production each totaled 20,000 units: Indiana's per-unit inventoriable cost under absorption costing is:
A) $9.50.
B) $25.00.
C) $28.00.
D) $33.00.
E) $40.50.
A) $9.50.
B) $25.00.
C) $28.00.
D) $33.00.
E) $40.50.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Variable manufacturing overhead becomes part of a unit's cost when variable costing is used.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Indiana Company incurred the following costs during the past year when planned production and actual production each totaled 20,000 units: If Indiana uses variable costing, the total inventoriable costs for the year would be:
A) $400,000.
B) $460,000.
C) $560,000.
D) $620,000.
E) $660,000.
A) $400,000.
B) $460,000.
C) $560,000.
D) $620,000.
E) $660,000.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Lone Star has computed the following unit costs for the year just ended: Under absorption costing, each unit of the company's inventory would be carried at:
A) $35.
B) $55.
C) $65.
D) $84.
E) None of the other answers are correct.
A) $35.
B) $55.
C) $65.
D) $84.
E) None of the other answers are correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
All of the following are expensed under variable costing except:
A) variable manufacturing overhead.
B) fixed manufacturing overhead.
C) variable selling and administrative costs.
D) fixed selling and administrative costs.
E) variable selling and administrative costs and fixed selling and administrative costs.
A) variable manufacturing overhead.
B) fixed manufacturing overhead.
C) variable selling and administrative costs.
D) fixed selling and administrative costs.
E) variable selling and administrative costs and fixed selling and administrative costs.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Indiana Company incurred the following costs during the past year when planned production and actual production each totaled 20,000 units: Indiana's per-unit inventoriable cost under variable costing is:
A) $9.50.
B) $25.00.
C) $28.00.
D) $33.00.
E) $40.50.
A) $9.50.
B) $25.00.
C) $28.00.
D) $33.00.
E) $40.50.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
For external-reporting purposes, generally accepted accounting principles require that net income be based on variable costing.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Delaware has computed the following unit costs for the year just ended: Which of the following choices correctly depicts the per-unit cost of inventory under variable costing and absorption costing?
A) Variable, $85; absorption, $105.
B) Variable, $85; absorption, $116.
C) Variable, $103; absorption, $105.
D) Variable, $103; absorption, $116.
E) None of the other answers are correct.
A) Variable, $85; absorption, $105.
B) Variable, $85; absorption, $116.
C) Variable, $103; absorption, $105.
D) Variable, $103; absorption, $116.
E) None of the other answers are correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
When units sold exceed units produced, absorption-costing income will be lower than variable-costing income.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Absorption costing is required for tax purposes.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
The underlying difference between absorption costing and variable costing lies in the treatment of:
A) direct labor.
B) variable manufacturing overhead.
C) fixed manufacturing overhead.
D) variable selling and administrative expenses.
E) fixed selling and administrative expenses.
A) direct labor.
B) variable manufacturing overhead.
C) fixed manufacturing overhead.
D) variable selling and administrative expenses.
E) fixed selling and administrative expenses.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Variable costing of inventory and absorption costing of inventory is relevant for which of the following types of businesses?
A) Manufacturing firms.
B) Not-for-profit companies.
C) Governmental units.
D) Service firms.
E) All of the other answers are correct.
A) Manufacturing firms.
B) Not-for-profit companies.
C) Governmental units.
D) Service firms.
E) All of the other answers are correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Which of the following statements pertain to both variable costing and absorption costing?
A) The income statement discloses the amount of gross margin generated during the reporting period.
B) Fixed selling and administrative expenses are treated in the same manner as fixed manufacturing overhead.
C) Both variable and absorption costing can be used for external financial reporting.
D) Variable selling costs are written-off as expenses of the accounting period.
E) Fixed manufacturing overhead is attached to each unit produced.
A) The income statement discloses the amount of gross margin generated during the reporting period.
B) Fixed selling and administrative expenses are treated in the same manner as fixed manufacturing overhead.
C) Both variable and absorption costing can be used for external financial reporting.
D) Variable selling costs are written-off as expenses of the accounting period.
E) Fixed manufacturing overhead is attached to each unit produced.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Consider the following comments about absorption- and variable-costing income statements:
I) A variable-costing income statement discloses a firm's contribution margin.
II) Cost of goods sold on an absorption-costing income statement includes fixed costs.
III) The amount of variable selling and administrative cost is the same on absorption- and variable-costing income statements.
Which of the above statements is (are) true?
A) I only.
B) II only.
C) I and II.
D) II and III.
E) I, II, and III.
I) A variable-costing income statement discloses a firm's contribution margin.
II) Cost of goods sold on an absorption-costing income statement includes fixed costs.
III) The amount of variable selling and administrative cost is the same on absorption- and variable-costing income statements.
Which of the above statements is (are) true?
A) I only.
B) II only.
C) I and II.
D) II and III.
E) I, II, and III.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Which of the following statements pertain to variable costing?
A) This method must be used for external financial reporting.
B) Fixed manufacturing overhead is attached to each unit produced.
C) The income statement not does disclose a company's contribution margin.
D) Variable manufacturing overhead becomes part of a unit's cost.
E) None of the other answers are correct.
A) This method must be used for external financial reporting.
B) Fixed manufacturing overhead is attached to each unit produced.
C) The income statement not does disclose a company's contribution margin.
D) Variable manufacturing overhead becomes part of a unit's cost.
E) None of the other answers are correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Consider the following comments about absorption- and variable-costing income statements:
I) A variable-costing income statement discloses a firm's gross margin.
II) Cost of goods sold on an absorption-costing income statement includes fixed costs.
III) The amount of variable selling and administrative cost is the same on absorption- and variable-costing income statements.
Which of the above statements is (are) true?
A) I only.
B) II only.
C) I and II.
D) II and III.
E) I, II, and III.
I) A variable-costing income statement discloses a firm's gross margin.
II) Cost of goods sold on an absorption-costing income statement includes fixed costs.
III) The amount of variable selling and administrative cost is the same on absorption- and variable-costing income statements.
Which of the above statements is (are) true?
A) I only.
B) II only.
C) I and II.
D) II and III.
E) I, II, and III.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Chino began business at the start of the current year. The company planned to produce 25,000 units, and actual production conformed to expectations. Sales totaled 22,000 units at $30 each. Costs incurred were: If there were no variances, the company's absorption-costing income would be:
A) $190,000.
B) $202,000.
C) $208,000.
D) $220,000.
E) None of the other answers are correct.
A) $190,000.
B) $202,000.
C) $208,000.
D) $220,000.
E) None of the other answers are correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Springer began business at the start of the current year. The company planned to produce 40,000 units, and actual production conformed to expectations. Sales totaled 37,000 units at $42 each. Costs incurred were: If there were no variances, the company's variable-costing income would be:
A) $155,000.
B) $212,000.
C) $240,500.
D) $592,000.
E) None of the other answers are correct.
A) $155,000.
B) $212,000.
C) $240,500.
D) $592,000.
E) None of the other answers are correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Springer began business at the start of the current year. The company planned to produce 40,000 units, and actual production conformed to expectations. Sales totaled 37,000 units at $42 each. Costs incurred were: If there were no variances, the company's absorption-costing income would be:
A) $155,000.
B) $230,000.
C) $240,500.
D) $592,000.
E) None of the other answers are correct.
A) $155,000.
B) $230,000.
C) $240,500.
D) $592,000.
E) None of the other answers are correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Franz began business at the start of this year and had the following costs: variable manufacturing cost per unit, $9; fixed manufacturing costs, $60,000; variable selling and administrative costs per unit, $2; and fixed selling and administrative costs, $220,000. The company sells its units for $45 each. Additional data follow. There were no variances.
The income (loss) under absorption costing is:
A) $(7,500).
B) $9,000.
C) $15,000.
D) $18,000.
E) None of the other answers are correct.
The income (loss) under absorption costing is:
A) $(7,500).
B) $9,000.
C) $15,000.
D) $18,000.
E) None of the other answers are correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
Which of the following conditions would cause absorption-costing income to be higher than variable-costing income?
A) Units sold exceeded units produced.
B) Units sold equaled units produced.
C) Units sold were less than units produced.
D) Sales prices decreased.
E) Selling expenses increased.
A) Units sold exceeded units produced.
B) Units sold equaled units produced.
C) Units sold were less than units produced.
D) Sales prices decreased.
E) Selling expenses increased.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Garcia's inventory increased during the year. On the basis of this information, income reported under absorption costing:
A) will be the same as that reported under variable costing.
B) will be higher than that reported under variable costing.
C) will be lower than that reported under variable costing.
D) will differ from that reported under variable costing, the direction of which cannot be determined from the information given.
E) will be less than that reported in the previous period.
A) will be the same as that reported under variable costing.
B) will be higher than that reported under variable costing.
C) will be lower than that reported under variable costing.
D) will differ from that reported under variable costing, the direction of which cannot be determined from the information given.
E) will be less than that reported in the previous period.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Which of the following product-costing systems is/are required for tax purposes?
A) Absorption costing.
B) Variable costing.
C) Throughput costing.
D) Either absorption or variable costing.
E) Either absorption, variable costing, or throughput costing.
A) Absorption costing.
B) Variable costing.
C) Throughput costing.
D) Either absorption or variable costing.
E) Either absorption, variable costing, or throughput costing.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
The following data relate to Lebeaux Corporation for the year just ended: Which of the following statements is correct?
A) Lebeaux's variable-costing income statement would show a gross margin of $270,000.
B) Lebeaux's variable costing income statement would show a contribution margin of $330,000.
C) Lebeaux's absorption-costing income statement would show a contribution margin of $330,000.
D) Lebeaux's absorption costing income statement would show a gross margin of $330,000.
E) Lebeaux's absorption-costing income statement would show a gross margin of $145,000.
A) Lebeaux's variable-costing income statement would show a gross margin of $270,000.
B) Lebeaux's variable costing income statement would show a contribution margin of $330,000.
C) Lebeaux's absorption-costing income statement would show a contribution margin of $330,000.
D) Lebeaux's absorption costing income statement would show a gross margin of $330,000.
E) Lebeaux's absorption-costing income statement would show a gross margin of $145,000.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
Roberts Corp., which began business at the start of the current year, had the following data:
Planned and actual production: 40,000 units
Sales: 37,000 units at $15 per unit
Production costs:
Variable: $4 per unit
Fixed: $260,000
Selling and administrative costs:
Variable: $1 per unit
Fixed: $32,000
The gross margin that the company would disclose on an absorption-costing income statement is:
A) $97,500.
B) $147,000.
C) $166,500.
D) $370,000.
E) None of the other answers are correct.
Planned and actual production: 40,000 units
Sales: 37,000 units at $15 per unit
Production costs:
Variable: $4 per unit
Fixed: $260,000
Selling and administrative costs:
Variable: $1 per unit
Fixed: $32,000
The gross margin that the company would disclose on an absorption-costing income statement is:
A) $97,500.
B) $147,000.
C) $166,500.
D) $370,000.
E) None of the other answers are correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Roberts Corp., which began business at the start of the current year, had the following data:
Planned and actual production: 40,000 units
Sales: 37,000 units at $15 per unit
Production costs:
Variable: $4 per unit
Fixed: $260,000
Selling and administrative costs:
Variable: $1 per unit
Fixed: $32,000
The contribution margin that the company would disclose on a variable-costing income statement is:
A) $97,500.
B) $147,000.
C) $166,500.
D) $370,000.
E) None of the other answers are correct.
Planned and actual production: 40,000 units
Sales: 37,000 units at $15 per unit
Production costs:
Variable: $4 per unit
Fixed: $260,000
Selling and administrative costs:
Variable: $1 per unit
Fixed: $32,000
The contribution margin that the company would disclose on a variable-costing income statement is:
A) $97,500.
B) $147,000.
C) $166,500.
D) $370,000.
E) None of the other answers are correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
Franz began business at the start of this year and had the following costs: variable manufacturing cost per unit, $9; fixed manufacturing costs, $60,000; variable selling and administrative costs per unit, $2; and fixed selling and administrative costs, $220,000. The company sells its units for $45 each. Additional data follow. There were no variances.
The income (loss) under variable costing is:
A) $(7,500).
B) $9,000.
C) $15,000.
D) $18,000.
E) None of the other answers are correct.
The income (loss) under variable costing is:
A) $(7,500).
B) $9,000.
C) $15,000.
D) $18,000.
E) None of the other answers are correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Which of the following conditions would cause absorption-costing income to be lower than variable-costing income?
A) Units sold exceeded units produced.
B) Units sold equaled units produced.
C) Units sold were less than units produced.
D) Sales prices decreased.
E) Selling expenses increased.
A) Units sold exceeded units produced.
B) Units sold equaled units produced.
C) Units sold were less than units produced.
D) Sales prices decreased.
E) Selling expenses increased.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
McArthur Corp., which began business at the start of the current year, had the following data:
Planned and actual production: 40,000 units
Sales: 38,000 units at $15 per unit
Production costs:
Variable: $5 per unit
Fixed: $260,000
Selling and administrative costs:
Variable: $1 per unit
Fixed: $32,000
The gross margin that the company would disclose on an absorption-costing income statement is:
A) $0.
B) $133,000.
C) $166,500.
D) $342,000.
E) None of the other answers are correct.
Planned and actual production: 40,000 units
Sales: 38,000 units at $15 per unit
Production costs:
Variable: $5 per unit
Fixed: $260,000
Selling and administrative costs:
Variable: $1 per unit
Fixed: $32,000
The gross margin that the company would disclose on an absorption-costing income statement is:
A) $0.
B) $133,000.
C) $166,500.
D) $342,000.
E) None of the other answers are correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
McArthur Corp., which began business at the start of the current year, had the following data:
Planned and actual production: 40,000 units
Sales: 38,000 units at $15 per unit
Production costs:
Variable: $5 per unit
Fixed: $260,000
Selling and administrative costs:
Variable: $1 per unit
Fixed: $32,000
The contribution margin that the company would disclose on a variable-costing income statement is:
A) $0.
B) $120,000.
C) $166,500.
D) $342,000.
E) None of the other answers are correct.
Planned and actual production: 40,000 units
Sales: 38,000 units at $15 per unit
Production costs:
Variable: $5 per unit
Fixed: $260,000
Selling and administrative costs:
Variable: $1 per unit
Fixed: $32,000
The contribution margin that the company would disclose on a variable-costing income statement is:
A) $0.
B) $120,000.
C) $166,500.
D) $342,000.
E) None of the other answers are correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Franz began business at the start of this year and had the following costs: variable manufacturing cost per unit, $9; fixed manufacturing costs, $60,000; variable selling and administrative costs per unit, $2; and fixed selling and administrative costs, $220,000. The company sells its units for $45 each. Additional data follow. There were no variances.
Income reported under absorption costing and variable costing is:
A) always the same.
B) typically different.
C) always higher under absorption costing.
D) always higher under variable costing.
E) always the same or higher under absorption costing.
Income reported under absorption costing and variable costing is:
A) always the same.
B) typically different.
C) always higher under absorption costing.
D) always higher under variable costing.
E) always the same or higher under absorption costing.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
Moneka reported $65,000 of income for the year by using absorption costing. The company had no beginning inventory, planned and actual production of 20,000 units, and sales of 18,000 units. Standard variable manufacturing costs were $20 per unit, and total budgeted fixed manufacturing overhead was $100,000. If there were no variances, income under variable costing would be:
A) $15,000.
B) $55,000.
C) $65,000.
D) $75,000.
E) $115,000.
A) $15,000.
B) $55,000.
C) $65,000.
D) $75,000.
E) $115,000.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
Which of the following situations would cause variable-costing income to be higher than absorption-costing income?
A) Units sold equaled 39,000 and units produced equaled 42,000.
B) Units sold and units produced were both 42,000.
C) Units sold equaled 55,000 and units produced equaled 49,000.
D) Sales prices decreased by $7 per unit during the accounting period.
E) Selling expenses increased by 10% during the accounting period.
A) Units sold equaled 39,000 and units produced equaled 42,000.
B) Units sold and units produced were both 42,000.
C) Units sold equaled 55,000 and units produced equaled 49,000.
D) Sales prices decreased by $7 per unit during the accounting period.
E) Selling expenses increased by 10% during the accounting period.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
Carter reported $106,000 of income for the year by using variable costing. The company had no beginning inventory, planned and actual production of 50,000 units, and sales of 47,000 units. Standard variable manufacturing costs were $15 per unit, and total budgeted fixed manufacturing overhead was $150,000. If there were no variances, income under absorption costing would be:
A) $52,000.
B) $97,000.
C) $106,000.
D) $115,000.
E) $160,000.
A) $52,000.
B) $97,000.
C) $106,000.
D) $115,000.
E) $160,000.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
Information taken from Giles Corporation's May accounting records follows. 
Required:
A. Assuming the use of variable costing, compute the inventoriable costs for the month.
B. Compute the month's inventoriable costs by using absorption costing.
C. Assume that anticipated and actual production totaled 20,000 units, and that 18,000 units were sold during May. Determine the amount of fixed manufacturing overhead and fixed selling and administrative costs that would be expensed for the month under (1) variable costing and (2) absorption costing.
D. Assume the same data as in requirement "C." Compute the contribution margin that would be reported on a variable-costing income statement.

Required:
A. Assuming the use of variable costing, compute the inventoriable costs for the month.
B. Compute the month's inventoriable costs by using absorption costing.
C. Assume that anticipated and actual production totaled 20,000 units, and that 18,000 units were sold during May. Determine the amount of fixed manufacturing overhead and fixed selling and administrative costs that would be expensed for the month under (1) variable costing and (2) absorption costing.
D. Assume the same data as in requirement "C." Compute the contribution margin that would be reported on a variable-costing income statement.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Which of the following situations would cause variable-costing income to be lower than absorption-costing income?
A) Units sold equaled 39,000 and units produced equaled 42,000.
B) Units sold and units produced were both 42,000.
C) Units sold equaled 55,000 and units produced equaled 49,000.
D) Sales prices decreased by $7 per unit during the accounting period.
E) Selling expenses increased by 10% during the accounting period.
A) Units sold equaled 39,000 and units produced equaled 42,000.
B) Units sold and units produced were both 42,000.
C) Units sold equaled 55,000 and units produced equaled 49,000.
D) Sales prices decreased by $7 per unit during the accounting period.
E) Selling expenses increased by 10% during the accounting period.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
The optimum level of product quality is where:
A) external failure costs are at a minimum.
B) total quality costs are at a minimum.
C) prevention costs are at a minimum.
D) internal failure costs are at a minimum.
E) All of the other answers are correct.
A) external failure costs are at a minimum.
B) total quality costs are at a minimum.
C) prevention costs are at a minimum.
D) internal failure costs are at a minimum.
E) All of the other answers are correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
Hirsch Company has per-unit fixed and variable manufacturing costs of $40 and $15, respectively. Variable selling and administrative costs are $9 per unit. Consider the two independent cases that follow for the firm.
Case A: Variable-costing income, $110,000; sales, 6,000 units; production, 6,000 units
Case B: Variable-costing income, $178,000; sales, 7,500 units; production, 7,100 units
Required:
A.
A. From a product-costing perspective, what is the basic difference between absorption costing and variable costing?
B.
B. Compute Hirsch's absorption-costing income in Case
C. Compute Hirsch's absorption-costing income in Case
Case A: Variable-costing income, $110,000; sales, 6,000 units; production, 6,000 units
Case B: Variable-costing income, $178,000; sales, 7,500 units; production, 7,100 units
Required:
A.
A. From a product-costing perspective, what is the basic difference between absorption costing and variable costing?
B.
B. Compute Hirsch's absorption-costing income in Case
C. Compute Hirsch's absorption-costing income in Case

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
Webster, Inc. began operations at the start of the current year, having a production target of 60,000 units. Actual production totaled 60,000 units, and the company sold 95% of its manufacturing output at $50 per unit. The following costs were incurred: 
Required:
A. Assuming the use of variable costing, compute the cost of Webster's ending finished-goods inventory.
B. Compute the company's contribution margin. Would Webster disclose the contribution margin on a variable-costing income statement or an absorption-costing income statement?
C. Assuming the use of absorption costing, how much fixed selling and administrative cost would Webster include in the ending finished-goods inventory?
D. Compute the company's gross margin.

Required:
A. Assuming the use of variable costing, compute the cost of Webster's ending finished-goods inventory.
B. Compute the company's contribution margin. Would Webster disclose the contribution margin on a variable-costing income statement or an absorption-costing income statement?
C. Assuming the use of absorption costing, how much fixed selling and administrative cost would Webster include in the ending finished-goods inventory?
D. Compute the company's gross margin.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
Consider the following statements about absorption- and variable-costing income:
I) Yearly income reported under absorption costing will differ from income reported under variable costing if production and sales volumes differ.
II) In the long-run, total income reported under absorption costing will often be close to that reported under variable costing.
III) Differences in income under absorption and variable costing can often be reconciled by multiplying the change in inventory (in units) by the variable manufacturing overhead cost per unit.
Which of the above statements is (are) true?
A) I only.
B) II only.
C) III only.
D) I and II.
E) II and III.
I) Yearly income reported under absorption costing will differ from income reported under variable costing if production and sales volumes differ.
II) In the long-run, total income reported under absorption costing will often be close to that reported under variable costing.
III) Differences in income under absorption and variable costing can often be reconciled by multiplying the change in inventory (in units) by the variable manufacturing overhead cost per unit.
Which of the above statements is (are) true?
A) I only.
B) II only.
C) III only.
D) I and II.
E) II and III.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
Which of the following is not a type of quality cost?
A) External failure costs.
B) Internal failure costs.
C) All of the answers are correct.
D) Prevention costs.
E) Appraisal costs.
A) External failure costs.
B) Internal failure costs.
C) All of the answers are correct.
D) Prevention costs.
E) Appraisal costs.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
The table that follows denotes selected characteristics of absorption costing and/or variable costing. 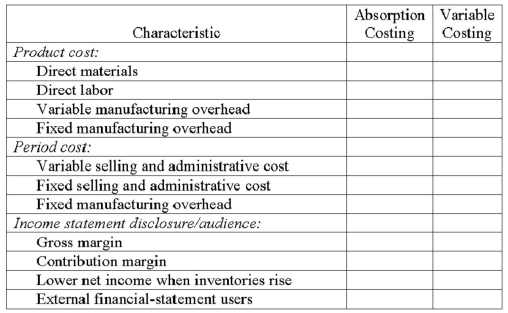
Changes to grid above:
Lower income when inventories rise (NOT "net" income)
External financial statement USE (NOT "users")
Required:
Evaluate each product-cost, period-cost, and income-statement/disclosure characteristic and determine whether it relates to absorption costing, variable costing, or both methods. Place an "X" in the proper column.

Changes to grid above:
Lower income when inventories rise (NOT "net" income)
External financial statement USE (NOT "users")
Required:
Evaluate each product-cost, period-cost, and income-statement/disclosure characteristic and determine whether it relates to absorption costing, variable costing, or both methods. Place an "X" in the proper column.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
Which of the following formulas can often reconcile the difference between absorption- and variable-costing income?
A) Change in inventory units × predetermined variable-overhead rate per unit.
B) Change in inventory units ÷ predetermined variable-overhead rate per unit.
C) Change in inventory units × predetermined fixed-overhead rate per unit.
D) Change in inventory units ÷ predetermined fixed-overhead rate per unit.
E) (Absorption-costing income - variable-costing income) × fixed-overhead rate per unit.
A) Change in inventory units × predetermined variable-overhead rate per unit.
B) Change in inventory units ÷ predetermined variable-overhead rate per unit.
C) Change in inventory units × predetermined fixed-overhead rate per unit.
D) Change in inventory units ÷ predetermined fixed-overhead rate per unit.
E) (Absorption-costing income - variable-costing income) × fixed-overhead rate per unit.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
The following data relate to Ventura Company, a new corporation, during a period when the firm produced and sold 100,000 units and 90,000 units, respectively: 
The company met its original planned production target of 100,000 units. There were no variances during the period, and the firm's selling price is $15 per unit.
Required:
A. What is the cost of Ventura's end-of-period finished-goods inventory under the variable-costing method?
B. Calculate the company's variable-costing income.
C. Calculate the company's absorption-costing income.

The company met its original planned production target of 100,000 units. There were no variances during the period, and the firm's selling price is $15 per unit.
Required:
A. What is the cost of Ventura's end-of-period finished-goods inventory under the variable-costing method?
B. Calculate the company's variable-costing income.
C. Calculate the company's absorption-costing income.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
The following data relate to Horatio, Inc., a new company: 
There were no variances during the period.
Required:
A. Determine the number of units in the ending finished-goods inventory.
B. Calculate the cost of the ending finished-goods inventory under (1) variable costing and (2) absorption costing.
C. Determine the company's variable-costing income.
D. Determine the company's absorption-costing income.

There were no variances during the period.
Required:
A. Determine the number of units in the ending finished-goods inventory.
B. Calculate the cost of the ending finished-goods inventory under (1) variable costing and (2) absorption costing.
C. Determine the company's variable-costing income.
D. Determine the company's absorption-costing income.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
Consider the following statements about absorption costing and variable costing:
I) Variable costing is consistent with contribution reporting and cost-volume-profit analysis.
II) Variable costing must be used for external financial reporting.
III) A number of companies use both absorption costing and variable costing.
Which of the above statements is (are) true?
A) I only.
B) II only.
C) III only.
D) I and II.
E) I and III.
I) Variable costing is consistent with contribution reporting and cost-volume-profit analysis.
II) Variable costing must be used for external financial reporting.
III) A number of companies use both absorption costing and variable costing.
Which of the above statements is (are) true?
A) I only.
B) II only.
C) III only.
D) I and II.
E) I and III.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
Which of the following statements about environmental costs is false?
A) Remediation costs include offsite, but not onsite, remediation costs.
B) Abatement costs include costs to reduce or eliminate pollution.
C) Monitoring costs include the costs of monitoring the regulatory environment as well as monitoring the production process to determine if pollution is being generated.
D) Private environmental costs are those borne by a company or individual.
E) Social environmental costs are those borne by the public at large.
A) Remediation costs include offsite, but not onsite, remediation costs.
B) Abatement costs include costs to reduce or eliminate pollution.
C) Monitoring costs include the costs of monitoring the regulatory environment as well as monitoring the production process to determine if pollution is being generated.
D) Private environmental costs are those borne by a company or individual.
E) Social environmental costs are those borne by the public at large.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
Consider the following statements about absorption costing and variable costing:
I) Variable costing is consistent with contribution reporting and cost-volume-profit analysis.
II) Absorption costing must be used for external financial reporting.
III) A number of companies use both absorption costing and variable costing.
Which of the above statements is (are) true?
A) I only.
B) II only.
C) III only.
D) I and II.
E) I, II, and III.
I) Variable costing is consistent with contribution reporting and cost-volume-profit analysis.
II) Absorption costing must be used for external financial reporting.
III) A number of companies use both absorption costing and variable costing.
Which of the above statements is (are) true?
A) I only.
B) II only.
C) III only.
D) I and II.
E) I, II, and III.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
Kim, Inc. began business at the start of the current year and maintains its accounting records on an absorption-cost basis. The following selected information appeared on the company's income statement and end-of-year balance sheet: 
Kim achieved its planned production level for the year. The company's fixed manufacturing overhead totaled $141,000, and the firm paid a 10% commission based on gross sales dollars to its sales force.
Required:
A. How many units did Kim plan to produce during the year?
B. How much fixed manufacturing overhead did the company apply to each unit produced?
C. Compute Kim's cost of goods sold.
D. How much variable cost did the company attach to each unit manufactured?

Kim achieved its planned production level for the year. The company's fixed manufacturing overhead totaled $141,000, and the firm paid a 10% commission based on gross sales dollars to its sales force.
Required:
A. How many units did Kim plan to produce during the year?
B. How much fixed manufacturing overhead did the company apply to each unit produced?
C. Compute Kim's cost of goods sold.
D. How much variable cost did the company attach to each unit manufactured?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
Costs of determining whether defects exist are called:
A) appraisal costs.
B) external failure costs.
C) internal failure costs.
D) prevention costs.
E) defects costs.
A) appraisal costs.
B) external failure costs.
C) internal failure costs.
D) prevention costs.
E) defects costs.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
For external-reporting purposes, generally accepted accounting principles require that net income be based on:
A) absorption costing.
B) variable costing.
C) direct costing.
D) semivariable costing.
E) activity-based costing.
A) absorption costing.
B) variable costing.
C) direct costing.
D) semivariable costing.
E) activity-based costing.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
Absorption and variable costing are two different methods of measuring income and costing inventory.
Required:
A. Product costs are defined as costs associated with the manufacturing process. How does the operational definition of product cost differ between absorption costing and variable costing?
B. An absorption-costing income statement will report gross profit or gross margin whereas a variable-costing income statement will report contribution margin. What is the difference between these terms?
Required:
A. Product costs are defined as costs associated with the manufacturing process. How does the operational definition of product cost differ between absorption costing and variable costing?
B. An absorption-costing income statement will report gross profit or gross margin whereas a variable-costing income statement will report contribution margin. What is the difference between these terms?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
Beach Bum Corporation has fixed manufacturing cost of $12 per unit. Consider the three independent cases that follow.
Case A: Absorption- and variable costing income each totaled $240,000 in a period when the firm produced 18,000 units.
Case B: Absorption-costing income totaled $320,000 in a period when finished-goods inventory levels rose by 7,000 units.
Case C: Absorption-costing income and variable-costing income respectively totaled $220,000 and $250,000 in a period when the beginning finished-goods inventory was 14,000 units.
Required:
A. In Case A, how many units were sold during the period?
B. In Case B, how much income would Beach Bum report under variable costing?
C. In Case C, how many units were in the ending finished-goods inventory?
Case A: Absorption- and variable costing income each totaled $240,000 in a period when the firm produced 18,000 units.
Case B: Absorption-costing income totaled $320,000 in a period when finished-goods inventory levels rose by 7,000 units.
Case C: Absorption-costing income and variable-costing income respectively totaled $220,000 and $250,000 in a period when the beginning finished-goods inventory was 14,000 units.
Required:
A. In Case A, how many units were sold during the period?
B. In Case B, how much income would Beach Bum report under variable costing?
C. In Case C, how many units were in the ending finished-goods inventory?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
The difference in income between absorption and variable costing can be explained by the change in finished-goods inventory (in units) multiplied by the standard fixed manufacturing overhead rate.
Required:
Explain why this calculation accounts for the difference noted.
Required:
Explain why this calculation accounts for the difference noted.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
Coastal Corporation, which uses throughput costing, began operations at the start of the current year. Planned and actual production equaled 20,000 units, and sales totaled 17,500 units at $95 per unit. Cost data for the year were as follows: 
Required:
A. Compute the company's total cost for the year.
B. How much of this cost would be held in year-end inventory under (1) absorption costing and (2) variable costing?
C. How much of the company's total cost for the year would appear on the period's income statement under (1) absorption costing and (2) variable costing?

Required:
A. Compute the company's total cost for the year.
B. How much of this cost would be held in year-end inventory under (1) absorption costing and (2) variable costing?
C. How much of the company's total cost for the year would appear on the period's income statement under (1) absorption costing and (2) variable costing?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 64 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








