Deck 15: Chemical Kinetics
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/128
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 15: Chemical Kinetics
1
For the reaction 2A + 3B 4C + 5D, the rate of the reaction in terms of B would be written as __________
A) - B/ t
B) + B/ t
C) -1/3 B/ t
D) +1/3 B/ t
E) -3 B/ t
A) - B/ t
B) + B/ t
C) -1/3 B/ t
D) +1/3 B/ t
E) -3 B/ t
-1/3 B/ t
2
For the reaction 2A + 3B 4C + 5D, the rate of the reaction in terms of C would be written as __________
A) + C/ t
B) +4 C/ t
C) +1/4 C/ t
D) -4 C/ t
E) -1/4 C/ t
A) + C/ t
B) +4 C/ t
C) +1/4 C/ t
D) -4 C/ t
E) -1/4 C/ t
+1/4 C/ t
3
Indicate which of the following compounds is not a component of photochemical smog.
A) O3
B) H2O
C) NO2
D) NO
E) Organic molecules
A) O3
B) H2O
C) NO2
D) NO
E) Organic molecules
H2O
4
At what time of day are ozone concentrations highest during a photochemical smog event?
A) in the morning before rush hour
B) in the morning just after rush hour
C) midmorning
D) noon
E) midafternoon
A) in the morning before rush hour
B) in the morning just after rush hour
C) midmorning
D) noon
E) midafternoon

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
For the reaction 2A + 3B 4C + 5D, the rate of the reaction in terms of A would be written as __________
A) - A/ t.
B) -1/2 A/ t.
C) + A/ t.
D) +1/2 A/ t.
E) -2 A/ t.
A) - A/ t.
B) -1/2 A/ t.
C) + A/ t.
D) +1/2 A/ t.
E) -2 A/ t.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
The device in automobiles that has decreased NO and partially oxidized hydrocarbons from exhaust gases is termed a(n) __________
A) catalytic intermediate.
B) photochemical inhibitor.
C) catalytic linker.
D) nitrogen monoxide reducer.
E) catalytic converter.
A) catalytic intermediate.
B) photochemical inhibitor.
C) catalytic linker.
D) nitrogen monoxide reducer.
E) catalytic converter.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
The order in which ozone, nitrogen monoxide, and nitrogen dioxide build up in the atmosphere over the course of the day is in the order __________ then __________ then __________
A) NO; NO2; O3.
B) NO; O3; NO2.
C) NO2; NO; O3.
D) NO2; O3; NO.
E) O3; NO; NO2.
A) NO; NO2; O3.
B) NO; O3; NO2.
C) NO2; NO; O3.
D) NO2; O3; NO.
E) O3; NO; NO2.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
In the combustion of methane, CH4(g) + 2 O2(g) CO2(g) + 2 H2O (g), which reactant has the greatest rate of disappearance?
A) CH4
B) O2
C) CO2
D) H2O
E) CH4 and O2 have the same rate of disappearance.
A) CH4
B) O2
C) CO2
D) H2O
E) CH4 and O2 have the same rate of disappearance.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Assuming that each of the following graphs has the same concentration and time axes, which has the greatest initial rate of disappearance of reactant?
A)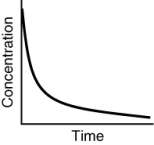
B)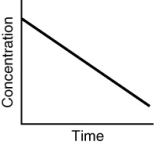
C)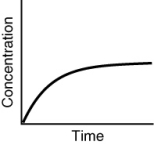
D)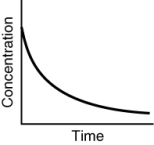
A)

B)

C)

D)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Indicate which of the following compounds is a component of photochemical smog.
A) H2O
B) CO2
C) N2O
D) O3
E) CO
A) H2O
B) CO2
C) N2O
D) O3
E) CO

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Which of the following statements is true about the instantaneous rate for the chemical reaction A B as the reaction progresses?
A) - A/ t increases while B/ t decreases
B) - A/ t decreases while B/ t increases
C) both - A/ t and B/ t decrease
D) both - A/ t and B/ t increase
E) The answer will vary depending on the reaction mechanism.
A) - A/ t increases while B/ t decreases
B) - A/ t decreases while B/ t increases
C) both - A/ t and B/ t decrease
D) both - A/ t and B/ t increase
E) The answer will vary depending on the reaction mechanism.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
The following graph shows the kinetics curves for the reaction of oxygen with hydrogen to form water: O2(g) + 2H2(g) 2H2O(g). Which curve is hydrogen? 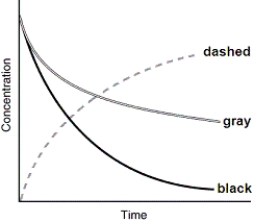
A) the dashed curve
B) the gray curve
C) the black curve
D) either the gray or the black curve
E) Any of these curves could be hydrogen.

A) the dashed curve
B) the gray curve
C) the black curve
D) either the gray or the black curve
E) Any of these curves could be hydrogen.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Large cities often issue ozone advisories. At what time of year would an advisory be likely to occur most often?
A) winter
B) spring
C) summer
D) fall
E) No season should have more advisories than another.
A) winter
B) spring
C) summer
D) fall
E) No season should have more advisories than another.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Smog created by the interaction of sunlight with nitrogen oxides and volatile organic compounds is termed __________ smog.
A) photolytic
B) photochemical
C) photophysical
D) acid
E) sulfurous
A) photolytic
B) photochemical
C) photophysical
D) acid
E) sulfurous

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Which of the following is not important as a contributing factor to photochemical smog?
A) stagnant air
B) sunlight
C) lots of traffic
D) irrigation
E) cars without catalytic converters
A) stagnant air
B) sunlight
C) lots of traffic
D) irrigation
E) cars without catalytic converters

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
NO2 contributes to the "brown haze" associated with photochemical smog events. At what time of day is NO2 concentration highest?
A) in the morning before rush hour
B) in the morning just after rush hour
C) midmorning
D) noon
E) midafternoon
A) in the morning before rush hour
B) in the morning just after rush hour
C) midmorning
D) noon
E) midafternoon

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
The greatest NO concentration is observed __________
A) in the morning before rush hour.
B) in the morning just after rush hour.
C) in midmorning.
D) at noon.
E) in midafternoon.
A) in the morning before rush hour.
B) in the morning just after rush hour.
C) in midmorning.
D) at noon.
E) in midafternoon.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
For the reaction 2A + 3B 4C + 5D, the rate of the reaction in terms of D would be written as __________
A) + D/ t
B) +5 D/ t
C) +1/5 D/ t
D) -5 D/ t
E) -1/5 D/ t
A) + D/ t
B) +5 D/ t
C) +1/5 D/ t
D) -5 D/ t
E) -1/5 D/ t

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
When one chemical is a precursor of another chemical in a series of reactions, the concentrations of the two species are said to be __________
A) catalytic.
B) volatile.
C) coalescent.
D) linked.
E) intermediate.
A) catalytic.
B) volatile.
C) coalescent.
D) linked.
E) intermediate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Which of the following is not a possible graph of concentration versus time for a reactant?
A)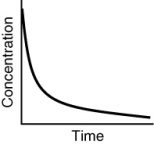
B)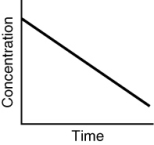
C)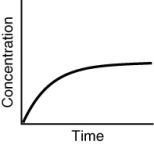
D)
A)

B)

C)

D)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
The rate of disappearance of HI in the reaction 2HI(g) I2(g) + H2(g) is shown in the following figure. What is the instantaneous rate of this reaction at t = 5 s? 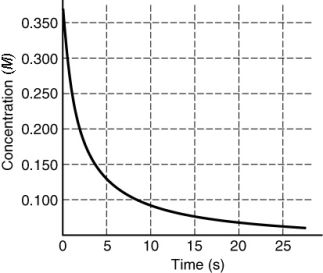
A) 0.2 M/s
B) 0.01 M/s
C) 0.02 M/s
D) 0.100 M/s
E) 0.04 M/s

A) 0.2 M/s
B) 0.01 M/s
C) 0.02 M/s
D) 0.100 M/s
E) 0.04 M/s

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
HI dissociates to form I2 and H2: 2HI(g) H2(g) + I2(g)
If the concentration of HI changes at a rate of -0.45 M/s, what is the rate of appearance of I2(g)?
A) 0.90 M/s
B) 0.45 M/s
C) 0.23 M/s
D) 1.00 M/s
E) 0.13 M/s
If the concentration of HI changes at a rate of -0.45 M/s, what is the rate of appearance of I2(g)?
A) 0.90 M/s
B) 0.45 M/s
C) 0.23 M/s
D) 1.00 M/s
E) 0.13 M/s

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
If the rate of the reaction: 2O3(g) 3O2(g)
Is 0.250 M/s over the first 5.50 s, how much oxygen will form during this time?
A) 1.38 M
B) 4.13 M
C) 0.69 M
D) 0.25 M
E) 0.46 M
Is 0.250 M/s over the first 5.50 s, how much oxygen will form during this time?
A) 1.38 M
B) 4.13 M
C) 0.69 M
D) 0.25 M
E) 0.46 M

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Which of the following does the initial rate of a chemical reaction depend on?
(I)Concentration of reactants
(II)Concentration of products
(III)Temperature
A) I
B) III
C) II
D) Both I and III
E) I, II, and III
(I)Concentration of reactants
(II)Concentration of products
(III)Temperature
A) I
B) III
C) II
D) Both I and III
E) I, II, and III

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
The difference between an average rate and an instantaneous rate is __________
A) the average rate is taken over a larger time period.
B) the instantaneous rate is taken from the slope of the curve at a specific time.
C) they are not different if the time interval chosen is small enough.
D) All the above are correct.
A) the average rate is taken over a larger time period.
B) the instantaneous rate is taken from the slope of the curve at a specific time.
C) they are not different if the time interval chosen is small enough.
D) All the above are correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
For the rate law Rate = k[A][B]3/2, the partial order with respect to A is __________, the partial order with respect to B is __________, and the total order is __________.
A) 0;![<strong>For the rate law Rate = k[A][B]<sup>3/2</sup>, the partial order with respect to A is __________, the partial order with respect to B is __________, and the total order is __________.</strong> A) 0; ; B) 1; ; 1 C) 1; ; D) 1; ; E) The orders cannot be determined without a chemical reaction.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_089c_c220_95d8_37a5819f901c_TB3833_11.jpg) ;
; ![<strong>For the rate law Rate = k[A][B]<sup>3/2</sup>, the partial order with respect to A is __________, the partial order with respect to B is __________, and the total order is __________.</strong> A) 0; ; B) 1; ; 1 C) 1; ; D) 1; ; E) The orders cannot be determined without a chemical reaction.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_089c_c221_95d8_551f97a9a0c8_TB3833_11.jpg)
B) 1;![<strong>For the rate law Rate = k[A][B]<sup>3/2</sup>, the partial order with respect to A is __________, the partial order with respect to B is __________, and the total order is __________.</strong> A) 0; ; B) 1; ; 1 C) 1; ; D) 1; ; E) The orders cannot be determined without a chemical reaction.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_089c_c222_95d8_e5f3afe2d79a_TB3833_11.jpg) ; 1
; 1
C) 1;![<strong>For the rate law Rate = k[A][B]<sup>3/2</sup>, the partial order with respect to A is __________, the partial order with respect to B is __________, and the total order is __________.</strong> A) 0; ; B) 1; ; 1 C) 1; ; D) 1; ; E) The orders cannot be determined without a chemical reaction.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_089c_c223_95d8_3510d385c049_TB3833_00.jpg) ;
; ![<strong>For the rate law Rate = k[A][B]<sup>3/2</sup>, the partial order with respect to A is __________, the partial order with respect to B is __________, and the total order is __________.</strong> A) 0; ; B) 1; ; 1 C) 1; ; D) 1; ; E) The orders cannot be determined without a chemical reaction.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_089c_c224_95d8_41f4e137443b_TB3833_11.jpg)
D) 1;![<strong>For the rate law Rate = k[A][B]<sup>3/2</sup>, the partial order with respect to A is __________, the partial order with respect to B is __________, and the total order is __________.</strong> A) 0; ; B) 1; ; 1 C) 1; ; D) 1; ; E) The orders cannot be determined without a chemical reaction.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_089c_e935_95d8_d31c4c811f96_TB3833_00.jpg) ;
; ![<strong>For the rate law Rate = k[A][B]<sup>3/2</sup>, the partial order with respect to A is __________, the partial order with respect to B is __________, and the total order is __________.</strong> A) 0; ; B) 1; ; 1 C) 1; ; D) 1; ; E) The orders cannot be determined without a chemical reaction.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_089c_e936_95d8_913091d33c85_TB3833_11.jpg)
E) The orders cannot be determined without a chemical reaction.
A) 0;
![<strong>For the rate law Rate = k[A][B]<sup>3/2</sup>, the partial order with respect to A is __________, the partial order with respect to B is __________, and the total order is __________.</strong> A) 0; ; B) 1; ; 1 C) 1; ; D) 1; ; E) The orders cannot be determined without a chemical reaction.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_089c_c220_95d8_37a5819f901c_TB3833_11.jpg) ;
; ![<strong>For the rate law Rate = k[A][B]<sup>3/2</sup>, the partial order with respect to A is __________, the partial order with respect to B is __________, and the total order is __________.</strong> A) 0; ; B) 1; ; 1 C) 1; ; D) 1; ; E) The orders cannot be determined without a chemical reaction.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_089c_c221_95d8_551f97a9a0c8_TB3833_11.jpg)
B) 1;
![<strong>For the rate law Rate = k[A][B]<sup>3/2</sup>, the partial order with respect to A is __________, the partial order with respect to B is __________, and the total order is __________.</strong> A) 0; ; B) 1; ; 1 C) 1; ; D) 1; ; E) The orders cannot be determined without a chemical reaction.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_089c_c222_95d8_e5f3afe2d79a_TB3833_11.jpg) ; 1
; 1C) 1;
![<strong>For the rate law Rate = k[A][B]<sup>3/2</sup>, the partial order with respect to A is __________, the partial order with respect to B is __________, and the total order is __________.</strong> A) 0; ; B) 1; ; 1 C) 1; ; D) 1; ; E) The orders cannot be determined without a chemical reaction.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_089c_c223_95d8_3510d385c049_TB3833_00.jpg) ;
; ![<strong>For the rate law Rate = k[A][B]<sup>3/2</sup>, the partial order with respect to A is __________, the partial order with respect to B is __________, and the total order is __________.</strong> A) 0; ; B) 1; ; 1 C) 1; ; D) 1; ; E) The orders cannot be determined without a chemical reaction.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_089c_c224_95d8_41f4e137443b_TB3833_11.jpg)
D) 1;
![<strong>For the rate law Rate = k[A][B]<sup>3/2</sup>, the partial order with respect to A is __________, the partial order with respect to B is __________, and the total order is __________.</strong> A) 0; ; B) 1; ; 1 C) 1; ; D) 1; ; E) The orders cannot be determined without a chemical reaction.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_089c_e935_95d8_d31c4c811f96_TB3833_00.jpg) ;
; ![<strong>For the rate law Rate = k[A][B]<sup>3/2</sup>, the partial order with respect to A is __________, the partial order with respect to B is __________, and the total order is __________.</strong> A) 0; ; B) 1; ; 1 C) 1; ; D) 1; ; E) The orders cannot be determined without a chemical reaction.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_089c_e936_95d8_913091d33c85_TB3833_11.jpg)
E) The orders cannot be determined without a chemical reaction.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
If the rate of appearance of O2 in the reaction: 2O3(g) 3O2(g)
Is 0.250 M/s over the first 5.50 s, how much oxygen will form during this time?
A) 1.38 M
B) 4.13 M
C) 0.69 M
D) 0.25 M
E) 0.46 M
Is 0.250 M/s over the first 5.50 s, how much oxygen will form during this time?
A) 1.38 M
B) 4.13 M
C) 0.69 M
D) 0.25 M
E) 0.46 M

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
For the rate law Rate = k[A][B]1/2, the partial order with respect to A is __________, the partial order with respect to B is __________, and the total order is __________.
A) 0;![<strong>For the rate law Rate = k[A][B]<sup>1/2</sup>, the partial order with respect to A is __________, the partial order with respect to B is __________, and the total order is __________.</strong> A) 0; ; B) 1; ; 1 C) 1; ; D) 1; ; E) The orders cannot be determined without a chemical reaction.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_089c_25d2_95d8_15588b075c3a_TB3833_11.jpg) ;
; ![<strong>For the rate law Rate = k[A][B]<sup>1/2</sup>, the partial order with respect to A is __________, the partial order with respect to B is __________, and the total order is __________.</strong> A) 0; ; B) 1; ; 1 C) 1; ; D) 1; ; E) The orders cannot be determined without a chemical reaction.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_089c_25d3_95d8_eb048897a822_TB3833_11.jpg)
B) 1;![<strong>For the rate law Rate = k[A][B]<sup>1/2</sup>, the partial order with respect to A is __________, the partial order with respect to B is __________, and the total order is __________.</strong> A) 0; ; B) 1; ; 1 C) 1; ; D) 1; ; E) The orders cannot be determined without a chemical reaction.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_089c_4ce4_95d8_ad48106178e1_TB3833_11.jpg) ; 1
; 1
C) 1;![<strong>For the rate law Rate = k[A][B]<sup>1/2</sup>, the partial order with respect to A is __________, the partial order with respect to B is __________, and the total order is __________.</strong> A) 0; ; B) 1; ; 1 C) 1; ; D) 1; ; E) The orders cannot be determined without a chemical reaction.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_089c_4ce5_95d8_a59a89d36982_TB3833_11.jpg) ;
; ![<strong>For the rate law Rate = k[A][B]<sup>1/2</sup>, the partial order with respect to A is __________, the partial order with respect to B is __________, and the total order is __________.</strong> A) 0; ; B) 1; ; 1 C) 1; ; D) 1; ; E) The orders cannot be determined without a chemical reaction.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_089c_4ce6_95d8_a79d7e6d927c_TB3833_11.jpg)
D) 1;![<strong>For the rate law Rate = k[A][B]<sup>1/2</sup>, the partial order with respect to A is __________, the partial order with respect to B is __________, and the total order is __________.</strong> A) 0; ; B) 1; ; 1 C) 1; ; D) 1; ; E) The orders cannot be determined without a chemical reaction.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_089c_4ce7_95d8_cf6c1f7b369e_TB3833_11.jpg) ;
; ![<strong>For the rate law Rate = k[A][B]<sup>1/2</sup>, the partial order with respect to A is __________, the partial order with respect to B is __________, and the total order is __________.</strong> A) 0; ; B) 1; ; 1 C) 1; ; D) 1; ; E) The orders cannot be determined without a chemical reaction.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_089c_73f8_95d8_01f0bb2cd98a_TB3833_00.jpg)
E) The orders cannot be determined without a chemical reaction.
A) 0;
![<strong>For the rate law Rate = k[A][B]<sup>1/2</sup>, the partial order with respect to A is __________, the partial order with respect to B is __________, and the total order is __________.</strong> A) 0; ; B) 1; ; 1 C) 1; ; D) 1; ; E) The orders cannot be determined without a chemical reaction.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_089c_25d2_95d8_15588b075c3a_TB3833_11.jpg) ;
; ![<strong>For the rate law Rate = k[A][B]<sup>1/2</sup>, the partial order with respect to A is __________, the partial order with respect to B is __________, and the total order is __________.</strong> A) 0; ; B) 1; ; 1 C) 1; ; D) 1; ; E) The orders cannot be determined without a chemical reaction.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_089c_25d3_95d8_eb048897a822_TB3833_11.jpg)
B) 1;
![<strong>For the rate law Rate = k[A][B]<sup>1/2</sup>, the partial order with respect to A is __________, the partial order with respect to B is __________, and the total order is __________.</strong> A) 0; ; B) 1; ; 1 C) 1; ; D) 1; ; E) The orders cannot be determined without a chemical reaction.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_089c_4ce4_95d8_ad48106178e1_TB3833_11.jpg) ; 1
; 1C) 1;
![<strong>For the rate law Rate = k[A][B]<sup>1/2</sup>, the partial order with respect to A is __________, the partial order with respect to B is __________, and the total order is __________.</strong> A) 0; ; B) 1; ; 1 C) 1; ; D) 1; ; E) The orders cannot be determined without a chemical reaction.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_089c_4ce5_95d8_a59a89d36982_TB3833_11.jpg) ;
; ![<strong>For the rate law Rate = k[A][B]<sup>1/2</sup>, the partial order with respect to A is __________, the partial order with respect to B is __________, and the total order is __________.</strong> A) 0; ; B) 1; ; 1 C) 1; ; D) 1; ; E) The orders cannot be determined without a chemical reaction.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_089c_4ce6_95d8_a79d7e6d927c_TB3833_11.jpg)
D) 1;
![<strong>For the rate law Rate = k[A][B]<sup>1/2</sup>, the partial order with respect to A is __________, the partial order with respect to B is __________, and the total order is __________.</strong> A) 0; ; B) 1; ; 1 C) 1; ; D) 1; ; E) The orders cannot be determined without a chemical reaction.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_089c_4ce7_95d8_cf6c1f7b369e_TB3833_11.jpg) ;
; ![<strong>For the rate law Rate = k[A][B]<sup>1/2</sup>, the partial order with respect to A is __________, the partial order with respect to B is __________, and the total order is __________.</strong> A) 0; ; B) 1; ; 1 C) 1; ; D) 1; ; E) The orders cannot be determined without a chemical reaction.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_089c_73f8_95d8_01f0bb2cd98a_TB3833_00.jpg)
E) The orders cannot be determined without a chemical reaction.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
The reaction A + 2B C
Is first order in B and A. The overall order of the reaction is __________
A) first.
B) second.
C) third.
D) zero.
E) fourth.
Is first order in B and A. The overall order of the reaction is __________
A) first.
B) second.
C) third.
D) zero.
E) fourth.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
For the rate law Rate = k[A]3/2[B], the partial order with respect to A is __________, the partial order with respect to B is __________, and the total order is __________.
A)![<strong>For the rate law Rate = k[A]<sup>3/2</sup>[B], the partial order with respect to A is __________, the partial order with respect to B is __________, and the total order is __________.</strong> A) ; 0; B) ; 1; 1 C) ; 1; D) ; 1; E) The orders cannot be determined without a chemical reaction.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_089c_e937_95d8_b5530712f0ad_TB3833_11.jpg) ; 0;
; 0; ![<strong>For the rate law Rate = k[A]<sup>3/2</sup>[B], the partial order with respect to A is __________, the partial order with respect to B is __________, and the total order is __________.</strong> A) ; 0; B) ; 1; 1 C) ; 1; D) ; 1; E) The orders cannot be determined without a chemical reaction.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_089d_1048_95d8_5f0baf37dd94_TB3833_11.jpg)
B)![<strong>For the rate law Rate = k[A]<sup>3/2</sup>[B], the partial order with respect to A is __________, the partial order with respect to B is __________, and the total order is __________.</strong> A) ; 0; B) ; 1; 1 C) ; 1; D) ; 1; E) The orders cannot be determined without a chemical reaction.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_089d_1049_95d8_033c14648101_TB3833_11.jpg) ; 1; 1
; 1; 1
C)![<strong>For the rate law Rate = k[A]<sup>3/2</sup>[B], the partial order with respect to A is __________, the partial order with respect to B is __________, and the total order is __________.</strong> A) ; 0; B) ; 1; 1 C) ; 1; D) ; 1; E) The orders cannot be determined without a chemical reaction.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_089d_104a_95d8_65c46d9f8741_TB3833_00.jpg) ; 1;
; 1; ![<strong>For the rate law Rate = k[A]<sup>3/2</sup>[B], the partial order with respect to A is __________, the partial order with respect to B is __________, and the total order is __________.</strong> A) ; 0; B) ; 1; 1 C) ; 1; D) ; 1; E) The orders cannot be determined without a chemical reaction.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_089d_104b_95d8_95a0c8978728_TB3833_00.jpg)
D)![<strong>For the rate law Rate = k[A]<sup>3/2</sup>[B], the partial order with respect to A is __________, the partial order with respect to B is __________, and the total order is __________.</strong> A) ; 0; B) ; 1; 1 C) ; 1; D) ; 1; E) The orders cannot be determined without a chemical reaction.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_089d_104c_95d8_394c2e40979d_TB3833_11.jpg) ; 1;
; 1; ![<strong>For the rate law Rate = k[A]<sup>3/2</sup>[B], the partial order with respect to A is __________, the partial order with respect to B is __________, and the total order is __________.</strong> A) ; 0; B) ; 1; 1 C) ; 1; D) ; 1; E) The orders cannot be determined without a chemical reaction.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_089d_375d_95d8_2ff52fdfde61_TB3833_11.jpg)
E) The orders cannot be determined without a chemical reaction.
A)
![<strong>For the rate law Rate = k[A]<sup>3/2</sup>[B], the partial order with respect to A is __________, the partial order with respect to B is __________, and the total order is __________.</strong> A) ; 0; B) ; 1; 1 C) ; 1; D) ; 1; E) The orders cannot be determined without a chemical reaction.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_089c_e937_95d8_b5530712f0ad_TB3833_11.jpg) ; 0;
; 0; ![<strong>For the rate law Rate = k[A]<sup>3/2</sup>[B], the partial order with respect to A is __________, the partial order with respect to B is __________, and the total order is __________.</strong> A) ; 0; B) ; 1; 1 C) ; 1; D) ; 1; E) The orders cannot be determined without a chemical reaction.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_089d_1048_95d8_5f0baf37dd94_TB3833_11.jpg)
B)
![<strong>For the rate law Rate = k[A]<sup>3/2</sup>[B], the partial order with respect to A is __________, the partial order with respect to B is __________, and the total order is __________.</strong> A) ; 0; B) ; 1; 1 C) ; 1; D) ; 1; E) The orders cannot be determined without a chemical reaction.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_089d_1049_95d8_033c14648101_TB3833_11.jpg) ; 1; 1
; 1; 1C)
![<strong>For the rate law Rate = k[A]<sup>3/2</sup>[B], the partial order with respect to A is __________, the partial order with respect to B is __________, and the total order is __________.</strong> A) ; 0; B) ; 1; 1 C) ; 1; D) ; 1; E) The orders cannot be determined without a chemical reaction.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_089d_104a_95d8_65c46d9f8741_TB3833_00.jpg) ; 1;
; 1; ![<strong>For the rate law Rate = k[A]<sup>3/2</sup>[B], the partial order with respect to A is __________, the partial order with respect to B is __________, and the total order is __________.</strong> A) ; 0; B) ; 1; 1 C) ; 1; D) ; 1; E) The orders cannot be determined without a chemical reaction.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_089d_104b_95d8_95a0c8978728_TB3833_00.jpg)
D)
![<strong>For the rate law Rate = k[A]<sup>3/2</sup>[B], the partial order with respect to A is __________, the partial order with respect to B is __________, and the total order is __________.</strong> A) ; 0; B) ; 1; 1 C) ; 1; D) ; 1; E) The orders cannot be determined without a chemical reaction.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_089d_104c_95d8_394c2e40979d_TB3833_11.jpg) ; 1;
; 1; ![<strong>For the rate law Rate = k[A]<sup>3/2</sup>[B], the partial order with respect to A is __________, the partial order with respect to B is __________, and the total order is __________.</strong> A) ; 0; B) ; 1; 1 C) ; 1; D) ; 1; E) The orders cannot be determined without a chemical reaction.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_089d_375d_95d8_2ff52fdfde61_TB3833_11.jpg)
E) The orders cannot be determined without a chemical reaction.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
For the rate law Rate = k[A]1/2[B], the partial order with respect to A is __________, the partial order with respect to B is __________, and the total order is __________.
A)![<strong>For the rate law Rate = k[A]<sup>1/2</sup>[B], the partial order with respect to A is __________, the partial order with respect to B is __________, and the total order is __________.</strong> A) ; 0; B) ; 1; 1 C) ; 1; D) ; 1; E) The orders cannot be determined without a chemical reaction.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_089c_73f9_95d8_d9dbfdc2a256_TB3833_11.jpg) ; 0;
; 0; ![<strong>For the rate law Rate = k[A]<sup>1/2</sup>[B], the partial order with respect to A is __________, the partial order with respect to B is __________, and the total order is __________.</strong> A) ; 0; B) ; 1; 1 C) ; 1; D) ; 1; E) The orders cannot be determined without a chemical reaction.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_089c_73fa_95d8_b17784fe9313_TB3833_11.jpg)
B)![<strong>For the rate law Rate = k[A]<sup>1/2</sup>[B], the partial order with respect to A is __________, the partial order with respect to B is __________, and the total order is __________.</strong> A) ; 0; B) ; 1; 1 C) ; 1; D) ; 1; E) The orders cannot be determined without a chemical reaction.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_089c_73fb_95d8_df52db40b72a_TB3833_11.jpg) ; 1; 1
; 1; 1
C)![<strong>For the rate law Rate = k[A]<sup>1/2</sup>[B], the partial order with respect to A is __________, the partial order with respect to B is __________, and the total order is __________.</strong> A) ; 0; B) ; 1; 1 C) ; 1; D) ; 1; E) The orders cannot be determined without a chemical reaction.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_089c_9b0c_95d8_199ed5670fbb_TB3833_11.jpg) ; 1;
; 1; ![<strong>For the rate law Rate = k[A]<sup>1/2</sup>[B], the partial order with respect to A is __________, the partial order with respect to B is __________, and the total order is __________.</strong> A) ; 0; B) ; 1; 1 C) ; 1; D) ; 1; E) The orders cannot be determined without a chemical reaction.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_089c_9b0d_95d8_036bc50ac9e2_TB3833_11.jpg)
D)![<strong>For the rate law Rate = k[A]<sup>1/2</sup>[B], the partial order with respect to A is __________, the partial order with respect to B is __________, and the total order is __________.</strong> A) ; 0; B) ; 1; 1 C) ; 1; D) ; 1; E) The orders cannot be determined without a chemical reaction.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_089c_9b0e_95d8_b573831708bf_TB3833_11.jpg) ; 1;
; 1; ![<strong>For the rate law Rate = k[A]<sup>1/2</sup>[B], the partial order with respect to A is __________, the partial order with respect to B is __________, and the total order is __________.</strong> A) ; 0; B) ; 1; 1 C) ; 1; D) ; 1; E) The orders cannot be determined without a chemical reaction.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_089c_9b0f_95d8_95701d0411c9_TB3833_11.jpg)
E) The orders cannot be determined without a chemical reaction.
A)
![<strong>For the rate law Rate = k[A]<sup>1/2</sup>[B], the partial order with respect to A is __________, the partial order with respect to B is __________, and the total order is __________.</strong> A) ; 0; B) ; 1; 1 C) ; 1; D) ; 1; E) The orders cannot be determined without a chemical reaction.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_089c_73f9_95d8_d9dbfdc2a256_TB3833_11.jpg) ; 0;
; 0; ![<strong>For the rate law Rate = k[A]<sup>1/2</sup>[B], the partial order with respect to A is __________, the partial order with respect to B is __________, and the total order is __________.</strong> A) ; 0; B) ; 1; 1 C) ; 1; D) ; 1; E) The orders cannot be determined without a chemical reaction.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_089c_73fa_95d8_b17784fe9313_TB3833_11.jpg)
B)
![<strong>For the rate law Rate = k[A]<sup>1/2</sup>[B], the partial order with respect to A is __________, the partial order with respect to B is __________, and the total order is __________.</strong> A) ; 0; B) ; 1; 1 C) ; 1; D) ; 1; E) The orders cannot be determined without a chemical reaction.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_089c_73fb_95d8_df52db40b72a_TB3833_11.jpg) ; 1; 1
; 1; 1C)
![<strong>For the rate law Rate = k[A]<sup>1/2</sup>[B], the partial order with respect to A is __________, the partial order with respect to B is __________, and the total order is __________.</strong> A) ; 0; B) ; 1; 1 C) ; 1; D) ; 1; E) The orders cannot be determined without a chemical reaction.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_089c_9b0c_95d8_199ed5670fbb_TB3833_11.jpg) ; 1;
; 1; ![<strong>For the rate law Rate = k[A]<sup>1/2</sup>[B], the partial order with respect to A is __________, the partial order with respect to B is __________, and the total order is __________.</strong> A) ; 0; B) ; 1; 1 C) ; 1; D) ; 1; E) The orders cannot be determined without a chemical reaction.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_089c_9b0d_95d8_036bc50ac9e2_TB3833_11.jpg)
D)
![<strong>For the rate law Rate = k[A]<sup>1/2</sup>[B], the partial order with respect to A is __________, the partial order with respect to B is __________, and the total order is __________.</strong> A) ; 0; B) ; 1; 1 C) ; 1; D) ; 1; E) The orders cannot be determined without a chemical reaction.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_089c_9b0e_95d8_b573831708bf_TB3833_11.jpg) ; 1;
; 1; ![<strong>For the rate law Rate = k[A]<sup>1/2</sup>[B], the partial order with respect to A is __________, the partial order with respect to B is __________, and the total order is __________.</strong> A) ; 0; B) ; 1; 1 C) ; 1; D) ; 1; E) The orders cannot be determined without a chemical reaction.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3833/11eaae02_089c_9b0f_95d8_95701d0411c9_TB3833_11.jpg)
E) The orders cannot be determined without a chemical reaction.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
A scientist conducts an experiment to determine the rate of the following reaction: N2(g) + O2(g) 2NO(g)
If the initial concentration of N2 was 0.500 M and the concentration of N2 was 0.450 M after 0.100 s, what is the rate of the reaction?
A) 0.500 M/s
B) 1.00 M/s
C) 5.00 M/s
D) 10.0 M/s
E) 0.250 M/s
If the initial concentration of N2 was 0.500 M and the concentration of N2 was 0.450 M after 0.100 s, what is the rate of the reaction?
A) 0.500 M/s
B) 1.00 M/s
C) 5.00 M/s
D) 10.0 M/s
E) 0.250 M/s

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
If the rate of formation of ammonia is 0.345 M/s, what is the rate of disappearance of N2? 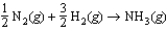
A) 0.173 M/s
B) 0.345 M/s
C) 0.690 M/s
D) 245 M/s
E) 0.518 M/s
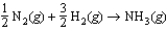
A) 0.173 M/s
B) 0.345 M/s
C) 0.690 M/s
D) 245 M/s
E) 0.518 M/s

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
A scientist conducts an experiment to determine the rate of NO formation in the reaction: N2(g) + O2(g) 2NO(g)
If the initial concentration of N2 was 0.500 M and the concentration of N2 was 0.450 M after 0.100 s, what is the rate of NO formation?
A) 0.500 M/s
B) 1.00 M/s
C) 5.00 M/s
D) 10.0 M/s
E) 0.250 M/s
If the initial concentration of N2 was 0.500 M and the concentration of N2 was 0.450 M after 0.100 s, what is the rate of NO formation?
A) 0.500 M/s
B) 1.00 M/s
C) 5.00 M/s
D) 10.0 M/s
E) 0.250 M/s

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
If the rate of formation of ammonia is 0.345 M/s, what is the rate of disappearance of N2? N2(g) + 3H2(g) 2NH3(g)
A) 0.173 M/s
B) 0.345 M/s
C) 0.690 M/s
D) 245 M/s
E) 0.518 M/s
A) 0.173 M/s
B) 0.345 M/s
C) 0.690 M/s
D) 245 M/s
E) 0.518 M/s

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
In a rate law, the partial orders are determined by __________
A) the reactant concentrations.
B) the stoichiometric coefficients.
C) the product concentrations.
D) experiment.
E) the difference between the forward and reverse rates.
A) the reactant concentrations.
B) the stoichiometric coefficients.
C) the product concentrations.
D) experiment.
E) the difference between the forward and reverse rates.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
If the reaction 3A + B + 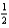 C 2D + E is first order overall, which of these could be the units of its rate constant, k?
C 2D + E is first order overall, which of these could be the units of its rate constant, k?
A) 1/s
B) M/s
C) 1/Ms
D) 1/Ms2
E) Ms
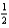 C 2D + E is first order overall, which of these could be the units of its rate constant, k?
C 2D + E is first order overall, which of these could be the units of its rate constant, k?A) 1/s
B) M/s
C) 1/Ms
D) 1/Ms2
E) Ms

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
Which of these could be the units of the rate constant for a first-order reaction?
A) M/s
B) 1/Ms
C) 1/Ms2
D) 1/s
E) Ms
A) M/s
B) 1/Ms
C) 1/Ms2
D) 1/s
E) Ms

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
Ammonia gas (NH3) is produced from hydrogen and nitrogen gas according to the following reaction: 3H2(g) + N2(g) 2NH3(g)
If the rate of production of ammonia is R(NH3), what is the rate of loss of hydrogen and nitrogen gas, respectively?
A) -R(H2) = 2/3 R(NH3); -R(N2) = 1/2 R(NH3)
B) -R(H2) = 3/2 R(NH3); -R(N2) = 2 R(NH3)
C) -R(H2) = 3/2 R(NH3); -R(N2) = 1/2 R(NH3)
D) -R(H2) = 2/3 R(NH3); -R(N2) = 2 R(NH3)
E) -R(H2) = R(NH3); -R(N2) = R(NH3)
If the rate of production of ammonia is R(NH3), what is the rate of loss of hydrogen and nitrogen gas, respectively?
A) -R(H2) = 2/3 R(NH3); -R(N2) = 1/2 R(NH3)
B) -R(H2) = 3/2 R(NH3); -R(N2) = 2 R(NH3)
C) -R(H2) = 3/2 R(NH3); -R(N2) = 1/2 R(NH3)
D) -R(H2) = 2/3 R(NH3); -R(N2) = 2 R(NH3)
E) -R(H2) = R(NH3); -R(N2) = R(NH3)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
A scientist conducts an experiment to determine the rate of the following reaction: N2(g) + O2(g) 2NO(g)
If the initial concentration of NO was 0.00 M and the concentration of NO was 0.050 M after 0.100 s, what is the rate of the reaction?
A) 0.500 M/s
B) 1.00 M/s
C) 5.00 M/s
D) 10.0 M/s
E) 0.250 M/s
If the initial concentration of NO was 0.00 M and the concentration of NO was 0.050 M after 0.100 s, what is the rate of the reaction?
A) 0.500 M/s
B) 1.00 M/s
C) 5.00 M/s
D) 10.0 M/s
E) 0.250 M/s

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
A second-order reaction (2A B) with a rate constant of 0.350 M-1s-1 is found to have a half-life of 3.45 s. What was the initial concentration of the reactant, [A]0?
A) 0.828 M
B) 0.201 M
C) 1.00 M
D) 1.21 M
E) 0.350 M
A) 0.828 M
B) 0.201 M
C) 1.00 M
D) 1.21 M
E) 0.350 M

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
The rate of a reaction is found to double when the concentration of one reactant is quadrupled. The order of the reaction with respect to this reactant is __________
A) first.
B) second.
C) one-quarter.
D) one-half.
E) third.
A) first.
B) second.
C) one-quarter.
D) one-half.
E) third.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
The first-order reaction A B, has k = 5.67 s-1. If [A]0 = 0.500 M, how long will it take [A] = 0.124 M?
A) 0.122 s
B) 0.100 s
C) 8.18 s
D) 0.244 s
E) 0.488 s
A) 0.122 s
B) 0.100 s
C) 8.18 s
D) 0.244 s
E) 0.488 s

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
Indicate which of the following plots would be obtained for a second-order reaction.
A)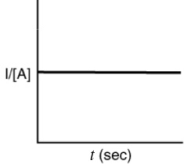
B)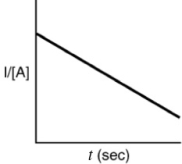
C)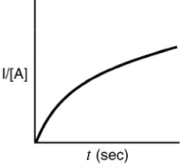
D)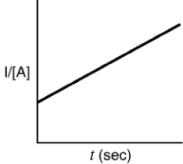
A)

B)

C)

D)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
The second-order reaction A + B C will obey pseudo first-order kinetics when __________
A) the concentrations of A and B are both small.
B) the concentration of one of the reactants does not change.
C) the concentration of C is large.
D) the concentrations of A and B are both large.
E) a catalyst changes the mechanism to a first-order reaction.
A) the concentrations of A and B are both small.
B) the concentration of one of the reactants does not change.
C) the concentration of C is large.
D) the concentrations of A and B are both large.
E) a catalyst changes the mechanism to a first-order reaction.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
Which of the following plots indicates that the reaction is zero order?
A)
B)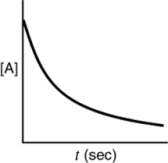
C)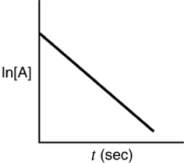
D)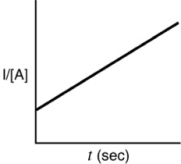
A)

B)

C)

D)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
Indicate which of the following plots would be obtained for a first-order reaction.
A)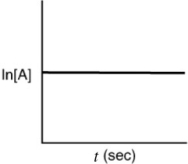
B)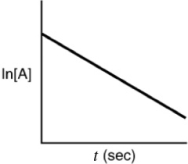
C)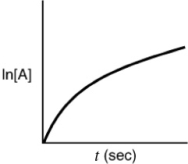
D)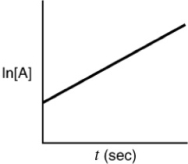
A)

B)

C)

D)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
The energy needed to form an activated complex is called __________
A) collision energy.
B) kinetic energy.
C) activation energy.
D) potential energy.
E) thermodynamic energy.
A) collision energy.
B) kinetic energy.
C) activation energy.
D) potential energy.
E) thermodynamic energy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
Which of these could be the units for the rate constant in a second-order reaction?
A) M-1 s
B) M s-1
C) M-1 s-1
D) M-2 s-1
E) Ms
A) M-1 s
B) M s-1
C) M-1 s-1
D) M-2 s-1
E) Ms

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
The half-life (t1/2) of a first-order reaction is 0.100 s. What is the rate constant?
A) 6.93 s-1
B) 0.693 s-1
C) 0.0693 s-1
D) 0.144 s-1
E) 3.01 s-1
A) 6.93 s-1
B) 0.693 s-1
C) 0.0693 s-1
D) 0.144 s-1
E) 3.01 s-1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
Which point as labeled by an asterisk (*) on the following energy profile is the transition state?
A)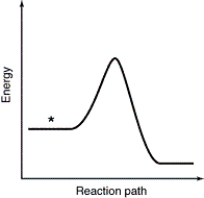
B)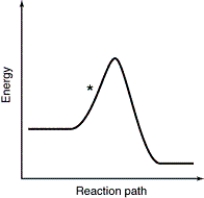
C)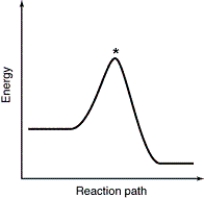
D)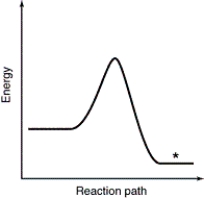
A)

B)

C)

D)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
Which of the following plots would indicate that a reaction was first order?
A)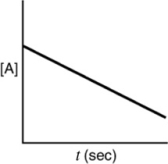
B)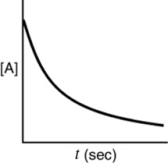
C)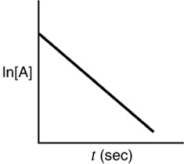
D)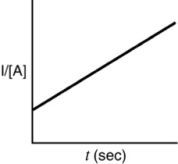
A)

B)

C)

D)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
The energy profiles for four different reactions are shown. Which reaction requires the most energetic collisions to reach the transition state? 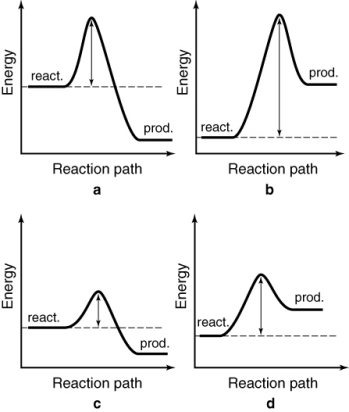
A) a
B) b
C) c
D) d

A) a
B) b
C) c
D) d

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
The reaction CHCl3(g) + Cl2(g) CCl4(g) + HCl(g) has the following rate law: Rate = k[CHCl3][Cl2]. If the concentration of CHCl3 is increased by a factor of five while the concentration of Cl2 is kept the same, the rate will __________
A) double.
B) triple.
C) stay the same.
D) increase by a factor of five.
E) decrease by a factor of one-fifth.
A) double.
B) triple.
C) stay the same.
D) increase by a factor of five.
E) decrease by a factor of one-fifth.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
The reaction 2NO(g) + O2(g) 2NO2(g) has the following rate law: Rate = k[O2][NO]2. If the concentration of NO is reduced by a factor of two, the rate will __________
A) double.
B) quadruple.
C) be reduced by one-quarter.
D) be reduced by one-half.
E) remain the same.
A) double.
B) quadruple.
C) be reduced by one-quarter.
D) be reduced by one-half.
E) remain the same.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
Collision theory assumes that the rate of a reaction depends on __________
A) the energy of collisions.
B) the orientation of colliding molecules.
C) the energy of collisions and the orientation of colliding molecules.
D) the change in energy between the products and the reactants.
E) the change in free energy between the reactants and products.
A) the energy of collisions.
B) the orientation of colliding molecules.
C) the energy of collisions and the orientation of colliding molecules.
D) the change in energy between the products and the reactants.
E) the change in free energy between the reactants and products.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
Which of the following plots indicates the reaction is second order?
A)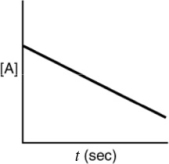
B)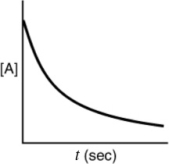
C)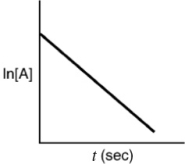
D)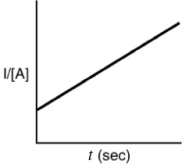
A)

B)

C)

D)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
The second-order reaction A B is found to have a rate constant of 0.978 M-1s-1. What is the half-life of this reaction when [A]0 = 0.0300 M?
A) 0.0293 s
B) 0.710 s
C) 34.1 s
D) 60.1 s
E) 24.3 s
A) 0.0293 s
B) 0.710 s
C) 34.1 s
D) 60.1 s
E) 24.3 s

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
The initial rate data for the reaction 2N2O5(g) 4NO2(g) + O2(g) is shown in the following table. Determine the value of the rate constant for this reaction. Experiment
[N2O5](M)
Rate (M/s)
1
2.56*103
450
2
1.28 *102
22.5
A) 4.09 s-1
B) 0.176 s-1
C) 0.0569 s-1
D) 0.225 s-1
E) 80.1 s-1
[N2O5](M)
Rate (M/s)
1
2.56*103
450
2
1.28 *102
22.5
A) 4.09 s-1
B) 0.176 s-1
C) 0.0569 s-1
D) 0.225 s-1
E) 80.1 s-1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
A reaction is first order in A. If the rate constant of the reaction is 3.45 *10-3 s-1, what is the half-life (t1/2) of the reaction?
A) 4.98 *10-3 s
B) 200 s
C) 3.45 *10-3 s
D) 100 s
E) 1.73 *10-3 s
A) 4.98 *10-3 s
B) 200 s
C) 3.45 *10-3 s
D) 100 s
E) 1.73 *10-3 s

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
The linear form of the Arrhenius equation is very useful, as it allows us to calculate the __________ from the slope and the __________ from the intercept.
A) frequency factor, activation energy
B) initial concentration, activation energy
C) activation energy, frequency factor
D) activation energy, Boltzmann constant
E) transition state, steric factor
A) frequency factor, activation energy
B) initial concentration, activation energy
C) activation energy, frequency factor
D) activation energy, Boltzmann constant
E) transition state, steric factor

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
Given the following data for the reaction A B, determine the activation energy, Ea, of the reaction. k (M/s)
T (K)
0)681
500
0)715
1000
A) 48.7 J/mol
B) 6.90 J/mol
C) 405 J/mol
D) 9.95 kJ/mol
E) 2.05 *10-2 kJ/mol
T (K)
0)681
500
0)715
1000
A) 48.7 J/mol
B) 6.90 J/mol
C) 405 J/mol
D) 9.95 kJ/mol
E) 2.05 *10-2 kJ/mol

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
The linear form of the Arrhenius equation is very useful, as a plot of ____________ allows us to calculate the activation energy and the frequency factor.
A) the rate constant vs. temperature
B) the logarithm of the rate constant vs. the temperature
C) the rate constant vs. the inverse temperature
D) the logarithm of the rate constant vs. the inverse temperature
E) the inverse rate constant vs. the logarithm of the temperature
A) the rate constant vs. temperature
B) the logarithm of the rate constant vs. the temperature
C) the rate constant vs. the inverse temperature
D) the logarithm of the rate constant vs. the inverse temperature
E) the inverse rate constant vs. the logarithm of the temperature

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
The following figure shows Arrhenius plots for four different reactions. Which reaction has the lowest activation energy? 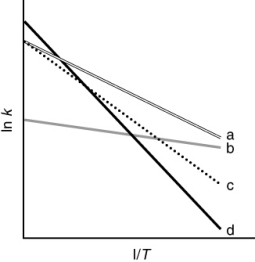
A) dashed
B) dotted
C) dash-dot
D) solid

A) dashed
B) dotted
C) dash-dot
D) solid

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
The energy profiles for four different reactions are shown. Which reaction requires the least energetic collisions to reach the transition state? 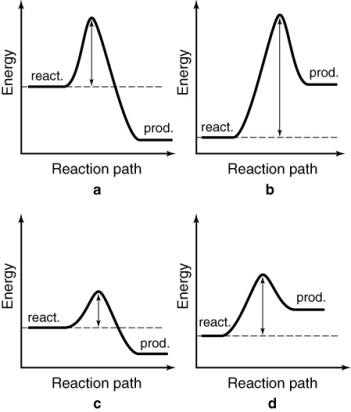
A) a
B) b
C) c
D) d

A) a
B) b
C) c
D) d

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
The following figure shows Arrhenius plots for four different reactions. Which reaction has the greatest activation energy? 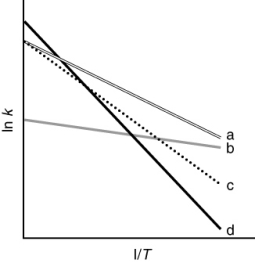
A) dashed
B) dotted
C) dash-dot
D) solid

A) dashed
B) dotted
C) dash-dot
D) solid

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
The following figure shows Arrhenius plots for four different reactions. Which reaction has the largest frequency factor? 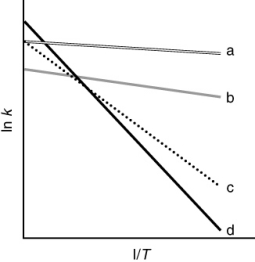
A) dashed
B) dotted
C) dash-dot
D) solid

A) dashed
B) dotted
C) dash-dot
D) solid

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
The linear form of the Arrhenius equation is very useful as it allows us to calculate the activation energy from the __________ and the frequency factor from the __________.
A) slope, intercept
B) half-life, rate constant
C) intercept, slope
D) rate constant, slope
E) change in ln k, change in (1/T)
A) slope, intercept
B) half-life, rate constant
C) intercept, slope
D) rate constant, slope
E) change in ln k, change in (1/T)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
Given the following data for the reaction A B, determine the frequency factor, A, of the reaction. k (M/s)
T (K)
0)730
250
0)739
450
A) +0.75
B) +0.719
C) +2.05
D) +0.287
E) -0.287
T (K)
0)730
250
0)739
450
A) +0.75
B) +0.719
C) +2.05
D) +0.287
E) -0.287

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
The following figure shows Arrhenius plots for four different reactions. Which reaction has the greatest temperature dependence? 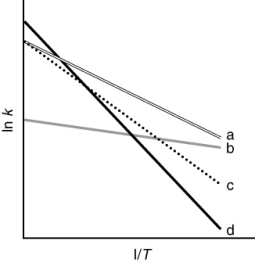
A) dashed
B) dotted
C) dash-dot
D) solid

A) dashed
B) dotted
C) dash-dot
D) solid

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
The linear form of __________ is very useful as it allows us to calculate the activation energy and the frequency factor.
A) the Boltzmann equation
B) the Arrhenius equation
C) Planck's equation
D) the rate law
E) the integrated rate law
A) the Boltzmann equation
B) the Arrhenius equation
C) Planck's equation
D) the rate law
E) the integrated rate law

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
Given the following data for the reaction A B, determine the activation energy, Ea, of the reaction. k (M/s)
T (K)
2)04 * 10-4
250
6)78* 10-3
400
A) 2.34 kJ/mol
B) 19.4 kJ/mol
C) 38.2 kJ/mol
D) 2.02 kJ/mol
E) 18.6 kJ/mol
T (K)
2)04 * 10-4
250
6)78* 10-3
400
A) 2.34 kJ/mol
B) 19.4 kJ/mol
C) 38.2 kJ/mol
D) 2.02 kJ/mol
E) 18.6 kJ/mol

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
The following energy profiles for four different reactions are shown. Which reaction is the most exothermic? 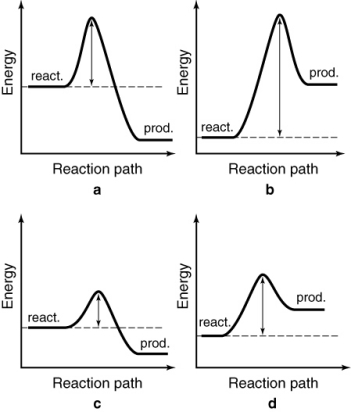
A) a
B) b
C) c
D) d

A) a
B) b
C) c
D) d

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
Given the following data for the reaction A B, determine the activation energy, Ea, of the reaction. k (M/s)
T (K)
0)730
250
0)739
450
A) 54.4 J/mol
B) 6.89 J/mol
C) 39.9 J/mol
D) 57.3 J/mol
E) 374 J/mol
T (K)
0)730
250
0)739
450
A) 54.4 J/mol
B) 6.89 J/mol
C) 39.9 J/mol
D) 57.3 J/mol
E) 374 J/mol

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
The energy profiles for four different reactions are shown. Which of the reactions will have the smallest rate constant?
A)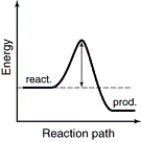
B)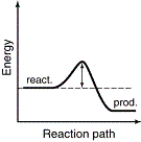
C)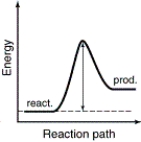
D)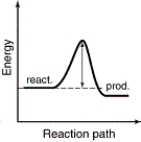
A)

B)

C)

D)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
The energy profiles for four different reactions are shown. Which of the reactions will have the largest rate constant? 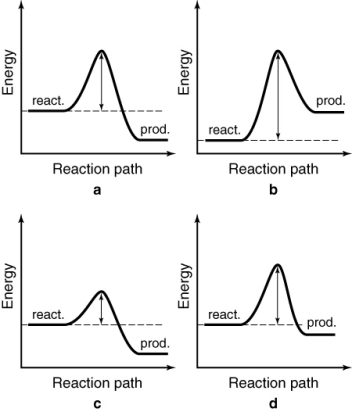
A) a
B) b
C) c
D) d

A) a
B) b
C) c
D) d

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
The following figure shows Arrhenius plots for four different reactions. Which reaction has the lowest frequency factor? 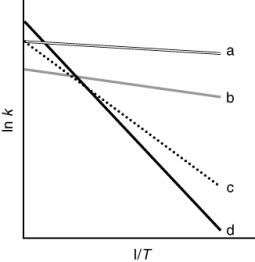
A) dashed
B) dotted
C) dash-dot
D) solid

A) dashed
B) dotted
C) dash-dot
D) solid

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
The following figure shows Arrhenius plots for four different reactions. Which reaction has the least temperature dependence? 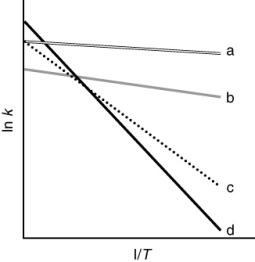
A) dashed
B) dotted
C) dash-dot
D) solid

A) dashed
B) dotted
C) dash-dot
D) solid

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
Given the following data for the reaction A B, determine the frequency factor, A, of the reaction. k (M/s)
T (K)
2)04 * 10-4
250
6)78 *10-3
400
A) 2.3
B) 5.3
C) 0.99
D) 0.63
E) 0.85
T (K)
2)04 * 10-4
250
6)78 *10-3
400
A) 2.3
B) 5.3
C) 0.99
D) 0.63
E) 0.85

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
The following energy profiles for four different reactions are shown. Which reaction is the most endothermic? 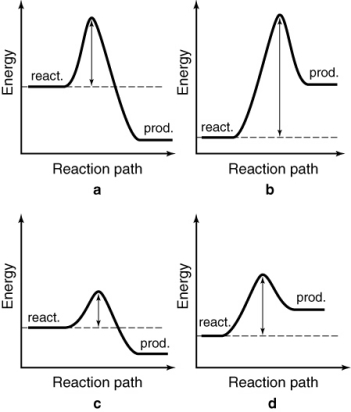
A) a
B) b
C) c
D) d

A) a
B) b
C) c
D) d

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 128 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








