Deck 3: Linear Programming: Sensitivity Analysis and Interpretation of Solution
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/44
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 3: Linear Programming: Sensitivity Analysis and Interpretation of Solution
1
If the range of feasibility for b1 is between 16 and 37,then if b1 = 22,the optimal solution will not change from the original optimal solution.
False
2
There is a dual price for every decision variable in a model.
False
3
If two or more objective function coefficients are changed simultaneously,further analysis is necessary to determine whether the optimal solution will change.
True
4
The dual price associated with a constraint is the change in the value of the solution per unit decrease in the right-hand side of the constraint.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
If the range of feasibility indicates that the original amount of a resource,which was 20,can increase by 5,then the amount of the resource can increase to 25.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Relevant costs should be reflected in the objective function,but sunk costs should not.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
When two or more objective function coefficients are changed simultaneously,further analysis is necessary to determine whether the optimal solution will change.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
When the right-hand sides of two constraints are each increased by one unit,the objective function value will be adjusted by the sum of the constraints' dual prices.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Classical sensitivity analysis provides no information about changes resulting from a change in the coefficient of a variable in a constraint.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
For a minimization problem,a positive dual price indicates the value of the objective function will increase.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
To solve a linear programming problem with thousands of variables and constraints,
A)a personal computer can be used.
B)a mainframe computer is required.
C)the problem must be partitioned into subparts.
D)unique software would need to be developed.
A)a personal computer can be used.
B)a mainframe computer is required.
C)the problem must be partitioned into subparts.
D)unique software would need to be developed.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
A small change in the objective function coefficient can necessitate modifying the optimal solution.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
In order to tell the impact of a change in a constraint coefficient,the change must be made and then the model resolved.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
The dual value and dual price are identical for a minimization problem.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
If the optimal value of a decision variable is zero and its reduced cost is zero,this indicates that alternative optimal solutions exist.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
The amount of a sunk cost will vary depending on the values of the decision variables.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
A negative dual price indicates that increasing the right-hand side of the associated constraint would be detrimental to the objective.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
If the dual price for the right-hand side of a ≤ constraint is zero,there is no upper limit on its range of feasibility.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Increasing the right-hand side of a nonbinding constraint will not cause a change in the optimal solution.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
The reduced cost of a variable is the dual value of the corresponding nonnegativity constraint.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Based on the per-unit increase in the right-hand side of the constraint,the dual price measures the
A)increase in the value of the optimal solution.
B)decrease in the value of the optimal solution.
C)improvement in the value of the optimal solution.
D)change in the value of the optimal solution.
A)increase in the value of the optimal solution.
B)decrease in the value of the optimal solution.
C)improvement in the value of the optimal solution.
D)change in the value of the optimal solution.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
The graphical solution procedure is useful only for linear programs involving
A)two decision variables.
B)more than two decision variables.
C)a single constraint.
D)None of these are correct.
A)two decision variables.
B)more than two decision variables.
C)a single constraint.
D)None of these are correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
A negative dual price for a constraint in a minimization problem means
A)as the right-hand side increases,the objective function value will increase.
B)as the right-hand side decreases,the objective function value will increase.
C)as the right-hand side increases,the objective function value will decrease.
D)as the right-hand side decreases,the objective function value will decrease.
A)as the right-hand side increases,the objective function value will increase.
B)as the right-hand side decreases,the objective function value will increase.
C)as the right-hand side increases,the objective function value will decrease.
D)as the right-hand side decreases,the objective function value will decrease.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
When the cost of a resource is sunk,then the dual price can be interpreted as the
A)minimum amount the firm should be willing to pay for one additional unit of the resource.
B)maximum amount the firm should be willing to pay for one additional unit of the resource.
C)minimum amount the firm should be willing to pay for multiple additional units of the resource.
D)maximum amount the firm should be willing to pay for multiple additional units of the resource.
A)minimum amount the firm should be willing to pay for one additional unit of the resource.
B)maximum amount the firm should be willing to pay for one additional unit of the resource.
C)minimum amount the firm should be willing to pay for multiple additional units of the resource.
D)maximum amount the firm should be willing to pay for multiple additional units of the resource.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
A cost that is incurred no matter what values the decision variables assume is a(n)
A)reduced cost.
B)optimal cost.
C)sunk cost.
D)dual cost.
A)reduced cost.
B)optimal cost.
C)sunk cost.
D)dual cost.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
An improvement in the value of the objective function per unit increase in a right-hand side is the
A)sensitivity value.
B)constraint coefficient.
C)slack value.
D)None of these are correct.
A)sensitivity value.
B)constraint coefficient.
C)slack value.
D)None of these are correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
The range of feasibility measures
A)the right-hand-side values for which the objective function value will not change.
B)the right-hand-side values for which the values of the decision variables will not change.
C)the right-hand-side values for which the dual prices will not change.
D)All of these are correct.
A)the right-hand-side values for which the objective function value will not change.
B)the right-hand-side values for which the values of the decision variables will not change.
C)the right-hand-side values for which the dual prices will not change.
D)All of these are correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
The amount by which an objective function coefficient can change before a different set of values for the decision variables becomes optimal is the
A)optimal solution.
B)dual solution.
C)range of optimality.
D)range of feasibility.
A)optimal solution.
B)dual solution.
C)range of optimality.
D)range of feasibility.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Sensitivity analysis information in computer output is based on the assumption that
A)no coefficient changes.
B)one coefficient changes.
C)two coefficients change.
D)all coefficients change.
A)no coefficient changes.
B)one coefficient changes.
C)two coefficients change.
D)all coefficients change.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
The cost that varies depending on the values of the decision variables is a
A)reduced cost.
B)relevant cost.
C)sunk cost.
D)dual cost.
A)reduced cost.
B)relevant cost.
C)sunk cost.
D)dual cost.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
In a linear programming problem,the binding constraints for the optimal solution are:
5X + 3Y ≤ 30
2X + 5Y ≤ 20
a.Fill in the blanks in the following sentence:
As long as the slope of the objective function stays between _______ and _______,the current optimal solution point will remain optimal.
b.Which of these objective functions will lead to the same optimal solution?
(1)2X + 1Y (2)7X + 8Y (3)80X + 60Y (4)25X + 35Y
5X + 3Y ≤ 30
2X + 5Y ≤ 20
a.Fill in the blanks in the following sentence:
As long as the slope of the objective function stays between _______ and _______,the current optimal solution point will remain optimal.
b.Which of these objective functions will lead to the same optimal solution?
(1)2X + 1Y (2)7X + 8Y (3)80X + 60Y (4)25X + 35Y

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Which of the following is NOT a question answered by standard sensitivity analysis information?
A)If the right-hand-side value of a constraint changes,will the objective function value change?
B)Over what range can a constraint's right-hand-side value change without the constraint's dual price possibly changing?
C)By how much will the objective function value change if the right-hand-side value of a constraint changes beyond the range of feasibility?
D)By how much will the objective function value change if a decision variable's coefficient in the objective function changes within the range of optimality?
A)If the right-hand-side value of a constraint changes,will the objective function value change?
B)Over what range can a constraint's right-hand-side value change without the constraint's dual price possibly changing?
C)By how much will the objective function value change if the right-hand-side value of a constraint changes beyond the range of feasibility?
D)By how much will the objective function value change if a decision variable's coefficient in the objective function changes within the range of optimality?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
Sensitivity analysis is sometimes referred to as
A)feasibility testing.
B)duality analysis.
C)alternative analysis.
D)postoptimality analysis.
A)feasibility testing.
B)duality analysis.
C)alternative analysis.
D)postoptimality analysis.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
Sensitivity analysis is concerned with how certain changes affect the
A)feasible solution.
B)unconstrained solution.
C)optimal solution.
D)degenerative solution.
A)feasible solution.
B)unconstrained solution.
C)optimal solution.
D)degenerative solution.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
The dual price for a < constraint will
A)always be < 0.
B)always be > 0.
C)be < 0 in a minimization problem and > 0 in a maximization problem.
D)always equal 0.
A)always be < 0.
B)always be > 0.
C)be < 0 in a minimization problem and > 0 in a maximization problem.
D)always equal 0.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
The amount the objective function coefficient of a decision variable would have to improve before that variable would have a positive value in the solution is the
A)dual price.
B)surplus variable.
C)reduced cost.
D)upper limit.
A)dual price.
B)surplus variable.
C)reduced cost.
D)upper limit.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
A constraint with a positive slack value
A)will have a positive dual price.
B)will have a negative dual price.
C)will have a dual price of zero.
D)has no restrictions for its dual price.
A)will have a positive dual price.
B)will have a negative dual price.
C)will have a dual price of zero.
D)has no restrictions for its dual price.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
An objective function reflects the relevant cost of labor hours used in production rather than treating them as a sunk cost.The correct interpretation of the dual price associated with the labor hours constraint is the
A)maximum premium (say for overtime)over the normal price that the company would be willing to pay.
B)upper limit on the total hourly wage the company would pay.
C)reduction in hours that could be sustained before the solution would change.
D)number of hours by which the right-hand side can change before there is a change in the solution point.
A)maximum premium (say for overtime)over the normal price that the company would be willing to pay.
B)upper limit on the total hourly wage the company would pay.
C)reduction in hours that could be sustained before the solution would change.
D)number of hours by which the right-hand side can change before there is a change in the solution point.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
If a decision variable is not positive in the optimal solution,its reduced cost is
A)what its objective function value would need to be before it could become positive.
B)the amount its objective function value would need to improve before it could become positive.
C)zero.
D)its dual price.
A)what its objective function value would need to be before it could become positive.
B)the amount its objective function value would need to improve before it could become positive.
C)zero.
D)its dual price.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
The optimal solution of this linear programming problem is at the intersection of constraints 1 and 2. 
a.
Over what range can the coefficient of x1 vary before the current solution is no longer optimal?
b.
Over what range can the coefficient of x2 vary before the current solution is no longer optimal?
c.Compute the dual prices for the three constraints.

a.
Over what range can the coefficient of x1 vary before the current solution is no longer optimal?
b.
Over what range can the coefficient of x2 vary before the current solution is no longer optimal?
c.Compute the dual prices for the three constraints.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
The binding constraints for this problem are the first and second. 
a.Keeping c2 fixed at 2,over what range can c1 vary before there is a change in the optimal solution point?
b.Keeping c1 fixed at 1,over what range can c2 vary before there is a change in the optimal solution point?
c.If the objective function becomes Min 1.5x1 + 2x2,what will be the optimal values of x1,x2,and the objective function?
d.If the objective function becomes Min 7x1 + 6x2,what constraints will be binding?
e.Find the dual price for each constraint in the original problem.

a.Keeping c2 fixed at 2,over what range can c1 vary before there is a change in the optimal solution point?
b.Keeping c1 fixed at 1,over what range can c2 vary before there is a change in the optimal solution point?
c.If the objective function becomes Min 1.5x1 + 2x2,what will be the optimal values of x1,x2,and the objective function?
d.If the objective function becomes Min 7x1 + 6x2,what constraints will be binding?
e.Find the dual price for each constraint in the original problem.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
Consider the following linear program:  The graphical solution to the problem is shown below.From the graph,we see that the optimal solution occurs at x1 = 5,x2 = 3,and z = 46.
The graphical solution to the problem is shown below.From the graph,we see that the optimal solution occurs at x1 = 5,x2 = 3,and z = 46. 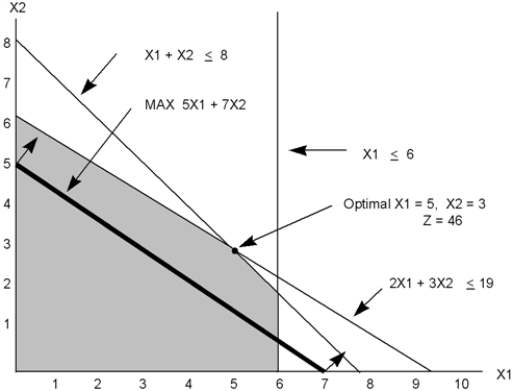
a.Calculate the range of optimality for each objective function coefficient.
b.Calculate the dual price for each resource.
 The graphical solution to the problem is shown below.From the graph,we see that the optimal solution occurs at x1 = 5,x2 = 3,and z = 46.
The graphical solution to the problem is shown below.From the graph,we see that the optimal solution occurs at x1 = 5,x2 = 3,and z = 46. 
a.Calculate the range of optimality for each objective function coefficient.
b.Calculate the dual price for each resource.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
Excel's Solver tool has been used in the spreadsheet below to solve a linear programming problem with a maximization objective function and all ≤ constraints. 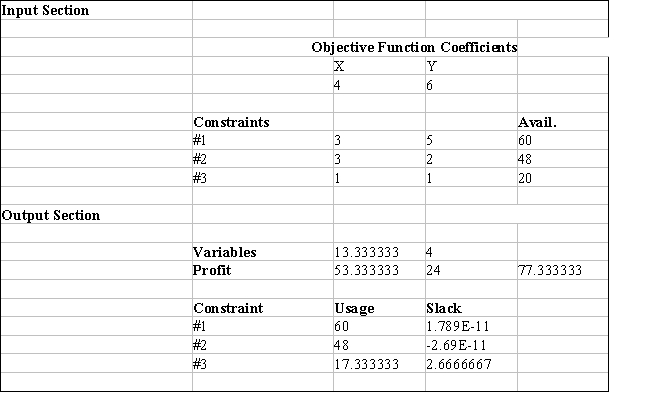
a.Give the original linear programming problem.
b.Give the complete optimal solution.

a.Give the original linear programming problem.
b.Give the complete optimal solution.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
Excel's Solver tool has been used in the spreadsheet below to solve a linear programming problem with a minimization objective function and all ≥ constraints. 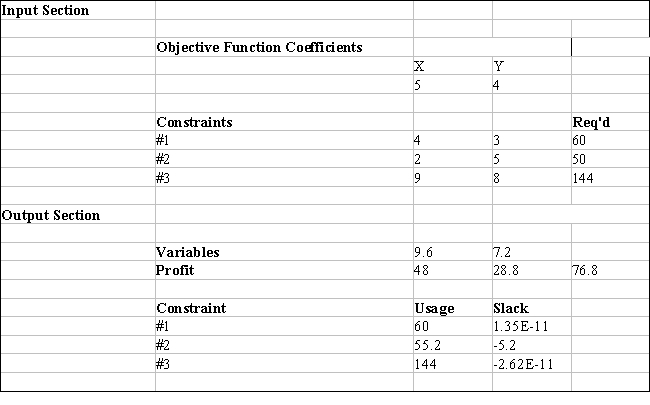
a.Give the original linear programming problem.
b.Give the complete optimal solution.

a.Give the original linear programming problem.
b.Give the complete optimal solution.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








