Deck 7: Cellular Respiration and Fermentation
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/100
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 7: Cellular Respiration and Fermentation
1
Metabolic pathways that release stored energy by breaking down complex molecules are known as
A) catabolic pathways.
B) anabolic pathways.
C) bioenergetic pathways.
D) endergonic pathways.
A) catabolic pathways.
B) anabolic pathways.
C) bioenergetic pathways.
D) endergonic pathways.
A
2
The complete oxidation of glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆) to carbon dioxide and water in aerobic respiration consumes how many molecules of oxygen (O₂)?
A) 1
B) 3
C) 6
D) 12
E) 36
A) 1
B) 3
C) 6
D) 12
E) 36
C
3
The complete reactions of cellular respiration in the presence of oxygen (C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6 O₂ → 6 CO₂ + 6 H₂O + energy) result in which of the following?
A) oxidation of O₂ and reduction of H₂O
B) oxidation of C₆H₁₂O₆ and reduction of O₂
C) reduction of CO₂ and oxidation of O₂
D) reduction of C₆H₁₂O₆ and oxidation of CO₂
A) oxidation of O₂ and reduction of H₂O
B) oxidation of C₆H₁₂O₆ and reduction of O₂
C) reduction of CO₂ and oxidation of O₂
D) reduction of C₆H₁₂O₆ and oxidation of CO₂
B
4
Which of the following statements about NAD+ is true?
A) NAD+ is the source of electrons used in oxidative phosphorylation.
B) NAD+ has more chemical energy than NADH.
C) NAD+ is oxidized by the action of dehydrogenase enzymes.
D) NAD+ is reduced to NADH during glycolysis.
A) NAD+ is the source of electrons used in oxidative phosphorylation.
B) NAD+ has more chemical energy than NADH.
C) NAD+ is oxidized by the action of dehydrogenase enzymes.
D) NAD+ is reduced to NADH during glycolysis.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
The oxygen consumed during cellular respiration is involved directly in which process or event?
A) glycolysis
B) accepting electrons at the end of the electron transport chain
C) the citric acid cycle
D) the oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA
E) the phosphorylation of ADP to form ATP
A) glycolysis
B) accepting electrons at the end of the electron transport chain
C) the citric acid cycle
D) the oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA
E) the phosphorylation of ADP to form ATP

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
The complete oxidation of glucose in aerobic respiration occurs through which of the following sequence of metabolic reactions?
A) glucose → citric acid cycle → glycolysis → pyruvate oxidation → electron transport chain
B) glucose → pyruvate oxidation → glycolysis → electron transport chain → citric acid cycle
C) glucose → glycolysis → pyruvate oxidation → citric acid cycle → electron transport chain
D) glucose → glycolysis → citric acid cycle → pyruvate oxidation → electron transport chain
E) glucose → pyruvate oxidation → citric acid cycle → glycolysis → electron transport chain
A) glucose → citric acid cycle → glycolysis → pyruvate oxidation → electron transport chain
B) glucose → pyruvate oxidation → glycolysis → electron transport chain → citric acid cycle
C) glucose → glycolysis → pyruvate oxidation → citric acid cycle → electron transport chain
D) glucose → glycolysis → citric acid cycle → pyruvate oxidation → electron transport chain
E) glucose → pyruvate oxidation → citric acid cycle → glycolysis → electron transport chain

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
In animal cells, glycolysis occurs in the
A) cytosol.
B) outer mitochondrial membrane.
C) inner mitochondrial membrane.
D) mitochondrial matrix.
E) nucleus.
A) cytosol.
B) outer mitochondrial membrane.
C) inner mitochondrial membrane.
D) mitochondrial matrix.
E) nucleus.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
When an electron is transferred to a more electronegative atom
A) it loses potential energy.
B) it gains potential energy.
C) it gains kinetic energy.
D) it oxidizes the more electronegative atom.
A) it loses potential energy.
B) it gains potential energy.
C) it gains kinetic energy.
D) it oxidizes the more electronegative atom.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
When a glucose molecule loses a hydrogen atom as the result of an oxidation-reduction reaction, the glucose molecule becomes
A) hydrolyzed.
B) hydrogenated.
C) oxidized.
D) reduced.
E) an oxidizing agent.
A) hydrolyzed.
B) hydrogenated.
C) oxidized.
D) reduced.
E) an oxidizing agent.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Which process in eukaryotic cells will proceed normally whether oxygen (O₂) is present or absent?
A) electron transport
B) glycolysis
C) the citric acid cycle
D) oxidative phosphorylation
E) chemiosmosis
A) electron transport
B) glycolysis
C) the citric acid cycle
D) oxidative phosphorylation
E) chemiosmosis

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
As a result of an oxidation-reduction reaction the oxidizing agent
A) gains electrons and gains potential energy.
B) gains electrons and loses potential energy.
C) loses electrons and loses potential energy.
D) loses electrons and gains potential energy.
A) gains electrons and gains potential energy.
B) gains electrons and loses potential energy.
C) loses electrons and loses potential energy.
D) loses electrons and gains potential energy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Which of the following indicates a primary path by which electrons travel downhill energetically during aerobic respiration?
A) glucose → citric acid cycle → ATP → NAD+
B) glucose → NADH → electron transport chain → oxygen
C) glucose → pyruvate → acetyl CoA → ATP → oxygen
D) glucose → glycolysis → electron transport chain → NADH → ATP
E) glucose → glycolysis → citric acid cycle → NADH → ATP
A) glucose → citric acid cycle → ATP → NAD+
B) glucose → NADH → electron transport chain → oxygen
C) glucose → pyruvate → acetyl CoA → ATP → oxygen
D) glucose → glycolysis → electron transport chain → NADH → ATP
E) glucose → glycolysis → citric acid cycle → NADH → ATP

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
The ATP produced in the citric acid cycle is generated by
A) chemiosmosis.
B) electron transport.
C) photophosphorylation.
D) oxidative phosphorylation.
E) substrate-level phosphorylation.
A) chemiosmosis.
B) electron transport.
C) photophosphorylation.
D) oxidative phosphorylation.
E) substrate-level phosphorylation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Substrate-level phosphorylation accounts for approximately what percentage of the ATP formed by the reactions of glycolysis?
A) 0%
B) 2%
C) 10%
D) 38%
E) 100%
A) 0%
B) 2%
C) 10%
D) 38%
E) 100%

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
In bacteria, ATP synthase is located
A) in the mitochondrial inner membrane.
B) in the mitochondrial outer membrane.
C) in the cytoplasm.
D) in the plasma membrane.
E) in the bacterial outer membrane.
A) in the mitochondrial inner membrane.
B) in the mitochondrial outer membrane.
C) in the cytoplasm.
D) in the plasma membrane.
E) in the bacterial outer membrane.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
The ATP produced in glycolysis is generated by
A) chemiosmosis.
B) electron transport.
C) photophosphorylation.
D) oxidative phosphorylation.
E) substrate-level phosphorylation.
A) chemiosmosis.
B) electron transport.
C) photophosphorylation.
D) oxidative phosphorylation.
E) substrate-level phosphorylation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Why are carbohydrates and fats considered high-energy foods?
A) They have a lot of oxygen atoms.
B) They have few nitrogen atoms.
C) They have a large number of electrons associated with hydrogen.
D) They have a lot of carbon atoms bound together by single covalent bonds.
E) They are easily reduced.
A) They have a lot of oxygen atoms.
B) They have few nitrogen atoms.
C) They have a large number of electrons associated with hydrogen.
D) They have a lot of carbon atoms bound together by single covalent bonds.
E) They are easily reduced.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
When a molecule of NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) gains a hydrogen atom (not a proton), the NAD+ molecule becomes
A) dehydrogenated.
B) oxidized.
C) reduced.
D) redoxed.
E) hydrolyzed.
A) dehydrogenated.
B) oxidized.
C) reduced.
D) redoxed.
E) hydrolyzed.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
In an oxidation-reduction reaction, the reducing agent
A) gains electrons and gains potential energy.
B) gains electrons and loses potential energy.
C) loses electrons and loses potential energy.
D) loses electrons and gains potential energy.
A) gains electrons and gains potential energy.
B) gains electrons and loses potential energy.
C) loses electrons and loses potential energy.
D) loses electrons and gains potential energy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
As a result of the transfer of an electron from a less electronegative atom to a more electronegative atom,
A) the more electronegative atom is reduced, and energy is released.
B) the more electronegative atom is reduced, and energy is consumed.
C) the more electronegative atom is oxidized, and energy is consumed.
D) the more electronegative atom is oxidized, and energy is released.
A) the more electronegative atom is reduced, and energy is released.
B) the more electronegative atom is reduced, and energy is consumed.
C) the more electronegative atom is oxidized, and energy is consumed.
D) the more electronegative atom is oxidized, and energy is released.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
In the complete reactions of aerobic respiration, the energy for the majority of ATP synthesis is provided by
A) transfer of electrons from organic molecules to acetyl CoA.
B) high-energy phosphate bonds from organic molecule intermediates in the citric acid cycle.
C) splitting water to produce oxygen.
D) a proton gradient across a membrane.
E) the production of carbon dioxide and oxygen in the electron transport chain.
A) transfer of electrons from organic molecules to acetyl CoA.
B) high-energy phosphate bonds from organic molecule intermediates in the citric acid cycle.
C) splitting water to produce oxygen.
D) a proton gradient across a membrane.
E) the production of carbon dioxide and oxygen in the electron transport chain.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
A molecule that is phosphorylated
A) has been reduced as a result of a redox reaction involving the loss of an inorganic phosphate.
B) has a decreased chemical energy and is less likely to provide energy for cellular work.
C) has been oxidized as a result of a redox reaction involving the gain of an inorganic phosphate.
D) has increased chemical potential energy that may be used to do cellular work.
A) has been reduced as a result of a redox reaction involving the loss of an inorganic phosphate.
B) has a decreased chemical energy and is less likely to provide energy for cellular work.
C) has been oxidized as a result of a redox reaction involving the gain of an inorganic phosphate.
D) has increased chemical potential energy that may be used to do cellular work.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
What fraction of the carbon dioxide exhaled by animals is generated by the oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA, if glucose is the sole energy source?
A) 1/6
B) 1/3
C) 1/2
D) 2/3
E) all of it
A) 1/6
B) 1/3
C) 1/2
D) 2/3
E) all of it

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Glycolysis results in a net production of which of the following from each molecule of glucose?
A) 2 NAD+, 2 pyruvate, and 2 ATP
B) 4 NADH, 2 pyruvate, and 4 ATP
C) 2 NADH, 2 pyruvate, and 2 ATP
D) 6 CO₂, 2 NADH, 2 pyruvate, and 2 ATP
E) 6 CO₂, 2 pyruvate, and 30 ATP
A) 2 NAD+, 2 pyruvate, and 2 ATP
B) 4 NADH, 2 pyruvate, and 4 ATP
C) 2 NADH, 2 pyruvate, and 2 ATP
D) 6 CO₂, 2 NADH, 2 pyruvate, and 2 ATP
E) 6 CO₂, 2 pyruvate, and 30 ATP

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
During aerobic respiration, which of the following directly donates electrons to the electron transport chain at the lowest energy level?
A) NAD+
B) NADH
C) ATP
D) FAD
E) FADH₂
A) NAD+
B) NADH
C) ATP
D) FAD
E) FADH₂

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
During aerobic respiration, which of the following directly donates electrons to the electron transport chain at the highest energy level?
A) NAD+
B) NADH
C) ATP
D) FAD
E) FADH₂
A) NAD+
B) NADH
C) ATP
D) FAD
E) FADH₂

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
In addition to ATP, what are the end products of glycolysis?
A) CO₂ and H₂O
B) CO₂ and pyruvate
C) NADH and pyruvate
D) CO₂ and NADH
E) H₂O, FADH₂, and citrate
A) CO₂ and H₂O
B) CO₂ and pyruvate
C) NADH and pyruvate
D) CO₂ and NADH
E) H₂O, FADH₂, and citrate

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
What fraction of the carbon dioxide exhaled by animals is generated by the reactions of the citric acid cycle, if glucose is the sole energy source?
A) 1/6
B) 1/3
C) 1/2
D) 2/3
E) all of it
A) 1/6
B) 1/3
C) 1/2
D) 2/3
E) all of it

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Substrate-level phosphorylation accounts for approximately what percentage of the ATP formed by the electron transport chain?
A) 0%
B) 2%
C) 10%
D) 38%
E) 100%
A) 0%
B) 2%
C) 10%
D) 38%
E) 100%

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
During glycolysis, when each molecule of glucose is catabolized to two molecules of pyruvate, most of the potential energy contained in glucose is
A) transferred to ADP, forming ATP.
B) released as heat.
C) retained in the two pyruvates.
D) stored in the NADH produced.
A) transferred to ADP, forming ATP.
B) released as heat.
C) retained in the two pyruvates.
D) stored in the NADH produced.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Which kind of metabolic poison would most directly interfere with glycolysis?
A) an agent that reacts with oxygen and depletes its concentration in the cell
B) an agent that binds to pyruvate and inactivates it
C) an agent that closely mimics the structure of glucose but is not metabolized
D) an agent that reacts with NADH and oxidizes it to NAD+
E) an agent that blocks the passage of electrons along the electron transport chain
A) an agent that reacts with oxygen and depletes its concentration in the cell
B) an agent that binds to pyruvate and inactivates it
C) an agent that closely mimics the structure of glucose but is not metabolized
D) an agent that reacts with NADH and oxidizes it to NAD+
E) an agent that blocks the passage of electrons along the electron transport chain

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Starting with one molecule of glucose, the energy-containing products of glycolysis are
A) 2 NAD+, 2 pyruvate, and 2 ATP.
B) 2 NADH, 2 pyruvate, and 2 ATP.
C) 2 FADH₂, 2 pyruvate, and 4 ATP.
D) 6 CO₂, 2 pyruvate, and 2 ATP.
E) 6 CO₂, 2 pyruvate, and 30 ATP.
A) 2 NAD+, 2 pyruvate, and 2 ATP.
B) 2 NADH, 2 pyruvate, and 2 ATP.
C) 2 FADH₂, 2 pyruvate, and 4 ATP.
D) 6 CO₂, 2 pyruvate, and 2 ATP.
E) 6 CO₂, 2 pyruvate, and 30 ATP.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
Why is glycolysis described as having an energy investment phase and an energy payoff phase?
A) Early steps consume energy from ATP and NADH, and later steps store an equal amount of energy in ATP and NAD+.
B) Early steps consume energy from ATP and NADH, and later steps store an increased amount of energy in ATP and NADH.
C) Early steps consume energy from ATP and NADH and later steps store an increased amount of energy in ATP.
D) Early steps consume energy from ATP, and later steps store an increased amount of energy in ATP and NADH.
E) Early steps consume energy from NADH, and later steps store an increased amount of energy in ATP and NADH.
A) Early steps consume energy from ATP and NADH, and later steps store an equal amount of energy in ATP and NAD+.
B) Early steps consume energy from ATP and NADH, and later steps store an increased amount of energy in ATP and NADH.
C) Early steps consume energy from ATP and NADH and later steps store an increased amount of energy in ATP.
D) Early steps consume energy from ATP, and later steps store an increased amount of energy in ATP and NADH.
E) Early steps consume energy from NADH, and later steps store an increased amount of energy in ATP and NADH.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
For each molecule of glucose consumed in glycolysis, there is a net consumption of which of the following?
A) 2 NAD+, 2 pyruvate, and 2 ATP
B) 4 NAD+, 2 pyruvate, and 4 ADP
C) 2 NAD+ and 4 ADP
D) 2 NAD+ and 2 ADP
E) 2 NADH and 2 ADP
A) 2 NAD+, 2 pyruvate, and 2 ATP
B) 4 NAD+, 2 pyruvate, and 4 ADP
C) 2 NAD+ and 4 ADP
D) 2 NAD+ and 2 ADP
E) 2 NADH and 2 ADP

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
How many carbon atoms are fed into the citric acid cycle as a result of the oxidation of one molecule of pyruvate?
A) 2
B) 4
C) 6
D) 8
E) 10
A) 2
B) 4
C) 6
D) 8
E) 10

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
The free energy for the oxidation of glucose to CO₂ and water is -686 kcal/mol, and the free energy for the reduction of NAD+ to NADH is +53 kcal/mol. Why are only two molecules of NADH formed during glycolysis when it appears that as many as a dozen could be formed?
A) Most of the free energy available from the oxidation of glucose is used in the production of ATP in glycolysis.
B) Glycolysis is a very inefficient reaction, with much of the energy of glucose released as heat.
C) Most of the free energy available from the oxidation of glucose remains in pyruvate, one of the products of glycolysis.
D) Glycolysis consists of many enzyme-catalyzed reactions, each of which extracts a small amount of energy from the glucose molecule.
A) Most of the free energy available from the oxidation of glucose is used in the production of ATP in glycolysis.
B) Glycolysis is a very inefficient reaction, with much of the energy of glucose released as heat.
C) Most of the free energy available from the oxidation of glucose remains in pyruvate, one of the products of glycolysis.
D) Glycolysis consists of many enzyme-catalyzed reactions, each of which extracts a small amount of energy from the glucose molecule.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Carbon dioxide (CO₂) is released during which of the following stages of cellular respiration?
A) glycolysis and the oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA
B) oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA and the citric acid cycle
C) the citric acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation
D) glycolysis and the citric acid cycle
A) glycolysis and the oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA
B) oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA and the citric acid cycle
C) the citric acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation
D) glycolysis and the citric acid cycle

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
Where are the proteins of the electron transport chain located?
A) cytosol
B) outer mitochondrial membrane
C) inner mitochondrial membrane
D) mitochondrial intermembrane space
E) mitochondrial matrix
A) cytosol
B) outer mitochondrial membrane
C) inner mitochondrial membrane
D) mitochondrial intermembrane space
E) mitochondrial matrix

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
In glycolysis, for each molecule of glucose oxidized to pyruvate,
A) two molecules of ATP are used and two molecules of ATP are produced.
B) two molecules of ATP are used and four molecules of ATP are produced.
C) four molecules of ATP are used and two molecules of ATP are produced.
D) two molecules of ATP are used and six molecules of ATP are produced.
A) two molecules of ATP are used and two molecules of ATP are produced.
B) two molecules of ATP are used and four molecules of ATP are produced.
C) four molecules of ATP are used and two molecules of ATP are produced.
D) two molecules of ATP are used and six molecules of ATP are produced.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
The primary role of oxygen in cellular respiration is to
A) donate high energy electrons to the electron transport chain.
B) serve as an acceptor for released carbon, forming CO₂.
C) serve as an acceptor for electrons and hydrogen, forming water.
D) combine with acetyl CoA, forming pyruvate.
A) donate high energy electrons to the electron transport chain.
B) serve as an acceptor for released carbon, forming CO₂.
C) serve as an acceptor for electrons and hydrogen, forming water.
D) combine with acetyl CoA, forming pyruvate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
The synthesis of ATP by oxidative phosphorylation, using the energy released by movement of protons across the membrane down their electrochemical gradient, is an example of
A) active transport.
B) an endergonic reaction coupled to an exergonic reaction.
C) a redox reaction.
D) allosteric regulation.
A) active transport.
B) an endergonic reaction coupled to an exergonic reaction.
C) a redox reaction.
D) allosteric regulation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
Approximately how many molecules of ATP are produced by substrate-level phosphorylation during the complete oxidation of a molecule of glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆) in aerobic cellular respiration?
A) 2
B) 4
C) 8
D) 30-32
A) 2
B) 4
C) 8
D) 30-32

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
The direct energy source that drives ATP synthesis during respiratory oxidative phosphorylation in eukaryotic cells is
A) oxidation of glucose to CO₂ and water.
B) the thermodynamically favorable flow of electrons from NADH to the mitochondrial electron transport carriers.
C) the final transfer of electrons to oxygen.
D) the proton-motive force across the inner mitochondrial membrane.
E) the thermodynamically favorable transfer of phosphate from glycolysis and the citric acid cycle intermediate molecules of ADP.
A) oxidation of glucose to CO₂ and water.
B) the thermodynamically favorable flow of electrons from NADH to the mitochondrial electron transport carriers.
C) the final transfer of electrons to oxygen.
D) the proton-motive force across the inner mitochondrial membrane.
E) the thermodynamically favorable transfer of phosphate from glycolysis and the citric acid cycle intermediate molecules of ADP.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
Approximately how many molecules of ATP are produced from the complete oxidation of two molecules of glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆) in aerobic cellular respiration?
A) 2
B) 4
C) 15
D) 30-32
E) 60-64
A) 2
B) 4
C) 15
D) 30-32
E) 60-64

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
In vertebrate animals, brown fat tissue's color is derived from abundant blood vessels and capillaries. White fat tissue, on the other hand, is specialized for fat storage and contains relatively few blood vessels or capillaries. Brown fat cells have a specialized protein that allows protons to diffuse across the inner mitochondrial membrane. Which of the following might be the function of the brown fat tissue?
A) to increase the rate of oxidative phosphorylation from its few mitochondria
B) to increase the metabolic rate when it is especially hot
C) to increase the rate of ATP production
D) to regulate temperature by converting most of the energy from NADH oxidation to heat
A) to increase the rate of oxidative phosphorylation from its few mitochondria
B) to increase the metabolic rate when it is especially hot
C) to increase the rate of ATP production
D) to regulate temperature by converting most of the energy from NADH oxidation to heat

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
The energy used to pump hydrogen ions from the mitochondrial matrix across the inner membrane and into the intermembrane space is derived from
A) ATP hydrolysis.
B) redox reactions in the electron transport chain.
C) decreasing the pH in the mitochondrial matrix.
D) splitting water to form oxygen and protons.
A) ATP hydrolysis.
B) redox reactions in the electron transport chain.
C) decreasing the pH in the mitochondrial matrix.
D) splitting water to form oxygen and protons.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
What carbon sources can yeast cells metabolize to make ATP from ADP under anaerobic conditions?
A) glucose
B) ethanol
C) pyruvate
D) lactic acid
A) glucose
B) ethanol
C) pyruvate
D) lactic acid

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
In liver cells, the inner mitochondrial membranes are about five times the area of the outer mitochondrial membranes. What purpose must this serve?
A) It increases the surface area for glycolysis.
B) It increases the surface area for the citric acid cycle.
C) It increases the surface area for oxidative phosphorylation.
D) It increases the surface area for substrate-level phosphorylation.
A) It increases the surface area for glycolysis.
B) It increases the surface area for the citric acid cycle.
C) It increases the surface area for oxidative phosphorylation.
D) It increases the surface area for substrate-level phosphorylation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
What is the proton-motive force?
A) the force required to remove an electron from hydrogen
B) the force provided by a transmembrane hydrogen ion gradient
C) the force that moves hydrogen into the intermembrane space
D) the force that moves hydrogen into the mitochondrion
E) the force that moves hydrogen to NAD+
A) the force required to remove an electron from hydrogen
B) the force provided by a transmembrane hydrogen ion gradient
C) the force that moves hydrogen into the intermembrane space
D) the force that moves hydrogen into the mitochondrion
E) the force that moves hydrogen to NAD+

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
When hydrogen ions are pumped from the mitochondrial matrix across the inner membrane and into the intermembrane space, the result is
A) the formation of ATP.
B) the reduction of NAD+.
C) a decrease in the pH of the mitochondrial matrix.
D) the creation of a proton-motive force.
A) the formation of ATP.
B) the reduction of NAD+.
C) a decrease in the pH of the mitochondrial matrix.
D) the creation of a proton-motive force.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
In a mitochondrion, if the matrix ATP concentration is high and the intermembrane space proton concentration is too low to generate sufficient proton-motive force, then
A) ATP synthase will increase the rate of ATP synthesis.
B) ATP synthase will synthesize ATP and pump protons into the intermembrane space.
C) ATP synthase will hydrolyze ATP and pump protons into the intermembrane space.
D) ATP synthase will hydrolyze ATP and pump protons into the matrix.
E) ATP synthase will synthesize ATP and pump protons into the matrix.
A) ATP synthase will increase the rate of ATP synthesis.
B) ATP synthase will synthesize ATP and pump protons into the intermembrane space.
C) ATP synthase will hydrolyze ATP and pump protons into the intermembrane space.
D) ATP synthase will hydrolyze ATP and pump protons into the matrix.
E) ATP synthase will synthesize ATP and pump protons into the matrix.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
In chemiosmosis, what is the most direct source of energy that is used to convert ADP + ℗i to ATP?
A) energy released as electrons flow through the electron transport system
B) energy released from substrate-level phosphorylation
C) energy released from dehydration synthesis reactions
D) energy released from movement of protons down their electrochemical gradient through ATP synthase
A) energy released as electrons flow through the electron transport system
B) energy released from substrate-level phosphorylation
C) energy released from dehydration synthesis reactions
D) energy released from movement of protons down their electrochemical gradient through ATP synthase

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
Energy released by the electron transport chain is used to pump H+ into which location in eukaryotic cells?
A) cytosol
B) outer mitochondrial membrane
C) inner mitochondrial membrane
D) mitochondrial intermembrane space
E) mitochondrial matrix
A) cytosol
B) outer mitochondrial membrane
C) inner mitochondrial membrane
D) mitochondrial intermembrane space
E) mitochondrial matrix

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
Brown fat cells produce a protein called thermogenin in their mitochondrial inner membrane. Thermogenin is a channel for facilitated transport of protons across the membrane. What will occur in the brown fat cells when they produce thermogenin?
A) ATP synthesis and heat generation will both increase.
B) ATP synthesis will increase, and heat generation will decrease.
C) ATP synthesis will decrease, and heat generation will increase.
D) ATP synthesis and heat generation will both decrease.
A) ATP synthesis and heat generation will both increase.
B) ATP synthesis will increase, and heat generation will decrease.
C) ATP synthesis will decrease, and heat generation will increase.
D) ATP synthesis and heat generation will both decrease.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
Inside an active mitochondrion, most electrons follow which pathway?
A) NADH → oxidative phosphorylation → ATP → oxygen
B) citric acid cycle → FADH₂ → electron transport chain → ATP
C) electron transport chain → citric acid cycle → ATP → oxygen
D) citric acid cycle → ATP → NADH → oxygen
E) citric acid cycle → NADH → electron transport chain → oxygen
A) NADH → oxidative phosphorylation → ATP → oxygen
B) citric acid cycle → FADH₂ → electron transport chain → ATP
C) electron transport chain → citric acid cycle → ATP → oxygen
D) citric acid cycle → ATP → NADH → oxygen
E) citric acid cycle → NADH → electron transport chain → oxygen

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
Chemiosmosis is used to synthesize ATP in which of the following?
A) only in mitochondria in animal cells
B) only in bacteria that generate proton gradients across their plasma membranes
C) only in mitochondria and chloroplasts
D) only in mitochondria and bacteria that generate proton gradients across their plasma membranes
E) in mitochondria, chloroplasts, and bacteria that generate proton gradients across their plasma membranes
A) only in mitochondria in animal cells
B) only in bacteria that generate proton gradients across their plasma membranes
C) only in mitochondria and chloroplasts
D) only in mitochondria and bacteria that generate proton gradients across their plasma membranes
E) in mitochondria, chloroplasts, and bacteria that generate proton gradients across their plasma membranes

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
Where in mitochondria is the enzyme ATP synthase localized?
A) mitochondrial matrix
B) electron transport chain
C) inner membrane
D) outer membrane
A) mitochondrial matrix
B) electron transport chain
C) inner membrane
D) outer membrane

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
Which of the following produces the most ATP when glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆) is completely oxidized to carbon dioxide (CO₂) and water?
A) glycolysis
B) fermentation
C) oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA
D) citric acid cycle
E) oxidative phosphorylation (chemiosmosis)
A) glycolysis
B) fermentation
C) oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA
D) citric acid cycle
E) oxidative phosphorylation (chemiosmosis)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
If a cell is able to synthesize 30 ATP molecules for each molecule of glucose completely oxidized to carbon dioxide and water, approximately how many ATP molecules can the cell synthesize for each molecule of pyruvate completely oxidized to carbon dioxide and water?
A) 2
B) 6
C) 14
D) 28
E) 60
A) 2
B) 6
C) 14
D) 28
E) 60

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
What is the source of the oxygen used to form water in the complete reactions of cellular respiration?
A) carbon dioxide (CO₂)
B) glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆)
C) pyruvate (C₃H₃O₃-)
D) molecular oxygen (O₂)
A) carbon dioxide (CO₂)
B) glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆)
C) pyruvate (C₃H₃O₃-)
D) molecular oxygen (O₂)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
One primary function of both alcohol fermentation and lactic acid fermentation is to
A) reduce NAD+ to NADH.
B) reduce FAD+ to FADH₂.
C) oxidize NADH to NAD+.
D) reduce FADH₂ to FAD+.
A) reduce NAD+ to NADH.
B) reduce FAD+ to FADH₂.
C) oxidize NADH to NAD+.
D) reduce FADH₂ to FAD+.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
Why is glycolysis considered to be one of the first metabolic pathways to have evolved?
A) It produces much less ATP than does oxidative phosphorylation.
B) It does not involve organelles or specialized structures, does not require oxygen, and is present in most organisms.
C) It is found in prokaryotic cells but not in eukaryotic cells.
D) It relies on chemiosmosis, which is a metabolic mechanism present only in prokaryotic cells.
A) It produces much less ATP than does oxidative phosphorylation.
B) It does not involve organelles or specialized structures, does not require oxygen, and is present in most organisms.
C) It is found in prokaryotic cells but not in eukaryotic cells.
D) It relies on chemiosmosis, which is a metabolic mechanism present only in prokaryotic cells.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
Which of the following occur(s) in the cytosol of a eukaryotic cell?
A) glycolysis and fermentation
B) fermentation and chemiosmosis
C) oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA
D) citric acid cycle
E) oxidative phosphorylation
A) glycolysis and fermentation
B) fermentation and chemiosmosis
C) oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA
D) citric acid cycle
E) oxidative phosphorylation

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
Yeast cells grown anaerobically can obtain energy by fermentation, which results in the production of
A) ATP, NADH, and pyruvate.
B) ATP and lactate.
C) ATP, CO₂, and lactate.
D) ATP, CO₂, and ethanol.
E) ATP, CO₂, and acetyl CoA.
A) ATP, NADH, and pyruvate.
B) ATP and lactate.
C) ATP, CO₂, and lactate.
D) ATP, CO₂, and ethanol.
E) ATP, CO₂, and acetyl CoA.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
In alcohol fermentation, NAD+ is regenerated from NADH by
A) oxidation of ethanol to acetaldehyde.
B) oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA.
C) reduction of pyruvate to lactate.
D) reduction of acetaldehyde to ethanol.
E) reduction of acetyl CoA to ethanol.
A) oxidation of ethanol to acetaldehyde.
B) oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA.
C) reduction of pyruvate to lactate.
D) reduction of acetaldehyde to ethanol.
E) reduction of acetyl CoA to ethanol.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
Yeast cells with defective mitochondria are incapable of cellular respiration. These cells will be able to grow by catabolizing which of the following carbon sources for energy?
A) glucose
B) proteins
C) fatty acids
D) pyruvate
A) glucose
B) proteins
C) fatty acids
D) pyruvate

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
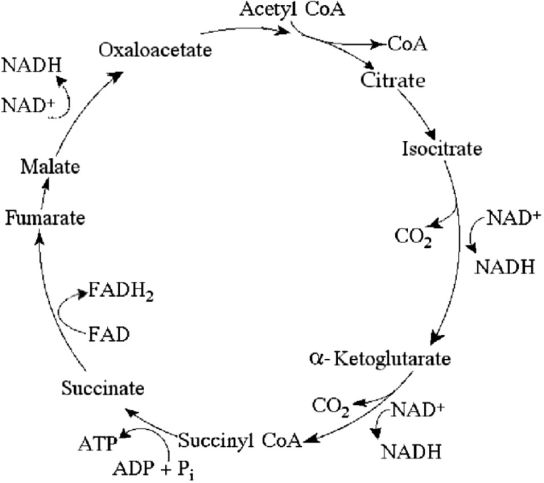 Figure 7.1
Figure 7.1Starting with one molecule of isocitrate and ending with fumarate, how many ATP molecules can be made through substrate-level phosphorylation (see Figure 7.1)?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 11
D) 12
E) 24

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
Which catabolic processes may have been used by cells on ancient Earth before free oxygen became available?
A) only glycolysis and fermentation
B) only glycolysis and the citric acid cycle
C) only glycolysis and pyruvate oxidation
D) only oxidative phosphorylation, using an electron acceptor other than oxygen
E) glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation, using an electron acceptor other than oxygen
A) only glycolysis and fermentation
B) only glycolysis and the citric acid cycle
C) only glycolysis and pyruvate oxidation
D) only oxidative phosphorylation, using an electron acceptor other than oxygen
E) glycolysis, pyruvate oxidation, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation, using an electron acceptor other than oxygen

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
Which of the following occur(s) in mitochondria?
A) glycolysis and fermentation
B) fermentation and chemiosmosis
C) glycolysis and oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA
D) oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA and the citric acid cycle
E) fermentation and oxidative phosphorylation
A) glycolysis and fermentation
B) fermentation and chemiosmosis
C) glycolysis and oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA
D) oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA and the citric acid cycle
E) fermentation and oxidative phosphorylation

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
What is the purpose of beta oxidation in respiration?
A) oxidation of glucose
B) oxidation of pyruvate
C) oxidation of proteins
D) oxidation of fatty acids
A) oxidation of glucose
B) oxidation of pyruvate
C) oxidation of proteins
D) oxidation of fatty acids

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
Which metabolic pathway requires a proton gradient?
A) the oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA
B) the citric acid cycle
C) oxidative phosphorylation
D) glycolysis
E) fermentation
A) the oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA
B) the citric acid cycle
C) oxidative phosphorylation
D) glycolysis
E) fermentation

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
Which one of the following is formed by the removal of a carbon (as CO₂) from a molecule of pyruvate?
A) lactate
B) glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
C) oxaloacetate
D) acetyl CoA
E) citrate
A) lactate
B) glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
C) oxaloacetate
D) acetyl CoA
E) citrate

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
During intense exercise, as skeletal muscle cells switch to fermentation, the human body will increase its catabolism of
A) fats only.
B) carbohydrates only.
C) proteins only.
D) fats, carbohydrates, and proteins.
E) fats and proteins only.
A) fats only.
B) carbohydrates only.
C) proteins only.
D) fats, carbohydrates, and proteins.
E) fats and proteins only.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
Which metabolic pathway generates a proton gradient?
A) the oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA
B) the citric acid cycle
C) chemiosmosis
D) the electron transport chain
E) glycolysis
A) the oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA
B) the citric acid cycle
C) chemiosmosis
D) the electron transport chain
E) glycolysis

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
Which statement best supports the hypothesis that glycolysis is an ancient metabolic pathway that originated before the last universal common ancestor of life on Earth?
A) Glycolysis is widespread and is found in the domains Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya.
B) Glycolysis neither uses nor requires O₂.
C) Glycolysis is found in all eukaryotic cells.
D) The enzymes of glycolysis are found in the cytosol rather than in a membrane-enclosed organelle.
E) Ancient prokaryotic cells existed long before oxygen was present in Earth's atmosphere.
A) Glycolysis is widespread and is found in the domains Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya.
B) Glycolysis neither uses nor requires O₂.
C) Glycolysis is found in all eukaryotic cells.
D) The enzymes of glycolysis are found in the cytosol rather than in a membrane-enclosed organelle.
E) Ancient prokaryotic cells existed long before oxygen was present in Earth's atmosphere.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
When an individual is exercising heavily and the muscle becomes oxygen-deprived, muscle cells convert pyruvate to lactate. What happens to the lactate in skeletal muscle cells?
A) It is reduced and converted back to pyruvate in muscle cells.
B) It is oxidized to CO₂ and water.
C) It is taken to the liver and converted back to pyruvate.
D) It oxidizes FADH₂ to FAD+.
E) It is converted to alcohol.
A) It is reduced and converted back to pyruvate in muscle cells.
B) It is oxidized to CO₂ and water.
C) It is taken to the liver and converted back to pyruvate.
D) It oxidizes FADH₂ to FAD+.
E) It is converted to alcohol.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
Which metabolic pathway is common to both cellular respiration and fermentation?
A) the oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA
B) the citric acid cycle
C) oxidative phosphorylation
D) glycolysis
E) chemiosmosis
A) the oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA
B) the citric acid cycle
C) oxidative phosphorylation
D) glycolysis
E) chemiosmosis

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
The ATP made during fermentation is generated by which of the following?
A) the electron transport chain
B) substrate-level phosphorylation
C) chemiosmosis
D) oxidative phosphorylation
E) aerobic respiration
A) the electron transport chain
B) substrate-level phosphorylation
C) chemiosmosis
D) oxidative phosphorylation
E) aerobic respiration

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
How do the catabolic products of beta oxidation enter into the citric acid cycle?
A) as pyruvate
B) as glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
C) as CO₂
D) as acetyl CoA
E) as glycerol
A) as pyruvate
B) as glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
C) as CO₂
D) as acetyl CoA
E) as glycerol

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
A mutation in yeast makes it unable to convert pyruvate to ethanol. How will this mutation affect these yeast cells?
A) The mutant yeast will produce lactate under anaerobic conditions.
B) The mutant yeast will be unable to grow anaerobically.
C) The mutant yeast will be unable to grow aerobically.
D) The mutant yeast will grow anaerobically only when provided glucose.
E) The mutant yeast will be unable to metabolize glucose.
A) The mutant yeast will produce lactate under anaerobic conditions.
B) The mutant yeast will be unable to grow anaerobically.
C) The mutant yeast will be unable to grow aerobically.
D) The mutant yeast will grow anaerobically only when provided glucose.
E) The mutant yeast will be unable to metabolize glucose.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








