Deck 22: Metabolic Pathways for Carbohydrates
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/83
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 22: Metabolic Pathways for Carbohydrates
1
Which coenzyme is the electron acceptor in the following reaction? 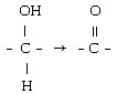
A) FAD
B) NAD+
C) FMN
D) NADH
E) FADH₂

A) FAD
B) NAD+
C) FMN
D) NADH
E) FADH₂
NAD+
2
Anabolic reactions are reactions that
A) use oxidation but not reduction.
B) break down large molecules into smaller ones.
C) take place in the mitochondria.
D) use energy.
E) give off energy.
A) use oxidation but not reduction.
B) break down large molecules into smaller ones.
C) take place in the mitochondria.
D) use energy.
E) give off energy.
use energy.
3
The symbol Pi stands for
A) inorganic phosphate.
B) inert pyrophosphate.
C) insoluble phosphate.
D) isomers of phosphate.
E) irreversible phosphorylation.
A) inorganic phosphate.
B) inert pyrophosphate.
C) insoluble phosphate.
D) isomers of phosphate.
E) irreversible phosphorylation.
inorganic phosphate.
4
The middle stage of catabolism is the point at which
A) acetyl CoA is produced.
B) monomers are produced from macromolecules.
C) macromolecules are made from monomers.
D) glycogen is converted to glucose.
E) excess nutrients are stored as fats.
A) acetyl CoA is produced.
B) monomers are produced from macromolecules.
C) macromolecules are made from monomers.
D) glycogen is converted to glucose.
E) excess nutrients are stored as fats.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
Which of the following is true for prokaryotic cells?
A) They are more complex than eukaryotic cells.
B) They are larger than eukaryotic cells.
C) They contain mitochondria.
D) They are found in animals.
E) They do not contain a nucleus.
A) They are more complex than eukaryotic cells.
B) They are larger than eukaryotic cells.
C) They contain mitochondria.
D) They are found in animals.
E) They do not contain a nucleus.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
The main compound used to release energy for metabolism is
A) sucrose.
B) glucose phosphate.
C) adenosine triphosphate.
D) ribonucleic acid.
E) NAD+.
A) sucrose.
B) glucose phosphate.
C) adenosine triphosphate.
D) ribonucleic acid.
E) NAD+.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
A compound that is formed in a metabolic oxidation is called a(n)
A) product.
B) enzyme.
C) metabolite.
D) food.
E) cofactor.
A) product.
B) enzyme.
C) metabolite.
D) food.
E) cofactor.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Protein synthesis takes place
A) in the mitochondria.
B) on the endoplasmic reticulum.
C) in the nucleus.
D) on the ribosomes.
E) in the cytosol.
A) in the mitochondria.
B) on the endoplasmic reticulum.
C) in the nucleus.
D) on the ribosomes.
E) in the cytosol.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Which coenzyme is the electron acceptor in the following reaction? 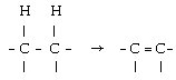
A) FAD
B) NAD+
C) FMN
D) NADH
E) FADH₂
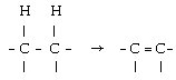
A) FAD
B) NAD+
C) FMN
D) NADH
E) FADH₂

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
The final products of catabolic reactions are
A) carbon dioxide, water, and ammonia.
B) glucose, lipids, and glycogen.
C) lipids, oxygen, and water.
D) RNA and DNA.
E) lipids and carbohydrates.
A) carbon dioxide, water, and ammonia.
B) glucose, lipids, and glycogen.
C) lipids, oxygen, and water.
D) RNA and DNA.
E) lipids and carbohydrates.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
The hydrolysis of ATP to ADP is
A) endothermic.
B) exothermic.
C) isothermic.
D) an oxidation.
E) a reduction.
A) endothermic.
B) exothermic.
C) isothermic.
D) an oxidation.
E) a reduction.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
The process by which complex molecules are broken down into simpler ones for the body's use is called
A) metabolism.
B) catabolism.
C) anabolism.
D) glucogenesis.
E) gluconeogenesis.
A) metabolism.
B) catabolism.
C) anabolism.
D) glucogenesis.
E) gluconeogenesis.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
How many main stages of catabolism are there?
A) one
B) two
C) three
D) four
E) five
A) one
B) two
C) three
D) four
E) five

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
The synthesis of glycogen can be classified as a(n)
A) catabolic reaction.
B) anabolic reaction.
C) digestion reaction.
D) phosphorylation reaction.
E) β-oxidation reaction.
A) catabolic reaction.
B) anabolic reaction.
C) digestion reaction.
D) phosphorylation reaction.
E) β-oxidation reaction.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Overall, catabolic reactions
A) release energy.
B) take in energy.
C) occur mainly in the liver.
D) occur outside the cell membrane.
E) take place in the nucleus of the cell.
A) release energy.
B) take in energy.
C) occur mainly in the liver.
D) occur outside the cell membrane.
E) take place in the nucleus of the cell.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
The release of pyrophosphate from ATP to give AMP and PPi, followed by the hydrolysis of the pyrophosphate, releases approximately the same amount of energy as
A) sucrose breakdown.
B) protein digestion.
C) glucose oxidation.
D) glycogen production.
E) ATP → ADP + Pi
A) sucrose breakdown.
B) protein digestion.
C) glucose oxidation.
D) glycogen production.
E) ATP → ADP + Pi

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
The components of ATP are
A) adenosine, ribose, and triphosphate.
B) aniline and triphosphate.
C) alanine, ribose, and triphosphate.
D) adenine, ribose, and triphosphate.
E) adenosine, deoxyribose, and triphosphate.
A) adenosine, ribose, and triphosphate.
B) aniline and triphosphate.
C) alanine, ribose, and triphosphate.
D) adenine, ribose, and triphosphate.
E) adenosine, deoxyribose, and triphosphate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
The process of building up new molecules in the cell is called
A) metabolism.
B) catabolism.
C) anabolism.
D) glycolysis.
E) transamination.
A) metabolism.
B) catabolism.
C) anabolism.
D) glycolysis.
E) transamination.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Which of the following does not require energy from ATP hydrolysis?
A) digestion
B) muscle contraction
C) transport across cell membranes
D) sending nerve signals
E) synthesis of an enzyme
A) digestion
B) muscle contraction
C) transport across cell membranes
D) sending nerve signals
E) synthesis of an enzyme

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
The first stage of catabolism is
A) the citric acid cycle.
B) production of pyruvate.
C) production of acetyl CoA.
D) buildup of macromolecules from monomers.
E) digestion of large molecules.
A) the citric acid cycle.
B) production of pyruvate.
C) production of acetyl CoA.
D) buildup of macromolecules from monomers.
E) digestion of large molecules.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Lactose intolerance occurs due to
A) an excess of galactose intake.
B) a deficiency of β-galactosidase.
C) a deficiency of lactase.
D) an overabundance of glucose.
E) overproduction of amylase.
A) an excess of galactose intake.
B) a deficiency of β-galactosidase.
C) a deficiency of lactase.
D) an overabundance of glucose.
E) overproduction of amylase.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Muscle contraction is an example of a(n)
A) anabolic process.
B) catabolic process.
C) glucose storage process.
D) protein degradation process.
E) lipid hydrolysis process.
A) anabolic process.
B) catabolic process.
C) glucose storage process.
D) protein degradation process.
E) lipid hydrolysis process.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Digestion of carbohydrates begins in the
A) mouth.
B) stomach.
C) pancreas.
D) small intestine.
E) large intestine.
A) mouth.
B) stomach.
C) pancreas.
D) small intestine.
E) large intestine.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Under aerobic conditions, pyruvate produced in glycolysis can be converted to
A) glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate.
B) lactic acid.
C) glucose-6-phosphate.
D) fructose-6-phosphate.
E) acetyl CoA.
A) glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate.
B) lactic acid.
C) glucose-6-phosphate.
D) fructose-6-phosphate.
E) acetyl CoA.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Muscle contraction requires
A) copper ion and ATP.
B) iron.
C) calcium ion and ATP.
D) lipid hydrolysis.
E) carbon dioxide.
A) copper ion and ATP.
B) iron.
C) calcium ion and ATP.
D) lipid hydrolysis.
E) carbon dioxide.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
FAD stands for
A) flavin adenosine dinucleotide.
B) folic acid diphosphate.
C) fumarate alcohol dehydrogenase.
D) folate adenosine diphosphate.
E) flavin adenine dinucleotide.
A) flavin adenosine dinucleotide.
B) folic acid diphosphate.
C) fumarate alcohol dehydrogenase.
D) folate adenosine diphosphate.
E) flavin adenine dinucleotide.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Which of the following metabolic pathways can occur in the absence of oxygen?
A) electron transport
B) oxidative phosphorylation
C) citric acid cycle
D) glycolysis
E) β-oxidation
A) electron transport
B) oxidative phosphorylation
C) citric acid cycle
D) glycolysis
E) β-oxidation

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
The portion of Coenzyme A that reacts with potential substrates is
A) an acid group.
B) an amino group.
C) a C=O group.
D) an alcohol group.
E) a thiol group.
A) an acid group.
B) an amino group.
C) a C=O group.
D) an alcohol group.
E) a thiol group.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Glycolysis is a(n) __________ process.
A) aerobic
B) anaerobic
C) anabolic
D) one-step
E) five-step
A) aerobic
B) anaerobic
C) anabolic
D) one-step
E) five-step

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
The overall process of glycolysis
A) requires oxygen.
B) uses up 4 ATP molecules.
C) requires acetyl CoA.
D) is an anabolic pathway.
E) produces 2 ATP molecules.
A) requires oxygen.
B) uses up 4 ATP molecules.
C) requires acetyl CoA.
D) is an anabolic pathway.
E) produces 2 ATP molecules.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
NAD+ stands for the coenzyme
A) niacin adenine dinucleotide.
B) nicotinic acid diphosphate.
C) nicotinamide diphosphate.
D) nicotine adenosine dinucleotide.
E) nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide.
A) niacin adenine dinucleotide.
B) nicotinic acid diphosphate.
C) nicotinamide diphosphate.
D) nicotine adenosine dinucleotide.
E) nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
In the process of glycolysis, glucose is converted to
A) pyruvate.
B) citrate.
C) sucrose.
D) oxaloacetate.
E) ribose.
A) pyruvate.
B) citrate.
C) sucrose.
D) oxaloacetate.
E) ribose.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
The process of glycolysis is regulated by
A) cell requirements for pyruvate.
B) allosteric control.
C) ATP needs.
D) feedback inhibition.
E) All of the above.
A) cell requirements for pyruvate.
B) allosteric control.
C) ATP needs.
D) feedback inhibition.
E) All of the above.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
NAD+ participates in reactions that produce
A) a CH₂ group.
B) a C=O bond.
C) phosphorylation.
D) ADP from ATP.
E) a C-C bond.
A) a CH₂ group.
B) a C=O bond.
C) phosphorylation.
D) ADP from ATP.
E) a C-C bond.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Coenzyme A is a molecule whose function is to
A) activate enzyme A.
B) undergo phosphorylation.
C) provide energy for the citric acid cycle.
D) produce acyl groups for reaction.
E) help break down macromolecules.
A) activate enzyme A.
B) undergo phosphorylation.
C) provide energy for the citric acid cycle.
D) produce acyl groups for reaction.
E) help break down macromolecules.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
In biochemical systems, the term reduction often refers to
A) a loss of hydrogen or electrons by a compound.
B) a gain of hydrogen or electrons by a compound.
C) a gain in oxygen.
D) a loss of electrons.
E) an energy-releasing reaction.
A) a loss of hydrogen or electrons by a compound.
B) a gain of hydrogen or electrons by a compound.
C) a gain in oxygen.
D) a loss of electrons.
E) an energy-releasing reaction.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
An enzyme that can facilitate the breakdown of starch into smaller units is
A) glucose phosphatase.
B) alcohol dehydrogenase.
C) amylase.
D) lactase.
E) maltase.
A) glucose phosphatase.
B) alcohol dehydrogenase.
C) amylase.
D) lactase.
E) maltase.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
In step 7 of glycolysis, ATP is generated when a phosphate group is transferred directly from 1,3-diphosphoglycerate to ADP in a process known as
A) oxidation.
B) direct phosphorylation.
C) reduction.
D) transamination.
E) oxidative phosphorylation.
A) oxidation.
B) direct phosphorylation.
C) reduction.
D) transamination.
E) oxidative phosphorylation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
An acyl group contains at least __________ carbon atom(s).
A) one
B) two
C) three
D) four
E) five
A) one
B) two
C) three
D) four
E) five

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
FAD is a coenzyme which usually participates in
A) oxidation of alcohols to aldehydes.
B) formation of carbon-carbon double bonds.
C) decarboxylation reactions.
D) phosphorylation reactions.
E) β-oxidation reactions.
A) oxidation of alcohols to aldehydes.
B) formation of carbon-carbon double bonds.
C) decarboxylation reactions.
D) phosphorylation reactions.
E) β-oxidation reactions.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
Most of the energy in the typical animal cell is produced in the __________.
A) cytosol
B) nucleus
C) mitochondria
D) lysosomes
E) endoplasmic reticulum
A) cytosol
B) nucleus
C) mitochondria
D) lysosomes
E) endoplasmic reticulum

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
The primary energy source for the brain is
A) lactate.
B) triacylglycerols.
C) amino acids.
D) fructose.
E) glucose.
A) lactate.
B) triacylglycerols.
C) amino acids.
D) fructose.
E) glucose.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
The synthesis of glycogen from glucose is called
A) glyceration.
B) gluconeogenesis.
C) glucogenesis.
D) glycogenesis.
E) glycolysis.
A) glyceration.
B) gluconeogenesis.
C) glucogenesis.
D) glycogenesis.
E) glycolysis.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
The net energy production in anaerobic glycolysis is __________.
A) 2 ATP
B) 4 ATP
C) 6 ATP
D) 8 ATP
E) 12 ATP
A) 2 ATP
B) 4 ATP
C) 6 ATP
D) 8 ATP
E) 12 ATP

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Reactions in the mitochondria produce most of the cell's energy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
The production of ethanol from glucose is termed __________.
A) fermentation
B) glycolysis
C) gluconeogenesis
D) β-oxidation
E) dehydrogenation
A) fermentation
B) glycolysis
C) gluconeogenesis
D) β-oxidation
E) dehydrogenation

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
When glycogen is broken down into glucose, the process is called
A) glycogenesis.
B) glycogenolysis.
C) gluconeogenesis.
D) lactate production.
E) glucagon production.
A) glycogenesis.
B) glycogenolysis.
C) gluconeogenesis.
D) lactate production.
E) glucagon production.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
When one glucose molecule undergoes glycolysis it generates
A) 6 ATP.
B) 6 ATP and 2 NADH.
C) 2 ATP and 2 NADH.
D) 2 ATP and 4 NADH.
E) 12 ATP.
A) 6 ATP.
B) 6 ATP and 2 NADH.
C) 2 ATP and 2 NADH.
D) 2 ATP and 4 NADH.
E) 12 ATP.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
When glucose is made from noncarbohydrate sources, the process is called
A) glycogenesis.
B) glycogenolysis.
C) gluconeogenesis.
D) lactate production.
E) glucagon production.
A) glycogenesis.
B) glycogenolysis.
C) gluconeogenesis.
D) lactate production.
E) glucagon production.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
Hydrolysis of sucrose takes place primarily in the __________.
A) mouth
B) stomach
C) pancreas
D) small intestine
E) large intestine
A) mouth
B) stomach
C) pancreas
D) small intestine
E) large intestine

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
The energy for most energy-requiring reactions in the cells of the body is obtained by the hydrolysis of __________.
A) ATP
B) ADP
C) AMP
D) cyclic AMP
E) GTP
A) ATP
B) ADP
C) AMP
D) cyclic AMP
E) GTP

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
Glycogenesis obtains energy from
A) ADP.
B) UTP.
C) Pi.
D) pyrophosphate.
E) pyruvate.
A) ADP.
B) UTP.
C) Pi.
D) pyrophosphate.
E) pyruvate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
Under anaerobic conditions, lactate is produced from
A) acetyl CoA.
B) pyruvate.
C) ATP.
D) carbon dioxide.
E) NAD+.
A) acetyl CoA.
B) pyruvate.
C) ATP.
D) carbon dioxide.
E) NAD+.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
Glycogen is normally stored in
A) heart and lung.
B) liver and muscle.
C) spleen and bone.
D) pancreas and muscle.
E) fat cells and muscle.
A) heart and lung.
B) liver and muscle.
C) spleen and bone.
D) pancreas and muscle.
E) fat cells and muscle.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
The compounds formed when fructose-1, 6-diphosphate is split are
A) pyruvic acid and lactic acid.
B) ethanol and acetyl CoA.
C) dihydroxyacetone phosphate and pyruvic acid.
D) dihydroxyacetone phosphate and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate.
E) glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate and pyruvic acid.
A) pyruvic acid and lactic acid.
B) ethanol and acetyl CoA.
C) dihydroxyacetone phosphate and pyruvic acid.
D) dihydroxyacetone phosphate and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate.
E) glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate and pyruvic acid.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
The cytosol is an aqueous solution of salts and enzymes.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
Energy production in the cell occurs primarily in the nucleus.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
The term that refers to all of the chemical reactions in living cells is __________.
A) glycolysis
B) β-oxidation
C) metabolism
D) anabolism
E) catabolism
A) glycolysis
B) β-oxidation
C) metabolism
D) anabolism
E) catabolism

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
When as much glycogen is stored as possible in the body, excess glucose is converted to
A) triacylglycerols.
B) fructose.
C) sucrose.
D) Coenzyme A.
E) ATP.
A) triacylglycerols.
B) fructose.
C) sucrose.
D) Coenzyme A.
E) ATP.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
Lysosomes digest and recycle old cell structures.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
ATP is the primary energy source for the cell.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
Digestion of a polysaccharide is an anabolic process.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
Catabolic reactions provide energy to generate ATP in the cell.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
Under aerobic conditions, pyruvate is converted to ethanol.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
Identify each of the following metabolic pathways.
glycogenesis
A)the production of glucose from noncarbohydrate molecules
B)the flow of lactate and glucose between muscle and liver
C)the synthesis of glycogen from glucose for storage purposes
D)breaking down of macromolecules
E)the conversion of glucose to lactic acid
F)the conversion of pyruviate to ethanol and CO₂
G)lipid metabolism
glycogenesis
A)the production of glucose from noncarbohydrate molecules
B)the flow of lactate and glucose between muscle and liver
C)the synthesis of glycogen from glucose for storage purposes
D)breaking down of macromolecules
E)the conversion of glucose to lactic acid
F)the conversion of pyruviate to ethanol and CO₂
G)lipid metabolism

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
Identify each of the following metabolic pathways.
fermentation
A)the production of glucose from noncarbohydrate molecules
B)the flow of lactate and glucose between muscle and liver
C)the synthesis of glycogen from glucose for storage purposes
D)breaking down of macromolecules
E)the conversion of glucose to lactic acid
F)the conversion of pyruviate to ethanol and CO₂
G)lipid metabolism
fermentation
A)the production of glucose from noncarbohydrate molecules
B)the flow of lactate and glucose between muscle and liver
C)the synthesis of glycogen from glucose for storage purposes
D)breaking down of macromolecules
E)the conversion of glucose to lactic acid
F)the conversion of pyruviate to ethanol and CO₂
G)lipid metabolism

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
The conversion of ATP to ADP and inorganic phosphate produces 7.3 kcal/mole of energy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
Oxidation involves the gain of electrons for a substance.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
A deficiency in the enzyme lactase causes lactose intolerance.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
In glycolysis, two ATPs are invested and six ATPs are synthesized.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
Identify each of the following metabolic pathways.
gluconeogenesis
A)the production of glucose from noncarbohydrate molecules
B)the flow of lactate and glucose between muscle and liver
C)the synthesis of glycogen from glucose for storage purposes
D)breaking down of macromolecules
E)the conversion of glucose to lactic acid
F)the conversion of pyruviate to ethanol and CO₂
G)lipid metabolism
gluconeogenesis
A)the production of glucose from noncarbohydrate molecules
B)the flow of lactate and glucose between muscle and liver
C)the synthesis of glycogen from glucose for storage purposes
D)breaking down of macromolecules
E)the conversion of glucose to lactic acid
F)the conversion of pyruviate to ethanol and CO₂
G)lipid metabolism

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
ATP contains a ribose sugar.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
FADH₂ is the oxidized form of FAD.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
NAD+ acts as a hydrogen acceptor in metabolic reactions.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
Pantothenic acid is a part of NADH.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
In glycogenesis, excess glucose is used to form glycogen.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
Identify each of the following metabolic pathways.
anaerobic glycolysis
A)the production of glucose from noncarbohydrate molecules
B)the flow of lactate and glucose between muscle and liver
C)the synthesis of glycogen from glucose for storage purposes
D)breaking down of macromolecules
E)the conversion of glucose to lactic acid
F)the conversion of pyruviate to ethanol and CO₂
G)lipid metabolism
anaerobic glycolysis
A)the production of glucose from noncarbohydrate molecules
B)the flow of lactate and glucose between muscle and liver
C)the synthesis of glycogen from glucose for storage purposes
D)breaking down of macromolecules
E)the conversion of glucose to lactic acid
F)the conversion of pyruviate to ethanol and CO₂
G)lipid metabolism

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
In gluconeogenesis, glucose is synthesized from noncarbohydrate material.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
The production of carbon dioxide and water in the body is an anabolic process.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
Digestion of carbohydrates begins in the mouth.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 83 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








