Deck 41: Conduction of Electricity in Solids
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/48
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 41: Conduction of Electricity in Solids
1
Which one of the following statements concerning electron energy bands in solids is true?
A) the bands occur as a direct consequence of the Fermi-Dirac distribution function
B) electrical conduction arises from the motion of electrons in completely filled bands
C) within a given band, all electron energy levels are equal to each other
D) an insulator has a large energy separation between the highest filled band and the lowest empty band
E) only insulators have energy bands
A) the bands occur as a direct consequence of the Fermi-Dirac distribution function
B) electrical conduction arises from the motion of electrons in completely filled bands
C) within a given band, all electron energy levels are equal to each other
D) an insulator has a large energy separation between the highest filled band and the lowest empty band
E) only insulators have energy bands
an insulator has a large energy separation between the highest filled band and the lowest empty band
2
At T = 0 K the probability that a state 0.50 eV below the Fermi level is occupied is:
A) 0
B) 5.0 *10-9
C) 5.0* 10-6
D) 5.0 * 10-3
E) 1
A) 0
B) 5.0 *10-9
C) 5.0* 10-6
D) 5.0 * 10-3
E) 1
1
3
Ther Fermi energy of a metal depends primarily on:
A) the temperature
B) the volume of the sample
C) the mass density of the metal
D) the size of the sample
E) the number density of conduction electrons
A) the temperature
B) the volume of the sample
C) the mass density of the metal
D) the size of the sample
E) the number density of conduction electrons
the number density of conduction electrons
4
At T = 0 K the probability that a state 0.50 eV above the Fermi level is occupied is:
A) 0
B) 5.0*10-9
C) 5.0 * 10-6
D) 5.0 * 10-3
E) 1
A) 0
B) 5.0*10-9
C) 5.0 * 10-6
D) 5.0 * 10-3
E) 1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 48 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
If E0 and ET are the average energies of the "free" electrons in a metal at 0 K and room temperature respectively, then the ratio ET/E0 is approximately:
A) 0
B) 1
C) 100
D) 106
E) infinity
A) 0
B) 1
C) 100
D) 106
E) infinity

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 48 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
The density of states for a metal depends primarily on:
A) the temperature
B) the energy associated with the state
C) the density of the metal
D) the volume of the sample
E) none of these
A) the temperature
B) the energy associated with the state
C) the density of the metal
D) the volume of the sample
E) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 48 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
For a metal at absolute temperature T, with Fermi energy EF, the occupancy probability is given by:
A)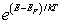
B)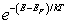
C)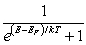
D)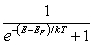
E)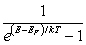
A)
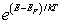
B)
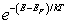
C)
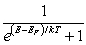
D)
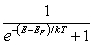
E)
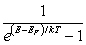

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 48 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
In a pure metal the collisions that are characterized by the mean free time in the expression for the resistivity are chiefly between:
A) electrons and other electrons
B) electrons with energy about equal to the Fermi energy and atoms
C) all electrons and atoms
D) electrons with energy much less than the Fermi energy and atoms
E) atoms and other atoms
A) electrons and other electrons
B) electrons with energy about equal to the Fermi energy and atoms
C) all electrons and atoms
D) electrons with energy much less than the Fermi energy and atoms
E) atoms and other atoms

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 48 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
A certain material has a resistivity of 7.8* 103 .m at room temperature and it increases as the temperature is raised by 100 C. The material is most likely:
A) a metal
B) a pure semiconductor
C) a heavily doped semiconductor
D) an insulator
E) none of the above
A) a metal
B) a pure semiconductor
C) a heavily doped semiconductor
D) an insulator
E) none of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 48 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
A certain material has a resistivity of 7.8 *10-8 .m at room temperature and it increases as the temperature is raised by 100 C. The material is most likely:
A) a metal
B) a pure semiconductor
C) a heavily doped semiconductor
D) an insulator
E) none of the above
A) a metal
B) a pure semiconductor
C) a heavily doped semiconductor
D) an insulator
E) none of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 48 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
A certain metal has 5.3 *1029 conduction electrons/m3 and an electrical resistivity of 1.9* 10-9 m.The average time between collisions of electrons with atoms in the metal is:
A) 5.6 * 10-33 s
B) 1.3*10-31 s
C) 9.9 * 10-22 s
D) 4.6 * 10-15 s
E) 3.5*10-14 s
A) 5.6 * 10-33 s
B) 1.3*10-31 s
C) 9.9 * 10-22 s
D) 4.6 * 10-15 s
E) 3.5*10-14 s

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 48 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
The Fermi-Dirac probability function P(E) varies between:
A) 0 and 1
B) 0 and infinity
C) 1 and infinity
D) -1 and 1
E) 0 and EF
A) 0 and 1
B) 0 and infinity
C) 1 and infinity
D) -1 and 1
E) 0 and EF

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 48 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Electrons in a full band do not contribute to the current when an electric field exists in a solid because:
A) the field cannot exert a force on them
B) the individual contributions cancel each other
C) they are not moving
D) they make transitions to other bands
E) they leave the solid
A) the field cannot exert a force on them
B) the individual contributions cancel each other
C) they are not moving
D) they make transitions to other bands
E) they leave the solid

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 48 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
A certain material has a resistivity of 7.8 *103 . m at room temperature and it decreases as the temperature is raised by 100 C. The material is most likely:
A) a metal
B) a pure semiconductor
C) a heavily doped semiconductor
D) an insulator
E) none of the above
A) a metal
B) a pure semiconductor
C) a heavily doped semiconductor
D) an insulator
E) none of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 48 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
In a metal at 0 K, the Fermi energy is:
A) the highest energy of any electron
B) the lowest energy of any electron
C) the mean thermal energy of the electrons
D) the energy of the top of the valence band
E) the energy at the bottom of the conduction band
A) the highest energy of any electron
B) the lowest energy of any electron
C) the mean thermal energy of the electrons
D) the energy of the top of the valence band
E) the energy at the bottom of the conduction band

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 48 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
The speed of an electron with energy equal to the Fermi energy for copper is on ther order of:
A) 106 m/s
B) 10-6 m/s
C) 10 m/s
D) 10-1 m/s
E) 109 m/s
A) 106 m/s
B) 10-6 m/s
C) 10 m/s
D) 10-1 m/s
E) 109 m/s

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 48 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
The occupancy probability for a state with energy equal to the Fermi energy is:
A) 0
B) 0.5
C) 1
D) 1.5
E) 2
A) 0
B) 0.5
C) 1
D) 1.5
E) 2

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 48 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
The number density n of conductions electrons, the resistivity , and the temperature coefficient of resistivity are given below for five materials. Which is a semiconductor?
A) n = 1029 m-3, = 10-8 . m, = +10-3 K-1
B) n = 1028 m-3, = 10-9 . m, = -10-3 K-1
C) n = 1028 m-3, = 10-9 . m, = +10-3 K-1
D) n = 1015 m-3, = 103 . m, = -10-2 K-1
E) n = 1022 m-3, = 10-7 . m, = +10-3 K-1
A) n = 1029 m-3, = 10-8 . m, = +10-3 K-1
B) n = 1028 m-3, = 10-9 . m, = -10-3 K-1
C) n = 1028 m-3, = 10-9 . m, = +10-3 K-1
D) n = 1015 m-3, = 103 . m, = -10-2 K-1
E) n = 1022 m-3, = 10-7 . m, = +10-3 K-1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 48 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Possible units for the density of states function N(E) are:
A) J/m3
B) 1/J
C) m-3
D) J-1.m-3
E) kg/m3
A) J/m3
B) 1/J
C) m-3
D) J-1.m-3
E) kg/m3

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 48 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
The energy gap (in eV) between the valence and conduction bands of an insulator is of the order:
A) 10-19
B) 0.001
C) 0.1
D) 10
E) 1000
A) 10-19
B) 0.001
C) 0.1
D) 10
E) 1000

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 48 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
The energy level diagram shown applies to: 
A) a conductor
B) an insulator
C) a semiconductor
D) an isolated molecule
E) an isolated atom

A) a conductor
B) an insulator
C) a semiconductor
D) an isolated molecule
E) an isolated atom

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 48 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
An acceptor replacement atom in silicon might have ______ electrons in its outer shell.
A) 3
B) 4
C) 5
D) 6
E) 7
A) 3
B) 4
C) 5
D) 6
E) 7

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 48 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
A given doped semiconductor can be identified as p or n type by:
A) measuring its electrical conductivity
B) measuring its magnetic susceptibility
C) measuring its coefficient of resistivity
D) measuring its heat capacity
E) performing a Hall effect experiment
A) measuring its electrical conductivity
B) measuring its magnetic susceptibility
C) measuring its coefficient of resistivity
D) measuring its heat capacity
E) performing a Hall effect experiment

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 48 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Application of a forward bias to a p-n junction:
A) narrows the depletion zone
B) increases the electric field in the depletion zone
C) increases the potential difference across the depletion zone
D) increases the number of donors on the n side
E) decreases the number of donors on the n side
A) narrows the depletion zone
B) increases the electric field in the depletion zone
C) increases the potential difference across the depletion zone
D) increases the number of donors on the n side
E) decreases the number of donors on the n side

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 48 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
For a pure semiconductor at room temperature the temperature coefficient of resistivity is determined primarily by:
A) the number of electrons in the conduction band
B) the number of replacement atoms
C) the binding energy of outer shell electrons
D) collisions between conduction electrons and atoms
E) none of the above
A) the number of electrons in the conduction band
B) the number of replacement atoms
C) the binding energy of outer shell electrons
D) collisions between conduction electrons and atoms
E) none of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 48 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Acceptor atoms introduced into a pure semiconductor at room temperature:
A) increase the number of electrons in the conduction band
B) increase the number of holes in the valence band
C) lower the Fermi level
D) increase the electrical resistivity
E) none of the above
A) increase the number of electrons in the conduction band
B) increase the number of holes in the valence band
C) lower the Fermi level
D) increase the electrical resistivity
E) none of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 48 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Donor atoms introduced into a pure semiconductor at room temperature:
A) increase the number of electrons in the conduction band
B) increase the number of holes in the valence band
C) lower the Fermi level
D) increase the electrical resistivity
E) none of the above
A) increase the number of electrons in the conduction band
B) increase the number of holes in the valence band
C) lower the Fermi level
D) increase the electrical resistivity
E) none of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 48 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
In an unbiased p-n junction:
A) the electric potential vanishes everywhere
B) the electric field vanishes everywhere
C) the drift current vanishes everywhere
D) the diffusion current vanishes everywhere
E) the diffusion and drift currents cancel each other
A) the electric potential vanishes everywhere
B) the electric field vanishes everywhere
C) the drift current vanishes everywhere
D) the diffusion current vanishes everywhere
E) the diffusion and drift currents cancel each other

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 48 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
At room temperature kT is about 0.0259 eV. The probability that a state 0.50 eV above the Fermi level is occupied at room temperature is:
A) 1
B) 0.05
C) 0.025
D) 5.0 * 10-6
E) 4.1 *10-9
A) 1
B) 0.05
C) 0.025
D) 5.0 * 10-6
E) 4.1 *10-9

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 48 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
The contact electric field in the depletion region of a p-n junction is produced by:
A) electrons in the conduction band alone
B) holes in the valence band alone
C) electrons and holes together
D) charged replacement atoms
E) an applied bias potential difference
A) electrons in the conduction band alone
B) holes in the valence band alone
C) electrons and holes together
D) charged replacement atoms
E) an applied bias potential difference

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 48 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
For a pure semiconductor the Fermi level is:
A) in the conduction band
B) well above the conduction band
C) in the valence band
D) well below the valence band
E) near the center of the gap between the valence and conduction bands
A) in the conduction band
B) well above the conduction band
C) in the valence band
D) well below the valence band
E) near the center of the gap between the valence and conduction bands

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 48 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
A hole refers to:
A) a proton
B) a positively charged electron
C) an electron which has somehow lost its charge
D) a microscopic defect in a solid
E) the absence of an electron in an otherwise filled band
A) a proton
B) a positively charged electron
C) an electron which has somehow lost its charge
D) a microscopic defect in a solid
E) the absence of an electron in an otherwise filled band

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 48 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
If the density of states is N(E) and the occupancy probability is P(E), then the density of unoccupied states is:
A) N(E) + P(E)
B) N(E)/P(E)
C) N(E) - P(E)
D) N(E)P(E)
E) P(E)/N(E)
A) N(E) + P(E)
B) N(E)/P(E)
C) N(E) - P(E)
D) N(E)P(E)
E) P(E)/N(E)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 48 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
At room temperature kT is about 0.0259 eV. The probability that a state 0.50 eV below the Fermi level is unoccupied at room temperature is:
A) 1
B) 0.05
C) 0.025
D) 5.0 *10-6
E) 4.1*10-9
A) 1
B) 0.05
C) 0.025
D) 5.0 *10-6
E) 4.1*10-9

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 48 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
For a metal at room temperature the temperature coefficient of resistivity is determined primarily by:
A) the number of electrons in the conduction band
B) the number of impurity atoms
C) the binding energy of outer shell electrons
D) collisions between conduction electrons and atoms
E) none of the above
A) the number of electrons in the conduction band
B) the number of impurity atoms
C) the binding energy of outer shell electrons
D) collisions between conduction electrons and atoms
E) none of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 48 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
The energy level diagram shown applies to: 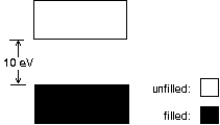
A) a conductor
B) an insulator
C) a semiconductor
D) an isolated atom
E) a free electron gas

A) a conductor
B) an insulator
C) a semiconductor
D) an isolated atom
E) a free electron gas

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 48 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
A pure semiconductor at room temperature has:
A) more electrons/m3 in its conduction band than holes/m3 in its valence band
B) more electrons/m3 in its conduction band than a typical metal
C) more electrons/m3 in its valence band than at T = 0 K
D) more holes/m3 in its valence band than electrons/m3 in its valence band
E) none of the above
A) more electrons/m3 in its conduction band than holes/m3 in its valence band
B) more electrons/m3 in its conduction band than a typical metal
C) more electrons/m3 in its valence band than at T = 0 K
D) more holes/m3 in its valence band than electrons/m3 in its valence band
E) none of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 48 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
A donor replacement atom in silicon might have ______ electrons in its outer shell.
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 48 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
The energy level diagram shown applies to: 
A) a conductor
B) an insulator
C) a semiconductor
D) an isolated molecule
E) an isolated atom

A) a conductor
B) an insulator
C) a semiconductor
D) an isolated molecule
E) an isolated atom

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 48 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
For an unbiased p-n junction, the energy at the bottom of the conduction band on the n side is:
A) higher than the energy at the bottom of the conduction band on the p side
B) lower than the energy at bottom of the conduction band on the p side
C) lower than energy at the top of the valence band on the n side
D) lower than energy at the top of the valence band on the p side
E) the same as the energy at the bottom of the conduction band on the p side
A) higher than the energy at the bottom of the conduction band on the p side
B) lower than the energy at bottom of the conduction band on the p side
C) lower than energy at the top of the valence band on the n side
D) lower than energy at the top of the valence band on the p side
E) the same as the energy at the bottom of the conduction band on the p side

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 48 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
A light emitting diode emits light when:
A) electrons are excited from the valence to the conduction band
B) electrons from the conduction band recombine with holes from the valence band
C) electrons collide with atoms
D) electrons are accelerated by the electric field in the depletion region
E) the junction gets hot
A) electrons are excited from the valence to the conduction band
B) electrons from the conduction band recombine with holes from the valence band
C) electrons collide with atoms
D) electrons are accelerated by the electric field in the depletion region
E) the junction gets hot

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 48 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
Which of the following is NOT true when a back bias is applied to a p-n junction?
A) Electrons flow from the p to the n side
B) Holes flow from the p to the n side
C) The electric field in the depletion zone increases
D) The potential difference across the depletion zone increases
E) The depletion zone narrows
A) Electrons flow from the p to the n side
B) Holes flow from the p to the n side
C) The electric field in the depletion zone increases
D) The potential difference across the depletion zone increases
E) The depletion zone narrows

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 48 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
The gap between the valence and conduction bands of a certain semiconductor is 0.85eV. When this semiconductor is used to form a light emitting diode, the wavelength of the light emitted:
A) is in a range above 1.5*10-6 m
B) is in a range below 1.5 *10-6 m
C) is always 1.5 *10-6 m
D) is in a range centered on 1.5 *10-6 m
E) has nothing to do with the gap
A) is in a range above 1.5*10-6 m
B) is in a range below 1.5 *10-6 m
C) is always 1.5 *10-6 m
D) is in a range centered on 1.5 *10-6 m
E) has nothing to do with the gap

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 48 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
When a forward bias is applied to a p-n junction the concentration of electrons on the p side:
A) increases slightly
B) increases dramatically
C) decreases slightly
D) decreases dramatically
E) does not change
A) increases slightly
B) increases dramatically
C) decreases slightly
D) decreases dramatically
E) does not change

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 48 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Switch S is closed to apply a potential difference V across a p-n junction as shown. Relative to the energy levels of the n-type material, with the switch open, the electron levels of the p-type material are: 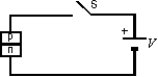
A) unchanged
B) lowered by the amount e-Ve/kT
C) lowered by the amount Ve
D) raised by the amount e-Ve/kT
E) raised by the amount Ve

A) unchanged
B) lowered by the amount e-Ve/kT
C) lowered by the amount Ve
D) raised by the amount e-Ve/kT
E) raised by the amount Ve

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 48 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
"LED" stands for:
A) Less Energy Donated
B) Light Energy Degrader
C) Luminescent Energy Developer
D) Laser Energy Detonator
E) none of the above
A) Less Energy Donated
B) Light Energy Degrader
C) Luminescent Energy Developer
D) Laser Energy Detonator
E) none of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 48 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
A sinusoidal potential difference Vin = Vmsin( t) is applied to the p-n junction as shown. Which graph correctly shows Vout as a function of time? 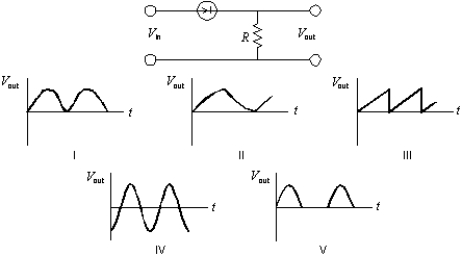
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) V

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 48 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
Application of a forward bias to a p-n junction:
A) increases the drift current in the depletion zone
B) increases the diffusion current in the depletion zone
C) decreases the drift current on the p side outside the depletion zone
D) decreases the drift current on the n side outside the depletion zone
E) does not change the current anywhere
A) increases the drift current in the depletion zone
B) increases the diffusion current in the depletion zone
C) decreases the drift current on the p side outside the depletion zone
D) decreases the drift current on the n side outside the depletion zone
E) does not change the current anywhere

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 48 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








