Deck 16: Waves I
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/71
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 16: Waves I
1
The displacement of a string is given by y(x,t) = ymsin(kx + t).
The speed of the wave is:
A) 2 k/
B) /k
C) k
D) 2 /k
E) k/2
The speed of the wave is:
A) 2 k/
B) /k
C) k
D) 2 /k
E) k/2
/k
2
For a given medium, the frequency of a wave is:
A) independent of wavelength
B) proportional to wavelength
C) inversely proportional to wavelength
D) proportional to the amplitude
E) inversely proportional to the amplitude
A) independent of wavelength
B) proportional to wavelength
C) inversely proportional to wavelength
D) proportional to the amplitude
E) inversely proportional to the amplitude
inversely proportional to wavelength
3
The displacement of a string carrying a traveling sinusoidal wave is given by 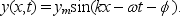 At time t = 0 the point at x = 0 has velocity v0 and displacement y0. The phase constant is given by tan =:
At time t = 0 the point at x = 0 has velocity v0 and displacement y0. The phase constant is given by tan =:
A) v0/ y0
B) y0/v0
C) v0/y0
D) y0/ v0
E) v0y0
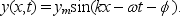 At time t = 0 the point at x = 0 has velocity v0 and displacement y0. The phase constant is given by tan =:
At time t = 0 the point at x = 0 has velocity v0 and displacement y0. The phase constant is given by tan =:A) v0/ y0
B) y0/v0
C) v0/y0
D) y0/ v0
E) v0y0
y0/v0
4
A traveling sinusoidal wave is shown below. At which point is the motion 180 out of phase with the motion at point P? 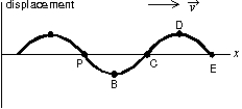
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
Three traveling sinusoidal waves are on identical strings, with the same tension. The mathematical forms of the waves are y1(x,t) = ymsin(3x - 6t), y2(x,t) = ymsin(4x - 8t), and y3(x,t) = ymsin(6x - 12t), where x is in meters and t is in seconds. Match each mathematical form to the appropriate graph below. 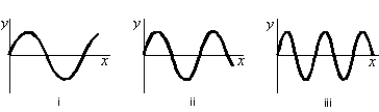
A) y1: i, y2: ii, y3: iii
B) y1: iii, y2: ii, y3: i
C) y1:i, y2: iii, y3: ii
D) y1: ii, y2: i, y3: iii
E) y1: iii, y2: i, y3: ii

A) y1: i, y2: ii, y3: iii
B) y1: iii, y2: ii, y3: i
C) y1:i, y2: iii, y3: ii
D) y1: ii, y2: i, y3: iii
E) y1: iii, y2: i, y3: ii

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Let f be the frequency, v the speed, and T the period of a sinusoidal traveling wave. The correct relationship is:
A) f = 1/T
B) f = v + T
C) f = vT
D) f = v/T
E) f = T/v
A) f = 1/T
B) f = v + T
C) f = vT
D) f = v/T
E) f = T/v

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
For a transverse wave on a string the string displacement is described by y(x,t) = f(x-at) where f is a given function and a is a positive constant. Which of the following does NOT necessarily follow from this statement?
A) The shape of the string at time t = 0 is given by f(x).
B) The shape of the waveform does not change as it moves along the string.
C) The waveform moves in the positive x direction.
D) The speed of the waveform is a.
E) The speed of the waveform is x/t.
A) The shape of the string at time t = 0 is given by f(x).
B) The shape of the waveform does not change as it moves along the string.
C) The waveform moves in the positive x direction.
D) The speed of the waveform is a.
E) The speed of the waveform is x/t.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
A wave is described by y(x,t) = 0.1 sin(3x + 10t), where x is in meters, y is in centimeters and t is in seconds. The angular wave number is:
A) 0.10 rad/m
B) 3 rad/m
C) 10) rad/m
D) (10 ) rad/m
E) 3.0 rad/cm
A) 0.10 rad/m
B) 3 rad/m
C) 10) rad/m
D) (10 ) rad/m
E) 3.0 rad/cm

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
A sinusoidal wave is traveling toward the right as shown. Which letter correctly labels the amplitude of the wave? 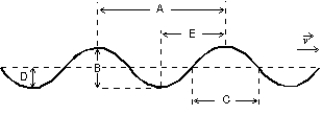
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Water waves in the sea are observed to have a wavelength of 300 m and a frequency of 0.07 Hz. The speed of these waves is:
A) 0.00021 m/s
B) 2.1 m/s
C) 21 m/s
D) 210 m/s
E) none of these
A) 0.00021 m/s
B) 2.1 m/s
C) 21 m/s
D) 210 m/s
E) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
The displacement of a string carrying a traveling sinusoidal wave is given by 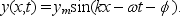 At time t = 0 the point at x = 0 has a velocity of 0 and a positive displacement. The phase constant is:
At time t = 0 the point at x = 0 has a velocity of 0 and a positive displacement. The phase constant is:
A) 45
B) 90
C) 135
D) 180
E) 270
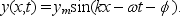 At time t = 0 the point at x = 0 has a velocity of 0 and a positive displacement. The phase constant is:
At time t = 0 the point at x = 0 has a velocity of 0 and a positive displacement. The phase constant is:A) 45
B) 90
C) 135
D) 180
E) 270

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
In the diagram below, the interval PQ represents: 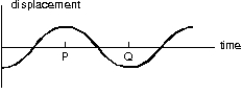
A) wavelength/2
B) wavelength
C) 2 * amplitude
D) period/2
E) period

A) wavelength/2
B) wavelength
C) 2 * amplitude
D) period/2
E) period

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
A sinusoidal transverse wave is traveling on a string. Any point on the string:
A) moves in the same direction as the wave
B) moves in simple harmonic motion with a different frequency than that of the wave
C) moves in simple harmonic motion with the same angular frequency as the wave
D) moves in uniform circular motion with a different angular speed than the wave
E) moves in uniform circular motion with the same angular speed as the wave
A) moves in the same direction as the wave
B) moves in simple harmonic motion with a different frequency than that of the wave
C) moves in simple harmonic motion with the same angular frequency as the wave
D) moves in uniform circular motion with a different angular speed than the wave
E) moves in uniform circular motion with the same angular speed as the wave

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
A wave is described by y(x,t) = 0.1 sin(3x - 10t), where x is in meters, y is in centimeters and t is in seconds. The angular frequency is:
A) 0.10 rad/s
B) 3.0 rad/s
C) 10 rad/s
D) 20 rad/s
E) (10/ rad/s
A) 0.10 rad/s
B) 3.0 rad/s
C) 10 rad/s
D) 20 rad/s
E) (10/ rad/s

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
A sinusoidal wave is traveling toward the right as shown. Which letter correctly labels the wavelength of the wave? 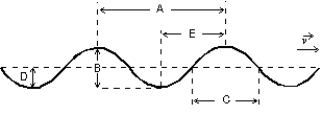
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
The displacement of a string is given by 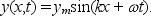 The wavelength of the wave is:
The wavelength of the wave is:
A) 2 k/
B) k/
C) k
D) 2 /k
E) k/2
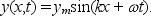 The wavelength of the wave is:
The wavelength of the wave is:A) 2 k/
B) k/
C) k
D) 2 /k
E) k/2

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Let f be the frequency, v the speed, and T the period of a sinusoidal traveling wave. The angular frequency is given by:
A) 1/T
B) 2 /T
C) vT
D) f/T
E) T/f
A) 1/T
B) 2 /T
C) vT
D) f/T
E) T/f

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Sinusoidal waves travel on five identical strings. Four of the strings have the same tension, but the fifth has a different tension. Use the mathematical forms of the waves, gives below, to identify the string with the different tension. In the expressions given below x and y are in centimeters and t is in seconds.
A) y(x,t) = (2 cm) sin (2x - 4t)
B) y(x,t) = (2 cm) sin (4x - 10t)
C) y(x,t) = (2 cm) sin (6x - 12t)
D) y(x,t) = (2 cm) sin (8x - 16t)
E) y(x,t) = (2 cm) sin (10x - 20t)
A) y(x,t) = (2 cm) sin (2x - 4t)
B) y(x,t) = (2 cm) sin (4x - 10t)
C) y(x,t) = (2 cm) sin (6x - 12t)
D) y(x,t) = (2 cm) sin (8x - 16t)
E) y(x,t) = (2 cm) sin (10x - 20t)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
The displacement of a string carrying a traveling sinusoidal wave is given by 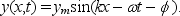 At time t = 0 the point at x = 0 has a displacement of 0 and is moving in the positive y direction. The phase constant is:
At time t = 0 the point at x = 0 has a displacement of 0 and is moving in the positive y direction. The phase constant is:
A) 45
B) 90
C) 135
D) 180
E) 270
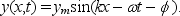 At time t = 0 the point at x = 0 has a displacement of 0 and is moving in the positive y direction. The phase constant is:
At time t = 0 the point at x = 0 has a displacement of 0 and is moving in the positive y direction. The phase constant is:A) 45
B) 90
C) 135
D) 180
E) 270

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Sinusoidal water waves are generated in a large ripple tank. The waves travel at 20 cm/s and their adjacent crests are 5.0 cm apart. The time required for each new whole cycle to be generated is:
A) 100 s
B) 4.0 s
C) 2.0 s
D) 0.5 s
E) 0.25 s
A) 100 s
B) 4.0 s
C) 2.0 s
D) 0.5 s
E) 0.25 s

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
The transverse wave shown is traveling from left to right in a medium. The direction of the instantaneous velocity of the medium at point P is: 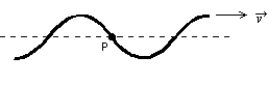
A)
B)
C)
D)
E) no direction since v = 0

A)
B)
C)
D)
E) no direction since v = 0

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Two identical but separate strings, with the same tension, carry sinusoidal waves with the same frequency. Wave A has an amplitude that is twice that of wave B and transmits energy at a rate that is __________ that of wave B.
A) half
B) twice
C) one-fourth
D) four times
E) eight times
A) half
B) twice
C) one-fourth
D) four times
E) eight times

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Any point on a string carrying a sinusoidal wave is moving with its maximum speed when:
A) the magnitude of its acceleration is a maximum
B) the magnitude of its displacement is a maximum
C) the magnitude of its displacement is a minimum
D) the magnitude of its displacement is half the amplitude
E) the magnitude of its displacement is one fourth the amplitude
A) the magnitude of its acceleration is a maximum
B) the magnitude of its displacement is a maximum
C) the magnitude of its displacement is a minimum
D) the magnitude of its displacement is half the amplitude
E) the magnitude of its displacement is one fourth the amplitude

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
A wave traveling to the right on a stretched string is shown below. The direction of the instantaneous velocity of the point P on the string is: 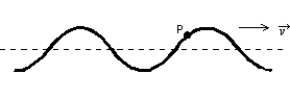
A)
B)
C)
D)
E) no direction since v = 0

A)
B)
C)
D)
E) no direction since v = 0

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
The tension in a string with a linear density of 0.0010 kg/m is 0.40 N. A 100 Hz sinusoidal wave on this string has a wavelength of:
A) 0.05 cm
B) 2.0 cm
C) 5.0 cm
D) 20 cm
E) 100 cm
A) 0.05 cm
B) 2.0 cm
C) 5.0 cm
D) 20 cm
E) 100 cm

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
The diagram shows three identical strings that have been put under tension by suspending masses of 5 kg each. For which is the wave speed the greatest? 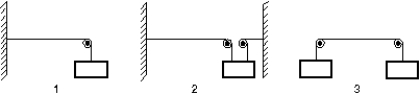
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 1 and 3 tie
E) 2 and 3 tie

A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 1 and 3 tie
E) 2 and 3 tie

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
A long string is constructed by joining the ends of 2 shorter strings. The tension in the strings is the same but string I has 4 times the linear mass density of string II. When a sinusoidal wave passes from string I to string II:
A) the frequency decreases by a factor of 4
B) the frequency decreases by a factor of 2
C) the wave speed decreases by a factor of 4
D) the wave speed decreases by a factor of 2
E) the wave speed increases by a factor of 2
A) the frequency decreases by a factor of 4
B) the frequency decreases by a factor of 2
C) the wave speed decreases by a factor of 4
D) the wave speed decreases by a factor of 2
E) the wave speed increases by a factor of 2

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
A source of frequency f sends waves of wavelength traveling with speed v in some medium. If the frequency is changed from f to 2f, then the new wavelength and new speed are (respectively):
A) 2 , v
B) /2, v
C) , 2v
D) , v/2
E) /2, 2v
A) 2 , v
B) /2, v
C) , 2v
D) , v/2
E) /2, 2v

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
A long string is constructed by joining the ends of two shorter strings. The tension in the strings is the same but string I has 4 times the linear mass density of string II. When a sinusoidal wave passes from string I to string II:
A) the frequency decreases by a factor of 4
B) the frequency decreases by a factor of 2
C) the wavelength decreases by a factor of 4
D) the wavelength decreases by a factor of 2
E) the wavelength increases by a factor of 2
A) the frequency decreases by a factor of 4
B) the frequency decreases by a factor of 2
C) the wavelength decreases by a factor of 4
D) the wavelength decreases by a factor of 2
E) the wavelength increases by a factor of 2

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
The time required for a small pulse to travel from A to B on a stretched cord shown is NOT altered by changing:
A) the linear mass density of the cord
B) the length between A and B
C) the shape of the pulse
D) the tension in the cord
E) none of the above (changes in all alter the time)
A) the linear mass density of the cord
B) the length between A and B
C) the shape of the pulse
D) the tension in the cord
E) none of the above (changes in all alter the time)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
The mathematical forms for the three sinusoidal traveling waves are gives by 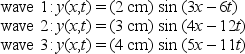 where x is in meters and t is in seconds. Of these waves:
where x is in meters and t is in seconds. Of these waves:
A) wave 1 has the greatest wave speed and the greatest maximum transverse string speed
B) wave 2 has the greatest wave speed and wave 1 has the greatest maxmium transverse string speed
C) wave 3 has the greatest wave speed and the greatest maximum transverse string speed
D) wave 2 has the greatest wave speed and wave 3 has the greatest maximum transverse string speed
E) wave 3 has the greatest wave speed and wave 2 has the greatest maximum transverse string speed
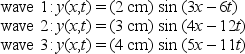 where x is in meters and t is in seconds. Of these waves:
where x is in meters and t is in seconds. Of these waves:A) wave 1 has the greatest wave speed and the greatest maximum transverse string speed
B) wave 2 has the greatest wave speed and wave 1 has the greatest maxmium transverse string speed
C) wave 3 has the greatest wave speed and the greatest maximum transverse string speed
D) wave 2 has the greatest wave speed and wave 3 has the greatest maximum transverse string speed
E) wave 3 has the greatest wave speed and wave 2 has the greatest maximum transverse string speed

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Here are the equations for the three waves traveling on separate strings. Rank them according to the maxium transverse speed, least to greatest. 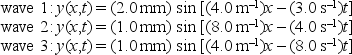
A) 1, 2, 3
B) 1, 3, 2
C) 2, 1, 3
D) 2, 3, 1
E) 3, 1, 2
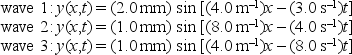
A) 1, 2, 3
B) 1, 3, 2
C) 2, 1, 3
D) 2, 3, 1
E) 3, 1, 2

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
Suppose the maximum speed of a string carrying a sinusoidal wave is vs. When the displacement of a point on the string is half its maximum, the speed of the point is:
A) vs/2
B) 2vs
C) vs/4
D) 3vs/4
E)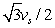
A) vs/2
B) 2vs
C) vs/4
D) 3vs/4
E)
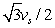

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
When a 100-Hz oscillator is used to generate a sinusoidal wave on a certain string the wavelength is 10 cm. When the tension in the string is doubled the generator produces a wave with a frequency and wavelength of:
A) 200 Hz and 20 cm
B) 141 Hz and 10 cm
C) 100 Hz and 20 cm
D) 100 Hz and 14 cm
E) 50 Hz and 14 cm
A) 200 Hz and 20 cm
B) 141 Hz and 10 cm
C) 100 Hz and 20 cm
D) 100 Hz and 14 cm
E) 50 Hz and 14 cm

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
A sinusoidal wave is generated by moving the end of a string up and down periodically. The generator must supply the greatest power when the end of the string:
A) has its greatest acceleration
B) has its greatest displacement
C) has half its greatest displacement
D) has one fourth its greatest displacement
E) has its least displacement
A) has its greatest acceleration
B) has its greatest displacement
C) has half its greatest displacement
D) has one fourth its greatest displacement
E) has its least displacement

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
A sinusoidal wave is generated by moving the end of a string up and down periodically. The generator does not supply any power when the end of the string
A) has its least acceleration
B) has its greatest displacement
C) has half its greatest displacement
D) has one fourth its greatest displacement
E) has its least displacement
A) has its least acceleration
B) has its greatest displacement
C) has half its greatest displacement
D) has one fourth its greatest displacement
E) has its least displacement

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Two identical but separate strings, with the same tension, carry sinusoidal waves with the same amplitude. Wave A has a frequency that is twice that of wave B and transmits energy at a rate that is __________ that of wave B.
A) half
B) twice
C) one-fourth
D) four times
E) eight times
A) half
B) twice
C) one-fourth
D) four times
E) eight times

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
The speed of a sinusoidal wave on a string depends on:
A) the frequency of the wave
B) the wavelength of the wave
C) the length of the string
D) the tension in the string
E) the amplitude of the wave
A) the frequency of the wave
B) the wavelength of the wave
C) the length of the string
D) the tension in the string
E) the amplitude of the wave

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
A string carries a sinusoidal wave with an amplitude of 2.0 cm and a frequency of 100 Hz. The maximum speed of any point on the string is:
A) 2.0 m/s
B) 4.0 m/s
C) 6.3 m/s
D) 13 m/s
E) unknown (not enough information is given)
A) 2.0 m/s
B) 4.0 m/s
C) 6.3 m/s
D) 13 m/s
E) unknown (not enough information is given)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Three separate strings are made of the same material. String 1 has length L and tension , string 2 has length 2L and tension 2 and string 3 has length 3L and tension 3 . A pulse is started at one end of each string. If the pulses start at the same time, the order in which they reach the other end is:
A) 1, 2, 3
B) 3, 2, 1
C) 2, 3, 1
D) 3, 1, 2
E) they all take the same time
A) 1, 2, 3
B) 3, 2, 1
C) 2, 3, 1
D) 3, 1, 2
E) they all take the same time

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
If is the wavelength of the each of the component sinusoidal traveling waves that form a standing wave, the distance between adjacent nodes in the standing wave is:
A) /4
B) /2
C) 3 /4
D)
E) 2
A) /4
B) /2
C) 3 /4
D)
E) 2

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
When a certain string is clamped at both ends, the lowest four resonant frequencies are measured to be 100, 150, 200, and 250 Hz. One of the resonant frequencies (below 200 Hz) is missing. What is it?
A) 25 Hz
B) 50 Hz
C) 75 Hz
D) 125 Hz
E) 225 Hz
A) 25 Hz
B) 50 Hz
C) 75 Hz
D) 125 Hz
E) 225 Hz

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
Two sinusoidal waves travel in the same direction and have the same frequency. Their amplitudes are y1m and y2m. The smallest possible amplitude of the resultant wave is:
A) y1m + y2m and occurs when they are 180 out of phase
B) y1m - y2m and occurs when they are 180 out of phase
C) y1m + y2m and occurs when they are in phase
D) y1m - y2m and occurs when they are in phase
E) y1m - y2m and occurs when they are 90 out of phase
A) y1m + y2m and occurs when they are 180 out of phase
B) y1m - y2m and occurs when they are 180 out of phase
C) y1m + y2m and occurs when they are in phase
D) y1m - y2m and occurs when they are in phase
E) y1m - y2m and occurs when they are 90 out of phase

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
Two sources, S1 and S2, each emit waves of wavelength in the same medium. The phase difference between the two waves, at the point P shown, is 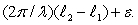 The quantity is:
The quantity is: 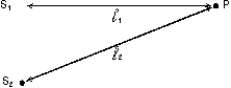
A) the distance S1S2
B) the angle S1PS2
C) /2
D) the phase difference between the two sources
E) zero for transverse waves, for longitudinal waves
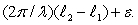 The quantity is:
The quantity is: 
A) the distance S1S2
B) the angle S1PS2
C) /2
D) the phase difference between the two sources
E) zero for transverse waves, for longitudinal waves

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
A wave on a stretched string is reflected from a fixed end P of the string. The phase difference, at P, between the incident and reflected waves is:
A) zero
B) rad
C) /2 rad
D) depends on the velocity of the wave
E) depends on the frequency of the wave
A) zero
B) rad
C) /2 rad
D) depends on the velocity of the wave
E) depends on the frequency of the wave

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
Two traveling waves y1 = A sin[k(x - vt)] and y2 = A sin[k(x + vt)] are superposed on the same string. The distance between the adjacent nodes is:
A) vt/
B) vt/2
C) /2k
D) /k
E) 2 /k
A) vt/
B) vt/2
C) /2k
D) /k
E) 2 /k

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
Two separated sources emit sinusoidal traveling waves that have the same wavelength and are in phase at their respective sources. One travels a distance 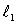 to get to the observation point while the other travels a distance
to get to the observation point while the other travels a distance 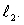 The amplitude is a minimum at the observation point if
The amplitude is a minimum at the observation point if 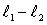 is:
is:
A) an odd multiple of /2
B) an odd multiple of /4
C) a multiple of
D) an odd multiple of /2
E) a multiple of
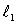 to get to the observation point while the other travels a distance
to get to the observation point while the other travels a distance 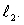 The amplitude is a minimum at the observation point if
The amplitude is a minimum at the observation point if 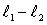 is:
is:A) an odd multiple of /2
B) an odd multiple of /4
C) a multiple of
D) an odd multiple of /2
E) a multiple of

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
Which of the following represents a standing wave?
A) y = (6.0 mm)sin[(3.0 m-1)x + (2.0 s-1)t] - (6.0 mm)cos[(3.0 m-1)x + 2.0]
B) y = (6.0 mm)cos[(3.0 m-1)x - (2.0 s-1)t] + (6.0 mm)cos[(2.0 s-1)t + 3.0 m-1)x]
C) y = (6.0 mm)cos[(3.0 m-1)x - (2.0 s-1)t] - (6.0 mm)sin[(2.0 s-1)t - 3.0]
D) y = (6.0 mm)sin[(3.0 m-1)x - (2.0 s-1)t] - (6.0 mm)cos[(2.0 s-1)t + 3.0 m-1)x]
E) y = (6.0 mm)sin[(3.0 m-1)x] + (6.0 mm)cos[(2.0 s-1)t]
A) y = (6.0 mm)sin[(3.0 m-1)x + (2.0 s-1)t] - (6.0 mm)cos[(3.0 m-1)x + 2.0]
B) y = (6.0 mm)cos[(3.0 m-1)x - (2.0 s-1)t] + (6.0 mm)cos[(2.0 s-1)t + 3.0 m-1)x]
C) y = (6.0 mm)cos[(3.0 m-1)x - (2.0 s-1)t] - (6.0 mm)sin[(2.0 s-1)t - 3.0]
D) y = (6.0 mm)sin[(3.0 m-1)x - (2.0 s-1)t] - (6.0 mm)cos[(2.0 s-1)t + 3.0 m-1)x]
E) y = (6.0 mm)sin[(3.0 m-1)x] + (6.0 mm)cos[(2.0 s-1)t]

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
The sum of two sinusoidal traveling waves is a sinusoidal traveling wave only if:
A) their amplitudes are the same and they travel in the same direction
B) their amplitudes are the same and they travel in opposite directions
C) their frequencies are the same and they travel in the same direction
D) their frequencies are the same and they travel in opposite directions
E) their frequencies are the same and their amplitudes are the same
A) their amplitudes are the same and they travel in the same direction
B) their amplitudes are the same and they travel in opposite directions
C) their frequencies are the same and they travel in the same direction
D) their frequencies are the same and they travel in opposite directions
E) their frequencies are the same and their amplitudes are the same

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
A wave on a string is reflected from a fixed end. The reflected wave:
A) is in phase with the original wave at the end
B) is 180 out of phase with the original wave at the end
C) has a larger amplitude than the original wave
D) has a larger speed than the original wave
E) cannot be transverse
A) is in phase with the original wave at the end
B) is 180 out of phase with the original wave at the end
C) has a larger amplitude than the original wave
D) has a larger speed than the original wave
E) cannot be transverse

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
Fully constructive interference between two sinusoidal waves of the same frequency occurs only if they:
A) travel in opposite directions and are in phase
B) travel in opposite directions and are 180 out of phase
C) travel in the same direction and are in phase
D) travel in the same direction and are 180 out of phase
E) travel in the same direction and are 90 out of phase
A) travel in opposite directions and are in phase
B) travel in opposite directions and are 180 out of phase
C) travel in the same direction and are in phase
D) travel in the same direction and are 180 out of phase
E) travel in the same direction and are 90 out of phase

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
A standing wave:
A) can be constructed from two similar waves traveling in opposite directions
B) must be transverse
C) must be longitudinal
D) has motionless points that are closer than half a wavelength
E) has a wave velocity that differs by a factor of two from what it would be for a traveling wave
A) can be constructed from two similar waves traveling in opposite directions
B) must be transverse
C) must be longitudinal
D) has motionless points that are closer than half a wavelength
E) has a wave velocity that differs by a factor of two from what it would be for a traveling wave

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
A transverse traveling sinusoidal wave on a string has a frequency of 100 Hz, a wavelength of 0.040 m and an amplitude of 2.0 mm. The maximum velocity in m/s of any point on the string is:
A) 0.2
B) 1.3
C) 4
D) 15
E) 25
A) 0.2
B) 1.3
C) 4
D) 15
E) 25

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
Two sinusoidal waves have the same angular frequency, the same amplitude ym, and travel in the same direction in the same medium. If they differ in phase by 50 , the amplitude of the resultant wave is given by
A) 0.64 ym
B) 1.3 ym
C) 0.91 ym
D) 1.8ym
E) 0.35 ym
A) 0.64 ym
B) 1.3 ym
C) 0.91 ym
D) 1.8ym
E) 0.35 ym

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
A transverse traveling sinusoidal wave on a string has a frequency of 100 Hz, a wavelength of 0.040 m and an amplitude of 2.0 mm. The maximum acceleration in m/s2 of any point on the string is:
A) 0
B) 130
C) 395
D) 790
E) 1600
A) 0
B) 130
C) 395
D) 790
E) 1600

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
Two traveling sinusoidal waves interfere to produce a wave with the mathematical form ![<strong>Two traveling sinusoidal waves interfere to produce a wave with the mathematical form If the value of \phi is appropriately chosen, the two waves might be:</strong> A) y<sub>1</sub>(x,t) = (y<sub>m</sub>/3) sin (kx + \omega t) and y<sub>2</sub>(x,t) = (y<sub>m</sub>/3) sin (kx + \omega t + \phi ) B) y<sub>1</sub>(x,t) = 0.7y<sub>m</sub> sin (kx - \omega t) and y<sub>2</sub>(x,t) = 0.7y<sub>m</sub> sin (kx - \omega t + \phi ) C) y<sub>1</sub>(x,t) = 0.7y<sub>m</sub> sin (kx - \omega t) and y<sub>2</sub>(x,t) = 0.7y<sub>m</sub> sin (kx + \omega t + \phi ) D) y<sub>1</sub>(x,t) = 0.7y<sub>m</sub> sin [(kx/2) - ( \omega t/2)] and y<sub>2</sub>(x,t) = 0.7y<sub>m</sub> sin [(kx/2) - ( \omega t/2) + \phi ] E) y<sub>1</sub>(x,t) = 0.7y<sub>m</sub> sin (kx + \omega t) and y<sub>2</sub>(x,t) = 0.7y<sub>m</sub> sin (kx + \omega t + \phi )](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3150/11eaafb8_001f_d279_a7a5_15d1266a1846_TB3150_00.jpg) If the value of is appropriately chosen, the two waves might be:
If the value of is appropriately chosen, the two waves might be:
A) y1(x,t) = (ym/3) sin (kx + t) and y2(x,t) = (ym/3) sin (kx + t + )
B) y1(x,t) = 0.7ym sin (kx - t) and y2(x,t) = 0.7ym sin (kx - t + )
C) y1(x,t) = 0.7ym sin (kx - t) and y2(x,t) = 0.7ym sin (kx + t + )
D) y1(x,t) = 0.7ym sin [(kx/2) - ( t/2)] and y2(x,t) = 0.7ym sin [(kx/2) - ( t/2) + ]
E) y1(x,t) = 0.7ym sin (kx + t) and y2(x,t) = 0.7ym sin (kx + t + )
![<strong>Two traveling sinusoidal waves interfere to produce a wave with the mathematical form If the value of \phi is appropriately chosen, the two waves might be:</strong> A) y<sub>1</sub>(x,t) = (y<sub>m</sub>/3) sin (kx + \omega t) and y<sub>2</sub>(x,t) = (y<sub>m</sub>/3) sin (kx + \omega t + \phi ) B) y<sub>1</sub>(x,t) = 0.7y<sub>m</sub> sin (kx - \omega t) and y<sub>2</sub>(x,t) = 0.7y<sub>m</sub> sin (kx - \omega t + \phi ) C) y<sub>1</sub>(x,t) = 0.7y<sub>m</sub> sin (kx - \omega t) and y<sub>2</sub>(x,t) = 0.7y<sub>m</sub> sin (kx + \omega t + \phi ) D) y<sub>1</sub>(x,t) = 0.7y<sub>m</sub> sin [(kx/2) - ( \omega t/2)] and y<sub>2</sub>(x,t) = 0.7y<sub>m</sub> sin [(kx/2) - ( \omega t/2) + \phi ] E) y<sub>1</sub>(x,t) = 0.7y<sub>m</sub> sin (kx + \omega t) and y<sub>2</sub>(x,t) = 0.7y<sub>m</sub> sin (kx + \omega t + \phi )](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB3150/11eaafb8_001f_d279_a7a5_15d1266a1846_TB3150_00.jpg) If the value of is appropriately chosen, the two waves might be:
If the value of is appropriately chosen, the two waves might be:A) y1(x,t) = (ym/3) sin (kx + t) and y2(x,t) = (ym/3) sin (kx + t + )
B) y1(x,t) = 0.7ym sin (kx - t) and y2(x,t) = 0.7ym sin (kx - t + )
C) y1(x,t) = 0.7ym sin (kx - t) and y2(x,t) = 0.7ym sin (kx + t + )
D) y1(x,t) = 0.7ym sin [(kx/2) - ( t/2)] and y2(x,t) = 0.7ym sin [(kx/2) - ( t/2) + ]
E) y1(x,t) = 0.7ym sin (kx + t) and y2(x,t) = 0.7ym sin (kx + t + )

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
Fully destructive interference between two sinusoidal waves of the same frequency and amplitude occurs only if they:
A) travel in opposite directions and are in phase
B) travel in opposite directions and are 180 out of phase
C) travel in the same direction and are in phase
D) travel in the same direction and are 180 out of phase
E) travel in the same direction and are 90 out of phase
A) travel in opposite directions and are in phase
B) travel in opposite directions and are 180 out of phase
C) travel in the same direction and are in phase
D) travel in the same direction and are 180 out of phase
E) travel in the same direction and are 90 out of phase

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
Two separated sources emit sinusoidal traveling waves that have the same wavelength and are in phase at their respective sources. One travels a distance 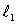 to get to the observation point while the other travels a distance
to get to the observation point while the other travels a distance 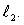 The amplitude is a maximum at the observation point if
The amplitude is a maximum at the observation point if 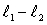 is:
is:
A) an odd multiple of /2
B) an odd multiple of /4
C) a multiple of
D) an odd multiple of /2
E) a multiple of
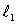 to get to the observation point while the other travels a distance
to get to the observation point while the other travels a distance 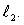 The amplitude is a maximum at the observation point if
The amplitude is a maximum at the observation point if 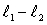 is:
is:A) an odd multiple of /2
B) an odd multiple of /4
C) a multiple of
D) an odd multiple of /2
E) a multiple of

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
The sinusoidal wave y(x,t) = ymsin(kx - t)
Is incident on the fixed end of a string at x = L. The reflected wave is given by:
A) ymsin(kx + t)
B) -ymsin(kx + t)
C) ymsin(kx + t - kL)
D) ymsin(kx + t - 2kL)
E) -ymsin(kx + t + 2kL)
Is incident on the fixed end of a string at x = L. The reflected wave is given by:
A) ymsin(kx + t)
B) -ymsin(kx + t)
C) ymsin(kx + t - kL)
D) ymsin(kx + t - 2kL)
E) -ymsin(kx + t + 2kL)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
When a certain string is clamped at both ends, the lowest four resonant frequencies are 50, 100, 150, and 200 Hz. When the string is also clamped at its midpoint, the lowest four resonant frequencies are:
A) 50, 100, 150, and 200 Hz
B) 50, 150, 250, and 300 Hz
C) 100, 200, 300, and 400 Hz
D) 25, 50 75, and 100 Hz
E) 75, 150, 225, and 300 Hz
A) 50, 100, 150, and 200 Hz
B) 50, 150, 250, and 300 Hz
C) 100, 200, 300, and 400 Hz
D) 25, 50 75, and 100 Hz
E) 75, 150, 225, and 300 Hz

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
Standing waves are produced by the interference of two traveling sinusoidal waves, each of frequency 100 Hz. The distance from the 2nd node to the 5th node is 60 cm. The wavelength of each of the two original waves is:
A) 50 cm
B) 40 cm
C) 30 cm
D) 20 cm
E) 15 cm
A) 50 cm
B) 40 cm
C) 30 cm
D) 20 cm
E) 15 cm

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
A string, clamped at its ends, vibrates in three segments. The string is 100 cm long. The wavelength is:
A) 33.3 cm
B) 66.7 cm
C) 150 cm
D) 300 cm
E) need to know the frequency
A) 33.3 cm
B) 66.7 cm
C) 150 cm
D) 300 cm
E) need to know the frequency

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
A stretched string, clamped at its ends, vibrates in its fundamental frequency. To double the fundamental frequency, one can change the string tension by a factor of:
A) 2
B) 4
C)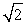
D) 1/2
E)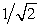
A) 2
B) 4
C)
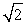
D) 1/2
E)
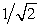

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
Two sinusoidal waves, each of wavelength 5 m and amplitude 10 cm, travel in opposite directions on a 20-m stretched string which is clamped at each end. Excluding the nodes at the ends of the string, how many nodes appear in the resulting standing wave?
A) 3
B) 4
C) 5
D) 7
E) 8
A) 3
B) 4
C) 5
D) 7
E) 8

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
A standing wave pattern is established in a string as shown. The wavelength of one of the component traveling waves is: 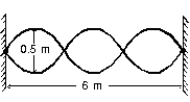
A) 0.25 m
B) 0.5 m
C) 1 m
D) 2 m
E) 4 m

A) 0.25 m
B) 0.5 m
C) 1 m
D) 2 m
E) 4 m

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
A 30-cm long string, with one end clamped and the other free to move transversely, is vibrating in its second harmonic. The wavelength of the constituent traveling waves is:
A) 10 cm
B) 30 cm
C) 40 cm
D) 60 cm
E) 120 cm
A) 10 cm
B) 30 cm
C) 40 cm
D) 60 cm
E) 120 cm

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
A string of length 100 cm is held fixed at both ends and vibrates in a standing wave pattern. The wavelengths of the constituent traveling waves CANNOT be:
A) 400 cm
B) 200 cm
C) 100 cm
D) 66.7 cm
E) 50 cm
A) 400 cm
B) 200 cm
C) 100 cm
D) 66.7 cm
E) 50 cm

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
When a string is vibrating in a standing wave pattern the power transmitted across an antinode, compared to the power transmitted across a node, is:
A) more
B) less
C) the same (zero)
D) the same (non-zero)
E) sometimes more, sometimes less, and sometimes the same
A) more
B) less
C) the same (zero)
D) the same (non-zero)
E) sometimes more, sometimes less, and sometimes the same

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
A 40-cm long string, with one end clamped and the other free to move transversely, is vibrating in its fundamental standing wave mode. The wavelength of the constituent traveling waves is:
A) 10 cm
B) 20 cm
C) 40 cm
D) 80 cm
E) 160 cm
A) 10 cm
B) 20 cm
C) 40 cm
D) 80 cm
E) 160 cm

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
A 40-cm long string, with one end clamped and the other free to move transversely, is vibrating in its fundamental standing wave mode. If the wave speed is 320 cm/s the frequency is:
A) 32 Hz
B) 16 Hz
C) 8 Hz
D) 4 Hz
E) 2 Hz
A) 32 Hz
B) 16 Hz
C) 8 Hz
D) 4 Hz
E) 2 Hz

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
A string of length L is clamped at each end and vibrates in a standing wave pattern. The wavelengths of the constituent traveling waves CANNOT be:
A) L
B) 2L
C) L/2
D) 2L/3
E) 4L
A) L
B) 2L
C) L/2
D) 2L/3
E) 4L

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 71 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








