Deck 23: Gauss Law
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/34
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 23: Gauss Law
1
A 30-N/C uniform electric field points perpendicularly toward the left face of a large neutral conducting sheet. The area charge density on the left and right faces, respectively, are:
A) -2.7 * 10-9 C/m2; +2.7 * 10-9 C/m 2
B) +2.7 * 10-9 C/m2; -2.7 * 10-9 C/m 2
C) -5.3 *10-9 C/m2; +5.3 * 10-9 C/m 2
D) +5.3 * 10-9 C/m2; -5.3 *10-9 C/m 2
E) 0; 0
A) -2.7 * 10-9 C/m2; +2.7 * 10-9 C/m 2
B) +2.7 * 10-9 C/m2; -2.7 * 10-9 C/m 2
C) -5.3 *10-9 C/m2; +5.3 * 10-9 C/m 2
D) +5.3 * 10-9 C/m2; -5.3 *10-9 C/m 2
E) 0; 0
-2.7 * 10-9 C/m2; +2.7 * 10-9 C/m 2
2
A hollow conductor is positively charged. A small uncharged metal ball is lowered by a silk thread through a small opening in the top of the conductor and allowed to touch its inner surface. After the ball is removed, it will have:
A) a positive charge
B) a negative charge
C) no appreciable charge
D) a charge whose sign depends on what part of the inner surface it touched
E) a charge whose sign depends on where the small hole is located in the conductor
A) a positive charge
B) a negative charge
C) no appreciable charge
D) a charge whose sign depends on what part of the inner surface it touched
E) a charge whose sign depends on where the small hole is located in the conductor
no appreciable charge
3
A point charge is placed at the center of a spherical Gaussian surface. The electric flux E is changed if:
A) the sphere is replaced by a cube of the same volume
B) the sphere is replaced by a cube of one-tenth the volume
C) the point charge is moved off center (but still inside the original sphere)
D) the point charge is moved to just outside the sphere
E) a second point charge is placed just outside the sphere
A) the sphere is replaced by a cube of the same volume
B) the sphere is replaced by a cube of one-tenth the volume
C) the point charge is moved off center (but still inside the original sphere)
D) the point charge is moved to just outside the sphere
E) a second point charge is placed just outside the sphere
the point charge is moved to just outside the sphere
4
A round wastepaper basket with a 0.15-m radius opening is in a uniform electric field of 300 N/C, perpendicular to the opening. The total flux through the sides and bottom, in N . m2/C, is:
A) 0
B) 4.2
C) 21
D) 280
E) can't tell without knowing the areas of the sides and bottom
A) 0
B) 4.2
C) 21
D) 280
E) can't tell without knowing the areas of the sides and bottom

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 34 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
A particle with charge 5.0- C is placed at the corner of a cube. The total electric flux in N.m2/C through all sides of the cube is:
A) 0
B) 7.1 * 104
C) 9.4 * 104
D) 1.4 * 105
E) 5.6 * 105
A) 0
B) 7.1 * 104
C) 9.4 * 104
D) 1.4 * 105
E) 5.6 * 105

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 34 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
A 3.5-cm radius hemisphere contains a total charge of 6.6 * 10-7 C. The flux through the rounded portion of the surface is 9.8 *104 N .m2/C. The flux through the flat base is:
A) 0
B) +2.3* 104 N .m2/C
C) -2.3 * 104 N .m2/C
D) -9.8 * 104 N .m2/C
E) +9.8 * 104 N .m2/C
A) 0
B) +2.3* 104 N .m2/C
C) -2.3 * 104 N .m2/C
D) -9.8 * 104 N .m2/C
E) +9.8 * 104 N .m2/C

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 34 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
The outer surface of the cardboard center of a paper towel roll:
A) is a possible Gaussian surface
B) cannot be a Gaussian surface because it encloses no charge
C) cannot be a Gaussian surface since it is not an insulator
D) cannot be a Gaussian surface since it is an insulator
E) none of the above
A) is a possible Gaussian surface
B) cannot be a Gaussian surface because it encloses no charge
C) cannot be a Gaussian surface since it is not an insulator
D) cannot be a Gaussian surface since it is an insulator
E) none of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 34 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
A point particle with charge q is placed inside a cube but not at its center. The electric flux through any one side of the cube:
A) is zero
B) is q/ 0
C) is q/4 0
D) is q/6 0
E) cannot be computed using Gauss' law
A) is zero
B) is q/ 0
C) is q/4 0
D) is q/6 0
E) cannot be computed using Gauss' law

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 34 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
A conducting sphere of radius 0.01 m has a charge of 1.0 * 10-9 C deposited on it. The magnitude of the electric field in N/C just outside the surface of the sphere is:
A) zero
B) 450
C) 900
D) 4500
E) 90,000
A) zero
B) 450
C) 900
D) 4500
E) 90,000

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 34 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
A point particle with charge q is at the center of a Gaussian surface in the form of a cube. The electric flux through any one face of the cube is:
A) q/ 0
B) q/4 0
C) q/4 0
D) q/8 0
E) q/16 0
A) q/ 0
B) q/4 0
C) q/4 0
D) q/8 0
E) q/16 0

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 34 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
A long line of charge with 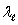 charge per unit length runs along the cylindrical axis of a cylindrical shell which carries a charge per unit length of c. The charge per unit length on the inner and outer surfaces of the shell, respectively are:
charge per unit length runs along the cylindrical axis of a cylindrical shell which carries a charge per unit length of c. The charge per unit length on the inner and outer surfaces of the shell, respectively are:
A)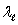 and c
and c
B)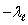 and c +
and c + 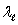
C)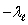 and c - c
and c - c
D)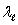 + c and c -
+ c and c - 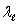
E)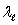 - c and c +
- c and c + 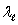
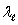 charge per unit length runs along the cylindrical axis of a cylindrical shell which carries a charge per unit length of c. The charge per unit length on the inner and outer surfaces of the shell, respectively are:
charge per unit length runs along the cylindrical axis of a cylindrical shell which carries a charge per unit length of c. The charge per unit length on the inner and outer surfaces of the shell, respectively are:A)
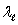 and c
and cB)
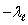 and c +
and c + 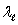
C)
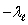 and c - c
and c - cD)
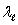 + c and c -
+ c and c - 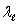
E)
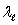 - c and c +
- c and c + 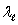

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 34 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
The flux of the electric field 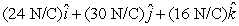 through a 2.0 m2 portion of the yz plane is:
through a 2.0 m2 portion of the yz plane is:
A) 32 N . m2/C
B) 34 N . m2/C
C) 42 N . m2/C
D) 48 N. m2/C
E) 60 N .m2/C
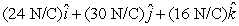 through a 2.0 m2 portion of the yz plane is:
through a 2.0 m2 portion of the yz plane is:A) 32 N . m2/C
B) 34 N . m2/C
C) 42 N . m2/C
D) 48 N. m2/C
E) 60 N .m2/C

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 34 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
10 C of charge are placed on a spherical conducting shell. A particle with a charge of -3-C point charge is placed at the center of the cavity. The net charge in coulombs on the inner surface of the shell is:
A) -7
B) -3
C) 0
D) +3
E) +7
A) -7
B) -3
C) 0
D) +3
E) +7

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 34 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Charge is distributed uniformly along a long straight wire. The electric field 2 cm from the wire is 20 N/C. The electric field 4 cm from the wire is:
A) 120 N/C
B) 80 N/C
C) 40 N/C
D) 10 N/C
E) 5 N/C
A) 120 N/C
B) 80 N/C
C) 40 N/C
D) 10 N/C
E) 5 N/C

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 34 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Choose the INCORRECT statement:
A) Gauss' law can be derived from Coulomb's law
B) Gauss' law states that the net number of lines crossing any closed surface in an outward direction is proportional to the net charge enclosed within the surface
C) Coulomb's law can be derived from Gauss' law and symmetry
D) Gauss' law applies to a closed surface of any shape
E) According to Gauss' law, if a closed surface encloses no charge, then the electric field must vanish everywhere on the surface
A) Gauss' law can be derived from Coulomb's law
B) Gauss' law states that the net number of lines crossing any closed surface in an outward direction is proportional to the net charge enclosed within the surface
C) Coulomb's law can be derived from Gauss' law and symmetry
D) Gauss' law applies to a closed surface of any shape
E) According to Gauss' law, if a closed surface encloses no charge, then the electric field must vanish everywhere on the surface

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 34 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
When a piece of paper is held with one face perpendicular to a uniform electric field the flux through it is 25 N . m2/C. When the paper is turned 25 with respect to the field the flux through it is:
A) 0
B) 12 N .m2/C
C) 21 N .m2/C
D) 23 N . m2/C
E) 25 N . m2/C
A) 0
B) 12 N .m2/C
C) 21 N .m2/C
D) 23 N . m2/C
E) 25 N . m2/C

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 34 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
The table below gives the electric flux in N .m2/C through the ends and round surfaces of four gaussian surfaces in the form of cylinders. Rank the cylinders according to the charge inside, from the most negative to the most positive. 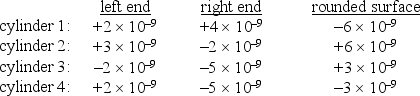
A) 1, 2, 3, 4
B) 4, 3, 2, 1
C) 3, 4, 2, 1
D) 3, 1, 4, 2
E) 4, 3, 1, 2
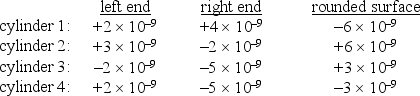
A) 1, 2, 3, 4
B) 4, 3, 2, 1
C) 3, 4, 2, 1
D) 3, 1, 4, 2
E) 4, 3, 1, 2

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 34 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
A physics instructor in an anteroom charges an electrostatic generator to 25 C, then carries it into the lecture hall. The net electric flux in N .m2/C through the lecture hall walls is:
A) 0
B) 25 * 10-6
C) 2.2 * 105
D) 2.8 *106
E) can't tell unless the lecture hall dimensions are given
A) 0
B) 25 * 10-6
C) 2.2 * 105
D) 2.8 *106
E) can't tell unless the lecture hall dimensions are given

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 34 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
10 C of charge are placed on a spherical conducting shell. A particle with a charge of -3C is placed at the center of the cavity. The net charge in coulombs on the outer surface of the shell is:
A) -7
B) -3
C) 0
D) +3
E) +7
A) -7
B) -3
C) 0
D) +3
E) +7

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 34 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Consider Gauss law: 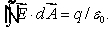 Which of the following is true?
Which of the following is true?
A)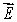 must be the electric field due to the enclosed charge
must be the electric field due to the enclosed charge
B) If q = 0 then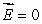 everywhere on the Gaussian surface
everywhere on the Gaussian surface
C) If the three particles inside have charges of +q, +q and -2q, then the integral is zero
D) On the surface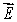 is everywhere parallel to
is everywhere parallel to 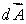
E) If a charge is placed outside the surface, then it cannot affect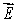 on the at any point on the surface
on the at any point on the surface
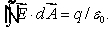 Which of the following is true?
Which of the following is true?A)
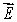 must be the electric field due to the enclosed charge
must be the electric field due to the enclosed chargeB) If q = 0 then
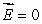 everywhere on the Gaussian surface
everywhere on the Gaussian surfaceC) If the three particles inside have charges of +q, +q and -2q, then the integral is zero
D) On the surface
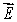 is everywhere parallel to
is everywhere parallel to 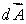
E) If a charge is placed outside the surface, then it cannot affect
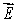 on the at any point on the surface
on the at any point on the surface
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 34 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Charge Q is distributed uniformly throughout a spherical insulating shell. The net electric flux in N . m2/C through the outer surface of the shell is:
A) 0
B) Q/ 0
C) 2Q/ 0
D) Q/4 0
E) Q/2 0
A) 0
B) Q/ 0
C) 2Q/ 0
D) Q/4 0
E) Q/2 0

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 34 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Positive charge Q is placed on a conducting spherical shell with inner radius R1 and outer radius R2. A point charge q is placed at the center of the cavity. The magnitude of the electric field produced by the charge on the inner surface at a point in the interior of the conductor a distance r from the center, is:
A) 0
B)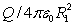
C)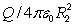
D) q/4 0r2
E) Q/4 0r2
A) 0
B)
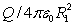
C)
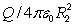
D) q/4 0r2
E) Q/4 0r2

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 34 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Positive charge Q is placed on a conducting spherical shell with inner radius R1 and outer radius R2. A particle with charge q is placed at the center of the cavity. The magnitude of the electric field at a point in the cavity, a distance r from the center, is:
A)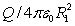
B)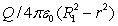
C) q/4 0r2
D) (q + Q)/4 0r2
E)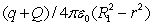
A)
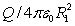
B)
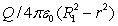
C) q/4 0r2
D) (q + Q)/4 0r2
E)
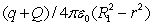

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 34 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Charge Q is distributed uniformly throughout a spherical insulating shell. The net electric flux in N . m2/C through the inner surface of the shell is:
A) 0
B) Q/ 0
C) 2Q/ 0
D) Q/4 0
E) Q/2 0
A) 0
B) Q/ 0
C) 2Q/ 0
D) Q/4 0
E) Q/2 0

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 34 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
A particle with charge Q is placed outside a large neutral conducting sheet. At any point in the interior of the sheet the electric field produced by charges on the surface is directed:
A) toward the surface
B) away from the surface
C) toward Q
D) away from Q
E) none of the above
A) toward the surface
B) away from the surface
C) toward Q
D) away from Q
E) none of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 34 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Charge is distributed uniformly on the surface of a large flat plate. The electric field 2 cm from the plate is 30 N/C. The electric field 4 cm from the plate is:
A) 120 N/C
B) 80 N/C
C) 30 N/C
D) 15 N/C
E) 7.5 N/C
A) 120 N/C
B) 80 N/C
C) 30 N/C
D) 15 N/C
E) 7.5 N/C

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 34 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
A solid insulating sphere of radius R contains a positive charge that is distrubuted with a volume charge density that does not depend on angle but does increase with distance from the sphere center. Which of the graphs below correctly gives the magnitude E of the electric field as a function of the distance r from the center of the sphere? 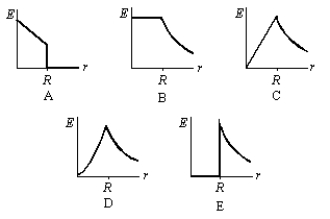
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 34 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Which of the following graphs represents the magnitude of the electric field as a function of the distance from the center of a solid charged conducting sphere of radius R? 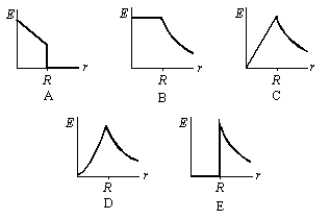
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 34 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Positive charge Q is placed on a conducting spherical shell with inner radius R1 and outer radius R2. A point charge q is placed at the center of the cavity. The magnitude of the electric field at a point outside the shell, a distance r from the center, is:
A)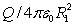
B)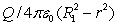
C) q/4 0r2
D) (q + Q)/4 0r2
E)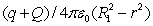
A)
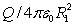
B)
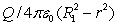
C) q/4 0r2
D) (q + Q)/4 0r2
E)
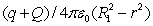

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 34 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
Two large insulating parallel plates carry charge of equal magnitude, one positive and the other negative, that is distributed uniformly over their inner surfaces. Rank the points 1 through 5 according to the magnitude of the electric field at the points, least to greatest. 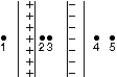
A) 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
B) 5, 4, 3, 2, 1
C) 1, 4, and 5 tie, then 2 and 3 tie
D) 2 and 3 tie, then 1 and 4 tie, then 5
E) 2 and 3 tie, then 1, 4, and 5 tie

A) 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
B) 5, 4, 3, 2, 1
C) 1, 4, and 5 tie, then 2 and 3 tie
D) 2 and 3 tie, then 1 and 4 tie, then 5
E) 2 and 3 tie, then 1, 4, and 5 tie

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 34 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Two large parallel plates carry positive charge of equal magnitude that is distributed uniformly over their inner surfaces. Rank the points 1 through 5 according to the magnitude of the electric field at the points, least to greatest. 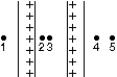
A) 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
B) 5, 4, 3, 2, 1
C) 1, 4, and 5 tie, then 2 and 3 tie
D) 2 and 3 tie, then 1 and 4 tie, then 5
E) 2 and 3 tie, then 1, 4, and 5 tie

A) 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
B) 5, 4, 3, 2, 1
C) 1, 4, and 5 tie, then 2 and 3 tie
D) 2 and 3 tie, then 1 and 4 tie, then 5
E) 2 and 3 tie, then 1, 4, and 5 tie

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 34 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Charge Q is distributed uniformly throughout an insulating sphere of radius R. The magnitude of the electric field at a point R/2 from the center is:
A) Q/4 0R2
B) Q/ 0R2
C) 3Q/4 0R2
D) Q/8 0R2
E) none of these
A) Q/4 0R2
B) Q/ 0R2
C) 3Q/4 0R2
D) Q/8 0R2
E) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 34 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
Positive charge Q is distributed uniformly throughout an insulating sphere of radius R, centered at the origin. A particle with a positive charge Q is placed at x = 2R on the x axis. The magnitude of the electric field at x = R/2 on the x axis is:
A) Q/4 0R2
B) Q/8 0R2
C) 7Q/18 0/R2
D) 11Q/18 0R2
E) none of these
A) Q/4 0R2
B) Q/8 0R2
C) 7Q/18 0/R2
D) 11Q/18 0R2
E) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 34 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
A spherical conducting shell has charge Q. A particle with charge q is placed at the center of the cavity. The charge on the inner surface of the shell and the charge on the outer surface of the shell, respectively, are:
A) 0, Q
B) q, Q - q
C) Q, 0
D) -q, Q + q
E) -q, 0
A) 0, Q
B) q, Q - q
C) Q, 0
D) -q, Q + q
E) -q, 0

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 34 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








