Deck 15: Acidbase Equilibria: Proton Transfer in Biological Systems
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/122
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 15: Acidbase Equilibria: Proton Transfer in Biological Systems
1
The base ionization constant Kb describes which of the following reactions for a weak base, B, in aqueous solution?
A)B +H+
 BH+
BH+
B)B +H3O+ BH++ H2O
BH++ H2O
C)B + H2O BH- + OH-
BH- + OH-
D)B + OH- BH- + O2-
BH- + O2-
E)BH+ + OH- B + H2O
B + H2O
A)B +H+
 BH+
BH+B)B +H3O+
 BH++ H2O
BH++ H2OC)B + H2O
 BH- + OH-
BH- + OH-D)B + OH-
 BH- + O2-
BH- + O2-E)BH+ + OH-
 B + H2O
B + H2OB + H2O  BH- + OH-
BH- + OH-
 BH- + OH-
BH- + OH- 2
In the following reaction in aqueous solution, the base reactant is ________ and its conjugate acid product is ________.
HCOOH + C5H5N HCOO- + C5H5NH+
HCOO- + C5H5NH+
A)HCOOH; HCOO-
B)C5H5N; HCOO-
C)HCOOH; C5H5NH+
D)C5H5N; C5H5NH+
E)C5H5N; OH-
HCOOH + C5H5N
 HCOO- + C5H5NH+
HCOO- + C5H5NH+A)HCOOH; HCOO-
B)C5H5N; HCOO-
C)HCOOH; C5H5NH+
D)C5H5N; C5H5NH+
E)C5H5N; OH-
C5H5N; C5H5NH+
3
Solutions of each of the hypothetical bases in the following table are prepared with an initial concentration of 0.100 M. Which of the four solutions will have the lowest pH and be least basic?

A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)All will have the same pH because the concentrations are the same.

A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
E)All will have the same pH because the concentrations are the same.
A
4
Which sketch best represents the qualitative molecular view of an aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide? (Water molecules are not shown explicitly.) 
A)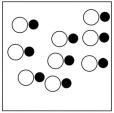
B)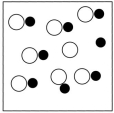
C)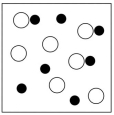
D)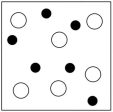

A)

B)

C)

D)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
In the following reaction in aqueous solution, the acid reactant is ________ and its conjugate base product is ________.
CH3NH2 + HSO4- CH3NH3+ + SO42-
CH3NH3+ + SO42-
A)CH3NH2; CH3NH3+
B)CH3NH2; SO42-
C)HSO4-; CH3NH3+
D)HSO4-; SO42-
E)HSO4-; H3O+
CH3NH2 + HSO4-
 CH3NH3+ + SO42-
CH3NH3+ + SO42-A)CH3NH2; CH3NH3+
B)CH3NH2; SO42-
C)HSO4-; CH3NH3+
D)HSO4-; SO42-
E)HSO4-; H3O+

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Which of the following is a strong acid?
A)HNO3
B)H2S
C)HNO2
D)HCO3-
E)HOCl
A)HNO3
B)H2S
C)HNO2
D)HCO3-
E)HOCl

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Which of the following is the conjugate acid of the hydrogen phosphate ion, HPO42-?
A)H3PO4
B)H2PO4-
C)HPO42-
D)PO43-
E)H3O+
A)H3PO4
B)H2PO4-
C)HPO42-
D)PO43-
E)H3O+

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Ammonia (NH3) acts as a weak base in aqueous solution. What is the acid that reacts with this base when ammonia is dissolved in water?
A)None, there are no acids in pure water.
B)H2O
C)NH4+
D)trick question, because no acids are present, ammonia cannot act as a base
E)oxygen that always is dissolved in water
A)None, there are no acids in pure water.
B)H2O
C)NH4+
D)trick question, because no acids are present, ammonia cannot act as a base
E)oxygen that always is dissolved in water

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
The acid ionization equilibrium constant, Ka, describes the reaction (where HA is a generic weak acid) ________
A)HA +OH- H2O +A-.
H2O +A-.
B)HA + H2O H3O+ + A-.
H3O+ + A-.
C)HA + H3O+ H2A- + H2O.
H2A- + H2O.
D)HA + H2A+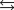 H2A-+ HA.
H2A-+ HA.
E)H3O+ +A-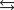 HA + H2O.
HA + H2O.
A)HA +OH-
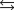 H2O +A-.
H2O +A-.B)HA + H2O
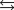 H3O+ + A-.
H3O+ + A-.C)HA + H3O+
 H2A- + H2O.
H2A- + H2O.D)HA + H2A+
 H2A-+ HA.
H2A-+ HA.E)H3O+ +A-
 HA + H2O.
HA + H2O.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Which one of the following is a conjugate acid-base pair?
A)NH3 and NH4+
B)H3O+ and OH-
C)NH2- and NH4+
D)H2O and O2-
E)NaF and F-
A)NH3 and NH4+
B)H3O+ and OH-
C)NH2- and NH4+
D)H2O and O2-
E)NaF and F-

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Which sketch best represents the qualitative molecular view of an aqueous solution of nitrous acid? (Water molecules are not shown explicitly.) 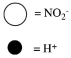
A)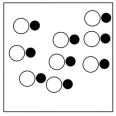
B)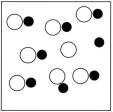
C)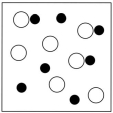
D)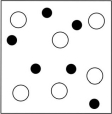

A)

B)

C)

D)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Three acids found in foods are lactic acid (in milk products), oxalic acid (in rhubarb), and malic acid (in apples). The pKa values are LA = 3.88, OA = 1.23, and MA = 3.40. Which list has these acids in order of decreasing acid strength?
A)LA > OA > MA
B)LA > MA > OA
C)OA > MA > LA
D)OA > LA > MA
E)MA > LA > OA
A)LA > OA > MA
B)LA > MA > OA
C)OA > MA > LA
D)OA > LA > MA
E)MA > LA > OA

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Which of the following is the conjugate base of the hydrogen carbonate ion, HCO3-?
A)H2CO3
B)HCO3-
C)CO32-
D)OH-
E)H3CO3+
A)H2CO3
B)HCO3-
C)CO32-
D)OH-
E)H3CO3+

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Which one of the following is not a strong base?
A)lithium hydroxide, LiOH
B)sodium hydroxide, NaOH
C)potassium hydroxide, KOH
D)calcium hydroxide, Ca(OH)2
E)ammonium hydroxide, NH4OH
A)lithium hydroxide, LiOH
B)sodium hydroxide, NaOH
C)potassium hydroxide, KOH
D)calcium hydroxide, Ca(OH)2
E)ammonium hydroxide, NH4OH

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Which one of the following is not a strong acid?
A)nitric acid, HNO3
B)sulfuric acid, H2SO4
C)carbonic acid, H2CO3
D)hydrochloric acid, HCl
E)perchloric acid, HClO4
A)nitric acid, HNO3
B)sulfuric acid, H2SO4
C)carbonic acid, H2CO3
D)hydrochloric acid, HCl
E)perchloric acid, HClO4

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Which one of the following is not a conjugate acid-base pair?
A)NH3 and NH2-
B)HNO3 and HNO2
C)HI and I-
D)H2PO4- and HPO42-
E)H2O and OH-
A)NH3 and NH2-
B)HNO3 and HNO2
C)HI and I-
D)H2PO4- and HPO42-
E)H2O and OH-

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Which one of the following is a strong acid?
A)nitrous acid, HNO2
B)sulfurous acid, H2SO3
C)carbonic acid, H2CO3
D)hydrofluoric acid, HF
E)perchloric acid, HClO4
A)nitrous acid, HNO2
B)sulfurous acid, H2SO3
C)carbonic acid, H2CO3
D)hydrofluoric acid, HF
E)perchloric acid, HClO4

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Which one of the following is a conjugate acid-base pair?
A)NaF and F-
B)HNO3 and HNO2
C)HI and I-
D)NH4+ and NH2-
E)H2O and H2O2
A)NaF and F-
B)HNO3 and HNO2
C)HI and I-
D)NH4+ and NH2-
E)H2O and H2O2

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
In the following reaction in aqueous solution, the acid reactant is ________ and its conjugate base product is ________.
CH3COOH +NH3 CH3COO-+NH4+
CH3COO-+NH4+
A)CH3COOH; CH3COO-
B)CH3COOH; NH4+
C)NH3; CH3COO-
D)NH3; NH4+
E)CH3COOH; H3O+
CH3COOH +NH3
 CH3COO-+NH4+
CH3COO-+NH4+A)CH3COOH; CH3COO-
B)CH3COOH; NH4+
C)NH3; CH3COO-
D)NH3; NH4+
E)CH3COOH; H3O+

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Which one of the following is not a conjugate acid-base pair?
A)NH3 and NH4+
B)H3O+ and OH-
C)H2PO4- and HPO42-
D)HS- and H2S
E)NH3 and NH2-
A)NH3 and NH4+
B)H3O+ and OH-
C)H2PO4- and HPO42-
D)HS- and H2S
E)NH3 and NH2-

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
A substance that can act as both an acid and base is ________
A)amphibious.
B)amphiprotic.
C)bacidic.
D)androgynous.
E)acibasic.
A)amphibious.
B)amphiprotic.
C)bacidic.
D)androgynous.
E)acibasic.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
When [H+] = 1.0 10-7 M in water at 25 C, then ________
A)pH = 1.
B)pH = 10-7.
C)[OH-] = 1.0 10-7 M.
D)[OH-] = 1.0 107 M.
E)[OH-] = 0 M.
A)pH = 1.
B)pH = 10-7.
C)[OH-] = 1.0 10-7 M.
D)[OH-] = 1.0 107 M.
E)[OH-] = 0 M.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Which one A-D is not related to the water autoionization constant, Kw?
A)[H3O+] [OH-]
B)1.0 10-14 at 25 C
C)2 H2O![<strong>Which one A-D is not related to the water autoionization constant, K<sub>w</sub>?</strong> A)[H<sub>3</sub>O<sup>+</sup>] [OH<sup>-</sup>] B)1.0 \times 10<sup>-14</sup> at 25<sup> \circ </sup>C C)2<sup> </sup>H<sub>2</sub>O H<sub>3</sub>O<sup>+</sup> + OH<sup>-</sup> D)pH = 7 at 25<sup> \circ </sup>C E)A-D are all related to K<sub>w</sub>.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3835/11eaa952_9b45_16a8_ae90_65a83aeac875_TB3835_11.jpg) H3O+ + OH-
H3O+ + OH-
D)pH = 7 at 25 C
E)A-D are all related to Kw.
A)[H3O+] [OH-]
B)1.0 10-14 at 25 C
C)2 H2O
![<strong>Which one A-D is not related to the water autoionization constant, K<sub>w</sub>?</strong> A)[H<sub>3</sub>O<sup>+</sup>] [OH<sup>-</sup>] B)1.0 \times 10<sup>-14</sup> at 25<sup> \circ </sup>C C)2<sup> </sup>H<sub>2</sub>O H<sub>3</sub>O<sup>+</sup> + OH<sup>-</sup> D)pH = 7 at 25<sup> \circ </sup>C E)A-D are all related to K<sub>w</sub>.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3835/11eaa952_9b45_16a8_ae90_65a83aeac875_TB3835_11.jpg) H3O+ + OH-
H3O+ + OH-D)pH = 7 at 25 C
E)A-D are all related to Kw.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Sometimes liquid ammonia, NH3, is used as a solvent rather than water. Which expression defines the ammonia autoionization counterpart of Kw?
A)[H3O+][OH-]
B)[NH3][NH4+]
C)[NH2-][NH4+]
D)[H3O+][NH2-]
E)[NH4+][OH-]
A)[H3O+][OH-]
B)[NH3][NH4+]
C)[NH2-][NH4+]
D)[H3O+][NH2-]
E)[NH4+][OH-]

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
What is the actual concentration of the molecular form of HF in a 1.0 M HF solution given that Ka of HF is 6.8 10-4?
A)2.6 10-2 M
B)0.97 M
C)1.59 M
D)6.8 10-4 M
E)1.0 M
A)2.6 10-2 M
B)0.97 M
C)1.59 M
D)6.8 10-4 M
E)1.0 M

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Use the following acid ionization constants to identify the correct decreasing order of base strengths for the conjugate bases.
HF Ka = 7.2 10-4
HNO2 Ka = 4.5 10-4
HCN Ka = 6.2 10-10
A)CN- > NO2- > F-
B)NO2- > F- > CN-
C)F- > CN- > NO2-
D)F- > NO2- > CN-
E)NO2- > CN- > F-
HF Ka = 7.2 10-4
HNO2 Ka = 4.5 10-4
HCN Ka = 6.2 10-10
A)CN- > NO2- > F-
B)NO2- > F- > CN-
C)F- > CN- > NO2-
D)F- > NO2- > CN-
E)NO2- > CN- > F-

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Three common weak bases are phosphate (P; PO43-, pKb = 1.3), carbonate (C; CO32-, pKb = 3.7), and acetate (A; CH3COO-, pKb = 9.3). Which response has these bases listed in order of increasing strength?
A)P < C < A
B)C < P < A
C)A < C < P
D)C < A < P
E)P < A < C
A)P < C < A
B)C < P < A
C)A < C < P
D)C < A < P
E)P < A < C

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
A cup of coffee has a hydroxide ion concentration of 1.0 10-10 M. What is the pH of this coffee?
A)1.0 10-4
B)4
C)10
D)7
E)(-10)
A)1.0 10-4
B)4
C)10
D)7
E)(-10)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Which statement A-D is not correct? Pure water at 25 C has ________
A)Kw = 1.0 10-14.
B)pOH = 7.
C)[H3O+] = [OH-].
D)pH = 7.
E)A-D are all correct.
A)Kw = 1.0 10-14.
B)pOH = 7.
C)[H3O+] = [OH-].
D)pH = 7.
E)A-D are all correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
When [H+] = 4.0 10-9 M in water at 25 C, then ________
A)pH = 9.40.
B)pH = 7.00.
C)pH = -8.40.
D)pH = 8.40.
E)pH = -9.40.
A)pH = 9.40.
B)pH = 7.00.
C)pH = -8.40.
D)pH = 8.40.
E)pH = -9.40.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Pure water at any temperature has ________
A)a pH less than 7.
B)a pOH more than 7.
C)[H3O+] =[OH-].
D)pH = 7.
E)no hydronium ions in it.
A)a pH less than 7.
B)a pOH more than 7.
C)[H3O+] =[OH-].
D)pH = 7.
E)no hydronium ions in it.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
A solution with a pOH of 4.3 has a [H+] of ________
A)6.8 10-9 M.
B)3.2 10-4 M.
C)4.8 10-5 M.
D)2.0 10-10 M.
E)4.3 M.
A)6.8 10-9 M.
B)3.2 10-4 M.
C)4.8 10-5 M.
D)2.0 10-10 M.
E)4.3 M.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
The pH of a popular soft drink is 3.4; what is its hydronium ion concentration?
A)5.0 10-4 M
B)4.0 10-4 M
C)2.5 103 M
D)1.0 10-7 M
E)5.0 10-5 M
A)5.0 10-4 M
B)4.0 10-4 M
C)2.5 103 M
D)1.0 10-7 M
E)5.0 10-5 M

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
Which expression defines the autoionization constant for water, Kw?
A)[H3O+][OH-]
B)[H2O][H3O+]
C)[OH-][H2O]
D)[H4O2+][O2-]
E)[H2O][H2O]
A)[H3O+][OH-]
B)[H2O][H3O+]
C)[OH-][H2O]
D)[H4O2+][O2-]
E)[H2O][H2O]

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
A solution with a pH of 9.50 has a pOH of ________
A)9.50.
B)0.50.
C)4.50.
D)23.5.
E)19.0.
A)9.50.
B)0.50.
C)4.50.
D)23.5.
E)19.0.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
When pure water autoionizes, which ions are produced?
A)O2-, OH-, H3O+, and H2O+
B)OH- and H3O+
C)O2- and H4O2+
D)H+ and OH-
E)2H+ and O2-
A)O2-, OH-, H3O+, and H2O+
B)OH- and H3O+
C)O2- and H4O2+
D)H+ and OH-
E)2H+ and O2-

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Three acids found in foods are lactic acid (in milk products), oxalic acid (in rhubarb), and malic acid (in apples). The pKa values are LA = 3.88, OA = 1.23, and MA = 3.40. Which list has the conjugate bases of these acids in order of decreasing strength?
A)lactate > oxalate > malate
B)oxalate > malate > lactate
C)lactate > malate > oxalate
D)oxalate > lactate > malate
E)malate > lactate > oxalate
A)lactate > oxalate > malate
B)oxalate > malate > lactate
C)lactate > malate > oxalate
D)oxalate > lactate > malate
E)malate > lactate > oxalate

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
A solution with a pOH of 6.92 has an [OH-] concentration of ________
A)1.20 10-7 M.
B)9.2 10-6 M.
C)6.8 10-6 M.
D)7.08 M.
E)6.92 M.
A)1.20 10-7 M.
B)9.2 10-6 M.
C)6.8 10-6 M.
D)7.08 M.
E)6.92 M.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
A solution with a pH of 2.50 has an [OH-] of ________
A)3.16 102.
B)3.16 10-12.
C)3.16 10-3.
D)3.16 1016.
E)3.16 1011.
A)3.16 102.
B)3.16 10-12.
C)3.16 10-3.
D)3.16 1016.
E)3.16 1011.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
The hydronium ion concentration of a dilute solution of vinegar is 1.45 10-5. What is the pH of this solution?
A)5.7
B)(-4.8)
C)4.8
D)(-5.7)
E)7.0
A)5.7
B)(-4.8)
C)4.8
D)(-5.7)
E)7.0

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
The concentration of acetic acid (pKa = 4.75) in vinegar is about 1.0 M. With this information, what do you predict the pH of vinegar to be?
A)4.75
B)2.4
C)4.0 10-3
D)7.0
E)5.35
A)4.75
B)2.4
C)4.0 10-3
D)7.0
E)5.35

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
What is the pOH of a 0.125 M solution of hydroxylamine? The Kb value for hydroxylamine is 1.1 10-8.
A)4.43
B)3.47
C)5.57
D)10.53
E)9.57
A)4.43
B)3.47
C)5.57
D)10.53
E)9.57

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
In evaluating the pH of an aqueous weak acid solution, ________ usually can be ignored.
A)the concentration of the weak acid
B)the concentration of hydronium ion produced by the autoionization of water
C)the reaction of the weak acid with water
D)the concentration of the ionized hydronium ion
E)the concentration of the conjugate base
A)the concentration of the weak acid
B)the concentration of hydronium ion produced by the autoionization of water
C)the reaction of the weak acid with water
D)the concentration of the ionized hydronium ion
E)the concentration of the conjugate base

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
The acidic ingredient in vinegar is acetic acid. The pH of vinegar is around 2.4, and the molar concentration of acetic acid in vinegar is around 0.85 M. Based on this information, determine the value of the acid ionization constant, Ka, for acetic acid.
A)2.5 10-5
B)5.0 10-5
C)4.7 10-3
D)1.9 10-5
E)7.4 10-3
A)2.5 10-5
B)5.0 10-5
C)4.7 10-3
D)1.9 10-5
E)7.4 10-3

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
What is the actual concentration of molecular NH3 in a 0.200 M solution of ammonia? The Kb value for ammonia is 1.80 10-5.
A)0.200 M
B)0.198 M
C)1.80 10-5 M
D)1.90 10-3 M
E)3.6 10-6 M
A)0.200 M
B)0.198 M
C)1.80 10-5 M
D)1.90 10-3 M
E)3.6 10-6 M

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
Diethylamine ((CH3CH2) NH2) is a weakly basic compound. Calculate the Kb for diethylamine if a 0.127 M solution is 9.61% ionized.
A)1.8 10-5
B)4.4 10-4
C)5.6 10-4
D)1.3 10-3
E)3.8 10-10
A)1.8 10-5
B)4.4 10-4
C)5.6 10-4
D)1.3 10-3
E)3.8 10-10

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
What is the concentration of the acetate ion in a 1.00 M CH3COOH solution given that the Ka of CH3COOH is 1.8 10-5?
A)4.20 10-3 M
B)0.996 M
C)1.00 M
D)2.84 10-4 M
E)5.62 10-5 M
A)4.20 10-3 M
B)0.996 M
C)1.00 M
D)2.84 10-4 M
E)5.62 10-5 M

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
Methylamine (CH3NH2) is a weakly basic compound. Calculate the Kb for methylamine if a 0.253 M solution is 4.07% ionized.
A)2.29 103
B)4.37 10-4
C)5.72
D)4.24 10-2
E)4.19 10-4
A)2.29 103
B)4.37 10-4
C)5.72
D)4.24 10-2
E)4.19 10-4

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
What is the concentration of ammonium ion in a 0.150 M solution of ammonia? The Kb value for ammonia is 1.80 10-5.
A)0.146 M
B)0.148 M
C)2.34 10-5 M
D)1.63 10-3 M
E)4.20 10-3 M
A)0.146 M
B)0.148 M
C)2.34 10-5 M
D)1.63 10-3 M
E)4.20 10-3 M

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
When values of Ka are small (e.g., 1 10-5) and concentrations of weak acids [HA] are relatively large (e.g., 0.10 M), the hydronium ion concentration of the solution can be calculated using which expression?
A)[H+] = Ka
B)[H+] = Ka[HA]
C)[H+] = (Ka[HA])1/2
D)[H+] = KaKb[HA]
E)[H=+] = Ka[HA]/[A-]
A)[H+] = Ka
B)[H+] = Ka[HA]
C)[H+] = (Ka[HA])1/2
D)[H+] = KaKb[HA]
E)[H=+] = Ka[HA]/[A-]

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
What is the concentration of [OH-] in a 0.20 M solution of ammonia? The Kb value for ammonia is 1.8 10-5.
A)3.6 10-6 M
B)1.8 10-5 M
C)0.20 M
D)1.9 10-3 M
E)4.2 10-4 M
A)3.6 10-6 M
B)1.8 10-5 M
C)0.20 M
D)1.9 10-3 M
E)4.2 10-4 M

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
What is the pH of a 0.500 M solution of trimethylamine (pKb = 4.13)?
A)2.22
B)11.8
C)0.00609
D)4.42
E)5.91
A)2.22
B)11.8
C)0.00609
D)4.42
E)5.91

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
What is the pH of a 0.030 M solution of oxalic acid? Ka for oxalic acid is 5.9 10-2.
A)1.66
B)1.37
C)2.78
D)12.67
E)12.34
A)1.66
B)1.37
C)2.78
D)12.67
E)12.34

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
Lactic acid is a major component of Ringer's solution, which is used as an intravenous fluid to maintain fluid balance in trauma patients. The pH of a 0.100 M lactic acid solution is around 2.44. Based on this information, determine the value of the acid ionization constant, Ka, for lactic acid.
A)1.2 10-2
B)1.4 10-4
C)4.7 10-3
D)1.8 10-4
E)7.4 10-3
A)1.2 10-2
B)1.4 10-4
C)4.7 10-3
D)1.8 10-4
E)7.4 10-3

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
What is the hydronium ion concentration of a 0.010 M solution of acetic acid? Ka for acetic acid is 1.8 10-5.
A)1.8 10-3
B)1.8 10-5
C)1.0 10-2
D)1.8 10-7
E)4.2 10-4
A)1.8 10-3
B)1.8 10-5
C)1.0 10-2
D)1.8 10-7
E)4.2 10-4

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
Formic acid is a weak acid naturally occurring in certain species of ants. Calculate the acid ionization constant for formic acid if a 0.213 M solution is 2.86% ionized. The abbreviated structural formula for formic acid is HCOOH.
A)7.2 10-4
B)6.4 10-4
C)1.8 10-4
D)1.9 10-5
E)3.5 10-8
A)7.2 10-4
B)6.4 10-4
C)1.8 10-4
D)1.9 10-5
E)3.5 10-8

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
A 0.100 M solution of a monoprotic weak acid has a pH of 3.00. What is the pKa of this acid?
A)5.00
B)0.999
C)3.00
D)9.99
E)6.00
A)5.00
B)0.999
C)3.00
D)9.99
E)6.00

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
Boric acid frequently is used as an eyewash to treat eye infections. The pH of a 0.050 M solution of boric acid is 5.28. What is the value of the boric acid ionization constant, Ka?
A)5.25 10-6
B)5.51 10-10
C)5.43 10-8
D)5.79 10-4
E)5.33 10-12
A)5.25 10-6
B)5.51 10-10
C)5.43 10-8
D)5.79 10-4
E)5.33 10-12

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
Butanoic acid contributes to the rancid odor of spoiled butter. Calculate the acid ionization constant for butanoic acid if a 0.155 M solution is 1.15% ionized. The abbreviated structural formula for butanoic acid is CH3CH2CH2COOH.
A)5.1 10-3
B)1.8 10-3
C)1.2 10-2
D)2.1 10-5
E)1.5 10-5
A)5.1 10-3
B)1.8 10-3
C)1.2 10-2
D)2.1 10-5
E)1.5 10-5

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
The first disinfectant used by Joseph Lister was called carbolic acid. This substance now is known as phenol, C6H5OH (pKa = 10.0). What is the pH of a 0.10 M solution of phenol?
A)3.5
B)10.0
C)6.5
D)5.5
E)4.5
A)3.5
B)10.0
C)6.5
D)5.5
E)4.5

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
Sodium hypochlorite is a common ingredient in household bleach. What is the pH of this bleach if it contains 5% NaOCl by mass? (pKa of HOCl = 7.46)
A)9
B)11
C)4
D)8
E)7
A)9
B)11
C)4
D)8
E)7

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
The degree of ionization of a strong acid is ________
A)dependent on the concentration of the acid.
B)between 1 and 10%.
C)between 10 and 100%.
D)100%.
E)dependent on which strong acid it is.
A)dependent on the concentration of the acid.
B)between 1 and 10%.
C)between 10 and 100%.
D)100%.
E)dependent on which strong acid it is.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
Identify the weakest and strongest acids in the group below. The weakest acid is listed first in the responses. HCl, H2S, PH3
A)HCl < H2S
B)HCl < PH3
C)H2S < HCl
D)H2S < PH3
E)PH3 < HCl
A)HCl < H2S
B)HCl < PH3
C)H2S < HCl
D)H2S < PH3
E)PH3 < HCl

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
In each of the following, the stronger acid is identified and an explanation is given. All except one are correct statements. Which one is not correct?
A)HCl > HF because the HF bond energy is larger than the HCl bond energy.
B)HCO3- > H2CO3 because the negative charge stabilizes the loss of a proton.
C)CCl3COOH > CH3COOH because electronegative substituents stabilize the conjugate base.
D)HBrO3 > HBrO2 because of the additional electronegative oxygen atom.
E)ClOH > BrOH because Cl is more electronegative than Br.
A)HCl > HF because the HF bond energy is larger than the HCl bond energy.
B)HCO3- > H2CO3 because the negative charge stabilizes the loss of a proton.
C)CCl3COOH > CH3COOH because electronegative substituents stabilize the conjugate base.
D)HBrO3 > HBrO2 because of the additional electronegative oxygen atom.
E)ClOH > BrOH because Cl is more electronegative than Br.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
Identify the weakest and strongest acids in the group below. The weakest acid is listed first in the responses. H2O, H2S, H2Se
A)H2Se < H2S
B)H2Se < H2O
C)H2S < H2Se
D)H2O < H2Se
E)H2O < H2S
A)H2Se < H2S
B)H2Se < H2O
C)H2S < H2Se
D)H2O < H2Se
E)H2O < H2S

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
What is the hydronium ion concentration of a 0.200 M solution of methylamine? The Kb value for methylamine is 4.38 10-4.
A)9.14 10-3
B)1.09 10-12
C)5.24 10-14
D)1.00 10-7
E)1.91 10-1
A)9.14 10-3
B)1.09 10-12
C)5.24 10-14
D)1.00 10-7
E)1.91 10-1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
Which one of the following statements is not correct?
A)HIO is a stronger acid than HClO.
B)HClO is a stronger acid than HBrO.
C)HClO3 is a stronger acid than HClO2.
D)HPO42- is a weaker acid than H2PO4-.
E)H2SO4 is a stronger acid than H2SO3.
A)HIO is a stronger acid than HClO.
B)HClO is a stronger acid than HBrO.
C)HClO3 is a stronger acid than HClO2.
D)HPO42- is a weaker acid than H2PO4-.
E)H2SO4 is a stronger acid than H2SO3.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
What is the pH of a 0.200 M solution of methylamine? The Kb value for methylamine is 4.38 10-4.
A)2.04
B)(-1.33)
C)10.53
D)15.33
E)11.96
A)2.04
B)(-1.33)
C)10.53
D)15.33
E)11.96

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
The analysis label on a 500 mL bottle of Fiji natural artesian water reports pH = 7.5 and 140 mg of bicarbonates, HCO3-. Calculate the pH expected as a result of the bicarbonates to see if these two numbers are consistent with each other. (Kb = 2.4 10-8 for HCO3-)
A)7.5
B)5.0
C)9.6
D)4.4
E)9.0
A)7.5
B)5.0
C)9.6
D)4.4
E)9.0

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
The degree of ionization of a weak acid ________
I. varies with the concentration of the acid.
II. depends on which weak acid it is.
III. is 100%.
IV. is greater than 50% but less than 100%.
A)I only
B)II only
C)III only
D)both I and II
E)IV only
I. varies with the concentration of the acid.
II. depends on which weak acid it is.
III. is 100%.
IV. is greater than 50% but less than 100%.
A)I only
B)II only
C)III only
D)both I and II
E)IV only

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
The pH of an aniline solution is 8.91, and the solution has a concentration of 0.17 M. The pKb of aniline is 9.42. What is the percent ionization of aniline?
A)1.2%
B)0.50%
C)2.1 10-3%
D)4.7 10-3%
E)6.3 10-5%
A)1.2%
B)0.50%
C)2.1 10-3%
D)4.7 10-3%
E)6.3 10-5%

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
A solution of the weak acid HF and a solution of the strong acid HCl have the same pH. Which solution will require the most sodium hydroxide, NaOH, to neutralize?
A)HCl, because it is a strong acid and dissociates completely.
B)HF, because its concentration is larger.
C)Both will require the same amount because the concentrations are equal.
D)Both will require the same amount because the H3O+concentrations are the same.
E)HCl, because the stronger acid has the higher concentration.
A)HCl, because it is a strong acid and dissociates completely.
B)HF, because its concentration is larger.
C)Both will require the same amount because the concentrations are equal.
D)Both will require the same amount because the H3O+concentrations are the same.
E)HCl, because the stronger acid has the higher concentration.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
Identify the weakest and strongest acids in the group below. The weakest acid is listed first in the responses. H2Te, H2S, H2Se
A)H2Se < H2S
B)H2S < H2Te
C)H2S < H2Se
D)H2Te < H2Se
E)H2Te < H2S
A)H2Se < H2S
B)H2S < H2Te
C)H2S < H2Se
D)H2Te < H2Se
E)H2Te < H2S

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
Which ending to the statement is not correct? The weak acid HY will be stronger than the weak acid HZ if ________
A)more Lewis resonance structures can be written for the Y group than for the Z group.
B)Y is more electronegative than Z.
C)the Y group has more oxygen atoms than the Z group.
D)the H-Y bond is weaker than the H-Z bond and other things are about the same.
E)the Y group contains Br rather than Cl, which is in the Z group.
A)more Lewis resonance structures can be written for the Y group than for the Z group.
B)Y is more electronegative than Z.
C)the Y group has more oxygen atoms than the Z group.
D)the H-Y bond is weaker than the H-Z bond and other things are about the same.
E)the Y group contains Br rather than Cl, which is in the Z group.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
The pH of vinegar is 2.4, and the acetic acid in vinegar has a concentration of about 0.85 M. The pKa of acetic acid is 4.75. What is the percent ionization of acetic acid in vinegar?
A)2.8%
B)4.7%
C)0.47%
D)0.21%
E)0.021%
A)2.8%
B)4.7%
C)0.47%
D)0.21%
E)0.021%

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
The pH of an ammonia solution is 11.6, and the solution has a concentration of about 0.20 M. The pKb of ammonia is 4.75. What is the percent ionization of ammonia?
A)2.0%
B)2.3%
C)1.2%
D)0.95%
E)5.4%
A)2.0%
B)2.3%
C)1.2%
D)0.95%
E)5.4%

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
Identify the weakest and strongest acids in the group below. The weakest acid is listed first in the responses. HOCl, HOBr, HOI
A)HOBr < HOCl
B)HOBr < HOI
C)HOCl < HOBr
D)HOCl < HOI
E)HOI < HOCl
A)HOBr < HOCl
B)HOBr < HOI
C)HOCl < HOBr
D)HOCl < HOI
E)HOI < HOCl

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
Vitamin C, which is ascorbic acid, is a diprotic acid with 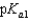 = 5.00 and
= 5.00 and 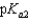 = 11.3. What is the pH of a 0.125 M solution of ascorbic acid?
= 11.3. What is the pH of a 0.125 M solution of ascorbic acid?
A)2.95
B)3.05
C)5.00
D)6.10
E)3.54
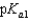 = 5.00 and
= 5.00 and 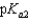 = 11.3. What is the pH of a 0.125 M solution of ascorbic acid?
= 11.3. What is the pH of a 0.125 M solution of ascorbic acid?A)2.95
B)3.05
C)5.00
D)6.10
E)3.54

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
The degree of ionization ________
A)increases with increasing concentration of a weak acid.
B)decreases with increasing concentration of a weak acid.
C)does not change with changing concentration of a weak acid.
D)is not related to the concentration of a weak acid.
E)is independent of the composition of the weak acid.
A)increases with increasing concentration of a weak acid.
B)decreases with increasing concentration of a weak acid.
C)does not change with changing concentration of a weak acid.
D)is not related to the concentration of a weak acid.
E)is independent of the composition of the weak acid.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
Identify the weakest and strongest acids in the group below. The weakest acid is listed first in the responses. HCl, HBr, HI
A)HCl < HI
B)HCl < HBr
C)HBr < HCl
D)HBr < HI
E)HI < HCl
A)HCl < HI
B)HCl < HBr
C)HBr < HCl
D)HBr < HI
E)HI < HCl

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








