Deck 28: Cold War Conflict and Consensus
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/79
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 28: Cold War Conflict and Consensus
1
How did Big Science foster the Green Revolution?
A)The vast pollution produced by modern industry sparked a widespread and popular revolt against modernization.
B)The threat of nuclear annihilation led radicals to join environmentalist political parties.
C)Research into agriculture greatly increased the world food supply, using fewer workers and resulting in more productivity per acre.
D)Industrial pollution in many areas caused breathing difficulties, leading governments to begin to regulate industry more thoroughly.
A)The vast pollution produced by modern industry sparked a widespread and popular revolt against modernization.
B)The threat of nuclear annihilation led radicals to join environmentalist political parties.
C)Research into agriculture greatly increased the world food supply, using fewer workers and resulting in more productivity per acre.
D)Industrial pollution in many areas caused breathing difficulties, leading governments to begin to regulate industry more thoroughly.
Research into agriculture greatly increased the world food supply, using fewer workers and resulting in more productivity per acre.
2
How did the Soviet Union initially organize the eastern European nations as it threw out pro-Nazi regimes?
A)It established direct military rule by the Soviet army with only a few local leaders in minor positions.
B)It created coalition governments of leftist political parties but reserved key government posts for Moscow-trained Communists.
C)It built independent governments that held free elections, all of which elected pro-Soviet political parties.
D)It handed power directly to the national Communist parties in each region.
A)It established direct military rule by the Soviet army with only a few local leaders in minor positions.
B)It created coalition governments of leftist political parties but reserved key government posts for Moscow-trained Communists.
C)It built independent governments that held free elections, all of which elected pro-Soviet political parties.
D)It handed power directly to the national Communist parties in each region.
It created coalition governments of leftist political parties but reserved key government posts for Moscow-trained Communists.
3
Which position did Christian Democrats across Europe endorse during the 1950s?
A)Nationalism
B)The Cold War against the Soviet Union
C)Soviet interests
D)Socialist economic policies
A)Nationalism
B)The Cold War against the Soviet Union
C)Soviet interests
D)Socialist economic policies
The Cold War against the Soviet Union
4
What did the Marshall Plan accomplish?
A)It demonstrated to Americans the futility of foreign aid, which enriched the rulers but rarely benefited local people.
B)It established the foundations of socialist policies throughout Europe.
C)It prevented economic collapse in western Europe.
D)It undermined the ability of free-market capitalism to develop in Europe.
A)It demonstrated to Americans the futility of foreign aid, which enriched the rulers but rarely benefited local people.
B)It established the foundations of socialist policies throughout Europe.
C)It prevented economic collapse in western Europe.
D)It undermined the ability of free-market capitalism to develop in Europe.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
Which six western European countries formed the European Economic Community, or Common Market, in 1957?
A)Great Britain, France, Belgium, the Netherlands, Luxembourg, and Italy
B)France, Belgium, the Netherlands, Luxembourg, Italy, and Spain
C)Belgium, the Netherlands, Luxembourg, Italy, West Germany, and Spain
D)France, Belgium, the Netherlands, Luxembourg, Italy, and West Germany
A)Great Britain, France, Belgium, the Netherlands, Luxembourg, and Italy
B)France, Belgium, the Netherlands, Luxembourg, Italy, and Spain
C)Belgium, the Netherlands, Luxembourg, Italy, West Germany, and Spain
D)France, Belgium, the Netherlands, Luxembourg, Italy, and West Germany

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Why was West Germany allowed to build an army after 1955?
A)The agreements preventing Germany from building an army expired in 1955, a decade after the war ended.
B)A German army would permit Germany to assist in the defense of Europe from attack by the Soviet Union.
C)France and Great Britain were convinced that Germany had embraced democracy and abandoned militarism.
D)The United States decided to withdraw troops from Germany in order to shift them to the growing conflict in Asia.
A)The agreements preventing Germany from building an army expired in 1955, a decade after the war ended.
B)A German army would permit Germany to assist in the defense of Europe from attack by the Soviet Union.
C)France and Great Britain were convinced that Germany had embraced democracy and abandoned militarism.
D)The United States decided to withdraw troops from Germany in order to shift them to the growing conflict in Asia.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
In the 1950s and 1960s, what became the basic objective of all western European governments?
A)Economic growth
B)Political independence from U.S. influence
C)Prevention of Soviet expansion
D)Securing control over colonial lands
A)Economic growth
B)Political independence from U.S. influence
C)Prevention of Soviet expansion
D)Securing control over colonial lands

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
How did the Soviet Union's treatment of Czechoslovakia in 1948 demonstrate its intention to consolidate its hold on eastern Europe?
A)When Czechoslovakia sought to declare itself a neutral power in the conflict between the Soviet Union and the United States, Stalin ordered Soviet troops to invade and seize the government.
B)Despite local protests, the Soviet Union established a massive military base in Czechoslovakia in order to easily send troops throughout central Europe.
C)Even though the Czech Communist Party had won significant electoral support, Stalin still orchestrated the overthrow of the government and establishment of a one-party Communist dictatorship.
D)When Czechoslovakia appealed to the United States for aid, the Soviet Union forbade the aid and any Western officials from entering Czech territory.
A)When Czechoslovakia sought to declare itself a neutral power in the conflict between the Soviet Union and the United States, Stalin ordered Soviet troops to invade and seize the government.
B)Despite local protests, the Soviet Union established a massive military base in Czechoslovakia in order to easily send troops throughout central Europe.
C)Even though the Czech Communist Party had won significant electoral support, Stalin still orchestrated the overthrow of the government and establishment of a one-party Communist dictatorship.
D)When Czechoslovakia appealed to the United States for aid, the Soviet Union forbade the aid and any Western officials from entering Czech territory.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
The advancement in military weaponry and the space race
A)inspired a new literary genre called science fiction.
B)fostered a revolution in computer technology.
C)created a sense of the superiority of the United States.
D)established a confidence in the benefits of scientific discovery.
A)inspired a new literary genre called science fiction.
B)fostered a revolution in computer technology.
C)created a sense of the superiority of the United States.
D)established a confidence in the benefits of scientific discovery.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
The growth of the middle class in the postwar era has been attributed primarily to
A)increased demand for technologists and managers.
B)the strength of family-owned businesses.
C)the high birthrate among this class.
D)increased opportunities for new businesses.
A)increased demand for technologists and managers.
B)the strength of family-owned businesses.
C)the high birthrate among this class.
D)increased opportunities for new businesses.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
What was the consequence of Franklin D. Roosevelt's agreement with Joseph Stalin at the Teheran Conference that the British-American armies would launch a frontal assault on France?
A)The United States would not be able to supply the Soviet Union with needed arms.
B)Great Britain would be able to protect its colonial holdings from Soviet influence.
C)British-American armies fighting in France would face the bulk of the German military.
D)Only Soviet troops would liberate eastern Europe.
A)The United States would not be able to supply the Soviet Union with needed arms.
B)Great Britain would be able to protect its colonial holdings from Soviet influence.
C)British-American armies fighting in France would face the bulk of the German military.
D)Only Soviet troops would liberate eastern Europe.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Changes in the structure of European society after the Second World War were primarily the result of
A)economic and technological transformation.
B)rising birthrates among the lower classes.
C)political and social revolution.
D)large-scale emigration.
A)economic and technological transformation.
B)rising birthrates among the lower classes.
C)political and social revolution.
D)large-scale emigration.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
After the war, why did national governments quickly establish authority over questions of guilt and punishment for those who had collaborated with the Nazi regime?
A)Governments wanted to turn attention away from the issue of collaboration.
B)Unofficial groups were seizing and executing alleged collaborators on their own.
C)Many Nazi collaborators were fleeing to South America.
D)Governments wanted to prevent the possibility of rebellion by a Nazi underground.
A)Governments wanted to turn attention away from the issue of collaboration.
B)Unofficial groups were seizing and executing alleged collaborators on their own.
C)Many Nazi collaborators were fleeing to South America.
D)Governments wanted to prevent the possibility of rebellion by a Nazi underground.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
What did the West German minister of the economy do in 1957 to foster economic growth?
A)He dismantled the extensive social welfare network.
B)He emphasized free-market capitalism.
C)He adopted the French model of a mixed economy.
D)He privatized major state-owned industries.
A)He dismantled the extensive social welfare network.
B)He emphasized free-market capitalism.
C)He adopted the French model of a mixed economy.
D)He privatized major state-owned industries.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
The ultimate goal of the plan for an international organization to coordinate coal and steel production in Europe in the 1950s was to
A)rebuild the European economy.
B)create a single, competitive market in Europe.
C)reduce the influence of the United States.
D)bind the six members of the European Coal and Steel Community so closely that war would be impossible.
A)rebuild the European economy.
B)create a single, competitive market in Europe.
C)reduce the influence of the United States.
D)bind the six members of the European Coal and Steel Community so closely that war would be impossible.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
At the time of the Yalta Conference in 1945, why was the position of the Soviet Union much stronger in negotiations with the United States and Great Britain?
A)The Soviet army already occupied much of eastern Europe.
B)The Soviet Union had developed the technology required to detonate a nuclear warhead.
C)The Soviet Union announced that it was not interested in taking part in the war against the Japanese.
D)The Soviet Union announced that it would not join a United Nations.
A)The Soviet army already occupied much of eastern Europe.
B)The Soviet Union had developed the technology required to detonate a nuclear warhead.
C)The Soviet Union announced that it was not interested in taking part in the war against the Japanese.
D)The Soviet Union announced that it would not join a United Nations.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
According to the best estimates, about how many people died in the Second World War?
A)15 million
B)35 million
C)50 million
D)80 million
A)15 million
B)35 million
C)50 million
D)80 million

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
How did the Soviet Union and eastern European Communist regimes treat displaced persons returning home after the war?
A)As additional burdens on already struggling societies
B)As politically unreliable because of their exposure to western European society
C)As conquering heroes to be celebrated and honored
D)As potential sources of support for unpopular regimes
A)As additional burdens on already struggling societies
B)As politically unreliable because of their exposure to western European society
C)As conquering heroes to be celebrated and honored
D)As potential sources of support for unpopular regimes

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
After the Second World War, the Soviet Union
A)experienced a period of general freedom.
B)underwent a consumer revolution.
C)reintroduced Lenin's New Economic Policy.
D)reestablished a harsh dictatorship.
A)experienced a period of general freedom.
B)underwent a consumer revolution.
C)reintroduced Lenin's New Economic Policy.
D)reestablished a harsh dictatorship.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
When did Jews in Palestine proclaim the state of Israel?
A)After Germany surrendered in May 1945
B)After the British withdrew from Palestine in 1948
C)After the United States proclaimed the Truman Doctrine in 1947
D)After the U.S. Congress promised economic assistance in 1949
A)After Germany surrendered in May 1945
B)After the British withdrew from Palestine in 1948
C)After the United States proclaimed the Truman Doctrine in 1947
D)After the U.S. Congress promised economic assistance in 1949

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Why did Charles de Gaulle withdraw France from NATO?
A)He viewed the United States as the main threat to French independence.
B)He wanted to develop a French nuclear program that the United States refused to endorse.
C)He sought to position France as a main trading partner of the Soviet Union.
D)He rejected U.S. efforts to promote decolonization.
A)He viewed the United States as the main threat to French independence.
B)He wanted to develop a French nuclear program that the United States refused to endorse.
C)He sought to position France as a main trading partner of the Soviet Union.
D)He rejected U.S. efforts to promote decolonization.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Why did the Council of Europe fail to evolve into a European parliament with sovereign rights?
A)France withdrew from NATO, provoking a split among all the nations as to the council's foreign policy goals.
B)The recession of the early 1960s caused all member states to grow leery of further entanglement.
C)Great Britain consistently opposed conceding any real political power and sovereignty to the council.
D)The Soviet Union threatened western Europe with nuclear annihilation if it unified into a single sovereign state.
A)France withdrew from NATO, provoking a split among all the nations as to the council's foreign policy goals.
B)The recession of the early 1960s caused all member states to grow leery of further entanglement.
C)Great Britain consistently opposed conceding any real political power and sovereignty to the council.
D)The Soviet Union threatened western Europe with nuclear annihilation if it unified into a single sovereign state.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Christian Democrats in which country promoted a "social-market economy" based on a combination of free-market liberalism, some state intervention, and an extensive social benefits network?
A)France
B)Belgium
C)West Germany
D)Italy
A)France
B)Belgium
C)West Germany
D)Italy

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
In 1954, Vietnam obtained independence from
A)China.
B)the United States.
C)Great Britain.
D)France.
A)China.
B)the United States.
C)Great Britain.
D)France.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
The Marshall Plan in 1947 was a response to
A)Soviet efforts to block access to West Berlin.
B)a western Europe on the verge of economic collapse.
C)the North Korean invasion of South Korea.
D)the Czech Communists' Stalinizing of the Czech government.
A)Soviet efforts to block access to West Berlin.
B)a western Europe on the verge of economic collapse.
C)the North Korean invasion of South Korea.
D)the Czech Communists' Stalinizing of the Czech government.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Why did Aleksandr Solzhenitsyn's One Day in the Life of Ivan Denisovich create such a sensation when it was published in 1962?
A)It showed how a low-level Soviet official was tempted to misuse his power for personal gain.
B)It portrayed in grim detail life in a Stalinist concentration camp.
C)It exposed the sordid activities of a petty criminal, a type that was not supposed to exist in a socialist society.
D)It presented a vivid picture of the future in which the Soviet system had triumphed completely.
A)It showed how a low-level Soviet official was tempted to misuse his power for personal gain.
B)It portrayed in grim detail life in a Stalinist concentration camp.
C)It exposed the sordid activities of a petty criminal, a type that was not supposed to exist in a socialist society.
D)It presented a vivid picture of the future in which the Soviet system had triumphed completely.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
What was socialist realism?
A)Recognition that building socialism would require hard work and sacrifice
B)The requirement that artists and writers idealize the working class and the Soviet Union in their work
C)The view that writers and artists in the West only produced what the capitalist market demanded and therefore had betrayed their artistic talents
D)A firm conviction that communism would prevail over capitalism in the near future
A)Recognition that building socialism would require hard work and sacrifice
B)The requirement that artists and writers idealize the working class and the Soviet Union in their work
C)The view that writers and artists in the West only produced what the capitalist market demanded and therefore had betrayed their artistic talents
D)A firm conviction that communism would prevail over capitalism in the near future

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Khrushchev's "secret speech" at the Twentieth Party Congress in 1956 was
A)an attack on the crimes of Western capitalism in the postwar period.
B)an impassioned call to support national liberation movements of nonindustrialized countries.
C)a surprising attack on Stalin and his crimes.
D)an apology for mistakes made in dealing with the Hungarian Revolution.
A)an attack on the crimes of Western capitalism in the postwar period.
B)an impassioned call to support national liberation movements of nonindustrialized countries.
C)a surprising attack on Stalin and his crimes.
D)an apology for mistakes made in dealing with the Hungarian Revolution.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
How did Mao Zedong gain the support of the peasantry in China?
A)He promised to provide all Chinese with guaranteed rice rations.
B)He provided guaranteed price supports for rice.
C)He promised to expropriate land from the large landowners.
D)He rejected all foreign aid to demonstrate his independence from foreign influence.
A)He promised to provide all Chinese with guaranteed rice rations.
B)He provided guaranteed price supports for rice.
C)He promised to expropriate land from the large landowners.
D)He rejected all foreign aid to demonstrate his independence from foreign influence.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
What does neocolonialism refer to?
A)The efforts of newly liberated colonies to establish their own empires by conquering weaker neighbors
B)The idea of a system designed to perpetuate Western economic domination and undermine political independence
C)The establishment of authoritarian dictatorships by corrupt African leaders like Joseph Mobutu in the Congo
D)Soviet attempts to extend their influence, particularly in the African continent
A)The efforts of newly liberated colonies to establish their own empires by conquering weaker neighbors
B)The idea of a system designed to perpetuate Western economic domination and undermine political independence
C)The establishment of authoritarian dictatorships by corrupt African leaders like Joseph Mobutu in the Congo
D)Soviet attempts to extend their influence, particularly in the African continent

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
How did the United States respond to the decolonization movement in the first years after the Second World War?
A)It encouraged European nations to let go of their former colonies.
B)It sought to claim colonial lands that Europeans abandoned.
C)It encouraged European powers to hold on to their empires to prevent new nations from coming under Communist influence.
D)It encouraged colonial rebellions as a way to keep the European powers subordinate to U.S. power.
A)It encouraged European nations to let go of their former colonies.
B)It sought to claim colonial lands that Europeans abandoned.
C)It encouraged European powers to hold on to their empires to prevent new nations from coming under Communist influence.
D)It encouraged colonial rebellions as a way to keep the European powers subordinate to U.S. power.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Who was the only Communist leader able to successfully resist Soviet domination?
A)Josip Broz Tito
B)Imre Nagy
C)Wladislaw Gomulka
D)Antonin Novotny
A)Josip Broz Tito
B)Imre Nagy
C)Wladislaw Gomulka
D)Antonin Novotny

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
The international military tribunal organized by the four Allied powers to try the highest-ranking Nazi military and civilian leaders was held in the city of
A)Munich.
B)Berlin.
C)Weimar.
D)Nuremberg.
A)Munich.
B)Berlin.
C)Weimar.
D)Nuremberg.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
What did Nikita Khrushchev's de-Stalinization campaign call for?
A)The Communist Party to retain its monopoly on political power
B)The Communist Party to stop recruiting new members
C)The Communist Party to permit elections at the local level
D)The Community Part to continue to emphasize heavy industry and military production at the expense of consumer goods and agriculture
A)The Communist Party to retain its monopoly on political power
B)The Communist Party to stop recruiting new members
C)The Communist Party to permit elections at the local level
D)The Community Part to continue to emphasize heavy industry and military production at the expense of consumer goods and agriculture

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
What was the result of breaking the Berlin blockade in 1948-1949?
A)The formation of the Warsaw Pact
B)The creation of two separate German states: West Germany and East Germany
C)The establishment of the Council for Mutual Economic Assistance
D)The announcement of the Truman Doctrine
A)The formation of the Warsaw Pact
B)The creation of two separate German states: West Germany and East Germany
C)The establishment of the Council for Mutual Economic Assistance
D)The announcement of the Truman Doctrine

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
How did the pieds-noirs complicate the experience of decolonization in Algeria?
A)As experienced veterans of World War II, these Islamic Algerians effectively resisted the French army's effort to secure the position of the French colonists.
B)Having been relocated to Algeria from Vietnam, they refused further relocation and demanded that the French government honor their commitments to protect them in Algeria.
C)As members of the Islamic Algerian poor who had benefited greatly from French rule, they rejected the call of Islamic leaders to take up arms against the French.
D)Having lived in Algeria for several generations, these European Algerians threatened revolt against France if France did not oppose the Islamic independence movement.
A)As experienced veterans of World War II, these Islamic Algerians effectively resisted the French army's effort to secure the position of the French colonists.
B)Having been relocated to Algeria from Vietnam, they refused further relocation and demanded that the French government honor their commitments to protect them in Algeria.
C)As members of the Islamic Algerian poor who had benefited greatly from French rule, they rejected the call of Islamic leaders to take up arms against the French.
D)Having lived in Algeria for several generations, these European Algerians threatened revolt against France if France did not oppose the Islamic independence movement.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
How did the East German government respond to the nationwide demonstrations against poor wages and working conditions in 1953?
A)It put down the strike with its military police force and then disbanded all labor unions.
B)It permitted Soviet troops to put down the revolt and jailed demonstrators, but then instituted reforms to respond to the demonstrators' strongest demands.
C)It admitted labor leaders to the governing economic council and implemented a wide array of reforms to improve working conditions and raise pay.
D)It crushed the revolt and instituted a purge of all Communist Party members who had expressed sympathy with the demonstrators.
A)It put down the strike with its military police force and then disbanded all labor unions.
B)It permitted Soviet troops to put down the revolt and jailed demonstrators, but then instituted reforms to respond to the demonstrators' strongest demands.
C)It admitted labor leaders to the governing economic council and implemented a wide array of reforms to improve working conditions and raise pay.
D)It crushed the revolt and instituted a purge of all Communist Party members who had expressed sympathy with the demonstrators.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
The Bretton Woods agreement of 1944
A)required all Western nations to abandon the gold standard.
B)linked western European currencies to the U.S. dollar.
C)recommended that nations have balanced budgets.
D)encouraged countries to set relatively low tariff rates.
A)required all Western nations to abandon the gold standard.
B)linked western European currencies to the U.S. dollar.
C)recommended that nations have balanced budgets.
D)encouraged countries to set relatively low tariff rates.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
What was the outcome of the decolonization of the Belgian Congo?
A)Belgium quickly withdrew from the Congo, granting it independence with irresponsible haste.
B)The Congolese political leaders promoted a Marxist agenda that included the confiscation of all lands and mineral wealth.
C)The Congolese army supported the democratically elected prime minister Patrice Lumumba.
D)The CIA helped to thwart a military coup against the democratically elected prime minister Patrice Lumumba.
A)Belgium quickly withdrew from the Congo, granting it independence with irresponsible haste.
B)The Congolese political leaders promoted a Marxist agenda that included the confiscation of all lands and mineral wealth.
C)The Congolese army supported the democratically elected prime minister Patrice Lumumba.
D)The CIA helped to thwart a military coup against the democratically elected prime minister Patrice Lumumba.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
To receive Marshall Plan aid, European states were required to cooperate with one another. What was the result of this cooperation?
A)The World Bank
B)The International Monetary Fund
C)The Organization for European Economic Cooperation
D)The Council for Mutual Economic Assistance
A)The World Bank
B)The International Monetary Fund
C)The Organization for European Economic Cooperation
D)The Council for Mutual Economic Assistance

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
Map 28.1: The Aftermath of World War II in Europe, ca. 1945-1950, shows Germany losing territory to which states? 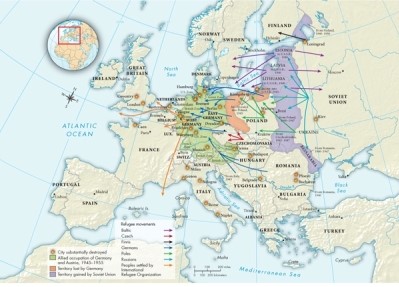
A)France and Belgium
B)France and the Netherlands
C)Poland and Czechoslovakia
D)Poland and the Soviet Union

A)France and Belgium
B)France and the Netherlands
C)Poland and Czechoslovakia
D)Poland and the Soviet Union

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
Why was it difficult for Soviet and Jewish displaced persons (DPs) to return to their homes after the war?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
Which of the following cities survived World War II relatively unscathed?
A)Paris
B)Berlin
C)Leningrad
D)Warsaw
A)Paris
B)Berlin
C)Leningrad
D)Warsaw

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
Based on Map 28.2: Cold War Europe in the 1950s, which unaligned countries did not participate in the Marshall Plan? 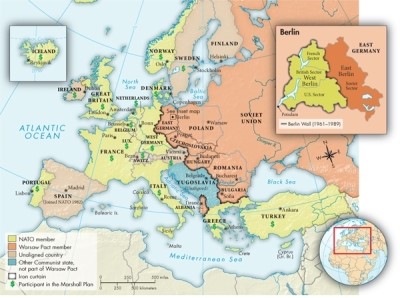
A)Spain and Ireland
B)Austria and Switzerland
C)Finland and Sweden
D)Spain and Finland

A)Spain and Ireland
B)Austria and Switzerland
C)Finland and Sweden
D)Spain and Finland

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
What was the significance of the Berlin Wall?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
The following is an excerpt from Franz Fanon's The Wretched of the Earth (Evaluating the Evidence 28.3). In it, he discusses the role of violence in decolonization: "National liberation, national renaissance, the restoration of nationhood to the people, commonwealth: whatever may be the heading used or the new formulas introduced, decolonization is always a violent phenomenon. At whatever level we study it-relationships between individuals, new names for sports clubs, the human admixture at cocktail parties, in the police, on the directing boards of national or private banks-decolonization is quite simply the replacing of a certain 'species' of men by another 'species' of men. Without any period of transition, there is a total, complete, and absolute substitution. . . ."
According to Fanon, decolonization
A)is always violent.
B)is best accomplished peacefully.
C)is impractical.
D)only results in superficial changes.
According to Fanon, decolonization
A)is always violent.
B)is best accomplished peacefully.
C)is impractical.
D)only results in superficial changes.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
Which of the following was true of World War II?
A)The French suffered the most casualties of any combatant nation.
B)The death toll far exceeded that of World War I.
C)Half of all Poles died in the war.
D)Relatively few noncombatants died in the war.
A)The French suffered the most casualties of any combatant nation.
B)The death toll far exceeded that of World War I.
C)Half of all Poles died in the war.
D)Relatively few noncombatants died in the war.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
What led to the formation of the European Coal and Steel Community in 1951?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
How did Leonid Brezhnev seek to counter the rule of Nikita Khrushchev?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
On Map 28.2: Cold War Europe in the 1950s, the "iron curtain" forms the western boundary of which countries? 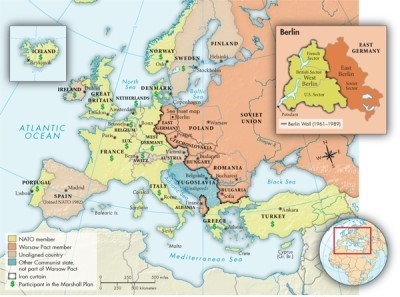
A)Poland, Czechoslovakia, Hungary, Romania, and Bulgaria
B)Yugoslavia, Hungary, Romania, Bulgaria, and Greece
C)East Germany, Czechoslovakia, Hungary, Romania, and Bulgaria
D)East Germany, Poland, Hungary, Romania, and Bulgaria

A)Poland, Czechoslovakia, Hungary, Romania, and Bulgaria
B)Yugoslavia, Hungary, Romania, Bulgaria, and Greece
C)East Germany, Czechoslovakia, Hungary, Romania, and Bulgaria
D)East Germany, Poland, Hungary, Romania, and Bulgaria

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
How can the Suez Canal incident be considered the death knell for imperialism?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
Why did opportunities for women in the workforce expand in the postwar era?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
What were the key sources for the emergence of the postwar European youth culture?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
Why was the decolonization process in Algeria so difficult?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
The following is an excerpt from the exchange in the Nixon-Khrushchev "Kitchen Debate" (Evaluating the Evidence 28.2). In it, Khrushchev responds to Nixon's description of consumer goods in the United States: Khrushchev: "The Americans have created their own image of the Soviet man and think he is as you want him to be. But he is not as you think. You think the Russian people will be dumbfounded to see these things [household appliances and consumer electronics], but the fact is that newly built Russian houses have all this equipment right now. Moreover, all you have to do to get a house is to be born in the Soviet Union. You are entitled to housing. I was born in the Soviet Union. So I have a right to a house. In America, if you don't have a dollar-you have the right to choose between sleeping in a house or on the pavement. Yet you say that we are slaves of communism. . . ."
According to Khrushchev, which of the following was an important difference between the Soviet Union and the United States?
A)In the Soviet Union, housing was a basic right.
B)In the Soviet Union, everyone was rich.
C)In the United States, all people are poor.
D)In the United States, housing was in short supply.
According to Khrushchev, which of the following was an important difference between the Soviet Union and the United States?
A)In the Soviet Union, housing was a basic right.
B)In the Soviet Union, everyone was rich.
C)In the United States, all people are poor.
D)In the United States, housing was in short supply.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
Why did Europeans find postcolonial migration troublesome?
A)Growing ethnic diversity threatened to overwhelm traditional European culture.
B)The large number of immigrant workers drove down property values.
C)Intellectuals worried that immigrant workers would never adopt European values and customs.
D)Immigrant workers were taking jobs away from European workers.
A)Growing ethnic diversity threatened to overwhelm traditional European culture.
B)The large number of immigrant workers drove down property values.
C)Intellectuals worried that immigrant workers would never adopt European values and customs.
D)Immigrant workers were taking jobs away from European workers.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
Why was the Truman Doctrine proclaimed in 1947?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
The following is an excerpt from the exchange in the Nixon-Khrushchev "Kitchen Debate" (Evaluating the Evidence 28.2). In it, Khrushchev responds to Nixon's description of consumer goods in the United States: Khrushchev: "The Americans have created their own image of the Soviet man and think he is as you want him to be. But he is not as you think. You think the Russian people will be dumbfounded to see these things [household appliances and consumer electronics], but the fact is that newly built Russian houses have all this equipment right now. Moreover, all you have to do to get a house is to be born in the Soviet Union. You are entitled to housing. I was born in the Soviet Union. So I have a right to a house. In America, if you don't have a dollar-you have the right to choose between sleeping in a house or on the pavement. Yet you say that we are slaves of communism. . . ."
Khrushchev claimed that Russians
A)did not need consumer goods to be happy.
B)had even more consumer goods than Americans.
C)had all the same consumer goods as Americans.
D)would one day rule the world.
Khrushchev claimed that Russians
A)did not need consumer goods to be happy.
B)had even more consumer goods than Americans.
C)had all the same consumer goods as Americans.
D)would one day rule the world.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
What sparked the Berlin blockade?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
The following is an excerpt from West German chancellor Ludwig Erhard's reflections on the expansion of consumption in postwar Europe (Evaluating the Evidence 28.1): "Consumer credit enables goods to be produced which could otherwise not find a market. . . . Now, consumer credit goes a step further and initiates an expansion of production (e.g. of refrigerators), and this expanded production creates new income which in its turn appears as additional purchasing power on the market. The volume of goods at the disposal of the economy has in other words been built up to a higher level, the national product and the national income have been extended. . . . In this connection of course the question of magnitude is of vital importance. Consumer credit cannot carry, but can usefully supplement an upswing of the economy as a whole. . . . The use of consumer credit [is] one of the means capable of subserving a general policy aimed at expanded consumption. . . ."
According to Erhard, why is consumer credit a good thing?
A)It enables common people to buy the same products as the wealthy.
B)It allows for an expansion of production, which creates new income and purchasing power.
C)It eliminates the need to wait until enough has been saved to make the desired purchase.
D)It can carry an upswing of the economy on its own.
According to Erhard, why is consumer credit a good thing?
A)It enables common people to buy the same products as the wealthy.
B)It allows for an expansion of production, which creates new income and purchasing power.
C)It eliminates the need to wait until enough has been saved to make the desired purchase.
D)It can carry an upswing of the economy on its own.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
How did patterns of migration change in postwar Europe, and how did immigrant communities affect European society?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
After the death of Joseph Stalin, the Soviet Union underwent a process of de-Stalinization. Describe this process. What impact did de-Stalinization have, domestically and internationally? Why did later Soviet leaders re-Stalinize?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
Early in the Cold War, Americans tended to perceive communism as a unified global conspiracy. Discuss the reasons for that perception and the extent to which it was a realistic view.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
Postwar Europe experienced a trend toward unity. What were the successes and failures of the movement? Who were its leaders, and what motivated them? What factors explain the successes and failures?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
Answer the following questions:
Marshall Plan
A)An economic organization of Communist states meant to help rebuild eastern Europe under Soviet auspices.
B)American plan for providing economic aid to western Europe to help it rebuild.
C)Center-right political parties that rose to power in western Europe after the Second World War.
D)The European Economic Community, created by six western European nations in 1957 as part of a larger search for European unity.
E)The liberalization of the post-Stalin Soviet Union led by reformer Nikita Khrushchev.
F)Soviet-backed military alliance of Eastern European nations.
G)Postwar refugees, including 13 million Germans, former Nazi prisoners and forced laborers, and orphaned children.
H)The North Atlantic Treaty Organization, an anti-Soviet military alliance of Western governments.
I)America's policy geared to containing communism to those countries already under Soviet control.
J)The postwar reversal of Europe's overseas expansion caused by the rising demand of the colonized peoples themselves, the declining power of European nations, and the freedoms promised by U.S. and Soviet ideals.
K)Policy of postcolonial governments to remain neutral in the Cold War and play both the United States and the Soviet Union for what they could get.
L)Government-run programs in western Europe designed to recruit labor for the booming postwar economy.
Marshall Plan
A)An economic organization of Communist states meant to help rebuild eastern Europe under Soviet auspices.
B)American plan for providing economic aid to western Europe to help it rebuild.
C)Center-right political parties that rose to power in western Europe after the Second World War.
D)The European Economic Community, created by six western European nations in 1957 as part of a larger search for European unity.
E)The liberalization of the post-Stalin Soviet Union led by reformer Nikita Khrushchev.
F)Soviet-backed military alliance of Eastern European nations.
G)Postwar refugees, including 13 million Germans, former Nazi prisoners and forced laborers, and orphaned children.
H)The North Atlantic Treaty Organization, an anti-Soviet military alliance of Western governments.
I)America's policy geared to containing communism to those countries already under Soviet control.
J)The postwar reversal of Europe's overseas expansion caused by the rising demand of the colonized peoples themselves, the declining power of European nations, and the freedoms promised by U.S. and Soviet ideals.
K)Policy of postcolonial governments to remain neutral in the Cold War and play both the United States and the Soviet Union for what they could get.
L)Government-run programs in western Europe designed to recruit labor for the booming postwar economy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
Answer the following questions:
Council for Mutual Economic Assistance (COMECON)
A)An economic organization of Communist states meant to help rebuild eastern Europe under Soviet auspices.
B)American plan for providing economic aid to western Europe to help it rebuild.
C)Center-right political parties that rose to power in western Europe after the Second World War.
D)The European Economic Community, created by six western European nations in 1957 as part of a larger search for European unity.
E)The liberalization of the post-Stalin Soviet Union led by reformer Nikita Khrushchev.
F)Soviet-backed military alliance of Eastern European nations.
G)Postwar refugees, including 13 million Germans, former Nazi prisoners and forced laborers, and orphaned children.
H)The North Atlantic Treaty Organization, an anti-Soviet military alliance of Western governments.
I)America's policy geared to containing communism to those countries already under Soviet control.
J)The postwar reversal of Europe's overseas expansion caused by the rising demand of the colonized peoples themselves, the declining power of European nations, and the freedoms promised by U.S. and Soviet ideals.
K)Policy of postcolonial governments to remain neutral in the Cold War and play both the United States and the Soviet Union for what they could get.
L)Government-run programs in western Europe designed to recruit labor for the booming postwar economy.
Council for Mutual Economic Assistance (COMECON)
A)An economic organization of Communist states meant to help rebuild eastern Europe under Soviet auspices.
B)American plan for providing economic aid to western Europe to help it rebuild.
C)Center-right political parties that rose to power in western Europe after the Second World War.
D)The European Economic Community, created by six western European nations in 1957 as part of a larger search for European unity.
E)The liberalization of the post-Stalin Soviet Union led by reformer Nikita Khrushchev.
F)Soviet-backed military alliance of Eastern European nations.
G)Postwar refugees, including 13 million Germans, former Nazi prisoners and forced laborers, and orphaned children.
H)The North Atlantic Treaty Organization, an anti-Soviet military alliance of Western governments.
I)America's policy geared to containing communism to those countries already under Soviet control.
J)The postwar reversal of Europe's overseas expansion caused by the rising demand of the colonized peoples themselves, the declining power of European nations, and the freedoms promised by U.S. and Soviet ideals.
K)Policy of postcolonial governments to remain neutral in the Cold War and play both the United States and the Soviet Union for what they could get.
L)Government-run programs in western Europe designed to recruit labor for the booming postwar economy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
How did the Cold War rivals respond to the process of decolonization? Would decolonization have occurred without the Cold War?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
Answer the following questions:
decolonization
A)An economic organization of Communist states meant to help rebuild eastern Europe under Soviet auspices.
B)American plan for providing economic aid to western Europe to help it rebuild.
C)Center-right political parties that rose to power in western Europe after the Second World War.
D)The European Economic Community, created by six western European nations in 1957 as part of a larger search for European unity.
E)The liberalization of the post-Stalin Soviet Union led by reformer Nikita Khrushchev.
F)Soviet-backed military alliance of Eastern European nations.
G)Postwar refugees, including 13 million Germans, former Nazi prisoners and forced laborers, and orphaned children.
H)The North Atlantic Treaty Organization, an anti-Soviet military alliance of Western governments.
I)America's policy geared to containing communism to those countries already under Soviet control.
J)The postwar reversal of Europe's overseas expansion caused by the rising demand of the colonized peoples themselves, the declining power of European nations, and the freedoms promised by U.S. and Soviet ideals.
K)Policy of postcolonial governments to remain neutral in the Cold War and play both the United States and the Soviet Union for what they could get.
L)Government-run programs in western Europe designed to recruit labor for the booming postwar economy.
decolonization
A)An economic organization of Communist states meant to help rebuild eastern Europe under Soviet auspices.
B)American plan for providing economic aid to western Europe to help it rebuild.
C)Center-right political parties that rose to power in western Europe after the Second World War.
D)The European Economic Community, created by six western European nations in 1957 as part of a larger search for European unity.
E)The liberalization of the post-Stalin Soviet Union led by reformer Nikita Khrushchev.
F)Soviet-backed military alliance of Eastern European nations.
G)Postwar refugees, including 13 million Germans, former Nazi prisoners and forced laborers, and orphaned children.
H)The North Atlantic Treaty Organization, an anti-Soviet military alliance of Western governments.
I)America's policy geared to containing communism to those countries already under Soviet control.
J)The postwar reversal of Europe's overseas expansion caused by the rising demand of the colonized peoples themselves, the declining power of European nations, and the freedoms promised by U.S. and Soviet ideals.
K)Policy of postcolonial governments to remain neutral in the Cold War and play both the United States and the Soviet Union for what they could get.
L)Government-run programs in western Europe designed to recruit labor for the booming postwar economy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
International affairs in the postwar era were dominated by the Cold War. What were the key events in its development? Which side was responsible? Given the political, military, and ideological situations at the time, was the Cold War unavoidable? Support your conclusions.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
Answer the following questions:
Christian Democrats
A)An economic organization of Communist states meant to help rebuild eastern Europe under Soviet auspices.
B)American plan for providing economic aid to western Europe to help it rebuild.
C)Center-right political parties that rose to power in western Europe after the Second World War.
D)The European Economic Community, created by six western European nations in 1957 as part of a larger search for European unity.
E)The liberalization of the post-Stalin Soviet Union led by reformer Nikita Khrushchev.
F)Soviet-backed military alliance of Eastern European nations.
G)Postwar refugees, including 13 million Germans, former Nazi prisoners and forced laborers, and orphaned children.
H)The North Atlantic Treaty Organization, an anti-Soviet military alliance of Western governments.
I)America's policy geared to containing communism to those countries already under Soviet control.
J)The postwar reversal of Europe's overseas expansion caused by the rising demand of the colonized peoples themselves, the declining power of European nations, and the freedoms promised by U.S. and Soviet ideals.
K)Policy of postcolonial governments to remain neutral in the Cold War and play both the United States and the Soviet Union for what they could get.
L)Government-run programs in western Europe designed to recruit labor for the booming postwar economy.
Christian Democrats
A)An economic organization of Communist states meant to help rebuild eastern Europe under Soviet auspices.
B)American plan for providing economic aid to western Europe to help it rebuild.
C)Center-right political parties that rose to power in western Europe after the Second World War.
D)The European Economic Community, created by six western European nations in 1957 as part of a larger search for European unity.
E)The liberalization of the post-Stalin Soviet Union led by reformer Nikita Khrushchev.
F)Soviet-backed military alliance of Eastern European nations.
G)Postwar refugees, including 13 million Germans, former Nazi prisoners and forced laborers, and orphaned children.
H)The North Atlantic Treaty Organization, an anti-Soviet military alliance of Western governments.
I)America's policy geared to containing communism to those countries already under Soviet control.
J)The postwar reversal of Europe's overseas expansion caused by the rising demand of the colonized peoples themselves, the declining power of European nations, and the freedoms promised by U.S. and Soviet ideals.
K)Policy of postcolonial governments to remain neutral in the Cold War and play both the United States and the Soviet Union for what they could get.
L)Government-run programs in western Europe designed to recruit labor for the booming postwar economy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
Answer the following questions:
nonalignment
A)An economic organization of Communist states meant to help rebuild eastern Europe under Soviet auspices.
B)American plan for providing economic aid to western Europe to help it rebuild.
C)Center-right political parties that rose to power in western Europe after the Second World War.
D)The European Economic Community, created by six western European nations in 1957 as part of a larger search for European unity.
E)The liberalization of the post-Stalin Soviet Union led by reformer Nikita Khrushchev.
F)Soviet-backed military alliance of Eastern European nations.
G)Postwar refugees, including 13 million Germans, former Nazi prisoners and forced laborers, and orphaned children.
H)The North Atlantic Treaty Organization, an anti-Soviet military alliance of Western governments.
I)America's policy geared to containing communism to those countries already under Soviet control.
J)The postwar reversal of Europe's overseas expansion caused by the rising demand of the colonized peoples themselves, the declining power of European nations, and the freedoms promised by U.S. and Soviet ideals.
K)Policy of postcolonial governments to remain neutral in the Cold War and play both the United States and the Soviet Union for what they could get.
L)Government-run programs in western Europe designed to recruit labor for the booming postwar economy.
nonalignment
A)An economic organization of Communist states meant to help rebuild eastern Europe under Soviet auspices.
B)American plan for providing economic aid to western Europe to help it rebuild.
C)Center-right political parties that rose to power in western Europe after the Second World War.
D)The European Economic Community, created by six western European nations in 1957 as part of a larger search for European unity.
E)The liberalization of the post-Stalin Soviet Union led by reformer Nikita Khrushchev.
F)Soviet-backed military alliance of Eastern European nations.
G)Postwar refugees, including 13 million Germans, former Nazi prisoners and forced laborers, and orphaned children.
H)The North Atlantic Treaty Organization, an anti-Soviet military alliance of Western governments.
I)America's policy geared to containing communism to those countries already under Soviet control.
J)The postwar reversal of Europe's overseas expansion caused by the rising demand of the colonized peoples themselves, the declining power of European nations, and the freedoms promised by U.S. and Soviet ideals.
K)Policy of postcolonial governments to remain neutral in the Cold War and play both the United States and the Soviet Union for what they could get.
L)Government-run programs in western Europe designed to recruit labor for the booming postwar economy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
Answer the following questions:
Common Market
A)An economic organization of Communist states meant to help rebuild eastern Europe under Soviet auspices.
B)American plan for providing economic aid to western Europe to help it rebuild.
C)Center-right political parties that rose to power in western Europe after the Second World War.
D)The European Economic Community, created by six western European nations in 1957 as part of a larger search for European unity.
E)The liberalization of the post-Stalin Soviet Union led by reformer Nikita Khrushchev.
F)Soviet-backed military alliance of Eastern European nations.
G)Postwar refugees, including 13 million Germans, former Nazi prisoners and forced laborers, and orphaned children.
H)The North Atlantic Treaty Organization, an anti-Soviet military alliance of Western governments.
I)America's policy geared to containing communism to those countries already under Soviet control.
J)The postwar reversal of Europe's overseas expansion caused by the rising demand of the colonized peoples themselves, the declining power of European nations, and the freedoms promised by U.S. and Soviet ideals.
K)Policy of postcolonial governments to remain neutral in the Cold War and play both the United States and the Soviet Union for what they could get.
L)Government-run programs in western Europe designed to recruit labor for the booming postwar economy.
Common Market
A)An economic organization of Communist states meant to help rebuild eastern Europe under Soviet auspices.
B)American plan for providing economic aid to western Europe to help it rebuild.
C)Center-right political parties that rose to power in western Europe after the Second World War.
D)The European Economic Community, created by six western European nations in 1957 as part of a larger search for European unity.
E)The liberalization of the post-Stalin Soviet Union led by reformer Nikita Khrushchev.
F)Soviet-backed military alliance of Eastern European nations.
G)Postwar refugees, including 13 million Germans, former Nazi prisoners and forced laborers, and orphaned children.
H)The North Atlantic Treaty Organization, an anti-Soviet military alliance of Western governments.
I)America's policy geared to containing communism to those countries already under Soviet control.
J)The postwar reversal of Europe's overseas expansion caused by the rising demand of the colonized peoples themselves, the declining power of European nations, and the freedoms promised by U.S. and Soviet ideals.
K)Policy of postcolonial governments to remain neutral in the Cold War and play both the United States and the Soviet Union for what they could get.
L)Government-run programs in western Europe designed to recruit labor for the booming postwar economy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
Answer the following questions:
guest worker programs
A)An economic organization of Communist states meant to help rebuild eastern Europe under Soviet auspices.
B)American plan for providing economic aid to western Europe to help it rebuild.
C)Center-right political parties that rose to power in western Europe after the Second World War.
D)The European Economic Community, created by six western European nations in 1957 as part of a larger search for European unity.
E)The liberalization of the post-Stalin Soviet Union led by reformer Nikita Khrushchev.
F)Soviet-backed military alliance of Eastern European nations.
G)Postwar refugees, including 13 million Germans, former Nazi prisoners and forced laborers, and orphaned children.
H)The North Atlantic Treaty Organization, an anti-Soviet military alliance of Western governments.
I)America's policy geared to containing communism to those countries already under Soviet control.
J)The postwar reversal of Europe's overseas expansion caused by the rising demand of the colonized peoples themselves, the declining power of European nations, and the freedoms promised by U.S. and Soviet ideals.
K)Policy of postcolonial governments to remain neutral in the Cold War and play both the United States and the Soviet Union for what they could get.
L)Government-run programs in western Europe designed to recruit labor for the booming postwar economy.
guest worker programs
A)An economic organization of Communist states meant to help rebuild eastern Europe under Soviet auspices.
B)American plan for providing economic aid to western Europe to help it rebuild.
C)Center-right political parties that rose to power in western Europe after the Second World War.
D)The European Economic Community, created by six western European nations in 1957 as part of a larger search for European unity.
E)The liberalization of the post-Stalin Soviet Union led by reformer Nikita Khrushchev.
F)Soviet-backed military alliance of Eastern European nations.
G)Postwar refugees, including 13 million Germans, former Nazi prisoners and forced laborers, and orphaned children.
H)The North Atlantic Treaty Organization, an anti-Soviet military alliance of Western governments.
I)America's policy geared to containing communism to those countries already under Soviet control.
J)The postwar reversal of Europe's overseas expansion caused by the rising demand of the colonized peoples themselves, the declining power of European nations, and the freedoms promised by U.S. and Soviet ideals.
K)Policy of postcolonial governments to remain neutral in the Cold War and play both the United States and the Soviet Union for what they could get.
L)Government-run programs in western Europe designed to recruit labor for the booming postwar economy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
Answer the following questions:
NATO
A)An economic organization of Communist states meant to help rebuild eastern Europe under Soviet auspices.
B)American plan for providing economic aid to western Europe to help it rebuild.
C)Center-right political parties that rose to power in western Europe after the Second World War.
D)The European Economic Community, created by six western European nations in 1957 as part of a larger search for European unity.
E)The liberalization of the post-Stalin Soviet Union led by reformer Nikita Khrushchev.
F)Soviet-backed military alliance of Eastern European nations.
G)Postwar refugees, including 13 million Germans, former Nazi prisoners and forced laborers, and orphaned children.
H)The North Atlantic Treaty Organization, an anti-Soviet military alliance of Western governments.
I)America's policy geared to containing communism to those countries already under Soviet control.
J)The postwar reversal of Europe's overseas expansion caused by the rising demand of the colonized peoples themselves, the declining power of European nations, and the freedoms promised by U.S. and Soviet ideals.
K)Policy of postcolonial governments to remain neutral in the Cold War and play both the United States and the Soviet Union for what they could get.
L)Government-run programs in western Europe designed to recruit labor for the booming postwar economy.
NATO
A)An economic organization of Communist states meant to help rebuild eastern Europe under Soviet auspices.
B)American plan for providing economic aid to western Europe to help it rebuild.
C)Center-right political parties that rose to power in western Europe after the Second World War.
D)The European Economic Community, created by six western European nations in 1957 as part of a larger search for European unity.
E)The liberalization of the post-Stalin Soviet Union led by reformer Nikita Khrushchev.
F)Soviet-backed military alliance of Eastern European nations.
G)Postwar refugees, including 13 million Germans, former Nazi prisoners and forced laborers, and orphaned children.
H)The North Atlantic Treaty Organization, an anti-Soviet military alliance of Western governments.
I)America's policy geared to containing communism to those countries already under Soviet control.
J)The postwar reversal of Europe's overseas expansion caused by the rising demand of the colonized peoples themselves, the declining power of European nations, and the freedoms promised by U.S. and Soviet ideals.
K)Policy of postcolonial governments to remain neutral in the Cold War and play both the United States and the Soviet Union for what they could get.
L)Government-run programs in western Europe designed to recruit labor for the booming postwar economy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
Answer the following questions:
Warsaw Pact
A)An economic organization of Communist states meant to help rebuild eastern Europe under Soviet auspices.
B)American plan for providing economic aid to western Europe to help it rebuild.
C)Center-right political parties that rose to power in western Europe after the Second World War.
D)The European Economic Community, created by six western European nations in 1957 as part of a larger search for European unity.
E)The liberalization of the post-Stalin Soviet Union led by reformer Nikita Khrushchev.
F)Soviet-backed military alliance of Eastern European nations.
G)Postwar refugees, including 13 million Germans, former Nazi prisoners and forced laborers, and orphaned children.
H)The North Atlantic Treaty Organization, an anti-Soviet military alliance of Western governments.
I)America's policy geared to containing communism to those countries already under Soviet control.
J)The postwar reversal of Europe's overseas expansion caused by the rising demand of the colonized peoples themselves, the declining power of European nations, and the freedoms promised by U.S. and Soviet ideals.
K)Policy of postcolonial governments to remain neutral in the Cold War and play both the United States and the Soviet Union for what they could get.
L)Government-run programs in western Europe designed to recruit labor for the booming postwar economy.
Warsaw Pact
A)An economic organization of Communist states meant to help rebuild eastern Europe under Soviet auspices.
B)American plan for providing economic aid to western Europe to help it rebuild.
C)Center-right political parties that rose to power in western Europe after the Second World War.
D)The European Economic Community, created by six western European nations in 1957 as part of a larger search for European unity.
E)The liberalization of the post-Stalin Soviet Union led by reformer Nikita Khrushchev.
F)Soviet-backed military alliance of Eastern European nations.
G)Postwar refugees, including 13 million Germans, former Nazi prisoners and forced laborers, and orphaned children.
H)The North Atlantic Treaty Organization, an anti-Soviet military alliance of Western governments.
I)America's policy geared to containing communism to those countries already under Soviet control.
J)The postwar reversal of Europe's overseas expansion caused by the rising demand of the colonized peoples themselves, the declining power of European nations, and the freedoms promised by U.S. and Soviet ideals.
K)Policy of postcolonial governments to remain neutral in the Cold War and play both the United States and the Soviet Union for what they could get.
L)Government-run programs in western Europe designed to recruit labor for the booming postwar economy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
Answer the following questions:
de-Stalinization
A)An economic organization of Communist states meant to help rebuild eastern Europe under Soviet auspices.
B)American plan for providing economic aid to western Europe to help it rebuild.
C)Center-right political parties that rose to power in western Europe after the Second World War.
D)The European Economic Community, created by six western European nations in 1957 as part of a larger search for European unity.
E)The liberalization of the post-Stalin Soviet Union led by reformer Nikita Khrushchev.
F)Soviet-backed military alliance of Eastern European nations.
G)Postwar refugees, including 13 million Germans, former Nazi prisoners and forced laborers, and orphaned children.
H)The North Atlantic Treaty Organization, an anti-Soviet military alliance of Western governments.
I)America's policy geared to containing communism to those countries already under Soviet control.
J)The postwar reversal of Europe's overseas expansion caused by the rising demand of the colonized peoples themselves, the declining power of European nations, and the freedoms promised by U.S. and Soviet ideals.
K)Policy of postcolonial governments to remain neutral in the Cold War and play both the United States and the Soviet Union for what they could get.
L)Government-run programs in western Europe designed to recruit labor for the booming postwar economy.
de-Stalinization
A)An economic organization of Communist states meant to help rebuild eastern Europe under Soviet auspices.
B)American plan for providing economic aid to western Europe to help it rebuild.
C)Center-right political parties that rose to power in western Europe after the Second World War.
D)The European Economic Community, created by six western European nations in 1957 as part of a larger search for European unity.
E)The liberalization of the post-Stalin Soviet Union led by reformer Nikita Khrushchev.
F)Soviet-backed military alliance of Eastern European nations.
G)Postwar refugees, including 13 million Germans, former Nazi prisoners and forced laborers, and orphaned children.
H)The North Atlantic Treaty Organization, an anti-Soviet military alliance of Western governments.
I)America's policy geared to containing communism to those countries already under Soviet control.
J)The postwar reversal of Europe's overseas expansion caused by the rising demand of the colonized peoples themselves, the declining power of European nations, and the freedoms promised by U.S. and Soviet ideals.
K)Policy of postcolonial governments to remain neutral in the Cold War and play both the United States and the Soviet Union for what they could get.
L)Government-run programs in western Europe designed to recruit labor for the booming postwar economy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
How did the consumer revolution of the late 1950s and the 1960s affect the Cold War? What aided the expansion of consumption?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
Answer the following questions:
displaced persons
A)An economic organization of Communist states meant to help rebuild eastern Europe under Soviet auspices.
B)American plan for providing economic aid to western Europe to help it rebuild.
C)Center-right political parties that rose to power in western Europe after the Second World War.
D)The European Economic Community, created by six western European nations in 1957 as part of a larger search for European unity.
E)The liberalization of the post-Stalin Soviet Union led by reformer Nikita Khrushchev.
F)Soviet-backed military alliance of Eastern European nations.
G)Postwar refugees, including 13 million Germans, former Nazi prisoners and forced laborers, and orphaned children.
H)The North Atlantic Treaty Organization, an anti-Soviet military alliance of Western governments.
I)America's policy geared to containing communism to those countries already under Soviet control.
J)The postwar reversal of Europe's overseas expansion caused by the rising demand of the colonized peoples themselves, the declining power of European nations, and the freedoms promised by U.S. and Soviet ideals.
K)Policy of postcolonial governments to remain neutral in the Cold War and play both the United States and the Soviet Union for what they could get.
L)Government-run programs in western Europe designed to recruit labor for the booming postwar economy.
displaced persons
A)An economic organization of Communist states meant to help rebuild eastern Europe under Soviet auspices.
B)American plan for providing economic aid to western Europe to help it rebuild.
C)Center-right political parties that rose to power in western Europe after the Second World War.
D)The European Economic Community, created by six western European nations in 1957 as part of a larger search for European unity.
E)The liberalization of the post-Stalin Soviet Union led by reformer Nikita Khrushchev.
F)Soviet-backed military alliance of Eastern European nations.
G)Postwar refugees, including 13 million Germans, former Nazi prisoners and forced laborers, and orphaned children.
H)The North Atlantic Treaty Organization, an anti-Soviet military alliance of Western governments.
I)America's policy geared to containing communism to those countries already under Soviet control.
J)The postwar reversal of Europe's overseas expansion caused by the rising demand of the colonized peoples themselves, the declining power of European nations, and the freedoms promised by U.S. and Soviet ideals.
K)Policy of postcolonial governments to remain neutral in the Cold War and play both the United States and the Soviet Union for what they could get.
L)Government-run programs in western Europe designed to recruit labor for the booming postwar economy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
Answer the following questions:
Truman Doctrine
A)An economic organization of Communist states meant to help rebuild eastern Europe under Soviet auspices.
B)American plan for providing economic aid to western Europe to help it rebuild.
C)Center-right political parties that rose to power in western Europe after the Second World War.
D)The European Economic Community, created by six western European nations in 1957 as part of a larger search for European unity.
E)The liberalization of the post-Stalin Soviet Union led by reformer Nikita Khrushchev.
F)Soviet-backed military alliance of Eastern European nations.
G)Postwar refugees, including 13 million Germans, former Nazi prisoners and forced laborers, and orphaned children.
H)The North Atlantic Treaty Organization, an anti-Soviet military alliance of Western governments.
I)America's policy geared to containing communism to those countries already under Soviet control.
J)The postwar reversal of Europe's overseas expansion caused by the rising demand of the colonized peoples themselves, the declining power of European nations, and the freedoms promised by U.S. and Soviet ideals.
K)Policy of postcolonial governments to remain neutral in the Cold War and play both the United States and the Soviet Union for what they could get.
L)Government-run programs in western Europe designed to recruit labor for the booming postwar economy.
Truman Doctrine
A)An economic organization of Communist states meant to help rebuild eastern Europe under Soviet auspices.
B)American plan for providing economic aid to western Europe to help it rebuild.
C)Center-right political parties that rose to power in western Europe after the Second World War.
D)The European Economic Community, created by six western European nations in 1957 as part of a larger search for European unity.
E)The liberalization of the post-Stalin Soviet Union led by reformer Nikita Khrushchev.
F)Soviet-backed military alliance of Eastern European nations.
G)Postwar refugees, including 13 million Germans, former Nazi prisoners and forced laborers, and orphaned children.
H)The North Atlantic Treaty Organization, an anti-Soviet military alliance of Western governments.
I)America's policy geared to containing communism to those countries already under Soviet control.
J)The postwar reversal of Europe's overseas expansion caused by the rising demand of the colonized peoples themselves, the declining power of European nations, and the freedoms promised by U.S. and Soviet ideals.
K)Policy of postcolonial governments to remain neutral in the Cold War and play both the United States and the Soviet Union for what they could get.
L)Government-run programs in western Europe designed to recruit labor for the booming postwar economy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 79 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








