Deck 7: Acids and Bases
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/119
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 7: Acids and Bases
1
The following three equations represent equilibria that lie far to the right.
HNO3(aq) + CN-(aq) HCN(aq) + NO3-(aq)
HCN(aq) + NO3-(aq)
HCN(aq) + OH-(aq) H2O(l) + CN-(aq)
H2O(l) + CN-(aq)
H2O(l) + CH3O-(aq) CH3OH(aq) + OH-(aq)
CH3OH(aq) + OH-(aq)
Identify the strongest base.
A) CH3OH
B) CH3O-
C) H2O
D) NO3-
E) CN-
HNO3(aq) + CN-(aq)
 HCN(aq) + NO3-(aq)
HCN(aq) + NO3-(aq)HCN(aq) + OH-(aq)
 H2O(l) + CN-(aq)
H2O(l) + CN-(aq)H2O(l) + CH3O-(aq)
 CH3OH(aq) + OH-(aq)
CH3OH(aq) + OH-(aq)Identify the strongest base.
A) CH3OH
B) CH3O-
C) H2O
D) NO3-
E) CN-
CH3O-
2
Which of the following is a conjugate acid-base pair?
A) H3O+/OH-
B) NH4+/NH3
C) Mg2+/Mg(OH)2
D) HCl/OCl2-
E) H3PO4/PO43-
A) H3O+/OH-
B) NH4+/NH3
C) Mg2+/Mg(OH)2
D) HCl/OCl2-
E) H3PO4/PO43-
NH4+/NH3
3
Which of the following does not represent a conjugate acid-base pair?
A) H3O+ and H2O
B) HCN and NH3
C) HF and F-
D) C5H5NH+ and C5H5N
E) none of these
A) H3O+ and H2O
B) HCN and NH3
C) HF and F-
D) C5H5NH+ and C5H5N
E) none of these
HCN and NH3
4
Identify the Brønsted acids and bases in the following equation (A = Brønsted acid, B = Brønsted base). HPO42- + HSO4-  H2PO4- + SO42-
H2PO4- + SO42-
A) A B B A
B) B A A B
C) A B A B
D) B B A A
E) B A B A
 H2PO4- + SO42-
H2PO4- + SO42-A) A B B A
B) B A A B
C) A B A B
D) B B A A
E) B A B A

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
The equilibrium constant for the reaction A- + H+  HA
HA
Is called
A) Kb
B)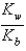
C) KwKa
D)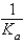
E) Ka
 HA
HAIs called
A) Kb
B)
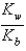
C) KwKa
D)
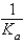
E) Ka

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
The conjugate base of a weak acid is
A) a strong base.
B) a strong acid.
C) a weak base.
D) a weak acid.
E) none of these
A) a strong base.
B) a strong acid.
C) a weak base.
D) a weak acid.
E) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
The strong acid HA is added to water. Which of the following is the strongest base in the system?
A) A-
B) HA
C) H3O+
D) H2A-
E) H2O
A) A-
B) HA
C) H3O+
D) H2A-
E) H2O

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
The acids HC2H3O2 and HF are both weak, but HF is a stronger acid than HC2H3O2. HCl is a strong acid. Order the following according to base strength.
A) Cl- > F- > C2H3O2- > H2O
B) C2H3O2- > F- > H2O > Cl-
C) C2H3O2- > F- > Cl- > H2O
D) F- > C2H3O2- > H2O > Cl-
E) none of these
A) Cl- > F- > C2H3O2- > H2O
B) C2H3O2- > F- > H2O > Cl-
C) C2H3O2- > F- > Cl- > H2O
D) F- > C2H3O2- > H2O > Cl-
E) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Given that the Ka for HOCl is 3.5 * 10-8, calculate the K value for the reaction of HOCl with OH-.
A) 3.5 * 10-22
B) 3.5 *10-8
C) 2.9 * 10-7
D) 3.5 * 106
E) none of these
A) 3.5 * 10-22
B) 3.5 *10-8
C) 2.9 * 10-7
D) 3.5 * 106
E) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Which reaction does not proceed far to the right?
A) HCN + OH- H2O + CN-
B) HCl + H2O H3O+ + Cl-
C)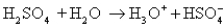
D) H3O+ + OH- 2H2O
E)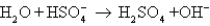
A) HCN + OH- H2O + CN-
B) HCl + H2O H3O+ + Cl-
C)
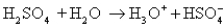
D) H3O+ + OH- 2H2O
E)
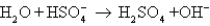

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
The hydrogen sulfate or bisulfate ion HSO4- can act as either an acid or a base in water solution. In which of the following equations does HSO4- act as an acid?
A) HSO4- + H2O SO42- + H3O+
B) HSO4- + H2O H2SO4 + OH-
C) HSO4- + H3O+ SO3 + 2H2O
D) HSO4- + OH- H2SO4 + O2-
E) none of these
A) HSO4- + H2O SO42- + H3O+
B) HSO4- + H2O H2SO4 + OH-
C) HSO4- + H3O+ SO3 + 2H2O
D) HSO4- + OH- H2SO4 + O2-
E) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Which of the following represents a conjugate acid-base pair?
A) H2PO4- and PO43-
B) HNO3 and NO3-
C) HCl and NaOH
D) HSO4- and SO32-
E) none of these
A) H2PO4- and PO43-
B) HNO3 and NO3-
C) HCl and NaOH
D) HSO4- and SO32-
E) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Which of the following is the equilibrium constant expression for the dissociation of the weak acid HOCl?
A)![<strong>Which of the following is the equilibrium constant expression for the dissociation of the weak acid HOCl?</strong> A) B) K = [H<sup>+</sup>][OCl<sup>-</sup>] C) D) E) none of these](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6420/11eaaf8d_c16d_80c9_892c_91380b63affc_TB6420_11.jpg)
B) K = [H+][OCl-]
C)![<strong>Which of the following is the equilibrium constant expression for the dissociation of the weak acid HOCl?</strong> A) B) K = [H<sup>+</sup>][OCl<sup>-</sup>] C) D) E) none of these](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6420/11eaaf8d_c16d_a7da_892c_2ba107f5d274_TB6420_11.jpg)
D)![<strong>Which of the following is the equilibrium constant expression for the dissociation of the weak acid HOCl?</strong> A) B) K = [H<sup>+</sup>][OCl<sup>-</sup>] C) D) E) none of these](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6420/11eaaf8d_c16d_a7db_892c_f52cf5832a05_TB6420_11.jpg)
E) none of these
A)
![<strong>Which of the following is the equilibrium constant expression for the dissociation of the weak acid HOCl?</strong> A) B) K = [H<sup>+</sup>][OCl<sup>-</sup>] C) D) E) none of these](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6420/11eaaf8d_c16d_80c9_892c_91380b63affc_TB6420_11.jpg)
B) K = [H+][OCl-]
C)
![<strong>Which of the following is the equilibrium constant expression for the dissociation of the weak acid HOCl?</strong> A) B) K = [H<sup>+</sup>][OCl<sup>-</sup>] C) D) E) none of these](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6420/11eaaf8d_c16d_a7da_892c_2ba107f5d274_TB6420_11.jpg)
D)
![<strong>Which of the following is the equilibrium constant expression for the dissociation of the weak acid HOCl?</strong> A) B) K = [H<sup>+</sup>][OCl<sup>-</sup>] C) D) E) none of these](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6420/11eaaf8d_c16d_a7db_892c_f52cf5832a05_TB6420_11.jpg)
E) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
In deciding which of two acids is the stronger, one must know
A) the pH of each acid solution only.
B) the concentration of each acid solution only.
C) the equilibrium constant of each acid only.
D) all of the these.
E) both the concentration and the equilibrium constant of each acid.
A) the pH of each acid solution only.
B) the concentration of each acid solution only.
C) the equilibrium constant of each acid only.
D) all of the these.
E) both the concentration and the equilibrium constant of each acid.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
The following three equations represent equilibria that lie far to the right.
HNO3(aq) + CN-(aq) HCN(aq) + NO3-(aq)
HCN(aq) + NO3-(aq)
HCN(aq) + OH-(aq) H2O(l) + CN-(aq)
H2O(l) + CN-(aq)
H2O(l) + CH3O-(aq) CH3OH(aq) + OH-(aq)
CH3OH(aq) + OH-(aq)
Identify the strongest acid.
A) HNO3
B) HCN
C) OH-
D) H2O
E) CH3OH
HNO3(aq) + CN-(aq)
 HCN(aq) + NO3-(aq)
HCN(aq) + NO3-(aq)HCN(aq) + OH-(aq)
 H2O(l) + CN-(aq)
H2O(l) + CN-(aq)H2O(l) + CH3O-(aq)
 CH3OH(aq) + OH-(aq)
CH3OH(aq) + OH-(aq)Identify the strongest acid.
A) HNO3
B) HCN
C) OH-
D) H2O
E) CH3OH

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
According to the Brønsted-Lowry definition, an acid is
A) a substance that can donate a proton to another species.
B) a substance that increases the hydroxide ion concentration in a solution.
C) a substance that can accept a proton from another species in solution.
D) an electron pair acceptor.
E) a substance that increases the hydrogen ion concentration in a solution.
A) a substance that can donate a proton to another species.
B) a substance that increases the hydroxide ion concentration in a solution.
C) a substance that can accept a proton from another species in solution.
D) an electron pair acceptor.
E) a substance that increases the hydrogen ion concentration in a solution.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Which of the following reactions is associated with the definition of Ka?
A) [Al(OH2)6]3+
![<strong>Which of the following reactions is associated with the definition of K<sub>a</sub>?</strong> A) [Al(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>6</sub>]<sup>3+ </sup> <sup> </sup> Al(OH)(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>5</sub><sup>2+</sup> + H<sup>+</sup> B) CN<sup>-</sup> + H<sup>+</sup> HCN C) OCl<sup>-</sup> + H<sub>2</sub>O HOCl + OH<sup>-</sup> D) Al<sup>3+</sup> + 6H<sub>2</sub>O Al(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>6</sub><sup>3+</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6420/11eaaf8d_c16c_9665_892c_0b16965a1968_TB6420_11.jpg) Al(OH)(OH2)52+ + H+
Al(OH)(OH2)52+ + H+
B) CN- + H+![<strong>Which of the following reactions is associated with the definition of K<sub>a</sub>?</strong> A) [Al(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>6</sub>]<sup>3+ </sup> <sup> </sup> Al(OH)(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>5</sub><sup>2+</sup> + H<sup>+</sup> B) CN<sup>-</sup> + H<sup>+</sup> HCN C) OCl<sup>-</sup> + H<sub>2</sub>O HOCl + OH<sup>-</sup> D) Al<sup>3+</sup> + 6H<sub>2</sub>O Al(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>6</sub><sup>3+</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6420/11eaaf8d_c16c_bd76_892c_293a2ac574ee_TB6420_11.jpg) HCN
HCN
C) OCl- + H2O![<strong>Which of the following reactions is associated with the definition of K<sub>a</sub>?</strong> A) [Al(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>6</sub>]<sup>3+ </sup> <sup> </sup> Al(OH)(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>5</sub><sup>2+</sup> + H<sup>+</sup> B) CN<sup>-</sup> + H<sup>+</sup> HCN C) OCl<sup>-</sup> + H<sub>2</sub>O HOCl + OH<sup>-</sup> D) Al<sup>3+</sup> + 6H<sub>2</sub>O Al(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>6</sub><sup>3+</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6420/11eaaf8d_c16c_bd77_892c_2f19c99bd669_TB6420_11.jpg) HOCl + OH-
HOCl + OH-
D) Al3+ + 6H2O![<strong>Which of the following reactions is associated with the definition of K<sub>a</sub>?</strong> A) [Al(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>6</sub>]<sup>3+ </sup> <sup> </sup> Al(OH)(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>5</sub><sup>2+</sup> + H<sup>+</sup> B) CN<sup>-</sup> + H<sup>+</sup> HCN C) OCl<sup>-</sup> + H<sub>2</sub>O HOCl + OH<sup>-</sup> D) Al<sup>3+</sup> + 6H<sub>2</sub>O Al(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>6</sub><sup>3+</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6420/11eaaf8d_c16c_e488_892c_3f728bec3419_TB6420_11.jpg) Al(OH2)63+
Al(OH2)63+
A) [Al(OH2)6]3+
![<strong>Which of the following reactions is associated with the definition of K<sub>a</sub>?</strong> A) [Al(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>6</sub>]<sup>3+ </sup> <sup> </sup> Al(OH)(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>5</sub><sup>2+</sup> + H<sup>+</sup> B) CN<sup>-</sup> + H<sup>+</sup> HCN C) OCl<sup>-</sup> + H<sub>2</sub>O HOCl + OH<sup>-</sup> D) Al<sup>3+</sup> + 6H<sub>2</sub>O Al(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>6</sub><sup>3+</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6420/11eaaf8d_c16c_9665_892c_0b16965a1968_TB6420_11.jpg) Al(OH)(OH2)52+ + H+
Al(OH)(OH2)52+ + H+B) CN- + H+
![<strong>Which of the following reactions is associated with the definition of K<sub>a</sub>?</strong> A) [Al(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>6</sub>]<sup>3+ </sup> <sup> </sup> Al(OH)(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>5</sub><sup>2+</sup> + H<sup>+</sup> B) CN<sup>-</sup> + H<sup>+</sup> HCN C) OCl<sup>-</sup> + H<sub>2</sub>O HOCl + OH<sup>-</sup> D) Al<sup>3+</sup> + 6H<sub>2</sub>O Al(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>6</sub><sup>3+</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6420/11eaaf8d_c16c_bd76_892c_293a2ac574ee_TB6420_11.jpg) HCN
HCNC) OCl- + H2O
![<strong>Which of the following reactions is associated with the definition of K<sub>a</sub>?</strong> A) [Al(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>6</sub>]<sup>3+ </sup> <sup> </sup> Al(OH)(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>5</sub><sup>2+</sup> + H<sup>+</sup> B) CN<sup>-</sup> + H<sup>+</sup> HCN C) OCl<sup>-</sup> + H<sub>2</sub>O HOCl + OH<sup>-</sup> D) Al<sup>3+</sup> + 6H<sub>2</sub>O Al(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>6</sub><sup>3+</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6420/11eaaf8d_c16c_bd77_892c_2f19c99bd669_TB6420_11.jpg) HOCl + OH-
HOCl + OH-D) Al3+ + 6H2O
![<strong>Which of the following reactions is associated with the definition of K<sub>a</sub>?</strong> A) [Al(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>6</sub>]<sup>3+ </sup> <sup> </sup> Al(OH)(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>5</sub><sup>2+</sup> + H<sup>+</sup> B) CN<sup>-</sup> + H<sup>+</sup> HCN C) OCl<sup>-</sup> + H<sub>2</sub>O HOCl + OH<sup>-</sup> D) Al<sup>3+</sup> + 6H<sub>2</sub>O Al(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>6</sub><sup>3+</sup>](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6420/11eaaf8d_c16c_e488_892c_3f728bec3419_TB6420_11.jpg) Al(OH2)63+
Al(OH2)63+
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
For the equilibrium that exists in an aqueous solution of nitrous acid (HNO2, a weak acid), the equilibrium constant expression is
A)![<strong>For the equilibrium that exists in an aqueous solution of nitrous acid (HNO<sub>2</sub>, a weak acid), the equilibrium constant expression is</strong> A) B) C) D) K = [H<sup>+</sup>][NO<sub>2</sub><sup>-</sup>] E) none of these](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6420/11eaaf8d_c16b_84ee_892c_65c276947469_TB6420_11.jpg)
B)![<strong>For the equilibrium that exists in an aqueous solution of nitrous acid (HNO<sub>2</sub>, a weak acid), the equilibrium constant expression is</strong> A) B) C) D) K = [H<sup>+</sup>][NO<sub>2</sub><sup>-</sup>] E) none of these](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6420/11eaaf8d_c16b_abff_892c_dbe254235c7f_TB6420_11.jpg)
C)![<strong>For the equilibrium that exists in an aqueous solution of nitrous acid (HNO<sub>2</sub>, a weak acid), the equilibrium constant expression is</strong> A) B) C) D) K = [H<sup>+</sup>][NO<sub>2</sub><sup>-</sup>] E) none of these](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6420/11eaaf8d_c16b_ac00_892c_e7f3be9adab9_TB6420_11.jpg)
D) K = [H+][NO2-]
E) none of these
A)
![<strong>For the equilibrium that exists in an aqueous solution of nitrous acid (HNO<sub>2</sub>, a weak acid), the equilibrium constant expression is</strong> A) B) C) D) K = [H<sup>+</sup>][NO<sub>2</sub><sup>-</sup>] E) none of these](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6420/11eaaf8d_c16b_84ee_892c_65c276947469_TB6420_11.jpg)
B)
![<strong>For the equilibrium that exists in an aqueous solution of nitrous acid (HNO<sub>2</sub>, a weak acid), the equilibrium constant expression is</strong> A) B) C) D) K = [H<sup>+</sup>][NO<sub>2</sub><sup>-</sup>] E) none of these](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6420/11eaaf8d_c16b_abff_892c_dbe254235c7f_TB6420_11.jpg)
C)
![<strong>For the equilibrium that exists in an aqueous solution of nitrous acid (HNO<sub>2</sub>, a weak acid), the equilibrium constant expression is</strong> A) B) C) D) K = [H<sup>+</sup>][NO<sub>2</sub><sup>-</sup>] E) none of these](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6420/11eaaf8d_c16b_ac00_892c_e7f3be9adab9_TB6420_11.jpg)
D) K = [H+][NO2-]
E) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Which of the following species is not amphoteric?
A) H2PO4-
B) HPO42-
C) H2O
D) HSO4-
E) All of these are amphoteric.
A) H2PO4-
B) HPO42-
C) H2O
D) HSO4-
E) All of these are amphoteric.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
The following acids are listed in order of decreasing acid strength in water. HI > HNO2 > CH3COOH > HClO > HCN
According to Brønsted-Lowry theory, which of the following ions is the weakest base?
A) ClO-
B) NO2-
C) CH3COO-
D) I-
E) CN-
According to Brønsted-Lowry theory, which of the following ions is the weakest base?
A) ClO-
B) NO2-
C) CH3COO-
D) I-
E) CN-

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Calculate the pH of a solution made by mixing equal volumes of a solution of HCl with a pH of 1.68 and a solution of HNO3 with a pH of 2.39. (Assume the volumes are additive.)
A) 4.06
B) 2.03
C) 2.39
D) 1.90
E) 1.60
A) 4.06
B) 2.03
C) 2.39
D) 1.90
E) 1.60

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
How many moles of benzoic acid, a monoprotic acid with Ka = 6.4 *10-5, must be dissolved in 500. mL of H2O to produce a solution with pH = 2.50?
A) 1.6 *10-1
B) 2.0 * 10-2
C) 7.8 *10-2
D) 0.50
E) none of these
A) 1.6 *10-1
B) 2.0 * 10-2
C) 7.8 *10-2
D) 0.50
E) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
The pH of a solution is raised from 3 to 5. Which statement is false?
A) The final [OH-] (at pH = 5) is 10-9 M.
B) The [H+] decreases by a factor of 20.
C) The initial solution could be 0.001 M HNO3.
D) The pOH decreases from 11 to 9.
E) The initial [H+] (at pH = 3) is 10-3 M.
A) The final [OH-] (at pH = 5) is 10-9 M.
B) The [H+] decreases by a factor of 20.
C) The initial solution could be 0.001 M HNO3.
D) The pOH decreases from 11 to 9.
E) The initial [H+] (at pH = 3) is 10-3 M.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
A monoprotic weak acid, when dissolved in water, is 0.92% dissociated and produces a solution with pH = 3.42. Calculate Ka for the acid.
A) 1.4 * 10-7
B) 2.8 * 10-3
C) 3.5 * 10-6
D) We need to know the initial concentration of the acid.
E) none of these
A) 1.4 * 10-7
B) 2.8 * 10-3
C) 3.5 * 10-6
D) We need to know the initial concentration of the acid.
E) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
At a particular temperature, the ion-product constant of water, Kw, is 4.4 *10-15. What is the pH of pure water at this temperature?
A) 6.26
B) 7.00
C) 6.82
D) 6.36
E) 7.18
A) 6.26
B) 7.00
C) 6.82
D) 6.36
E) 7.18

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
In pure liquid ammonia, the equilibrium concentrations of both NH4+ and NH2- are 3 *10-14 M. Which of the following equations always holds for liquid ammonia solutions?
A) pNH4+ = log [pNH4+]
B) pNH4+ = 27.0
C) pNH4+ - pNH2- = 13.5
D) pNH4+ = 27.0 - pNH2-
E) pNH4+ + pNH2- = 13.5
A) pNH4+ = log [pNH4+]
B) pNH4+ = 27.0
C) pNH4+ - pNH2- = 13.5
D) pNH4+ = 27.0 - pNH2-
E) pNH4+ + pNH2- = 13.5

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Calculate the pH of the following aqueous solutions. Choose your answer from the given pH ranges. 0.1 M NaCN (pKa for HCN = 9.31)
A) pH 11.00-14.00
B) pH 3.00-5.99
C) pH 0.00-2.99
D) pH 6.00-8.99
E) pH 9.00-10.99
A) pH 11.00-14.00
B) pH 3.00-5.99
C) pH 0.00-2.99
D) pH 6.00-8.99
E) pH 9.00-10.99

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Find the pH of a solution at 25°C in which [OH-] = 2.5 * 10-9 M.
A) 6.50
B) 8.60
C) 7.40
D) 2.50
E) 5.40
A) 6.50
B) 8.60
C) 7.40
D) 2.50
E) 5.40

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Calculate the pH of a 1.9 M solution of HNO3.
A) -0.64
B) -0.28
C) 14.28
D) 13.72
E) 0.28
A) -0.64
B) -0.28
C) 14.28
D) 13.72
E) 0.28

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
Calculate [H+] in a solution that has a pH of 9.7.
A) 1 *10-1 M
B) 5 *10-5 M
C) 10 M
D) 4 M
E) 2*10-10 M
A) 1 *10-1 M
B) 5 *10-5 M
C) 10 M
D) 4 M
E) 2*10-10 M

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
For a neutral solution, it must be true that
A) pH = 7.00.
B) [H+] = [OH-].
C) [H2O] = 1 *10-14
D) [H+] = 0 M.
E) At least two of these must be true.
A) pH = 7.00.
B) [H+] = [OH-].
C) [H2O] = 1 *10-14
D) [H+] = 0 M.
E) At least two of these must be true.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
For nitrous acid, HNO2, Ka = 4.0 * 10-4. Calculate the pH of 0.27 M HNO2.
A) 2.83
B) 1.98
C) 3.40
D) 0.57
E) 4.54
A) 2.83
B) 1.98
C) 3.40
D) 0.57
E) 4.54

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
What concentration of HF (Ka = 7.2 * 10-4) has the same pH as that of 0.069 M HCl?
A) 6.6 M
B) 5.0 *10-6 M
C) 1.0 * 10-2 M
D) 0.069 M
E) 0.15 M
A) 6.6 M
B) 5.0 *10-6 M
C) 1.0 * 10-2 M
D) 0.069 M
E) 0.15 M

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
The pH of a 0.013 M weak acid solution is 5.27. Calculate Ka for this acid.
A) 1.9 *10-9
B) 2.2 * 10-9
C) 5.4* 10-6
D) 2.6*10-16
E) 4.2*10-8
A) 1.9 *10-9
B) 2.2 * 10-9
C) 5.4* 10-6
D) 2.6*10-16
E) 4.2*10-8

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
HCl gas is in a 1.21-L cylinder at 0.870 atm and 28.0° C. This gas is dissolved in 750.0 mL of water. Calculate the pH of this solution (assume no volume change).
A) 0.950
B) 2.52
C) 1.25
D) 1.37
E) none of these
A) 0.950
B) 2.52
C) 1.25
D) 1.37
E) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
Calculate the pH of a 0.040 M perchloric acid (HClO4) solution.
A) 1.40
B) 2.10
C) 12.60
D) 11.90
E) none of these
A) 1.40
B) 2.10
C) 12.60
D) 11.90
E) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
As water is heated, its pH decreases. This means that
A) [OH-] > [H+].
B) [H+] > [OH-].
C) the water is no longer neutral.
D) Two of these are correct.
E) None of these is correct.
A) [OH-] > [H+].
B) [H+] > [OH-].
C) the water is no longer neutral.
D) Two of these are correct.
E) None of these is correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
Which of the following indicates the most acidic solution?
A) pOH = 5.9
B) [H+] = 0.3 M
C) [H+] = 1.0 *10-4 M
D) [OH-] = 0.5 M
E) pH = 1.2
A) pOH = 5.9
B) [H+] = 0.3 M
C) [H+] = 1.0 *10-4 M
D) [OH-] = 0.5 M
E) pH = 1.2

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
The pH of a 0.6 M solution of a weak acid is 4.0. What percent of the acid has ionized?
A) 0.02%
B) 7%
C) 4%
D) 0.06%
E) 2%
A) 0.02%
B) 7%
C) 4%
D) 0.06%
E) 2%

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Solid calcium hydroxide is dissolved in water until the pH of the solution is 10.94. What is the hydroxide ion concentration [OH-] of the solution?
A) 3.06 M
B) 1.1 *10-11 M
C) 1.0 *10-14 M
D) 8.7 *10-4 M
E) none of these
A) 3.06 M
B) 1.1 *10-11 M
C) 1.0 *10-14 M
D) 8.7 *10-4 M
E) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
The pKa of HOCl is 7.5. Calculate the pH of a 0.5 M solution of HOCl.
A) 0.3
B) 6.5
C) 7.5
D) 10.1
E) 3.9
A) 0.3
B) 6.5
C) 7.5
D) 10.1
E) 3.9

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
A 0.050 M aqueous solution of a weak monoprotic acid is 1.2% ionized at equilibrium at 25° C. Calculate Ka for this acid.
A) 7.3 * 10-33
B) 29
C) 3.4 *10-2
D) 6.4 *10-8
E) none of these
A) 7.3 * 10-33
B) 29
C) 3.4 *10-2
D) 6.4 *10-8
E) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
Calculate the pOH of a 0.70 M solution of acetic acid (Ka = 1.8 *10-5) at 25°C.
A) 2.72
B) 9.26
C) 4.90
D) 11.55
E) 2.45
A) 2.72
B) 9.26
C) 4.90
D) 11.55
E) 2.45

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
Calculate the pH of the following aqueous solutions. Choose your answer from the given pH ranges. 0.1 M methylamine (pKb = 3.36)
A) pH 11.00-14.00
B) pH 6.00-8.99
C) pH 3.00-5.99
D) pH 0.00-2.99
E) pH 9.00-10.99
A) pH 11.00-14.00
B) pH 6.00-8.99
C) pH 3.00-5.99
D) pH 0.00-2.99
E) pH 9.00-10.99

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Calculate the pH of a 0.10 M solution of HOCl, Ka = 3.5 * 10-8.
A) 8.46
B) 4.23
C) 1.00
D) 3.73
E) 3.23
A) 8.46
B) 4.23
C) 1.00
D) 3.73
E) 3.23

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
Which of the following reactions is associated with the definition of Kb?
A) [Al(OH2)6]3+![<strong>Which of the following reactions is associated with the definition of K<sub>b</sub>?</strong> A) [Al(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>6</sub>]<sup>3+ </sup> Al(OH)(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>5</sub><sup>2+</sup> + H<sup>+</sup> B) OCl<sup>-</sup> + H<sub>2</sub>O HOCl + OH<sup>-</sup> C) Al<sup>3+</sup> + 6H<sub>2</sub>O Al(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>6</sub><sup>3+</sup> D) CN<sup>-</sup> + H<sup>+</sup> HCN](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6420/11eaaf8d_c171_2a51_892c_4bc7b54f1f17_TB6420_11.jpg) Al(OH)(OH2)52+ + H+
Al(OH)(OH2)52+ + H+
B) OCl- + H2O![<strong>Which of the following reactions is associated with the definition of K<sub>b</sub>?</strong> A) [Al(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>6</sub>]<sup>3+ </sup> Al(OH)(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>5</sub><sup>2+</sup> + H<sup>+</sup> B) OCl<sup>-</sup> + H<sub>2</sub>O HOCl + OH<sup>-</sup> C) Al<sup>3+</sup> + 6H<sub>2</sub>O Al(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>6</sub><sup>3+</sup> D) CN<sup>-</sup> + H<sup>+</sup> HCN](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6420/11eaaf8d_c171_5162_892c_2b07f4027124_TB6420_11.jpg) HOCl + OH-
HOCl + OH-
C) Al3+ + 6H2O![<strong>Which of the following reactions is associated with the definition of K<sub>b</sub>?</strong> A) [Al(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>6</sub>]<sup>3+ </sup> Al(OH)(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>5</sub><sup>2+</sup> + H<sup>+</sup> B) OCl<sup>-</sup> + H<sub>2</sub>O HOCl + OH<sup>-</sup> C) Al<sup>3+</sup> + 6H<sub>2</sub>O Al(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>6</sub><sup>3+</sup> D) CN<sup>-</sup> + H<sup>+</sup> HCN](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6420/11eaaf8d_c171_5163_892c_430fbc5cf106_TB6420_11.jpg) Al(OH2)63+
Al(OH2)63+
D) CN- + H+![<strong>Which of the following reactions is associated with the definition of K<sub>b</sub>?</strong> A) [Al(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>6</sub>]<sup>3+ </sup> Al(OH)(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>5</sub><sup>2+</sup> + H<sup>+</sup> B) OCl<sup>-</sup> + H<sub>2</sub>O HOCl + OH<sup>-</sup> C) Al<sup>3+</sup> + 6H<sub>2</sub>O Al(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>6</sub><sup>3+</sup> D) CN<sup>-</sup> + H<sup>+</sup> HCN](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6420/11eaaf8d_c171_7874_892c_4309864ba6e7_TB6420_11.jpg) HCN
HCN
A) [Al(OH2)6]3+
![<strong>Which of the following reactions is associated with the definition of K<sub>b</sub>?</strong> A) [Al(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>6</sub>]<sup>3+ </sup> Al(OH)(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>5</sub><sup>2+</sup> + H<sup>+</sup> B) OCl<sup>-</sup> + H<sub>2</sub>O HOCl + OH<sup>-</sup> C) Al<sup>3+</sup> + 6H<sub>2</sub>O Al(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>6</sub><sup>3+</sup> D) CN<sup>-</sup> + H<sup>+</sup> HCN](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6420/11eaaf8d_c171_2a51_892c_4bc7b54f1f17_TB6420_11.jpg) Al(OH)(OH2)52+ + H+
Al(OH)(OH2)52+ + H+B) OCl- + H2O
![<strong>Which of the following reactions is associated with the definition of K<sub>b</sub>?</strong> A) [Al(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>6</sub>]<sup>3+ </sup> Al(OH)(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>5</sub><sup>2+</sup> + H<sup>+</sup> B) OCl<sup>-</sup> + H<sub>2</sub>O HOCl + OH<sup>-</sup> C) Al<sup>3+</sup> + 6H<sub>2</sub>O Al(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>6</sub><sup>3+</sup> D) CN<sup>-</sup> + H<sup>+</sup> HCN](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6420/11eaaf8d_c171_5162_892c_2b07f4027124_TB6420_11.jpg) HOCl + OH-
HOCl + OH-C) Al3+ + 6H2O
![<strong>Which of the following reactions is associated with the definition of K<sub>b</sub>?</strong> A) [Al(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>6</sub>]<sup>3+ </sup> Al(OH)(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>5</sub><sup>2+</sup> + H<sup>+</sup> B) OCl<sup>-</sup> + H<sub>2</sub>O HOCl + OH<sup>-</sup> C) Al<sup>3+</sup> + 6H<sub>2</sub>O Al(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>6</sub><sup>3+</sup> D) CN<sup>-</sup> + H<sup>+</sup> HCN](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6420/11eaaf8d_c171_5163_892c_430fbc5cf106_TB6420_11.jpg) Al(OH2)63+
Al(OH2)63+D) CN- + H+
![<strong>Which of the following reactions is associated with the definition of K<sub>b</sub>?</strong> A) [Al(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>6</sub>]<sup>3+ </sup> Al(OH)(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>5</sub><sup>2+</sup> + H<sup>+</sup> B) OCl<sup>-</sup> + H<sub>2</sub>O HOCl + OH<sup>-</sup> C) Al<sup>3+</sup> + 6H<sub>2</sub>O Al(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>6</sub><sup>3+</sup> D) CN<sup>-</sup> + H<sup>+</sup> HCN](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6420/11eaaf8d_c171_7874_892c_4309864ba6e7_TB6420_11.jpg) HCN
HCN
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
The pH of a 0.100 M solution of an aqueous weak acid (HA) is 3.20. What is Ka for the weak acid?
A) 4.0 * 10-6
B) 6.3*10-4
C) 7.2 *10-5
D) 3.2
E) none of these
A) 4.0 * 10-6
B) 6.3*10-4
C) 7.2 *10-5
D) 3.2
E) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
A 0.240 M solution of the salt NaA has pH = 8.40. Calculate Ka for the acid HA.
A) 2.63 * 10-11
B) 3.80 * 10-4
C) 1.05 * 10-5
D) 6.60 *10-17
E) none of these
A) 2.63 * 10-11
B) 3.80 * 10-4
C) 1.05 * 10-5
D) 6.60 *10-17
E) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
If an acid, HA, is 10.0% dissociated in a 1.0 M solution, what is Ka for this acid?
A) 6.3 * 10-2
B) 9.1 * 10-2
C) 8.1 * 10-1
D) 1.1 * 10-2
E) none of these
A) 6.3 * 10-2
B) 9.1 * 10-2
C) 8.1 * 10-1
D) 1.1 * 10-2
E) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
The pH of a 0.22 M solution of a weak monoprotic acid, HA, is 2.74. Calculate Ka for this acid.
A) 3.3 * 10-6
B) 1.5 *10-5
C) 5.5 * 10-10
D) 2.2 * 10-4
E) 1.8* 10-3
A) 3.3 * 10-6
B) 1.5 *10-5
C) 5.5 * 10-10
D) 2.2 * 10-4
E) 1.8* 10-3

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
Which of the following aqueous solutions will have the highest pH? For NH3, Kb = 1.8 * 10-5; for C2H3O2-, Kb = 5.6 *10-10.
A) 2.0 M NH3
B) 2.0 M HCl
C) 2.0 M NaOH
D) 2.0 M HC2H3O2
E) All these solutions will have the same pH.
A) 2.0 M NH3
B) 2.0 M HCl
C) 2.0 M NaOH
D) 2.0 M HC2H3O2
E) All these solutions will have the same pH.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
In a solution prepared by dissolving 0.100 mol of propionic acid in enough water to make 1.00 L of solution, the pH is observed to be 1.35. What is Ka for propionic acid (HC3H5O2)?
A) 4.5 * 10-2
B) 2.0 * 10-2
C) 5.0 * 10-12
D) 3.6 * 10-2
E) none of these
A) 4.5 * 10-2
B) 2.0 * 10-2
C) 5.0 * 10-12
D) 3.6 * 10-2
E) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
Calculate [H+] in a 0.012 M solution of HCN, Ka = 6.2 *10-10.
A) 3.0 *10-7 M
B) 3.7 * 10-9 M
C) 6.2 *10-10 M
D) 2.7 * 10-6 M
E) 2.3 * 10-4 M
A) 3.0 *10-7 M
B) 3.7 * 10-9 M
C) 6.2 *10-10 M
D) 2.7 * 10-6 M
E) 2.3 * 10-4 M

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
A 2.5 M solution of a weak acid is 0.52% ionized. What is Ka for this acid?
A) 1.3 * 10-2
B) 6.8* 10-5
C) 0.11
D) 1.1* 10-5
E) none of these
A) 1.3 * 10-2
B) 6.8* 10-5
C) 0.11
D) 1.1* 10-5
E) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
Which of the following reactions is associated with the definition of Kb?
A) CN- + H+![<strong>Which of the following reactions is associated with the definition of K<sub>b</sub>?</strong> A) CN<sup>-</sup> + H<sup>+</sup> HCN B) Cr<sup>3+</sup> + 6H<sub>2</sub>O Cr(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>6</sub><sup>3+</sup> C) Zn(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>6</sub><sup>2+</sup> [Zn(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>5</sub>OH]<sup>+</sup> + H<sup>+</sup> D) F<sup>-</sup> + H<sub>2</sub>O HF + OH<sup>-</sup> E) none of these](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6420/11eaaf8d_c171_9f85_892c_23692252ed25_TB6420_11.jpg) HCN
HCN
B) Cr3+ + 6H2O![<strong>Which of the following reactions is associated with the definition of K<sub>b</sub>?</strong> A) CN<sup>-</sup> + H<sup>+</sup> HCN B) Cr<sup>3+</sup> + 6H<sub>2</sub>O Cr(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>6</sub><sup>3+</sup> C) Zn(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>6</sub><sup>2+</sup> [Zn(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>5</sub>OH]<sup>+</sup> + H<sup>+</sup> D) F<sup>-</sup> + H<sub>2</sub>O HF + OH<sup>-</sup> E) none of these](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6420/11eaaf8d_c171_c696_892c_230170a3857e_TB6420_11.jpg) Cr(OH2)63+
Cr(OH2)63+
C) Zn(OH2)62+![<strong>Which of the following reactions is associated with the definition of K<sub>b</sub>?</strong> A) CN<sup>-</sup> + H<sup>+</sup> HCN B) Cr<sup>3+</sup> + 6H<sub>2</sub>O Cr(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>6</sub><sup>3+</sup> C) Zn(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>6</sub><sup>2+</sup> [Zn(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>5</sub>OH]<sup>+</sup> + H<sup>+</sup> D) F<sup>-</sup> + H<sub>2</sub>O HF + OH<sup>-</sup> E) none of these](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6420/11eaaf8d_c171_c697_892c_ff40dbc8cde4_TB6420_11.jpg) [Zn(OH2)5OH]+ + H+
[Zn(OH2)5OH]+ + H+
D) F- + H2O![<strong>Which of the following reactions is associated with the definition of K<sub>b</sub>?</strong> A) CN<sup>-</sup> + H<sup>+</sup> HCN B) Cr<sup>3+</sup> + 6H<sub>2</sub>O Cr(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>6</sub><sup>3+</sup> C) Zn(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>6</sub><sup>2+</sup> [Zn(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>5</sub>OH]<sup>+</sup> + H<sup>+</sup> D) F<sup>-</sup> + H<sub>2</sub>O HF + OH<sup>-</sup> E) none of these](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6420/11eaaf8d_c171_eda8_892c_6b4398ccf22d_TB6420_11.jpg) HF + OH-
HF + OH-
E) none of these
A) CN- + H+
![<strong>Which of the following reactions is associated with the definition of K<sub>b</sub>?</strong> A) CN<sup>-</sup> + H<sup>+</sup> HCN B) Cr<sup>3+</sup> + 6H<sub>2</sub>O Cr(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>6</sub><sup>3+</sup> C) Zn(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>6</sub><sup>2+</sup> [Zn(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>5</sub>OH]<sup>+</sup> + H<sup>+</sup> D) F<sup>-</sup> + H<sub>2</sub>O HF + OH<sup>-</sup> E) none of these](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6420/11eaaf8d_c171_9f85_892c_23692252ed25_TB6420_11.jpg) HCN
HCNB) Cr3+ + 6H2O
![<strong>Which of the following reactions is associated with the definition of K<sub>b</sub>?</strong> A) CN<sup>-</sup> + H<sup>+</sup> HCN B) Cr<sup>3+</sup> + 6H<sub>2</sub>O Cr(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>6</sub><sup>3+</sup> C) Zn(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>6</sub><sup>2+</sup> [Zn(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>5</sub>OH]<sup>+</sup> + H<sup>+</sup> D) F<sup>-</sup> + H<sub>2</sub>O HF + OH<sup>-</sup> E) none of these](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6420/11eaaf8d_c171_c696_892c_230170a3857e_TB6420_11.jpg) Cr(OH2)63+
Cr(OH2)63+C) Zn(OH2)62+
![<strong>Which of the following reactions is associated with the definition of K<sub>b</sub>?</strong> A) CN<sup>-</sup> + H<sup>+</sup> HCN B) Cr<sup>3+</sup> + 6H<sub>2</sub>O Cr(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>6</sub><sup>3+</sup> C) Zn(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>6</sub><sup>2+</sup> [Zn(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>5</sub>OH]<sup>+</sup> + H<sup>+</sup> D) F<sup>-</sup> + H<sub>2</sub>O HF + OH<sup>-</sup> E) none of these](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6420/11eaaf8d_c171_c697_892c_ff40dbc8cde4_TB6420_11.jpg) [Zn(OH2)5OH]+ + H+
[Zn(OH2)5OH]+ + H+D) F- + H2O
![<strong>Which of the following reactions is associated with the definition of K<sub>b</sub>?</strong> A) CN<sup>-</sup> + H<sup>+</sup> HCN B) Cr<sup>3+</sup> + 6H<sub>2</sub>O Cr(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>6</sub><sup>3+</sup> C) Zn(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>6</sub><sup>2+</sup> [Zn(OH<sub>2</sub>)<sub>5</sub>OH]<sup>+</sup> + H<sup>+</sup> D) F<sup>-</sup> + H<sub>2</sub>O HF + OH<sup>-</sup> E) none of these](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6420/11eaaf8d_c171_eda8_892c_6b4398ccf22d_TB6420_11.jpg) HF + OH-
HF + OH-E) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
Calculate the pH of a 0.02 M solution of KOH.
A) 1.7
B) We cannot calculate the answer unless a volume is given.
C) 12.3
D) 2.0
E) 12.0
A) 1.7
B) We cannot calculate the answer unless a volume is given.
C) 12.3
D) 2.0
E) 12.0

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
Calculate the pOH of a 0.10 M solution of Ba(OH)2.
A) 13.30
B) 0.70
C) 13.00
D) 1.00
E) none of these
A) 13.30
B) 0.70
C) 13.00
D) 1.00
E) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
How much water should be added to 10.0 mL of 12.0 M HCl so that it has the same pH as 0.90 M acetic acid (Ka = 1.8*0 10-5)? (Assume the volumes are additive.)
A) 30 mL
B) 3 L
C) 30 L
D) 300 L
E) 300 mL
A) 30 mL
B) 3 L
C) 30 L
D) 300 L
E) 300 mL

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
Calculate the pH of a solution made by a mixture of the following acids: 0.40 M HC2H3O2 (Ka = 1.8 *10-5), 0.10 M HOCl (Ka = 3.5 *10-8), and 0.20 M HCN (Ka = 6.2 *10-10).
A) 2.57
B) 3.92
C) 4.95
D) 4.23
E) 3.49
A) 2.57
B) 3.92
C) 4.95
D) 4.23
E) 3.49

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
The pH of a solution made of 0.100 mol of a weak monoprotic acid HA in 1.000 L of solution is 1.470. Calculate Ka for this acid.
A) 29.5
B) 0
C) 0.100
D) 0.0174
E) 0.0339
A) 29.5
B) 0
C) 0.100
D) 0.0174
E) 0.0339

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
Calculate [H+] in a 1.0 M solution of Na2CO3 (for H2CO3, Ka1 = 4.3 * 10-7 and Ka2 = 5.6 * 10-11).
A) 6.6 *10-4 M
B) 7.5 *10-13 M
C) 7.5 * 10-6 M
D) 1.3 * 10-2 M
E) none of these
A) 6.6 *10-4 M
B) 7.5 *10-13 M
C) 7.5 * 10-6 M
D) 1.3 * 10-2 M
E) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
A 0.10-mol sample of a diprotic acid, H2A, is dissolved in 250 mL of water. Ka1 for this acid is 1.0 * 10-5 and Ka2 is 1.0 *10-10. Calculate the concentration of A2- in this solution.
A) 2.0 * 10-3 M
B) 4.0 * 10-6 M
C) 0.40 M
D) 1.0 * 10-10 M
E) 1.0 * 10-5 M
A) 2.0 * 10-3 M
B) 4.0 * 10-6 M
C) 0.40 M
D) 1.0 * 10-10 M
E) 1.0 * 10-5 M

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
A 2.58-g sample of NaOH(s) is added to enough water to make 600.0 mL of solution at 25°C. What is the pH of this solution?
A) 10.03
B) 0.97
C) 13.03
D) 14.63
E) 12.59
A) 10.03
B) 0.97
C) 13.03
D) 14.63
E) 12.59

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
The pH of a 2.1 *10-3 M solution of a weak base is 9.87. Calculate Kb for this base.
A) 2.6 * 10-6
B) 1.2 * 10-4
C) 6.4 *10-8
D) 8.7 *10-18
E) none of these
A) 2.6 * 10-6
B) 1.2 * 10-4
C) 6.4 *10-8
D) 8.7 *10-18
E) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
Calculate the pH of a 0.048 M solution of KOH.
A) 12.68
B) 11.32
C) 1.32
D) 2.68
E) none of these
A) 12.68
B) 11.32
C) 1.32
D) 2.68
E) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
Calculate the pH of a solution made by mixing equal volumes of a solution of NaOH with a pH of 11.40 and a solution of KOH with a pH of 10.30. (Assume the volumes are additive.)
A) 11.13
B) 1.10
C) 10.85
D) 21.70
E) none of these
A) 11.13
B) 1.10
C) 10.85
D) 21.70
E) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
Calculate the pH of a 0.50 M NH3 (Kb = 1.8 *10-5) solution.
A) 4.78
B) 2.52
C) 7.00
D) 13.72
E) none of these
A) 4.78
B) 2.52
C) 7.00
D) 13.72
E) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
Calculate the percentage of pyridine (C5H5N) that forms pyridinium ion, C5H5NH+, in a 0.10 M aqueous solution of pyridine (Kb = 1.7 * 10-9).
A) 0.77%
B) 0.060%
C) 0.0060%
D) 1.6%
E) 0.013%
A) 0.77%
B) 0.060%
C) 0.0060%
D) 1.6%
E) 0.013%

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
Consider two separate solutions of equal concentration. The first solution contains sodium hydroxide, and the second solution contains barium hydroxide. Which solution has the lower pH?
A) The barium hydroxide solution.
B) The sodium hydroxide solution.
C) We need to know the concentrations to answer this question.
D) The pH's of the two solutions are equal.
E) We need to know the volumes to answer this question.
A) The barium hydroxide solution.
B) The sodium hydroxide solution.
C) We need to know the concentrations to answer this question.
D) The pH's of the two solutions are equal.
E) We need to know the volumes to answer this question.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
What is [OH-] in a 0.50 M pyridine (C5H5N; Kb = 1.7 * 10-9) solution?
A) 1.8 * 10-9 M
B) 2.9 *10-5 M
C) 0.50 M
D) 3.3 *10-10 M
E) none of these
A) 1.8 * 10-9 M
B) 2.9 *10-5 M
C) 0.50 M
D) 3.3 *10-10 M
E) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
Calculate the pH of a 0.05 M solution of ascorbic acid (Ka1 = 7.9 *10-5; Ka2 = 1.6 * 10-12).
A) 5.4
B) 3.1
C) 6.5
D) 1.3
E) 2.7
A) 5.4
B) 3.1
C) 6.5
D) 1.3
E) 2.7

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
The conjugate acid and conjugate base of bicarbonate ion, HCO3-, are, respectively,
A) H3O+ and OH-
B) H2CO3 and OH-
C) H3O+ and CO32-
D) H2CO3 and CO32-
E) CO32- and OH-
A) H3O+ and OH-
B) H2CO3 and OH-
C) H3O+ and CO32-
D) H2CO3 and CO32-
E) CO32- and OH-

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
What is the pH in a solution of 1.0 M H2A (Ka1 = 1.0 *10-6; Ka2 = 1.0 *10-14)?
A) 10.00
B) 3.00
C) 4.00
D) 13.00
E) 7.00
A) 10.00
B) 3.00
C) 4.00
D) 13.00
E) 7.00

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
The pH of a 0.132 M solution of a weak base is 10.88 at 25°C. Calculate the pH of a 0.0392 M solution of the base at 25°C.
A) 10.61
B) 11.40
C) 3.23
D) 3.39
E) 10.35
A) 10.61
B) 11.40
C) 3.23
D) 3.39
E) 10.35

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
Calculate the pH of a 5.0 M solution of aniline (C6H5NH2; Kb = 3.8 *10-10).
A) 9.64
B) 9.30
C) 4.36
D) -0.070
E) none of these
A) 9.64
B) 9.30
C) 4.36
D) -0.070
E) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
What is the equilibrium constant for the following reaction? NH4+ + OH-  NH3 + H2O
NH3 + H2O
A)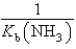
B)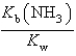
C)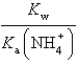
D)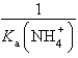
E)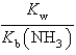
 NH3 + H2O
NH3 + H2OA)
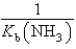
B)
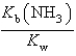
C)
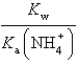
D)
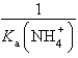
E)
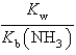

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
Calculate the pH of a solution that is 7.22 *10-4 M C6H5NH2. Kb is 3.8 *10-10.
A) 6.28
B) 7.72
C) 6.50
D) 7.50
E) none of these
A) 6.28
B) 7.72
C) 6.50
D) 7.50
E) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
Of the bases NaOH, H2O, CN-, SO42-, and HPO42-, which is the weakest? (Ka for HCN is 6.2 *10-10; Ka for HSO4- is 1.2 *10-2; and Ka3 for H3PO4, is 4.8*10-13)
A) CN-
B) HPO42-
C) SO42-
D) NaOH
E) H2O
A) CN-
B) HPO42-
C) SO42-
D) NaOH
E) H2O

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
Which of the following species is present in the greatest concentration in a 0.100 M H2SO4 solution in H2O?
A) H2SO4
B) H3O+
C) All species are in equilibrium and therefore have the same concentration.
D) HSO4-
E) SO42-
A) H2SO4
B) H3O+
C) All species are in equilibrium and therefore have the same concentration.
D) HSO4-
E) SO42-

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
The dihydrogenphosphate ion, H2PO4-, has both a conjugate acid and a conjugate base. These are, respectively,
A) H2PO4- and HPO42-
B) HPO42- and H3PO4
C) HPO42- and PO43-
D) H3PO4 and PO43-
E) H3PO4 and HPO42-
A) H2PO4- and HPO42-
B) HPO42- and H3PO4
C) HPO42- and PO43-
D) H3PO4 and PO43-
E) H3PO4 and HPO42-

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 119 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








