Deck 14: Liquids and Solids
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/39
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 14: Liquids and Solids
1
When a water molecule forms a hydrogen bond with another water molecule, which atoms are involved in the interaction?
A) a hydrogen from one molecule and a hydrogen from the other molecule
B) a hydrogen from one molecule and an oxygen from the other molecule
C) an oxygen from one molecule and an oxygen from the other molecule
D) two hydrogens from one molecule and one oxygen from the other molecule
E) two hydrogens from one molecule and one hydrogen from the other molecule
A) a hydrogen from one molecule and a hydrogen from the other molecule
B) a hydrogen from one molecule and an oxygen from the other molecule
C) an oxygen from one molecule and an oxygen from the other molecule
D) two hydrogens from one molecule and one oxygen from the other molecule
E) two hydrogens from one molecule and one hydrogen from the other molecule
a hydrogen from one molecule and an oxygen from the other molecule
2
The bonding forces that hold the atoms of a molecule together are called intermolecular forces, whereas the forces that occur among molecules that cause them to aggregate to form a solid or a liquid are called intramolecular forces.
False
3
The normal freezing point of water is
A) 0°F
B) 273 K
C) 32°C
D) 373°C
E) none of these
A) 0°F
B) 273 K
C) 32°C
D) 373°C
E) none of these
273 K
4
The bonds between hydrogen and oxygen in a water molecule can be characterized as
A) hydrogen bonds.
B) London forces.
C) intermolecular forces.
D) intramolecular forces.
E) dispersion forces.
A) hydrogen bonds.
B) London forces.
C) intermolecular forces.
D) intramolecular forces.
E) dispersion forces.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 39 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
At 1 atm of pressure and a temperature of 0°C, which phase(s) of H2O can exist?
A) ice and water
B) ice and water vapor
C) water only
D) water vapor only
E) ice only
A) ice and water
B) ice and water vapor
C) water only
D) water vapor only
E) ice only

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 39 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Which of the following has the lowest vapor pressure?
A) H2O
B) NaCl
C) NH3
D) O2
E) CH4
A) H2O
B) NaCl
C) NH3
D) O2
E) CH4

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 39 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
The molar heat of fusion of water is 6.02 kJ/mol. Calculate the energy required to melt 14.7 g of water.
A) 6.02 kJ
B) 4.91 kJ
C) 88.5 kJ
D) 44.0 kJ
E) none of these
A) 6.02 kJ
B) 4.91 kJ
C) 88.5 kJ
D) 44.0 kJ
E) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 39 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
At 1 atm pressure, liquid water always changes to gaseous water at 100oC.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 39 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
The molar heat of fusion of water is 6.02 kJ/mol. Calculate the energy required to melt 44.3 g of water.
A)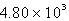 kJ
kJ
B) 267 kJ
C) 2.46 kJ
D) 133 kJ
E) 14.8 kJ
A)
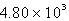 kJ
kJB) 267 kJ
C) 2.46 kJ
D) 133 kJ
E) 14.8 kJ

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 39 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
The molar heats of fusion of water and iodine are 6.02 kJ/mol and 16.7 kJ/mol, respectively. It will take more energy to melt a gram of ice than to melt a gram of solid iodine.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 39 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Calculate the quantity of energy required to change 7.72 mol of liquid water to steam at 100oC. The molar heat of vaporization of water is 40.6 kJ/mol.
A) 5.26 kJ
B) 40.6 kJ
C) 313 kJ
D) 77.2 kJ
E) 48.3 kJ
A) 5.26 kJ
B) 40.6 kJ
C) 313 kJ
D) 77.2 kJ
E) 48.3 kJ

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 39 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
The specific heat capacity of liquid water is 4.18 J/g oC. Calculate the quantity of energy required to heat 10.4 g of water from 26.5oC to 83.7oC.
A)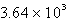 J
J
B)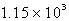 J
J
C) 23.9 J
D)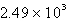 J
J
E) none of these
A)
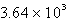 J
JB)
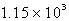 J
JC) 23.9 J
D)
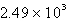 J
JE) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 39 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
The molar heat of fusion of water is 6.02 kJ/mol. Calculate the energy required to melt 3.13 mol of ice.
A) 1.92 kJ
B) 6.02 kJ
C) 18.8 kJ
D) 339 kJ
E) none of these
A) 1.92 kJ
B) 6.02 kJ
C) 18.8 kJ
D) 339 kJ
E) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 39 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
The specific heat capacity of liquid water is 4.18 J/g oC. Calculate the quantity of energy required to heat 1.46 g of water from 26.5oC to 83.7oC. (Ignore significant figures for this problem.)
A) 349 J
B) 511 J
C) 162 J
D) 83.5 J
E) 673 J
A) 349 J
B) 511 J
C) 162 J
D) 83.5 J
E) 673 J

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 39 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
The normal boiling point of water is
A) 0°F
B) 32°F
C) 273 K
D) 373 K
E) none of these
A) 0°F
B) 32°F
C) 273 K
D) 373 K
E) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 39 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Calculate the quantity of energy required to change 22.8 g of liquid water to steam at 100oC. The molar heat of vaporization of water is 40.6 kJ/mol.
A) 10.1 kJ
B) 51.4 kJ
C) 0.562 kJ
D) 32.1 kJ
E)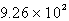 kJ
kJ
A) 10.1 kJ
B) 51.4 kJ
C) 0.562 kJ
D) 32.1 kJ
E)
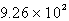 kJ
kJ
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 39 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
The freezing point of helium is approximately -270°C. The freezing point of xenon is -112°C. Both of these are in the noble gas family. Which of the following statements is supported by these data?
A) Helium and xenon form highly polar molecules.
B) As the molar mass of the noble gas increases, the freezing point decreases.
C) The London forces between the helium molecules are greater than the London forces between the xenon molecules.
D) The London forces between the helium molecules are less than the London forces between the xenon molecules.
E) none of these
A) Helium and xenon form highly polar molecules.
B) As the molar mass of the noble gas increases, the freezing point decreases.
C) The London forces between the helium molecules are greater than the London forces between the xenon molecules.
D) The London forces between the helium molecules are less than the London forces between the xenon molecules.
E) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 39 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
More than two-thirds of the earth's surface is covered by water.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 39 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Choose the state of water in which the water molecules are farthest apart on average.
A) steam (vapor)
B) liquid
C) ice (solid)
D) all the same
A) steam (vapor)
B) liquid
C) ice (solid)
D) all the same

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 39 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Which of the following should have the lowest boiling point?
A) CH4
B) C2H6
C) C3H8
D) C4H10
E) C5H12
A) CH4
B) C2H6
C) C3H8
D) C4H10
E) C5H12

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 39 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
What is the major attractive force in CO?
A) dipole-dipole
B) London dispersion
C) ionic
D) hydrogen bonding
E) none of these
A) dipole-dipole
B) London dispersion
C) ionic
D) hydrogen bonding
E) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 39 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Of the following substances, choose the one with the greatest vapor pressure.
A) He(l)
B) Ne(l)
C) Ar(l)
D) Xe(l)
E) Rn(l)
A) He(l)
B) Ne(l)
C) Ar(l)
D) Xe(l)
E) Rn(l)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 39 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
What is the major attractive force in O2?
A) dipole-dipole
B) London dispersion
C) ionic
D) hydrogen bonding
E) none of these
A) dipole-dipole
B) London dispersion
C) ionic
D) hydrogen bonding
E) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 39 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
The normal boiling point of liquid W is lower than that of X, which is lower than that of Y. Which of the following is the correct order of increasing vapor pressure of the thee liquids at STP?
A) Y, X, W
B) X, W, Y
C) W, Y, X
D) W, X, Y
E) X, Y, W
A) Y, X, W
B) X, W, Y
C) W, Y, X
D) W, X, Y
E) X, Y, W

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 39 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
As the temperature of a liquid increases, the vapor pressure of the liquid generally
A) increases
B) decreases
C) stays the same
D) depends on the type of intermolecular forces
A) increases
B) decreases
C) stays the same
D) depends on the type of intermolecular forces

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 39 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
What is the major attractive force in K2O?
A) dipole-dipole
B) London dispersion
C) ionic
D) hydrogen bonding
E) none of these
A) dipole-dipole
B) London dispersion
C) ionic
D) hydrogen bonding
E) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 39 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Which of the following is true for ionic solids dissolved in water?
A) The solution will conduct electricity.
B) The solid will dissolve into neutral molecules.
C) The solution will not conduct electricity.
D) The ions in solution will form a large crystal.
E) none of these
A) The solution will conduct electricity.
B) The solid will dissolve into neutral molecules.
C) The solution will not conduct electricity.
D) The ions in solution will form a large crystal.
E) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 39 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
An alloy has metallic properties.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 39 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Name the type of crystalline solid formed by sodium chloride.
A) ionic solid
B) molecular solid
C) atomic solid
D) amorphous solid
E) none of these
A) ionic solid
B) molecular solid
C) atomic solid
D) amorphous solid
E) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 39 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
Which of the following has the highest melting temperature?
A) H2O
B) CO2
C) S8
D) MgF2
E) P4
A) H2O
B) CO2
C) S8
D) MgF2
E) P4

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 39 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Rank the following compounds from lowest to highest boiling point. CH3OH CH4 H2O C2H6
A) H2O < CH3OH < C2H6 < CH4
B) C2H6 < CH4 < CH3OH < H2O
C) CH4 < C2H6 < CH3OH < H2O
D) CH4 < C2H6 < H2O < CH3OH
E) CH4 < CH3OH < C2H6 < H2O
A) H2O < CH3OH < C2H6 < CH4
B) C2H6 < CH4 < CH3OH < H2O
C) CH4 < C2H6 < CH3OH < H2O
D) CH4 < C2H6 < H2O < CH3OH
E) CH4 < CH3OH < C2H6 < H2O

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 39 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Consider the following compounds: CO NH3 CO2 CH4 H2
Which compound has the highest boiling point?
A) CO
B) NH3
C) CO2
D) CH4
E) At least two of the above compounds have equally high boiling points.
Which compound has the highest boiling point?
A) CO
B) NH3
C) CO2
D) CH4
E) At least two of the above compounds have equally high boiling points.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 39 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
The Pvap for water at 100.0°C is
A) 85 torr
B) 760 torr
C) 175 torr
D) 1 torr
E) More information is needed.
A) 85 torr
B) 760 torr
C) 175 torr
D) 1 torr
E) More information is needed.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 39 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
What is the major attractive force in CH4?
A) dipole-dipole
B) London dispersion
C) ionic
D) hydrogen bonding
E) none of these
A) dipole-dipole
B) London dispersion
C) ionic
D) hydrogen bonding
E) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 39 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Name the type of crystalline solid formed by argon.
A) atomic solid
B) molecular solid
C) ionic solid
D) amorphous solid
E) none of these
A) atomic solid
B) molecular solid
C) ionic solid
D) amorphous solid
E) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 39 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
Consider the following compounds: CO NH3 CO2 CH4 H2
How many of the compounds above exhibit London dispersion forces?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5
How many of the compounds above exhibit London dispersion forces?
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 39 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Select the two compounds that are more likely to be a gas at room temperature (as opposed to a liquid).
a.
CH3OH
b.
CH4
c.
H2O
d.
C2H6
a.
CH3OH
b.
CH4
c.
H2O
d.
C2H6

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 39 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
Name the type of crystalline solid formed by SiO2.
A) molecular solid
B) atomic solid
C) ionic solid
D) amorphous solid
E) none of these
A) molecular solid
B) atomic solid
C) ionic solid
D) amorphous solid
E) none of these

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 39 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
Select the two compounds that are more likely to be a liquid at room temperature (as opposed to a gas).
a.
CH3OH
b.
CH4
c.
H2O
d.
C2H6
a.
CH3OH
b.
CH4
c.
H2O
d.
C2H6

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 39 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








