Deck 1: Basic Concepts in Immunology
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/44
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 1: Basic Concepts in Immunology
1
Most B and T lymphocytes in the circulation appear as small, inactive cells, with little cytoplasm, few cytoplasmic organelles, and nuclei containing condensed inactive chromatin. Yet these cells comprise the adaptive immune response, without which individuals die in infancy. What is the explanation for this apparent dichotomy?
B and T lymphocytes are a heterogeneous population, comprised of cells that each express a unique antigen receptor. As a consequence, only a small number of B and T lymphocytes will respond to any particular pathogenic infection. The vast majority of the circulating cells will never encounter the pathogen that binds to their antigen receptor; hence these cells remain in a naive, inactive state.
2
A common mechanism by which sensor cells in the host detect micro-organisms relies on the production of unique microbial components not found in the host. Propose a strategy by which a clever microbe could evade this type of response.
Sensor cells commonly recognize unique microbial components, such as bacterial lipopolysaccharide or other cell wall constituents. A clever microbe could evade this response by altering its membrane or cell wall components so that they are no longer recognized by the sensor cell receptors.
3
Given the enormous heterogeneity of antigen receptors expressed on the populations of naive B and T lymphocytes, the adaptive immune response relies on a process whereby the rare lymphocyte that binds to the antigen is first induced to proliferate, before it can perform its effector function. For B cells, there is a clever mechanism that ensures that the specificity of the antibody secreted by the plasma cell will recognize the same pathogen that initially stimulated the B cell antigen receptor and induced B cell proliferation. This mechanism is:
A) The naive B cell expresses an array of different B cell antigen receptors, and randomly chooses which specificity of antibody to secrete as a plasma cell.
B) The naive B cell expresses a single specificity of B cell antigen receptor, and then up-regulates the expression of this receptor so it can bind tightly to the pathogen.
C) The plasma cell proliferates after it has finished secreting antibody to generate more plasma cells with specificity for the pathogen.
D) The plasma cell traps secreted antibody molecules in its extracellular matrix and uses these antibodies to bind to the pathogen.
E) The naive B cell expresses a membrane-bound form of the antibody as a receptor, and secretes that same antibody when it differentiates into a plasma cell.
A) The naive B cell expresses an array of different B cell antigen receptors, and randomly chooses which specificity of antibody to secrete as a plasma cell.
B) The naive B cell expresses a single specificity of B cell antigen receptor, and then up-regulates the expression of this receptor so it can bind tightly to the pathogen.
C) The plasma cell proliferates after it has finished secreting antibody to generate more plasma cells with specificity for the pathogen.
D) The plasma cell traps secreted antibody molecules in its extracellular matrix and uses these antibodies to bind to the pathogen.
E) The naive B cell expresses a membrane-bound form of the antibody as a receptor, and secretes that same antibody when it differentiates into a plasma cell.
The naive B cell expresses a membrane-bound form of the antibody as a receptor, and secretes that same antibody when it differentiates into a plasma cell.
4
When macrophages in a tissue encounter bacteria, they release cytokines that induce an inflammatory response. These cytokines act on other immune cells, to recruit them to the site of infection and to enhance their activities. In addition, these cytokines act on the endothelial cells of the blood vessel wall to:
A) Increase their permeability, allowing fluid and proteins to leak into the tissue
B) Solidify the tight junctions to prevent the bacteria from entering the blood
C) Proliferate, allowing the blood vessel to enlarge
D) Up-regulate microbicidal mechanisms, so they can kill bacteria
E) Secrete anti-microbial peptides
A) Increase their permeability, allowing fluid and proteins to leak into the tissue
B) Solidify the tight junctions to prevent the bacteria from entering the blood
C) Proliferate, allowing the blood vessel to enlarge
D) Up-regulate microbicidal mechanisms, so they can kill bacteria
E) Secrete anti-microbial peptides

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
The skin and bodily secretions provide the first line of defense against infection. One response in this category that is common during upper respiratory virus infections is:
A) Production of antibodies
B) Infiltration by white blood cells
C) Mucus production
D) Increased saliva production
E) Fever
A) Production of antibodies
B) Infiltration by white blood cells
C) Mucus production
D) Increased saliva production
E) Fever

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
The antibody protein is often depicted as an uppercase letter Y, with the two variable regions (antigen-binding domains) pointing up, and the stem consisting of the Fc region (constant domain). An analogy has been made between an antibody protein and a guided missile, with one type of antibody domain functioning as the guidance system, and the other type of domain as the 'payload.' Which antibody domain serves as the guidance system, and which as the payload? Explain your answer.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Pathogenic organisms cause damage to the host by a variety of mechanisms, depending on the category of the pathogen and its mode of replication in the host. Give an example of two different types of pathogens that are unlikely to be dealt with by the same mechanism of immune protection.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Innate lymphoid cells and NK cells are effector cells that respond rapidly after encountering a pathogen. Several different subsets of innate lymphoid cells exist, and each is specialized to respond to a category of pathogen (e.g., viruses, extracellular bacteria, helminthic parasites, etc). Innate lymphoid cells reside primarily in tissues such as the lungs, the lining of the gastrointestinal tract, and the skin, because these sites represent the major routes of entry of pathogens into the body.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Some Pattern Recognition Receptors (PRRs) recognize nucleic acids, like RNA or DNA. Since our own cells contain human RNA and DNA, the activation of innate immune pathways by these PRRs must rely on additional criteria to discriminate self from nonself. Additional criteria include everything EXCEPT:
A) The subcellular location of the RNA
B) The presence of adenosine residues in viral RNA
C) The methylation state of the DNA
D) Unique structures found on viral RNA
E) The subcellular location of the DNA
A) The subcellular location of the RNA
B) The presence of adenosine residues in viral RNA
C) The methylation state of the DNA
D) Unique structures found on viral RNA
E) The subcellular location of the DNA

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Our immune system efficiently kills all categories of microbes that attempt to colonize our bodies.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
The clonal selection theory was first proposed in the 1950s, decades before the molecular details of B and T lymphocyte development and lymphocyte antigen recognition responses were elucidated. Nonetheless, Burnet, who proposed this theory, correctly inferred several key aspects of adaptive immune responses. One key postulate that Burnet proposed was that:
A) Cells of the innate immune system are distinct from those of the adaptive immune system.
B) Cells of the adaptive immune system are generated from a pluripotent hematopoietic stem cell that resides in the bone marrow.
C) B and T lymphocytes are closely related cells that have distinct properties from myeloid cells.
D) Circulating antibodies are generated by many different antibody-secreting cells, each of which expresses a single type of antibody on its surface as a receptor.
E) Antibodies binding to pathogens lead to efficient pathogen clearance by phagocytic cells.
A) Cells of the innate immune system are distinct from those of the adaptive immune system.
B) Cells of the adaptive immune system are generated from a pluripotent hematopoietic stem cell that resides in the bone marrow.
C) B and T lymphocytes are closely related cells that have distinct properties from myeloid cells.
D) Circulating antibodies are generated by many different antibody-secreting cells, each of which expresses a single type of antibody on its surface as a receptor.
E) Antibodies binding to pathogens lead to efficient pathogen clearance by phagocytic cells.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
The antigen receptor on a T cell recognizes a degraded fragment of a protein (i.e., a peptide) bound to a specialized cell surface peptide-binding receptor called an MHC molecule. One key aspect of this system is that the peptides displayed on MHC molecules can be derived from intracellular proteins. This mode of antigen recognition is particularly important in allowing the adaptive immune response to detect infections by:
A) Large helminthic parasites in the gastrointestinal tract
B) Intracellular pathogens, such as viruses and some protozoa
C) Extracellular bacteria that colonize the lungs
D) Fungi that form hyphae in the bronchial airways
E) Fungal infections in the skin epithelium
A) Large helminthic parasites in the gastrointestinal tract
B) Intracellular pathogens, such as viruses and some protozoa
C) Extracellular bacteria that colonize the lungs
D) Fungi that form hyphae in the bronchial airways
E) Fungal infections in the skin epithelium

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
A common characteristic of a site of infection, such as a pimple on the skin, is pus. What is responsible for the white color of pus?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Adaptive immune responses are slow to develop, taking days to weeks after exposure to reach their peak. However, these responses are more specific than innate responses, and also generate immunological memory. These latter features, which provide enhanced protection upon re-infection with the same pathogen, are the basis of:
A) Vaccines
B) Antibiotics
C) Systemic shock
D) Complement activation
E) Phagocytosis
A) Vaccines
B) Antibiotics
C) Systemic shock
D) Complement activation
E) Phagocytosis

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
For cells of the innate immune system, each individual cell has multiple pattern recognition receptors, and can recognize many different pathogens. In contrast, cells of the adaptive immune system each express only a single antigen receptor, and have a single specificity for pathogen recognition.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Dendritic cells are phagocytic, but also capable of ingesting large amounts of extracellular fluid and its contents, a process known as macropinocytosis. What specialized function do dendritic cells have in immunity that might account for their need to perform macropinocytosis?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
In the absence of an infection, most granulocytes (neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils) are found circulating in the blood, whereas other subsets of myeloid cells reside in tissues.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
In patients with lymphomas, the cancer cells invade the bone marrow and destroy the environment required for normal hematopoiesis. This leads to bone marrow failure, which disrupts the production of hematopoietic cell lineages. All of the following cell types would be affected by this EXCEPT:
A) Red blood cells
B) Macrophages
C) Lymphocytes
D) Endothelial cells
E) Granulocytes
A) Red blood cells
B) Macrophages
C) Lymphocytes
D) Endothelial cells
E) Granulocytes

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
In the 1970s, immunologists discovered the genetic mechanism allowing a population of B cells to produce an enormous diversity of different antibodies. At the time, this discovery shocked the field of biology, as it called into question the ‘immutable’ nature of DNA, which was known to be the genetic material transmitted from generation to generation during the propagation of the species. Briefly describe this startling mechanism.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Unlike B lymphocytes, T lymphocytes do not generate a secreted form of their antigen receptor after they are activated and proliferate. This is because the effector functions of T cells are restricted to:
A) Responses important in protozoan infections, but not other types of infections
B) Interactions with large helminthic parasites, which cannot be phagocytosed
C) Interactions with other cells, such as virus-infected cells or other immune cells
D) Responses important in mucosal surfaces (e.g., the lung), where antibodies cannot go
E) Stimulating B cells and not any other types of cells
A) Responses important in protozoan infections, but not other types of infections
B) Interactions with large helminthic parasites, which cannot be phagocytosed
C) Interactions with other cells, such as virus-infected cells or other immune cells
D) Responses important in mucosal surfaces (e.g., the lung), where antibodies cannot go
E) Stimulating B cells and not any other types of cells

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Inherited immunodeficiency diseases result from a single gene defect in one component of the immune system. By identifying the class of microbial pathogens a given immunodeficient individual becomes susceptible to, studies of these diseases indicate:
A) Which type of antibiotics each patient should be given
B) The essential immune mechanism required for resistance to each category of pathogen
C) Whether the disease is a genetically inherited or an acquired form of immunodeficiency
D) Whether the immunodeficiency disease is likely to be transmitted to another individual
E) Whether the disease is likely to be life-threatening or not
A) Which type of antibiotics each patient should be given
B) The essential immune mechanism required for resistance to each category of pathogen
C) Whether the disease is a genetically inherited or an acquired form of immunodeficiency
D) Whether the immunodeficiency disease is likely to be transmitted to another individual
E) Whether the disease is likely to be life-threatening or not

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
The spleen is a secondary lymphoid organ that performs several functions. In addition to its role as a site for initiating adaptive immune responses, the spleen is important in removing dead or damaged red blood cells from the circulation. Its immune function is important because blood-borne pathogens will not be transported to draining lymph nodes via the lymph fluid.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
TH1, TH2, TH17, and T follicular helper (TFH) cells represent four different subsets of CD4 effector cells. Each of these subsets produces a distinct set of cytokines when stimulated, that in turn, act to mobilize distinct immune effector mechanisms. While TH1, TH2, and TH17 cells recruit and activate innate immune cells, TFH cells act to amplify the adaptive immune response.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
One surprising aspect of the immune system is that individuals make responses to human tissues from a different individual, causing serious problems for organ and tissue transplantation. The basis for this immune response is:
A) The extensive polymorphism of MHC genes in the human population
B) The fact that transplanted tissues often carry infectious microbes into the recipient
C) The fact that individuals may differ in their blood group antigens (i.e., their blood type)
D) The presence of many antigen-presenting-cells in the transplanted tissue
E) The presence of many B and T lymphocytes in the transplanted tissue
A) The extensive polymorphism of MHC genes in the human population
B) The fact that transplanted tissues often carry infectious microbes into the recipient
C) The fact that individuals may differ in their blood group antigens (i.e., their blood type)
D) The presence of many antigen-presenting-cells in the transplanted tissue
E) The presence of many B and T lymphocytes in the transplanted tissue

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Individuals with defects in T cell development have a severe immunodeficiency disease called SCID (severe combined immunodeficiency disease). In these individuals, the absence of all T cells causes defects in both cell-mediated (T cell-based) and humoral (antibody-based) immune responses. The defect in antibody responses in SCID patients is due to:
A) The important role of T cells in regulating B cell development in the bone marrow
B) The inter-dependence of T cells and B cells for the normal development of secondary lymphoid organs.
C) The absence of phagocytic cells needed for antibody-dependent pathogen clearance in SCID patients
D) The poor survival of B cells in patients with defects in their T cells
E) The important role of T follicular helper cells in generating protective antibody responses
A) The important role of T cells in regulating B cell development in the bone marrow
B) The inter-dependence of T cells and B cells for the normal development of secondary lymphoid organs.
C) The absence of phagocytic cells needed for antibody-dependent pathogen clearance in SCID patients
D) The poor survival of B cells in patients with defects in their T cells
E) The important role of T follicular helper cells in generating protective antibody responses

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
The immune system evolved to protect us against infections from pathogenic microorganisms. However, immune responses can also cause, rather than prevent disease. Give two examples of situations in which an immune response causes a disease, whereas the absence of a response has no consequences.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
The effector activities important in eliminating infectious organisms from our bodies can be categorized into four different groups: cytotoxicity, intracellular immunity, mucosal and barrier immunity, and extracellular immunity. Briefly describe why the immune system requires four different effector modules for maximum protection.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Secondary (or peripheral) lymphoid organs are sites for initiation of adaptive immune responses. Given the rarity of lymphocytes specific for any given antigen and the vast amount of body tissue that must be protected, the system of secondary lymphoid tissues is efficient because:
A) It concentrates antigens in centralized locations for rare lymphocytes to encounter
B) It provides the optimal environment for the rapid proliferation of lymphocytes
C) It traps the pathogens and antigens in a contained environment so they cannot spread to other tissues in the body
D) It helps the innate immune cells eliminate the infection by using lymphatic fluid to drain pathogens from the infected tissue
E) It filters the lymph fluid and removes pathogenic organisms before they can enter the bloodstream
A) It concentrates antigens in centralized locations for rare lymphocytes to encounter
B) It provides the optimal environment for the rapid proliferation of lymphocytes
C) It traps the pathogens and antigens in a contained environment so they cannot spread to other tissues in the body
D) It helps the innate immune cells eliminate the infection by using lymphatic fluid to drain pathogens from the infected tissue
E) It filters the lymph fluid and removes pathogenic organisms before they can enter the bloodstream

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Lymph nodes function as meeting points between antigen-bearing dendritic cells arriving from the tissue and recirculating B and T lymphocytes. Whereas the dendritic cells coming from the tissue enter the lymph node via the afferent lymphatic vessels, the recirculating lymphocytes enter the lymph node:
A) Also from the lymph fluid draining the tissue
B) Directly from their primary lymphoid organ where they develop
C) From the blood by crossing the high endothelial venules
D) By being trapped in the lymphoid follicle by resident macrophages
E) By being carried there by dendritic cells
A) Also from the lymph fluid draining the tissue
B) Directly from their primary lymphoid organ where they develop
C) From the blood by crossing the high endothelial venules
D) By being trapped in the lymphoid follicle by resident macrophages
E) By being carried there by dendritic cells

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
The pattern recognition receptors on cells of the innate immune system are genetically encoded, meaning that their sequences and specificities are determined prior to the development of the individual. In contrast, the antigen receptors of B and T lymphocytes arise from a random rearrangement process that occurs differently in each lymphocyte as it develops. One potential problem entailed by the random process that generates lymphocyte antigen receptors is the possibility that:
A) Some antigen receptors might recognize the individuals on cells or antigens
B) Many lymphocytes might generate antigen receptors that don't recognize anything
C) Many lymphocytes might generate antigen receptors that recognize multiple different pathogens
D) Some antigen receptors might recognize foreign tissues and lead to graft rejection during organ transplantation
E) Some lymphocytes might not generate functional antigen receptor proteins
A) Some antigen receptors might recognize the individuals on cells or antigens
B) Many lymphocytes might generate antigen receptors that don't recognize anything
C) Many lymphocytes might generate antigen receptors that recognize multiple different pathogens
D) Some antigen receptors might recognize foreign tissues and lead to graft rejection during organ transplantation
E) Some lymphocytes might not generate functional antigen receptor proteins

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
When complement proteins are covalently deposited onto the surface of a bacterium, this can sometimes lead to direct lysis of the bacterium. However, more commonly, the deposition of complement proteins onto the bacterial surface does not directly harm the bacterium. Instead, these complement proteins aid in bacterial elimination by:
A) Recruiting antibodies to the bacterial surface, leading the antibody-dependent neutralization
B) Providing a mechanism for phagocytes to use their Fc receptors to recognize and ingest the bacterium
C) Cross-linking carbohydrate structures on the bacterial surface, thereby preventing the bacterium from replicating
D) Stimulating B lymphocytes to produce more antibodies against the bacterium
E) Providing a mechanism for phagocytes bearing complement receptors to recognize and ingest the bacterium
A) Recruiting antibodies to the bacterial surface, leading the antibody-dependent neutralization
B) Providing a mechanism for phagocytes to use their Fc receptors to recognize and ingest the bacterium
C) Cross-linking carbohydrate structures on the bacterial surface, thereby preventing the bacterium from replicating
D) Stimulating B lymphocytes to produce more antibodies against the bacterium
E) Providing a mechanism for phagocytes bearing complement receptors to recognize and ingest the bacterium

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
The best evidence supporting the concept of immunological memory is:
A) The increased numbers of antigen receptors expressed by lymphocytes after primary exposure to an antigen
B) The increased levels of cytokines made by lymphocytes after primary exposure to an antigen
C) The increased rapidity and magnitude of the secondary response to the same antigen
D) The increased swelling of lymph nodes during the secondary response to the same antigen
E) The long lifespan of vertebrates, which would be impossible without immunological memory
A) The increased numbers of antigen receptors expressed by lymphocytes after primary exposure to an antigen
B) The increased levels of cytokines made by lymphocytes after primary exposure to an antigen
C) The increased rapidity and magnitude of the secondary response to the same antigen
D) The increased swelling of lymph nodes during the secondary response to the same antigen
E) The long lifespan of vertebrates, which would be impossible without immunological memory

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
The majority of vaccines work by eliciting pathogen-specific antibodies that circulate in our bodies and protect us in the event that we are later exposed to that specific pathogen. For most viruses and bacterial toxins that we are vaccinated against, these pre-existing antibodies are protective because:
A) They neutralize the virus or toxin, preventing it from attaching to and entering our cells.
B) They bind to the virus or toxin and carry it to the liver where it can be degraded.
C) They bind to the virus or toxin and directly induce lysis.
D) They induce mucus production that helps flush the toxin or virus out of the body.
E) They bind to epithelial cells and induce the production of antimicrobial peptides.
A) They neutralize the virus or toxin, preventing it from attaching to and entering our cells.
B) They bind to the virus or toxin and carry it to the liver where it can be degraded.
C) They bind to the virus or toxin and directly induce lysis.
D) They induce mucus production that helps flush the toxin or virus out of the body.
E) They bind to epithelial cells and induce the production of antimicrobial peptides.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
The mucosal tissues of the body have their own unique set of immune structures that function as sites for initiating adaptive immune responses. The necessity for mucosa-associated lymphoid tissues to have unique cell types (M cells) and structures is because:
A) The mucous layer lining mucosal surfaces makes it difficult for normal antigen-presenting cells to function.
B) The epithelial surfaces that line the gut, lungs, and nasal passages prevent antigen-presenting cells from accessing microbes and microbial products.
C) The epithelial cells found in mucosal tissues are distinct from those that provide barrier functions to the skin.
D) Mucosal sites, where most pathogens access the body, are exposed to vast numbers of diverse microbes.
E) Mucosal tissues lack innate sensor cells that can respond to PAMPs and provide short-term innate immune protection.
A) The mucous layer lining mucosal surfaces makes it difficult for normal antigen-presenting cells to function.
B) The epithelial surfaces that line the gut, lungs, and nasal passages prevent antigen-presenting cells from accessing microbes and microbial products.
C) The epithelial cells found in mucosal tissues are distinct from those that provide barrier functions to the skin.
D) Mucosal sites, where most pathogens access the body, are exposed to vast numbers of diverse microbes.
E) Mucosal tissues lack innate sensor cells that can respond to PAMPs and provide short-term innate immune protection.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
T cells expressing the co-receptor CD8 are generally cytotoxic cells, with an important function in eliminating virus infections that can occur in many different cell types and tissues. In contrast, CD4 T cells directly interact with a very restricted set of cells, such as dendritic cells, macrophages, and B cells. Describe one important mechanism that accounts for this division of labor between CD8 and CD4 T cells.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
Several subsets of innate lymphoid cells (ILCs) have been identified that share their patterns of cytokine production with the known subsets of T cells. The combined activity of related ILC and T cell subsets is effective in eradicating pathogenic infections because:
A) ILCs cannot kill the pathogen, whereas the antigen-specific T cells can kill the pathogen.
B) The early response of ILCs that reside at the site of infection is followed by the later more robust response of pathogen-specific T cells that migrate to the site of infection.
C) The ILCs activate B cells to induce antibody responses whereas the T cells are able to directly eliminate the pathogen.
D) The ILCs are induced to migrate from the site of infection to the draining lymph nodes where they activate the antigen-specific T cells.
E) The ILCs are activated to secrete antimicrobial compounds which cause them to lyse, releasing RNA and DNA that act on T cells to stimulate T cell cytotoxic activities.
A) ILCs cannot kill the pathogen, whereas the antigen-specific T cells can kill the pathogen.
B) The early response of ILCs that reside at the site of infection is followed by the later more robust response of pathogen-specific T cells that migrate to the site of infection.
C) The ILCs activate B cells to induce antibody responses whereas the T cells are able to directly eliminate the pathogen.
D) The ILCs are induced to migrate from the site of infection to the draining lymph nodes where they activate the antigen-specific T cells.
E) The ILCs are activated to secrete antimicrobial compounds which cause them to lyse, releasing RNA and DNA that act on T cells to stimulate T cell cytotoxic activities.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Naive B and T lymphocytes are small, quiescent cells with little cytoplasm and low metabolic activity. Yet within hours after being activated following encounter with their antigen, these cells enlarge and up-regulate many biosynthetic and metabolic pathways. Approximately one day later, the cells begin dividing, and for several days they are the most rapidly dividing cells in the body, undergoing 2-4 rounds of cell division every day. In order to maintain this phenomenal rate of cell division, lymphoblasts must:
A) Use the large energy stores accumulated by them when they were naive quiescent cells prior to their activation
B) Engulf their neighboring small quiescent lymphocytes in order to take their lipids and proteins for raw material
C) Up-regulate synthesis of mRNA and proteins, some of which encode for glucose transporters and enzymes used for glycolysis
D) Phagocytose extracellular proteins and lipids and degrade them for energy production
E) Macropinocytose metabolites and sugars from the blood for use in glycolysis
A) Use the large energy stores accumulated by them when they were naive quiescent cells prior to their activation
B) Engulf their neighboring small quiescent lymphocytes in order to take their lipids and proteins for raw material
C) Up-regulate synthesis of mRNA and proteins, some of which encode for glucose transporters and enzymes used for glycolysis
D) Phagocytose extracellular proteins and lipids and degrade them for energy production
E) Macropinocytose metabolites and sugars from the blood for use in glycolysis

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
One factor that contributes to the enhanced secondary response to an antigen is the increased number of antigen-specific lymphocytes present after the primary response; these are known as memory cells.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
Dendritic cells, also called 'antigen-presenting-cells' are considered the bridge between the innate and the adaptive immune responses. Describe two key features of dendritic cells that are essential for them to provide this bridging function.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
An infant with recurrent bacterial and fungal infections is suspected to have an immunodeficiency disease. Within two days after exposure to a pathogen, the organisms have proliferated to dangerous levels requiring immediate systemic antibiotic treatment. It is unlikely that this infant has a defect in B or T lymphocyte responses to the infection because:
A) Bacteria and fungi do not require B cell or T cell responses for their clearance.
B) Bacteria and fungi are not efficiently transported to draining lymph nodes to initiate adaptive immune responses.
C) Systemic infections of bacteria and fungi are usually cleared by the spleen.
D) The defective immune response occurs too rapidly following infection to be due to a defect in B or T lymphocytes responses.
E) Adaptive immune responses require dendritic cells to take up and degrade pathogens.
A) Bacteria and fungi do not require B cell or T cell responses for their clearance.
B) Bacteria and fungi are not efficiently transported to draining lymph nodes to initiate adaptive immune responses.
C) Systemic infections of bacteria and fungi are usually cleared by the spleen.
D) The defective immune response occurs too rapidly following infection to be due to a defect in B or T lymphocytes responses.
E) Adaptive immune responses require dendritic cells to take up and degrade pathogens.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
Vaccination against many infectious diseases has provided enormous benefit in developed countries, leading to the virtual eradication of diseases such as polio, measles, smallpox, and others. However, efforts to create long-lasting vaccines against some viral infections, like Influenza and HIV, have not been successful to date because:
A) Viruses like HIV and Influenza undergo antigenic variation to evade previous immune responses.
B) Viruses like HIV and Influenza spread too rapidly in the population for a vaccine to be effective.
C) Viruses like HIV and Influenza have RNA, rather than DNA genomes, and are resistant to current vaccine strategies.
D) Viruses like HIV and Influenza infect via mucosal surfaces, a route that is not well protected by current vaccine strategies.
E) Viruses like HIV and Influenza are transmitted vertically (from mother to child) during fetal development, so babies are infected before they can be vaccinated.
A) Viruses like HIV and Influenza undergo antigenic variation to evade previous immune responses.
B) Viruses like HIV and Influenza spread too rapidly in the population for a vaccine to be effective.
C) Viruses like HIV and Influenza have RNA, rather than DNA genomes, and are resistant to current vaccine strategies.
D) Viruses like HIV and Influenza infect via mucosal surfaces, a route that is not well protected by current vaccine strategies.
E) Viruses like HIV and Influenza are transmitted vertically (from mother to child) during fetal development, so babies are infected before they can be vaccinated.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
The immune system uses several types of effector modules to protect us against different categories of pathogens. Four major types of pathogens are shown in Figure . 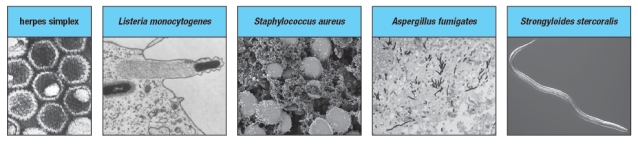
a) Which of these categories might be effectively eliminated by innate immune responses that include antimicrobial peptides and phagocytic cells such as neutrophils and macrophages? Explain your answer.
b) Which of these categories of pathogenic organisms might be most effectively dealt with by antibodies, if the innate response is insufficient for their eradication?
c) Which of these categories of pathogenic organisms would require T lymphocyte responses for their elimination?

a) Which of these categories might be effectively eliminated by innate immune responses that include antimicrobial peptides and phagocytic cells such as neutrophils and macrophages? Explain your answer.
b) Which of these categories of pathogenic organisms might be most effectively dealt with by antibodies, if the innate response is insufficient for their eradication?
c) Which of these categories of pathogenic organisms would require T lymphocyte responses for their elimination?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
One major difference between the innate and adaptive immune responses is in the mechanism by which pathogens are recognized. Innate immune cells use pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) to recognize conserved determinants shared by all the members of a category of pathogens, whereas adaptive immune cells (B and T lymphocytes) have highly specific antigen receptors.
a) Which of the patterns of receptor expression in Figure represent innate immune cells?
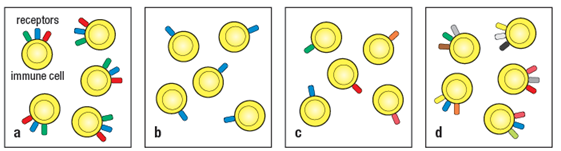
b) Which of the patterns of receptor expression represent B and T lymphocytes?
c) Following an infection, how does the population of innate cells change? Starting with the cartoon representing your answer to part (a), draw the population present at one week post-infection.
d) Following infection, how does the population of B and T lymphocytes change? Starting with the cartoon representing your answer to part (b), draw the population present at one week post-infection.
a) Which of the patterns of receptor expression in Figure represent innate immune cells?

b) Which of the patterns of receptor expression represent B and T lymphocytes?
c) Following an infection, how does the population of innate cells change? Starting with the cartoon representing your answer to part (a), draw the population present at one week post-infection.
d) Following infection, how does the population of B and T lymphocytes change? Starting with the cartoon representing your answer to part (b), draw the population present at one week post-infection.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
For each of the panels A–D in Figure , identify the most likely component(s) of the immune response indicated by the red arrow, and briefly describe your reasoning. 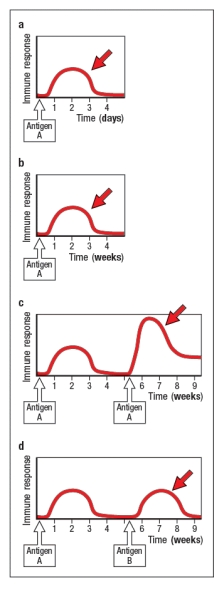


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 44 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








