Deck 8: Evolution in Finite Populations
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/50
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 8: Evolution in Finite Populations
1
In the figure, assuming all evolutionary processes are similar in A-D, which genealogy is expected to carry the largest number of neutral alleles? 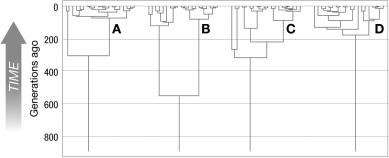
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
B
2
The figure shows the level of diversity at three loci in two species of elephant seals. Which of the following could be true of these species according to the data? B
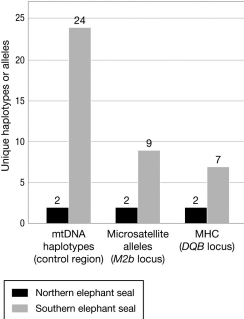
A) The northern elephant seals have a higher mutation rate than the southern elephant seals.
B) The northern elephant seals have a larger effective population size than the southern elephant seals.
C) The northern elephant seals experience balancing selection at these loci and the southern elephant seals experience directional selection.
D) The northern elephant seals experienced a population bottleneck, but the southern elephant seals did not.

A) The northern elephant seals have a higher mutation rate than the southern elephant seals.
B) The northern elephant seals have a larger effective population size than the southern elephant seals.
C) The northern elephant seals experience balancing selection at these loci and the southern elephant seals experience directional selection.
D) The northern elephant seals experienced a population bottleneck, but the southern elephant seals did not.
The northern elephant seals experienced a population bottleneck, but the southern elephant seals did not.
3
Which of the following is an example of a population bottleneck?
A) A long-endangered species recovers and increases population size.
B) A large population of frogs is greatly reduced due to a drought.
C) Butterfly migration patterns are disrupted by climate change.
D) A beneficial mutation goes to fixation in a population.
A) A long-endangered species recovers and increases population size.
B) A large population of frogs is greatly reduced due to a drought.
C) Butterfly migration patterns are disrupted by climate change.
D) A beneficial mutation goes to fixation in a population.
B
4
Genetic drift is caused by ________ processes.
A) random
B) directed
C) mutational
D) selective
A) random
B) directed
C) mutational
D) selective

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
Consider a population with an effective size of 4,000 and 32 segregating alleles. On average, how many generations would it take for all 32 alleles to coalesce to a single, ancestral allele?
A) 32
B) 128
C) 1,000
D) 16,000
A) 32
B) 128
C) 1,000
D) 16,000

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
F-statistics can be used to quantify the effects of genetic drift by measuring
A) the change in identity by descent over time.
B) effective population size.
C) the rate of change in allele frequencies.
D) the relative strength of selection on two alleles.
A) the change in identity by descent over time.
B) effective population size.
C) the rate of change in allele frequencies.
D) the relative strength of selection on two alleles.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
The figure shows the genealogies for two different genes. Which of the following is a reasonable explanation for the observed difference? 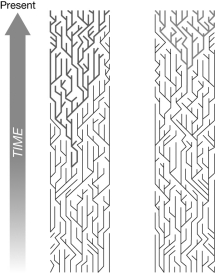
A) The gene in A is neutral. The gene in B experienced balancing selection.
B) The population size is smaller in A than B.
C) The gene in A is neutral. The gene in B experienced positive selection.
D) The mutation rate is lower in gene A than gene B.

A) The gene in A is neutral. The gene in B experienced balancing selection.
B) The population size is smaller in A than B.
C) The gene in A is neutral. The gene in B experienced positive selection.
D) The mutation rate is lower in gene A than gene B.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Population bottlenecks can result in rapid fixation or loss of alleles in otherwise large populations because the bottleneck
A) selectively eliminates or fixes alleles.
B) reduces the effective population size.
C) allows migrant alleles to overwhelm native alleles.
D) creates many new small populations.
A) selectively eliminates or fixes alleles.
B) reduces the effective population size.
C) allows migrant alleles to overwhelm native alleles.
D) creates many new small populations.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
A new mutation arises in a population of spiders (which are diploid) with an effective population size of 116. If that mutation is neutral, what is the probability that it will go to fixation?
A) 0.0043
B) 0.045
C) 0
D) 0.50
A) 0.0043
B) 0.045
C) 0
D) 0.50

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Genetic drift causes changes in
A) the strength of natural selection.
B) allele frequencies.
C) population size.
D) the genetic code.
A) the strength of natural selection.
B) allele frequencies.
C) population size.
D) the genetic code.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
What is the effect of small population size on the degree of heterozygosity in a population?
A) Heterozygosity will increase over time.
B) Heterozygosity will decrease over time.
C) Heterozygosity will not change.
D) Heterozygosity will be subject to natural selection.
A) Heterozygosity will increase over time.
B) Heterozygosity will decrease over time.
C) Heterozygosity will not change.
D) Heterozygosity will be subject to natural selection.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Which of the following is true of cannibalistic beetles in a box and the coalescent process?
A) Events of interest occur rapidly early on, but more slowly later.
B) Genetic drift is most important when the population size is large.
C) The process runs backward in time.
D) The last event of interest occurs the most quickly.
A) Events of interest occur rapidly early on, but more slowly later.
B) Genetic drift is most important when the population size is large.
C) The process runs backward in time.
D) The last event of interest occurs the most quickly.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
The two graphs show the change in allele frequency, p, over 100 generations. Each graph shows 10 different populations, all experiencing the same evolutionary forces. What is the most likely difference between the populations shown in the top graph compared to the populations in the bottom graph? 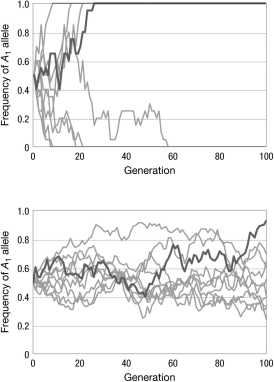
A) There is no difference between the populations; the differences in the graphs are due to chance.
B) The populations in the graph on top have a longer generation time than the populations in the bottom graph.
C) The populations in the graph on top are experiencing genetic drift; the populations in the graph on bottom are experiencing directional selection.
D) The population sizes in the graph on top are smaller than the population sizes in the graph on the bottom.

A) There is no difference between the populations; the differences in the graphs are due to chance.
B) The populations in the graph on top have a longer generation time than the populations in the bottom graph.
C) The populations in the graph on top are experiencing genetic drift; the populations in the graph on bottom are experiencing directional selection.
D) The population sizes in the graph on top are smaller than the population sizes in the graph on the bottom.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
A rancher genotypes all of her 150 head of cattle. In her herd, 25 are A1A1, 75 are A1A2, and 50 are A2A2. Assuming there is random mating, no selection, no mutation, and no new cattle are introduced into the population, what is the probability that the A1 allele will be fixed?
A) 0
B) 0.4167
C) 0.6588
D) 1
A) 0
B) 0.4167
C) 0.6588
D) 1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Consider a collection of 50 distinct alleles, each at equal frequency in a population. The time before the first coalescent event will be shortest if
A) Ne = 100.
B) Ne = 100,000.
C) Ne = 100,000,000.
D) Ne = the census population size.
A) Ne = 100.
B) Ne = 100,000.
C) Ne = 100,000,000.
D) Ne = the census population size.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
If we trace the genealogies of two gene copies back in time, the point at which they are descended from the same ancestral gene copy is called the
A) coalescent point.
B) stable equilibrium.
C) genetic drift.
D) population divergence point.
A) coalescent point.
B) stable equilibrium.
C) genetic drift.
D) population divergence point.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
The effective population size is often lower than the census size of a population because
A) inbreeding depression decreases the fitness of inbred progeny.
B) populations cannot recover from decreases in heterozygosity.
C) scientists cannot accurately count the number of individuals in a population.
D) individuals contribute unequally to future generations.
A) inbreeding depression decreases the fitness of inbred progeny.
B) populations cannot recover from decreases in heterozygosity.
C) scientists cannot accurately count the number of individuals in a population.
D) individuals contribute unequally to future generations.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Imagine an island archipelago where all of the islands are founded by individuals heterozygous at a particular locus. If there is no migration or mutation, and the alleles at that locus are neutral, what do you expect the island populations to look like after many generations?
A) Some island populations will have fixed one allele, and other populations will have fixed the other allele.
B) The populations on every island will have fixed the same allele.
C) The island populations will have high levels of genetic diversity at this locus.
D) We cannot predict any outcome because genetic drift is a random process.
A) Some island populations will have fixed one allele, and other populations will have fixed the other allele.
B) The populations on every island will have fixed the same allele.
C) The island populations will have high levels of genetic diversity at this locus.
D) We cannot predict any outcome because genetic drift is a random process.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Population bottlenecks occur when
A) a large number of genetically diverse individuals found a new population.
B) population size dramatically increases.
C) a consistently large population experiences a brief period of small size.
D) inbreeding is high.
A) a large number of genetically diverse individuals found a new population.
B) population size dramatically increases.
C) a consistently large population experiences a brief period of small size.
D) inbreeding is high.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
The figure shows the relationship between the size of an island and the number of alleles found at microsatellite loci in lizard populations. What do these data demonstrate? 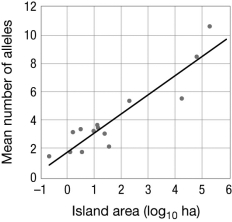
A) Lizards are more successful on larger islands.
B) Effective population size does not affect allelic diversity.
C) Populations on smaller islands experience more natural selection.
D) Genetic drift is stronger in smaller populations.

A) Lizards are more successful on larger islands.
B) Effective population size does not affect allelic diversity.
C) Populations on smaller islands experience more natural selection.
D) Genetic drift is stronger in smaller populations.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
The graphs show the results of simulations of changes in the frequency of a neutral allele. Each graph shows 10 different runs of the simulation. What is the most likely difference between these simulations? Explain your reasoning. 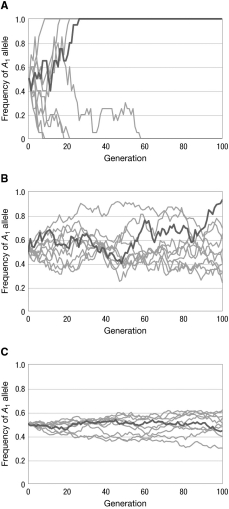


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
The solution to the puzzle of why the rate of substitution is approximately constant per year, despite drastic differences in generation time among species, relies on the
A) relationship between the strength of selection and the number of new mutations.
B) inverse relationship between generation time and population size.
C) effect of neutral mutations on generation time.
D) number of new mutations that experience heterozygote advantage.
A) relationship between the strength of selection and the number of new mutations.
B) inverse relationship between generation time and population size.
C) effect of neutral mutations on generation time.
D) number of new mutations that experience heterozygote advantage.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Consider a series of island populations each founded by a single individual that is heterozygous at a particular locus. If the alleles at this locus are neutral, and there is no mutation or migration, describe what the variation will look like after many generations within each population and between populations. Why?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
A researcher examines a microsatellite locus in a wild population of D. melanogaster. She finds that in a sample of 50 individuals, 20 different alleles are segregating. According to the neutral theory, these alleles are most likely experiencing
A) balancing selection.
B) directional selection.
C) genetic drift.
D) neutral selection.
A) balancing selection.
B) directional selection.
C) genetic drift.
D) neutral selection.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Consider a population of lizards living on the coast of Africa. A storm creates piles of debris that the lizards use to raft to a faraway uninhabited island. Which evolutionary process is happening?
A) mutation selection balance
B) frequency-dependent selection
C) the founder effect
D) coalescence
A) mutation selection balance
B) frequency-dependent selection
C) the founder effect
D) coalescence

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Refer to the figure of the genetic code shown to answer the following question. Which of the following mutations to a codon is most likely to be selectively neutral? 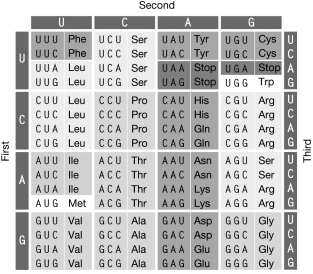
A) UUG CUG
B) AUA AUG
C) AAC AAA
D) UGC UGA

A) UUG CUG
B) AUA AUG
C) AAC AAA
D) UGC UGA

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
The nearly neutral theory predicts that substitution rate is
A) equal to divergence time.
B) independent of population size.
C) lower in smaller populations.
D) higher in smaller populations.
A) equal to divergence time.
B) independent of population size.
C) lower in smaller populations.
D) higher in smaller populations.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
A founder event changes allele frequencies because
A) only a subset of alleles in the original population are represented in the newly founded population.
B) selection in the newly founded population differs from selection in the original population.
C) coalescent processes generate alleles that share a common history.
D) mutation is higher in the newly founded population than in the original population.
A) only a subset of alleles in the original population are represented in the newly founded population.
B) selection in the newly founded population differs from selection in the original population.
C) coalescent processes generate alleles that share a common history.
D) mutation is higher in the newly founded population than in the original population.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Consider a population of size Ne with a new mutation that confers a fitness advantage of 1 + s. This new allele will be more likely to go to fixation due to selection if
A) Ne is large and s is large.
B) Ne is small and s is large.
C) Ne is large and s is small.
D) Ne is small and s is small.
A) Ne is large and s is large.
B) Ne is small and s is large.
C) Ne is large and s is small.
D) Ne is small and s is small.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
A population of fruit flies was maintained at 4,000 individuals for 10 generations. During the 11th generation, the researcher in charge of the flies forgot to buy fly food and only 100 flies survived. Estimate the effective population size of this population over the first 11 generations.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
When both mutation and genetic drift are operating on a locus, heterozygosity will be lowest when
A) Ne is large and µ is large.
B) Ne is small and µ is large.
C) Ne is large and µ is small.
D) Ne is small and µ is small.
A) Ne is large and µ is large.
B) Ne is small and µ is large.
C) Ne is large and µ is small.
D) Ne is small and µ is small.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
In a diploid population, the threshold at which selection will outweigh drift occurs when s (the selective advantage) is greater than
A) 1/2Ne.
B) Ne.
C) Ne/2.
D) 4Ne.
A) 1/2Ne.
B) Ne.
C) Ne/2.
D) 4Ne.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
The neutral theory of molecular evolution posits that most mutations are ________ and most substitutions are ________.
A) neutral; neutral
B) deleterious; neutral
C) beneficial; deleterious
D) neutral; beneficial
A) neutral; neutral
B) deleterious; neutral
C) beneficial; deleterious
D) neutral; beneficial

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
The figure shows the Ka /Ks values for two regulatory genes in pairs of species in (A) North American tarweeds and (B) Hawaiian silverswords. The dashed lines are the mean Ka/Ks values. What do these data indicate about how these genes are evolving differently in these two groups of taxa? A
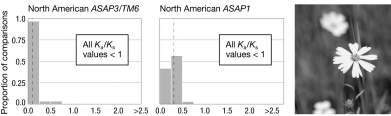
B
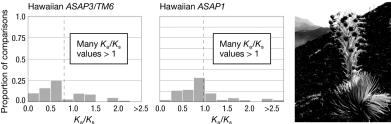
A) They are evolving neutrally in the tarweeds and under purifying selection in the silverswords.
B) There have been more mutations in this gene in the silverswords than the tarweeds.
C) They have experienced purifying selection in the tarweeds and positive selection in the silverswords.
D) They have undergone gene conversion in the tarweeds but not in the silverswords.

B

A) They are evolving neutrally in the tarweeds and under purifying selection in the silverswords.
B) There have been more mutations in this gene in the silverswords than the tarweeds.
C) They have experienced purifying selection in the tarweeds and positive selection in the silverswords.
D) They have undergone gene conversion in the tarweeds but not in the silverswords.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Consider a population of 10,000 pigeons founded by a population in which no alleles were identical by descent. After 30 generations in this Wright-Fisher population, what will the expected identity by descent be?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
When both drift and selection are acting on a locus (alleles are not neutral and the population size is finite), which of the following can occur?
A) Natural selection can increase the effect of genetic drift.
B) Neutral mutations are subject to natural selection.
C) Genetic drift can result in heterozygous advantage.
D) Beneficial mutations can be lost from the population.
A) Natural selection can increase the effect of genetic drift.
B) Neutral mutations are subject to natural selection.
C) Genetic drift can result in heterozygous advantage.
D) Beneficial mutations can be lost from the population.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Imagine that, of three species, it is known that species 1 and 3 were separated 10 million years ago, based on geologic measurements. Genetic analysis at a neutral locus indicates that these species differ by 100 substitutions. If there are 10 substitutions separating species 1 and 2, approximately how long ago did these species diverge?
A) 0.1 million years ago
B) 1 million years ago
C) 10 million years ago
D) 100 million years ago
A) 0.1 million years ago
B) 1 million years ago
C) 10 million years ago
D) 100 million years ago

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
If neutral mutations occur at the rate of 0.5 per individual per generation, the rate of neutral substitutions per generation in that population will equal
A) 2Ne * 0.5.
B) (1/2Ne) *0.5.
C) 2Ne.
D) 0.5.
A) 2Ne * 0.5.
B) (1/2Ne) *0.5.
C) 2Ne.
D) 0.5.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
The figure shows aligned homologous gene sequences from two species. What is the dominant evolutionary force acting on this gene in these species? 
A) positive selection
B) recombination
C) genetic drift
D) purifying selection

A) positive selection
B) recombination
C) genetic drift
D) purifying selection

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
The molecular clock has limited usefulness for estimating divergence times among species in part due to the saturation of DNA sequences. This occurs because
A) DNA sequences are unable to revert back to previous allelic states.
B) the variation in the substitution rate between closely related lineages prevents accurate estimation of divergence time.
C) variation in population sizes among lineages changes the effect of genetic drift.
D) in highly diverged lineages, substitutions will occur at sites that have been substituted previously.
A) DNA sequences are unable to revert back to previous allelic states.
B) the variation in the substitution rate between closely related lineages prevents accurate estimation of divergence time.
C) variation in population sizes among lineages changes the effect of genetic drift.
D) in highly diverged lineages, substitutions will occur at sites that have been substituted previously.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
A comparison of 11,000 protein-coding genes from humans and chimpanzees revealed a significantly higher ratio of nonsynonymous to synonymous polymorphism in humans compared to the ratio of nonsynonymous to synonymous substitutions between the two species, that is, pN/pS > dN/dS. What does this indicate about the variation in human populations?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
Gene trees and species trees both depict evolutionary relationships. What is the difference between these two types of trees?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
Consider two species, 1 and 2, that experience different mutation rates with m1 < m2, and have populations sizes of Ne1 < Ne2. Which species would you expect to have a lower frequency of heterozygotes at a neutral locus? Explain your reasoning.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
Do you expect to find more or less variation in a population with short coalescence times relative to a population with long coalescence times? Explain your answer.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Explain why the probability of fixation of a new beneficial allele is independent of population size
in Haldane's model of selection and drift.
in Haldane's model of selection and drift.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
Why might a wind-pollinated plant experience different levels of diversity in mitochondrial versus nuclear loci following a postglacial recolonization event?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
Ka measures the rate of nonsynonymous substitutions. Why is the ratio of Ka /Ks used to test for positive selection rather than just Ka alone?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
The neutral theory predicts a constant rate of substitutions per generation; however, molecular clock estimates show that substitutions accumulate annually regardless of the generation time. What explanation for this discrepancy is illustrated in the figure? 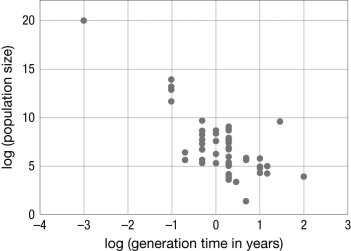


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
How are the neutral theory of molecular evolution and the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium similar?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
In a population of mice there are two alleles for coat color, with the brown allele beneficial over the white allele. Under what conditions would the alleles be effectively neutral if the effective population size is 200?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 50 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








