Deck 13: Vector Calculus
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/56
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 13: Vector Calculus
1
Use Stokes' Theorem to evaluate 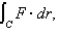 where
where 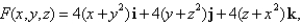 and
and 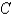 is the triangle with vertices
is the triangle with vertices 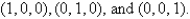
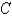 is oriented counterclockwise as viewed from above.
is oriented counterclockwise as viewed from above.
A)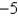
B)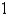
C)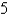
D)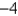
E)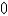
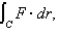 where
where 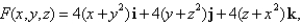 and
and 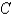 is the triangle with vertices
is the triangle with vertices 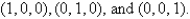
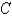 is oriented counterclockwise as viewed from above.
is oriented counterclockwise as viewed from above.A)
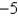
B)
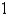
C)
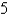
D)
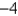
E)
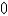
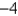
2
Assuming that S satisfies the conditions of the Divergence Theorem and the scalar functions and components of the vector fields have continuous second order partial derivatives,find 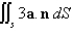 where a is the constant vector.
where a is the constant vector.
A) 3
B) 5
C) 7
D) 6
E) 8
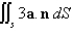 where a is the constant vector.
where a is the constant vector.A) 3
B) 5
C) 7
D) 6
E) 8
3
3
Use Stokes' Theorem to evaluate 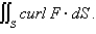
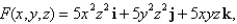
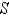 is the part of the paraboloid
is the part of the paraboloid 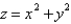 that lies inside the cylinder
that lies inside the cylinder 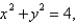 oriented upword.
oriented upword.
A) 2
B) 0
C) 1
D) 3
E) 4
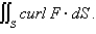
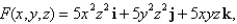
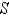 is the part of the paraboloid
is the part of the paraboloid 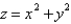 that lies inside the cylinder
that lies inside the cylinder 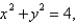 oriented upword.
oriented upword.A) 2
B) 0
C) 1
D) 3
E) 4
0
4
Set up,but do not evaluate,a double integral for the area of the surface with parametric equations 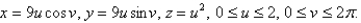
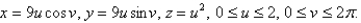

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
Use Gauss's Law to find the charge contained in the solid hemisphere 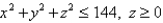 ,if the electric field is
,if the electric field is 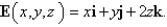
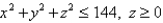 ,if the electric field is
,if the electric field is 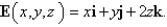

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Use Stokes' Theorem to evaluate 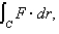 where
where 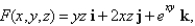
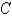 is the circle
is the circle 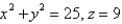 .
. 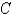 is oriented counterclockwise as viewed from above.
is oriented counterclockwise as viewed from above.
A)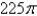
B)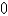
C)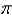
D)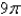
E)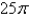
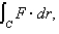 where
where 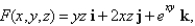
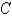 is the circle
is the circle 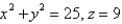 .
. 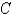 is oriented counterclockwise as viewed from above.
is oriented counterclockwise as viewed from above.A)
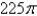
B)
C)
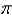
D)
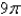
E)
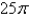

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Use Stoke's theorem to evaluate 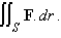
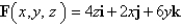 C is the curve of intersection of the plane z = x + 9 and the cylinder
C is the curve of intersection of the plane z = x + 9 and the cylinder 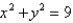
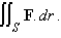
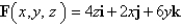 C is the curve of intersection of the plane z = x + 9 and the cylinder
C is the curve of intersection of the plane z = x + 9 and the cylinder 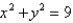

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
A fluid with density 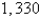 flows with velocity
flows with velocity 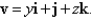 Find the rate of flow upward through the paraboloid
Find the rate of flow upward through the paraboloid 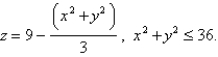
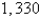 flows with velocity
flows with velocity 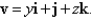 Find the rate of flow upward through the paraboloid
Find the rate of flow upward through the paraboloid 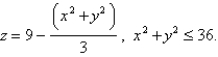

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Evaluate the surface integral. 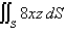 S is the part of the plane
S is the part of the plane 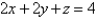 that lies in the first octant.
that lies in the first octant.
A)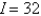
B)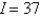
C)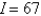
D)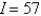
E)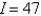
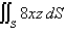 S is the part of the plane
S is the part of the plane 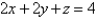 that lies in the first octant.
that lies in the first octant.A)
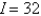
B)
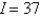
C)
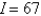
D)
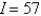
E)
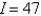

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Suppose that 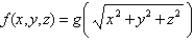 where g is a function of one variable such that
where g is a function of one variable such that 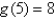 . Evaluate
. Evaluate 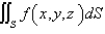 where S is the sphere
where S is the sphere 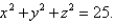
A)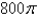
B)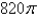
C)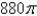
D)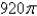
E) None of these
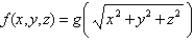 where g is a function of one variable such that
where g is a function of one variable such that 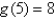 . Evaluate
. Evaluate 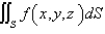 where S is the sphere
where S is the sphere 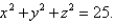
A)
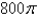
B)
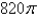
C)
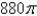
D)
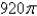
E) None of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Match the equation with one of the graphs below. 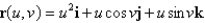
A)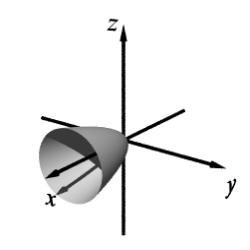
B)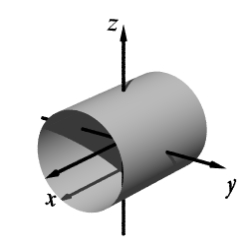
C)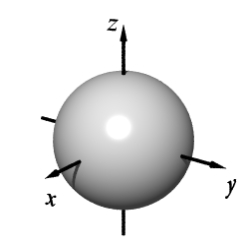
D)
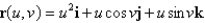
A)

B)

C)

D)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
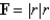 ,where
,where 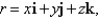 S consists of the hemisphere
S consists of the hemisphere 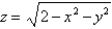 and the disk
and the disk 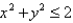 in the
in the 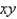 -plane.
-plane.A)
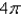
B)
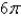
C)
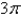
D)
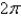
E)
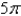

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Find the moment of inertia about the z-axis of a thin funnel in the shape of a cone 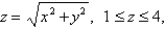 if its density function is
if its density function is 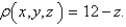
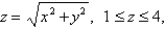 if its density function is
if its density function is 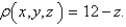

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Evaluate the surface integral 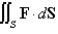 for the given vector field F and the oriented surface S.In other words,find the flux of F across S.
for the given vector field F and the oriented surface S.In other words,find the flux of F across S. 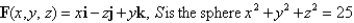 in the first octant,
in the first octant,
with orientation toward the origin.
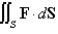 for the given vector field F and the oriented surface S.In other words,find the flux of F across S.
for the given vector field F and the oriented surface S.In other words,find the flux of F across S. 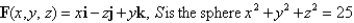 in the first octant,
in the first octant,with orientation toward the origin.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Evaluate the surface integral 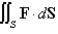 for the given vector field F and the oriented surface S.In other words,find the flux of F across S.
for the given vector field F and the oriented surface S.In other words,find the flux of F across S. 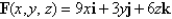

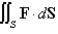 for the given vector field F and the oriented surface S.In other words,find the flux of F across S.
for the given vector field F and the oriented surface S.In other words,find the flux of F across S. 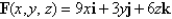


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Use the Divergence Theorem to calculate the surface integral 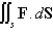 ; that is,calculate the flux of
; that is,calculate the flux of 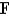 across
across 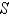 .
. 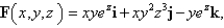 S is the surface of the box bounded by the coordinate planes and the planes
S is the surface of the box bounded by the coordinate planes and the planes 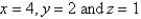 .
.
A)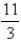
B)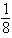
C)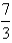
D)
E)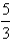
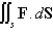 ; that is,calculate the flux of
; that is,calculate the flux of 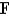 across
across 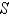 .
. 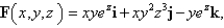 S is the surface of the box bounded by the coordinate planes and the planes
S is the surface of the box bounded by the coordinate planes and the planes 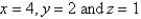 .
.A)
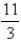
B)
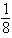
C)
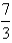
D)

E)
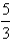

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
The temperature at the point 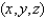 in a substance with conductivity
in a substance with conductivity 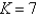 is
is 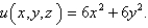 Find the rate of heat flow inward across the cylindrical
Find the rate of heat flow inward across the cylindrical 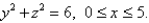
A)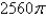
B)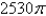
C)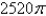
D)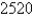
E)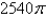
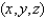 in a substance with conductivity
in a substance with conductivity 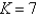 is
is 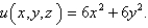 Find the rate of heat flow inward across the cylindrical
Find the rate of heat flow inward across the cylindrical 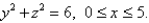
A)
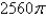
B)
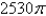
C)
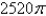
D)
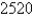
E)
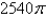

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
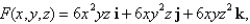
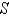 is the surface of the box enclosed by the planes
is the surface of the box enclosed by the planes 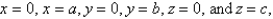 where
where 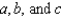 are positive numbers.
are positive numbers.A)
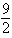
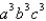
B)
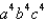
C)
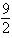
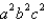
D) 12
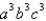
E) 12
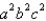

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Evaluate the surface integral.Round your answer to four decimal places. 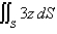 S is surface
S is surface 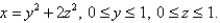
A)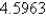
B)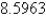
C)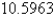
D)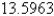
E)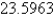
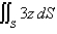 S is surface
S is surface 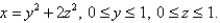
A)
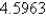
B)
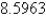
C)
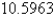
D)
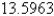
E)
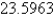

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Use Stokes' Theorem to evaluate 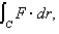 where
where 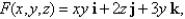
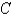 is the curve of intersection of the plane
is the curve of intersection of the plane 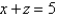 and the cylinder
and the cylinder 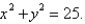
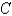 is oriented counterclockwise as viewed from above.
is oriented counterclockwise as viewed from above.
A)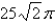
B)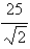
C)
D)
E)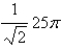
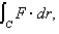 where
where 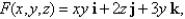
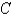 is the curve of intersection of the plane
is the curve of intersection of the plane 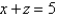 and the cylinder
and the cylinder 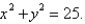
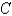 is oriented counterclockwise as viewed from above.
is oriented counterclockwise as viewed from above.A)
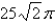
B)
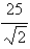
C)

D)

E)
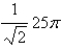

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Let f be a scalar field.Determine whether the expression is meaningful.If so,state whether the expression represents a scalar field or a vector field.
curl f
curl f

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Let 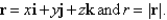
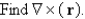
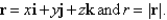
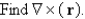

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Use Green's Theorem to find the work done by the force 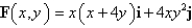 in moving a particle from the origin along the x-axis to (1,0)then along the line segment to
in moving a particle from the origin along the x-axis to (1,0)then along the line segment to
(0,1)and then back to the origin along the y-axis.
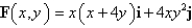 in moving a particle from the origin along the x-axis to (1,0)then along the line segment to
in moving a particle from the origin along the x-axis to (1,0)then along the line segment to(0,1)and then back to the origin along the y-axis.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Determine whether or not vector field is conservative.If it is conservative,find a function f such that 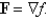
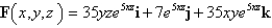
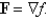
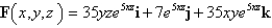

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Use Green's Theorem to evaluate the line integral along the positively oriented closed curve C. 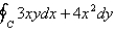 ,where C is the triangle with vertices
,where C is the triangle with vertices 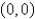 ,
, 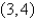 ,and
,and 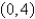 .
.
A)
B)
C)
D)
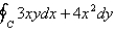 ,where C is the triangle with vertices
,where C is the triangle with vertices 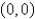 ,
, 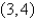 ,and
,and 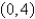 .
.A)
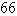
B)

C)
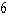
D)
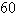

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Let f be a scalar field.Determine whether the expression is meaningful.If so,state whether the expression represents a scalar field or a vector field. 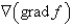
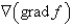

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Let 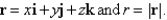
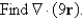
A) 18
B) 45
C) 27
D) 9
E) None of these
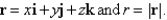
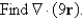
A) 18
B) 45
C) 27
D) 9
E) None of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Determine whether F is conservative.If so,find a function f such that 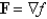 .
. 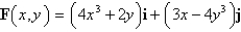
A)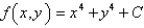
B)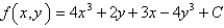
C)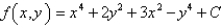
D) not conservative
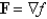 .
. 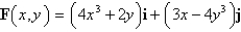
A)
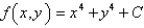
B)
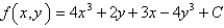
C)
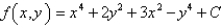
D) not conservative

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Use Green's Theorem to evaluate the line integral along the positively oriented closed curve C. 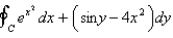 , where C is the boundary of the region bounded by the parabolas
, where C is the boundary of the region bounded by the parabolas 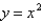 and
and 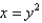 .
.
A)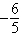 + e
+ e
B)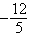
C)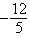 + e
+ e
D)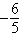
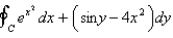 , where C is the boundary of the region bounded by the parabolas
, where C is the boundary of the region bounded by the parabolas 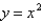 and
and 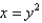 .
.A)
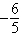 + e
+ eB)
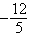
C)
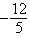 + e
+ eD)
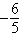

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
Find the area of the surface S where S is the part of the surface 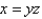 that lies inside the cylinder
that lies inside the cylinder 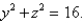
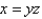 that lies inside the cylinder
that lies inside the cylinder 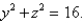

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Find the curl of the vector field. 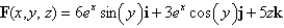
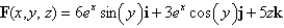

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Find an equation of the tangent plane to the parametric surface represented by r at the specified point. 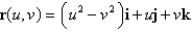 ;
; 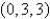
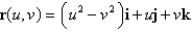 ;
; 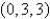

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
Find the curl of the vector field. 


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
Find the curl of the vector field F. 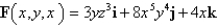
A)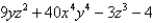
B)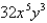
C)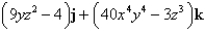
D)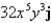
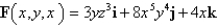
A)
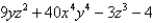
B)
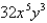
C)
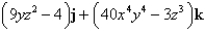
D)
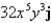

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Find the area of the surface S where S is the part of the plane 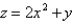 that lies above the triangular region with vertices
that lies above the triangular region with vertices 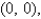
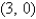 ,and
,and 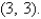
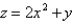 that lies above the triangular region with vertices
that lies above the triangular region with vertices 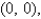
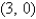 ,and
,and 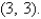

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
Find (a)the divergence and (b)the curl of the vector field F. 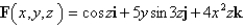
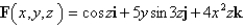

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
A plane lamina with constant density 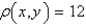 occupies a region in the xy-plane bounded by a simple closed path C.Its moments of inertia about the axes are
occupies a region in the xy-plane bounded by a simple closed path C.Its moments of inertia about the axes are 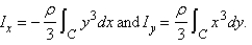 Find the moments of inertia about the axes,if C is a rectangle with vertices (0,0),(4,0), (4,5)and
Find the moments of inertia about the axes,if C is a rectangle with vertices (0,0),(4,0), (4,5)and 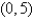 .
.
A)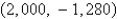
B)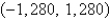
C)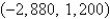
D)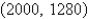
E)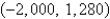
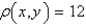 occupies a region in the xy-plane bounded by a simple closed path C.Its moments of inertia about the axes are
occupies a region in the xy-plane bounded by a simple closed path C.Its moments of inertia about the axes are 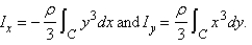 Find the moments of inertia about the axes,if C is a rectangle with vertices (0,0),(4,0), (4,5)and
Find the moments of inertia about the axes,if C is a rectangle with vertices (0,0),(4,0), (4,5)and 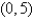 .
.A)
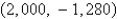
B)
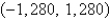
C)
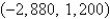
D)
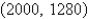
E)
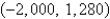

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
A particle starts at the point 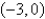 ,moves along the x-axis to (3,0)and then along the semicircle
,moves along the x-axis to (3,0)and then along the semicircle 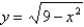 to the starting point.Use Green's Theorem to find the work done on this particle by the force field
to the starting point.Use Green's Theorem to find the work done on this particle by the force field 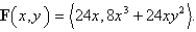
A)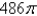
B)
C)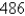
D) 0
E)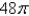
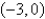 ,moves along the x-axis to (3,0)and then along the semicircle
,moves along the x-axis to (3,0)and then along the semicircle 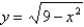 to the starting point.Use Green's Theorem to find the work done on this particle by the force field
to the starting point.Use Green's Theorem to find the work done on this particle by the force field 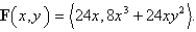
A)
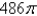
B)

C)
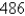
D) 0
E)
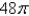

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
Let D be a region bounded by a simple closed path C in the xy.Then the coordinates of the centroid 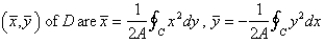 where A is the area of D. Find the centroid of the triangle with vertices (0,0),(
where A is the area of D. Find the centroid of the triangle with vertices (0,0),( 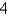 ,0)and (0,
,0)and (0, 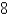 ).
).
A)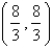
B)
C)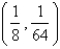
D)
E)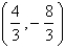
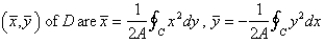 where A is the area of D. Find the centroid of the triangle with vertices (0,0),(
where A is the area of D. Find the centroid of the triangle with vertices (0,0),( 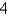 ,0)and (0,
,0)and (0, 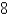 ).
).A)
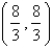
B)

C)
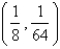
D)

E)
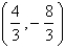

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Find the divergence of the vector field. 


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
Suppose that F is an inverse square force field,that is, 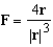 where
where 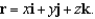 Find the work done by F in moving an object from a point
Find the work done by F in moving an object from a point 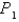 along a path to a point
along a path to a point 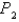 in terms of the distances
in terms of the distances 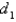 and
and 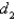 from these points to the origin.
from these points to the origin.
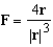 where
where 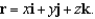 Find the work done by F in moving an object from a point
Find the work done by F in moving an object from a point 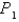 along a path to a point
along a path to a point 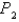 in terms of the distances
in terms of the distances 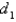 and
and 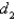 from these points to the origin.
from these points to the origin.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
The flow lines (or streamlines)of a vector field are the paths followed by a particle whose velocity field is the given vector field.Thus,the vectors in a vector field are tangent to the flow lines.The flow lines of the vector field 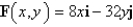 satisfy the differential equations
satisfy the differential equations 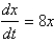 and
and 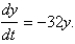 Solve these differential equations to find the equations of the family of flow lines.
Solve these differential equations to find the equations of the family of flow lines.
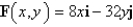 satisfy the differential equations
satisfy the differential equations 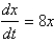 and
and 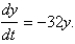 Solve these differential equations to find the equations of the family of flow lines.
Solve these differential equations to find the equations of the family of flow lines.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
Find the exact mass of a thin wire in the shape of the helix 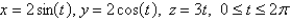 if the density is 5.
if the density is 5.
A)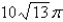
B)
C)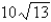
D)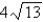
E)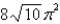
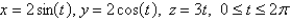 if the density is 5.
if the density is 5.A)
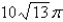
B)

C)
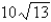
D)
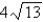
E)
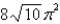

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
Find the gradient vector field of
A)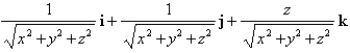
B)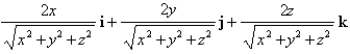
C)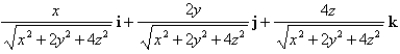
D)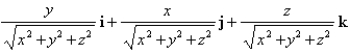
E) None of these
A)
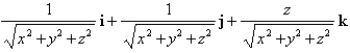
B)
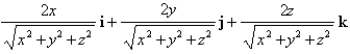
C)
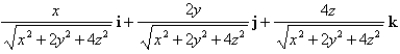
D)
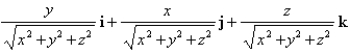
E) None of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Determine whether or not F is a conservative vector field.If it is,find a function f such that 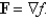
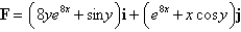
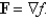
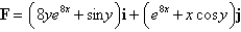

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
A particle is moving in a velocity field 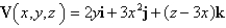 At time t = 1 the particle is located at the point (1,5,5).
At time t = 1 the particle is located at the point (1,5,5).
a)What is the velocity of the particle at t = 1?
b)What is the approximate location of the particle at t = 1.01?
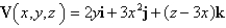 At time t = 1 the particle is located at the point (1,5,5).
At time t = 1 the particle is located at the point (1,5,5).a)What is the velocity of the particle at t = 1?
b)What is the approximate location of the particle at t = 1.01?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
A thin wire is bent into the shape of a semicircle 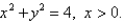 If the linear density is 4 ,find the exact mass of the wire.
If the linear density is 4 ,find the exact mass of the wire.
A)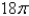
B)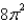
C)
D)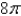
E)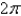
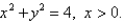 If the linear density is 4 ,find the exact mass of the wire.
If the linear density is 4 ,find the exact mass of the wire.A)
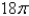
B)
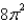
C)

D)
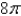
E)
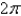

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
Find a function f such that 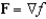 ,and use it to evaluate
,and use it to evaluate 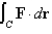 along the given curve C.
along the given curve C. 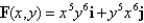
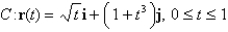
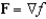 ,and use it to evaluate
,and use it to evaluate 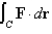 along the given curve C.
along the given curve C. 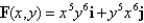
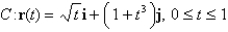

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
Find the work done by the force field 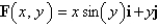 on a particle that moves along the parabola
on a particle that moves along the parabola 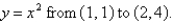
A)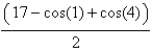
B)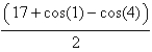
C)
D)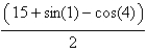
E)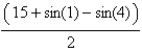
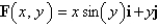 on a particle that moves along the parabola
on a particle that moves along the parabola 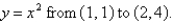
A)
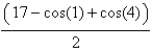
B)
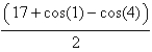
C)

D)
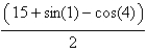
E)
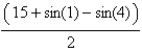

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
Find the gradient vector field of 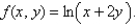
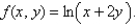

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
Evaluate 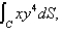 where C is the right half of the circle
where C is the right half of the circle 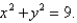
A)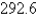
B)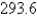
C)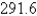
D)
E)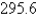
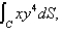 where C is the right half of the circle
where C is the right half of the circle 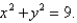
A)
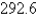
B)
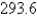
C)
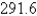
D)

E)
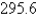

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
Let 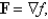 where
where 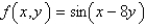 . Which of the following equations does the line segment from
. Which of the following equations does the line segment from 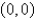 to
to 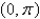 satisfy?
satisfy?
A)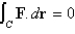
B)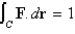
C) none of these
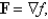 where
where 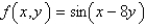 . Which of the following equations does the line segment from
. Which of the following equations does the line segment from 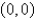 to
to 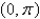 satisfy?
satisfy?A)
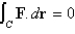
B)
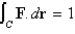
C) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
Which plot illustrates the vector field 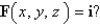
A)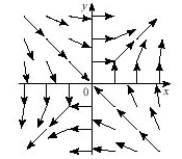
B)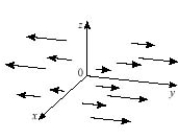
C)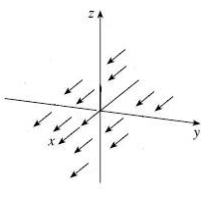
D)
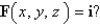
A)

B)

C)

D)


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
Find the work done by the force field 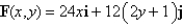 in moving an object along an arch of the cycloid
in moving an object along an arch of the cycloid 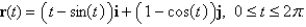
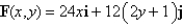 in moving an object along an arch of the cycloid
in moving an object along an arch of the cycloid 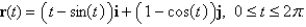

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
Evaluate the line integral over the given curve C. 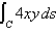 ,where C is the line segment joining (-2,-1)to (4,5)
,where C is the line segment joining (-2,-1)to (4,5)
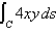 ,where C is the line segment joining (-2,-1)to (4,5)
,where C is the line segment joining (-2,-1)to (4,5)
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
Evaluate the line integral over the given curve C.  ;
; 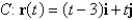 ,
, 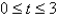
A)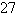
B)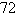
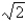
C)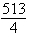
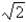
D)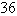
 ;
; 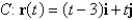 ,
, 
A)
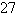
B)
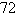
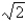
C)
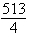
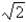
D)
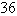

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 56 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








