Deck 13: Vector Calculus
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/240
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 13: Vector Calculus
1
Let and let S be the boundary surface of the solid E bounded by , and . Evaluate the surface integral .
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
G)
H)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
G)
H)
2
Find the flux of 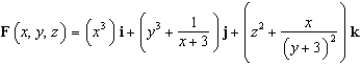 across the surface of the solid bounded by
across the surface of the solid bounded by 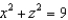 , and the planes
, and the planes 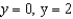 .
.
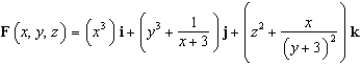 across the surface of the solid bounded by
across the surface of the solid bounded by 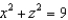 , and the planes
, and the planes 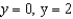 .
.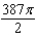
3
Let and let S be the boundary surface of the solid . Evaluate the surface integral .
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
G)
H)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
G)
H)
4
Let and let S be the boundary surface of the solid . Evaluate the surface integral .
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
G)
H)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
G)
H)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
Let and let S be the boundary surface of the solid . Evaluate the surface integral .
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
G)
H)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
G)
H)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Let and let S be the boundary surface of the solid . Evaluate the surface integral .
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
G)
H)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
G)
H)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Let 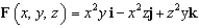 and let S be the surface of the rectangular box bounded by the planes
and let S be the surface of the rectangular box bounded by the planes  , and
, and 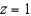 . Evaluate the surface integral
. Evaluate the surface integral 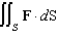 .
.
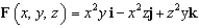 and let S be the surface of the rectangular box bounded by the planes
and let S be the surface of the rectangular box bounded by the planes  , and
, and 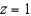 . Evaluate the surface integral
. Evaluate the surface integral 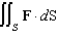 .
.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Let 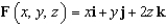 and let S be the boundary surface of the solid
and let S be the boundary surface of the solid 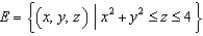 . Evaluate the surface integral
. Evaluate the surface integral 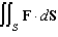 .
.
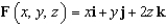 and let S be the boundary surface of the solid
and let S be the boundary surface of the solid 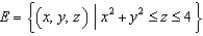 . Evaluate the surface integral
. Evaluate the surface integral 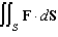 .
.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Let 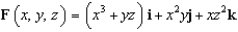 and let S be the surface of the solid bounded by the spheres
and let S be the surface of the solid bounded by the spheres 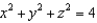 and
and 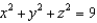 . Evaluate the surface integral
. Evaluate the surface integral 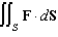 .
.
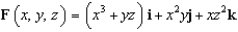 and let S be the surface of the solid bounded by the spheres
and let S be the surface of the solid bounded by the spheres 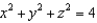 and
and 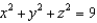 . Evaluate the surface integral
. Evaluate the surface integral 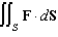 .
.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Evaluate 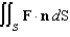 , where S is the cube bounded by the planes
, where S is the cube bounded by the planes 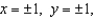 and
and 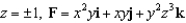 , and n is the outward normal.
, and n is the outward normal.
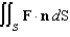 , where S is the cube bounded by the planes
, where S is the cube bounded by the planes 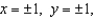 and
and 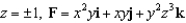 , and n is the outward normal.
, and n is the outward normal.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Let 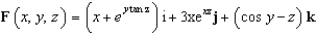 and let S be the surface with equation
and let S be the surface with equation 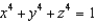 . Evaluate the surface integral
. Evaluate the surface integral 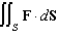 .
.
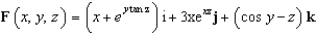 and let S be the surface with equation
and let S be the surface with equation 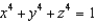 . Evaluate the surface integral
. Evaluate the surface integral 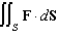 .
.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Let and let S be the boundary surface of the solid . Evaluate the surface integral .
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
G)
H)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
G)
H)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Use the Divergence Theorem to evaluate where and S is the surface of the cylinder , bounded by the planes and .
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
G)
H)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
G)
H)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Find the flux of 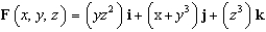 across the surface of the solid bounded by the paraboloid
across the surface of the solid bounded by the paraboloid 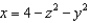 and the
and the 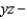 plane.
plane.
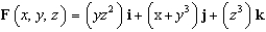 across the surface of the solid bounded by the paraboloid
across the surface of the solid bounded by the paraboloid 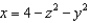 and the
and the 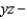 plane.
plane.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Let 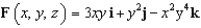 and let S be the surface of the tetrahedron with vertices
and let S be the surface of the tetrahedron with vertices 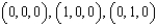 , and
, and 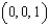 . Evaluate the surface integral
. Evaluate the surface integral 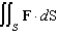 .
.
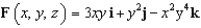 and let S be the surface of the tetrahedron with vertices
and let S be the surface of the tetrahedron with vertices 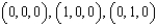 , and
, and 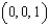 . Evaluate the surface integral
. Evaluate the surface integral 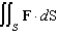 .
.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Let and let S be the boundary surface of the solid . Evaluate the surface integral .
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
G)
H)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
G)
H)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Use the Divergence Theorem to evaluate where and S is the sphere .
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
G)
H)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
G)
H)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Let and let S be the boundary surface of the solid . Evaluate the surface integral .
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
G)
H)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
G)
H)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Let 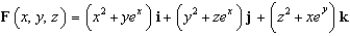 and let S be the boundary surface of the solid
and let S be the boundary surface of the solid 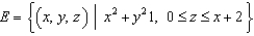 . Evaluate the surface integral
. Evaluate the surface integral 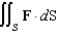 .
.
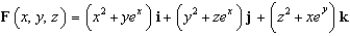 and let S be the boundary surface of the solid
and let S be the boundary surface of the solid 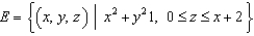 . Evaluate the surface integral
. Evaluate the surface integral 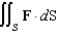 .
.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Evaluate the flux integral 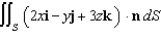 over the boundary of the ball
over the boundary of the ball 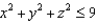 .
.
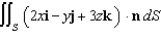 over the boundary of the ball
over the boundary of the ball 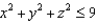 .
.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Evaluate 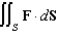 , where S is the boundary surface of the solid sphere
, where S is the boundary surface of the solid sphere 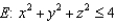 and
and 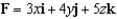
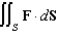 , where S is the boundary surface of the solid sphere
, where S is the boundary surface of the solid sphere 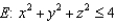 and
and 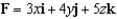

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Evaluate 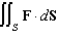 , where S is the boundary surface of the region outside the sphere
, where S is the boundary surface of the region outside the sphere 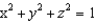 and inside the ball
and inside the ball 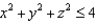 and
and 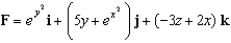 .
.
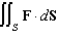 , where S is the boundary surface of the region outside the sphere
, where S is the boundary surface of the region outside the sphere 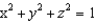 and inside the ball
and inside the ball 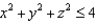 and
and 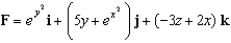 .
.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Let . Evaluate the line integral along the elliptical path .
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
G)
H)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
G)
H)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Let S be the outwardly-oriented surface of a solid region E where the volume of E is 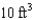 . If
. If 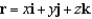 and
and 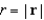 , evaluate the surface integral
, evaluate the surface integral 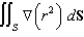 .
.
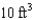 . If
. If 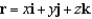 and
and 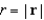 , evaluate the surface integral
, evaluate the surface integral 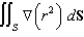 .
.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Use Stokes' Theorem to evaluate where C is the circle .
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
G)
H)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
G)
H)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Evaluate 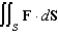 , where
, where 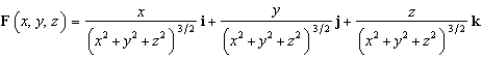 and S is the sphere
and S is the sphere 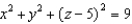 .
.
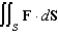 , where
, where 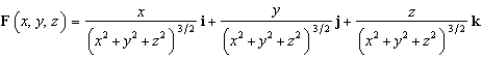 and S is the sphere
and S is the sphere 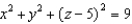 .
.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Use Stokes' Theorem to evaluate 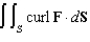 where
where 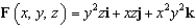 and S is the part of the paraboloid
and S is the part of the paraboloid 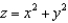 that lies inside the cylinder
that lies inside the cylinder 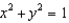 , oriented upward.
, oriented upward.
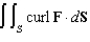 where
where 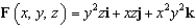 and S is the part of the paraboloid
and S is the part of the paraboloid 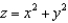 that lies inside the cylinder
that lies inside the cylinder 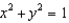 , oriented upward.
, oriented upward.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Let . Evaluate the line integral along the elliptical path .
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
G)
H)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
G)
H)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Let . Evaluate the line integral along the rectangular path from to to to to .
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
G)
H)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
G)
H)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
Let . Evaluate over the surface S given by , with downward orientation.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
G)
H)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
G)
H)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Find the flux of 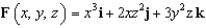 across the surface of the solid bounded by the paraboloid
across the surface of the solid bounded by the paraboloid 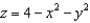 and the
and the 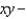 plane.
plane.
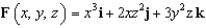 across the surface of the solid bounded by the paraboloid
across the surface of the solid bounded by the paraboloid 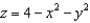 and the
and the 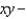 plane.
plane.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Evaluate 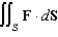 , where
, where 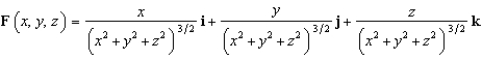 and S is the sphere
and S is the sphere 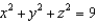 .
.
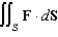 , where
, where 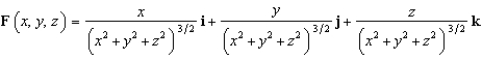 and S is the sphere
and S is the sphere 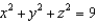 .
.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
Find the flux of 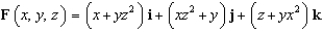 across the surface of the solid bounded by the paraboloid
across the surface of the solid bounded by the paraboloid 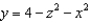 and the
and the 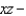 plane.
plane.
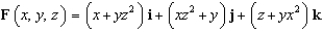 across the surface of the solid bounded by the paraboloid
across the surface of the solid bounded by the paraboloid 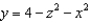 and the
and the 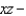 plane.
plane.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
Let 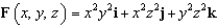 . Let C be the rectangular path from
. Let C be the rectangular path from 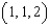 to
to 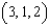 to
to 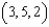 to
to 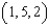 to
to 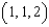 . Use Stokes' Theorem to evaluate the line integral
. Use Stokes' Theorem to evaluate the line integral 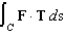 , where T is the unit tangent vector to C.
, where T is the unit tangent vector to C.
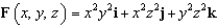 . Let C be the rectangular path from
. Let C be the rectangular path from 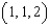 to
to 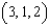 to
to 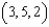 to
to 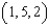 to
to 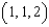 . Use Stokes' Theorem to evaluate the line integral
. Use Stokes' Theorem to evaluate the line integral 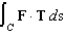 , where T is the unit tangent vector to C.
, where T is the unit tangent vector to C.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Find the flux of 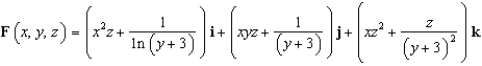 across the surface of the solid
across the surface of the solid 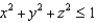 .
.
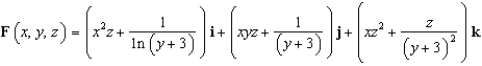 across the surface of the solid
across the surface of the solid 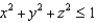 .
.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
Evaluate 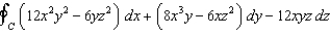 , where the path C is the curve of intersection of the paraboloid
, where the path C is the curve of intersection of the paraboloid 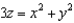 with the plane
with the plane 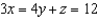 .
.
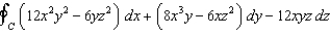 , where the path C is the curve of intersection of the paraboloid
, where the path C is the curve of intersection of the paraboloid 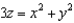 with the plane
with the plane 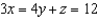 .
.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Let . Evaluate the line integral , where C is the curve of intersection of the paraboloid and the cylinder .
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
G)
H)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
G)
H)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
Use Stokes' Theorem to evaluate where C is the circle .
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
G)
H)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
G)
H)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
Use Stokes' Theorem to evaluate where C is the triangle with vertices , and , oriented counter clockwise as viewed from above.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
G)
H)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
G)
H)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Let 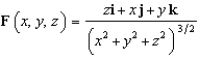 and let S be the boundary surface of the solid
and let S be the boundary surface of the solid 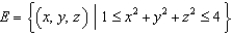 . Evaluate the surface integral
. Evaluate the surface integral 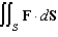 .
.
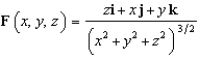 and let S be the boundary surface of the solid
and let S be the boundary surface of the solid 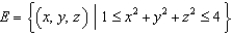 . Evaluate the surface integral
. Evaluate the surface integral 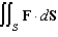 .
.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
A surface has the shape of the cone between and with the density function . Find the mass of the surface.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
G)
H)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
G)
H)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
Consider the surfaces 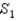 :
: 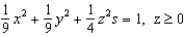 , and
, and 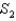 :
: 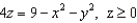 , and let F be a vector field with continuous partial derivatives everywhere. Why do we know that
, and let F be a vector field with continuous partial derivatives everywhere. Why do we know that 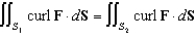 ?
?
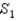 :
: 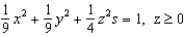 , and
, and 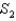 :
: 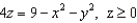 , and let F be a vector field with continuous partial derivatives everywhere. Why do we know that
, and let F be a vector field with continuous partial derivatives everywhere. Why do we know that 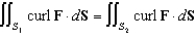 ?
?
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
Use Stokes' Theorem to evaluate 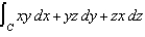 , where C is the triangle with vertices
, where C is the triangle with vertices 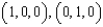 , and
, and 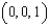 , oriented counterclockwise as viewed from above.
, oriented counterclockwise as viewed from above.
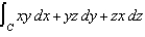 , where C is the triangle with vertices
, where C is the triangle with vertices 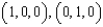 , and
, and 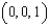 , oriented counterclockwise as viewed from above.
, oriented counterclockwise as viewed from above.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
Use Stokes' Theorem to evaluate 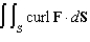 where
where 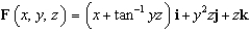 and S is the part of the hemisphere
and S is the part of the hemisphere 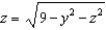 that lies inside the cylinder
that lies inside the cylinder 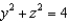 , oriented in the direction of the positive x-axis.
, oriented in the direction of the positive x-axis.
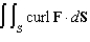 where
where 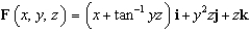 and S is the part of the hemisphere
and S is the part of the hemisphere 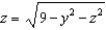 that lies inside the cylinder
that lies inside the cylinder 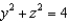 , oriented in the direction of the positive x-axis.
, oriented in the direction of the positive x-axis.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Evaluate the surface integral , where and S is the part of the plane in the first octant with downward orientation.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
G)
H)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
G)
H)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
Evaluate , where and S is the cube bounded by .
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
G)
H)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
G)
H)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
Evaluate the surface integral , where S is that part of the plane that lies above the square with vertices , and .
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
G)
H)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
G)
H)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
Verify that Stokes' Theorem is true for the vector field 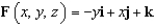 and the cone
and the cone 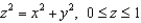 , oriented upward.
, oriented upward.
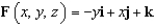 and the cone
and the cone 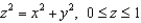 , oriented upward.
, oriented upward.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
Let . Evaluate the surface integral , where S is that part of the plane that lies above the square with vertices , and and has upward orientation.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
G)
H)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
G)
H)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
Evaluate where and S is the part of the surface that lies above the plane and has upward orientation.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
G)
H)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
G)
H)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
Let S be the parametric surface 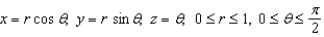 . Use Stokes' Theorem to evaluate
. Use Stokes' Theorem to evaluate 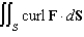 , where
, where 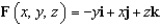 .
.
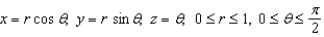 . Use Stokes' Theorem to evaluate
. Use Stokes' Theorem to evaluate 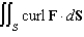 , where
, where 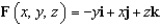 .
.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
Use Stokes' Theorem to evaluate 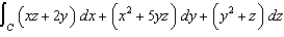 , where C is the curve of intersection of the paraboloid
, where C is the curve of intersection of the paraboloid 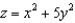 and the cylinder
and the cylinder 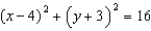 , oriented counterclockwise as viewed from above.
, oriented counterclockwise as viewed from above.
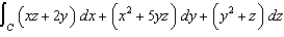 , where C is the curve of intersection of the paraboloid
, where C is the curve of intersection of the paraboloid 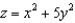 and the cylinder
and the cylinder 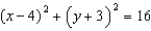 , oriented counterclockwise as viewed from above.
, oriented counterclockwise as viewed from above.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
An upper hemisphere is given by with the density function . Find the mass of the sphere.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
G)
H)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
G)
H)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
Evaluate the surface integral 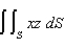 , where S is the triangle with vertices
, where S is the triangle with vertices 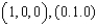 , and
, and 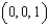
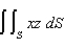 , where S is the triangle with vertices
, where S is the triangle with vertices 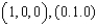 , and
, and 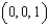

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
Let . Evaluate the surface integral , where S is that part of the plane that lies above the square with vertices , and and has upward orientation.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
G)
H)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
G)
H)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
Evaluate the surface integral , where S is that part of the cylinder that lies above the square with vertices , and .
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
G)
H)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
G)
H)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
Use Stokes' Theorem to evaluate 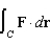 where
where 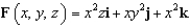 and C is the curve of intersection of the plane
and C is the curve of intersection of the plane 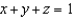 and the cylinder
and the cylinder 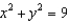 .
.
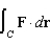 where
where 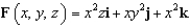 and C is the curve of intersection of the plane
and C is the curve of intersection of the plane 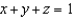 and the cylinder
and the cylinder 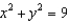 .
.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
Evaluate , where and S is the cube bounded by .
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
G)
H)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
G)
H)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
Evaluate the surface integral , where S is that part of the plane that lies above the square with vertices , and .
A)
B)
C)
D)2
E)
F)
G)
H)
A)
B)
C)
D)2
E)
F)
G)
H)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
Use Stokes' Theorem to evaluate 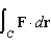 where
where 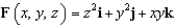 and C is the triangle with vertices
and C is the triangle with vertices 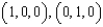 , and
, and 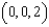
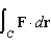 where
where 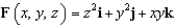 and C is the triangle with vertices
and C is the triangle with vertices 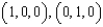 , and
, and 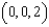

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
A fluid has density 1500 and velocity field 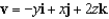 . Find the rate of flow outward through the sphere
. Find the rate of flow outward through the sphere 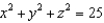 .
.
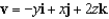 . Find the rate of flow outward through the sphere
. Find the rate of flow outward through the sphere 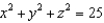 .
.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
Evaluate 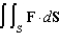 , where
, where 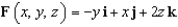 and S is the upper half of the sphere
and S is the upper half of the sphere 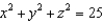 , with upward orientation.
, with upward orientation.
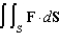 , where
, where 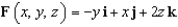 and S is the upper half of the sphere
and S is the upper half of the sphere 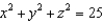 , with upward orientation.
, with upward orientation.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
Evaluate the surface integral 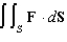 for the vector field
for the vector field 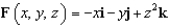 where S is part of the cone
where S is part of the cone 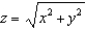 between the planes z = 1 and z = 2 with upward orientation.
between the planes z = 1 and z = 2 with upward orientation.
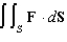 for the vector field
for the vector field 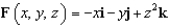 where S is part of the cone
where S is part of the cone 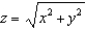 between the planes z = 1 and z = 2 with upward orientation.
between the planes z = 1 and z = 2 with upward orientation.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
Evaluate the flux of the vector field 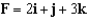 through the plane region with the given orientation as shown below.
through the plane region with the given orientation as shown below. 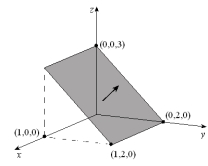
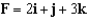 through the plane region with the given orientation as shown below.
through the plane region with the given orientation as shown below. 

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
Evaluate 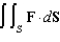 where
where 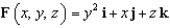 and S is the part of the surface
and S is the part of the surface 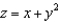 that lies above the rectangle
that lies above the rectangle 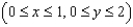 and has upward orientation.
and has upward orientation.
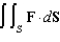 where
where 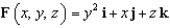 and S is the part of the surface
and S is the part of the surface 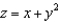 that lies above the rectangle
that lies above the rectangle 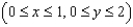 and has upward orientation.
and has upward orientation.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
Evaluate the surface integral 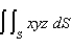 , where S is the part of the sphere
, where S is the part of the sphere 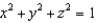 that lies above the cone
that lies above the cone 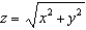 .
.
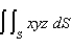 , where S is the part of the sphere
, where S is the part of the sphere 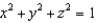 that lies above the cone
that lies above the cone 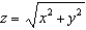 .
.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
Evaluate the surface integral 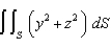 , where S is the part of the paraboloid
, where S is the part of the paraboloid 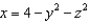 that lies in front of the plane
that lies in front of the plane 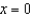 .
.
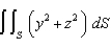 , where S is the part of the paraboloid
, where S is the part of the paraboloid 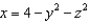 that lies in front of the plane
that lies in front of the plane 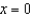 .
.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
Compute the surface integral 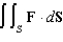 if
if 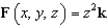 and S is the piece of the sphere
and S is the piece of the sphere 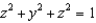 in the second octant
in the second octant 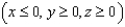 .
.
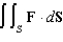 if
if 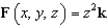 and S is the piece of the sphere
and S is the piece of the sphere 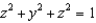 in the second octant
in the second octant 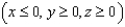 .
.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
Consider the top half of the ellipsoid 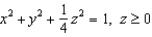 parametrized by
parametrized by 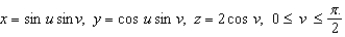 . Find a normal vector N at the point determined by
. Find a normal vector N at the point determined by 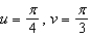 , and determine if it is upward and/or outward.
, and determine if it is upward and/or outward.
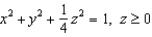 parametrized by
parametrized by 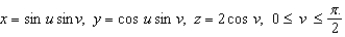 . Find a normal vector N at the point determined by
. Find a normal vector N at the point determined by 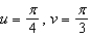 , and determine if it is upward and/or outward.
, and determine if it is upward and/or outward.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
Evaluate the flux of the vector field 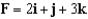 through the plane region with the given orientation as shown below.
through the plane region with the given orientation as shown below. 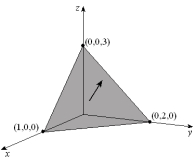
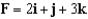 through the plane region with the given orientation as shown below.
through the plane region with the given orientation as shown below. 

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
Evaluate the surface integral 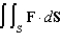 for the vector field
for the vector field 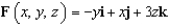 , where S is the hemisphere
, where S is the hemisphere 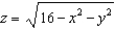 with upward orientation.
with upward orientation.
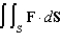 for the vector field
for the vector field 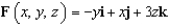 , where S is the hemisphere
, where S is the hemisphere 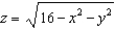 with upward orientation.
with upward orientation.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
Find the flux of the vector field 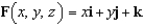 across the paraboloid given by
across the paraboloid given by 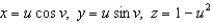 with
with 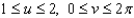 and upward orientation:
and upward orientation:
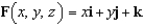 across the paraboloid given by
across the paraboloid given by 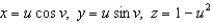 with
with 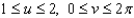 and upward orientation:
and upward orientation:
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
Find the z-coordinate of the centroid of the upper hemisphere with uniform density whose equation is given by 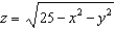 .
.
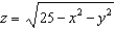 .
.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
Find the mass of the sphere 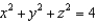 whose density at each point is proportional to its distance to the
whose density at each point is proportional to its distance to the 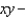 plane.
plane.
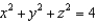 whose density at each point is proportional to its distance to the
whose density at each point is proportional to its distance to the 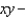 plane.
plane.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
Evaluate 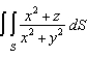 , where S is the part of the surface
, where S is the part of the surface 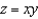 that lies between the cylinders
that lies between the cylinders 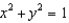 and
and 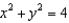 .
.
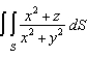 , where S is the part of the surface
, where S is the part of the surface 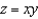 that lies between the cylinders
that lies between the cylinders 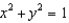 and
and 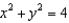 .
.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
Evaluate 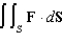 , where
, where 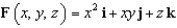 and S is the part of the surface
and S is the part of the surface 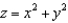 below the plane
below the plane 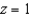 , with upward orientation.
, with upward orientation.
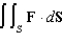 , where
, where 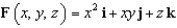 and S is the part of the surface
and S is the part of the surface 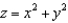 below the plane
below the plane 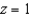 , with upward orientation.
, with upward orientation.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
Evaluate the surface integral 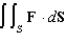 for the vector field
for the vector field 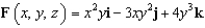 where S is the part of the elliptic paraboloid
where S is the part of the elliptic paraboloid 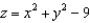 that lies below the square
that lies below the square 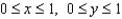 and has downward orientation.
and has downward orientation.
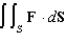 for the vector field
for the vector field 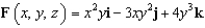 where S is the part of the elliptic paraboloid
where S is the part of the elliptic paraboloid 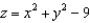 that lies below the square
that lies below the square 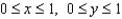 and has downward orientation.
and has downward orientation.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
Let . Find the curl of F.
A) i
B) j
C)
D)
E)
F)
G)
H)
A) i
B) j
C)
D)
E)
F)
G)
H)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
Find the mass of a thin funnel in the shape of a cone 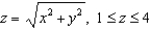 , is its density
, is its density
function is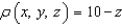 .
.
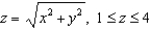 , is its density
, is its densityfunction is
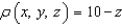 .
.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
Let . Find the curl of F.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
G)
H)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
F)
G)
H)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 240 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








