Deck 4: The Three-Dimensional Structure of Proteins
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/100
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 4: The Three-Dimensional Structure of Proteins
1
The -keratin chains indicated by the diagram below have undergone one chemical step. To alter the shape of the -keratin chains-as in hair waving-what subsequent steps are required? 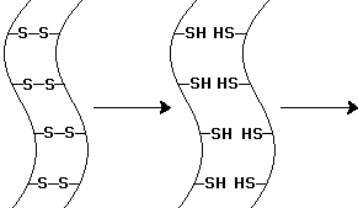
A) chemical oxidation and then shape remodeling
B) chemical reduction and then chemical oxidation
C) chemical reduction and then shape remodeling
D) shape remodeling and then chemical oxidation
E) shape remodeling and then chemical reduction

A) chemical oxidation and then shape remodeling
B) chemical reduction and then chemical oxidation
C) chemical reduction and then shape remodeling
D) shape remodeling and then chemical oxidation
E) shape remodeling and then chemical reduction
shape remodeling and then chemical oxidation
2
The three-dimensional conformation of a protein may be strongly influenced by amino acid residues that are very far apart in sequence. This relationship is in contrast to secondary structure, where the amino acid residues are:
A) always side by side.
B) generally near each other in sequence.
C) invariably restricted to about 7 of the 20 standard amino acids.
D) often on different polypeptide strands.
E) usually near the polypeptide chain's amino terminus or carboxyl terminus.
A) always side by side.
B) generally near each other in sequence.
C) invariably restricted to about 7 of the 20 standard amino acids.
D) often on different polypeptide strands.
E) usually near the polypeptide chain's amino terminus or carboxyl terminus.
B
3
A D-amino acid would interrupt an helix made of L-amino acids. Another naturally occurring hindrance to the formation of an helix is the presence of:
A) a negatively charged Arg residue.
B) a nonpolar residue near the carboxyl terminus.
C) a positively charged Lys residue.
D) a Pro residue.
E) two Ala residues side by side.
A) a negatively charged Arg residue.
B) a nonpolar residue near the carboxyl terminus.
C) a positively charged Lys residue.
D) a Pro residue.
E) two Ala residues side by side.
a Pro residue.
4
In an helix, the R groups on the amino acid residues:
A) alternate between the outside and the inside of the helix.
B) are found on the outside of the helix spiral.
C) cause only right-handed helices to form.
D) generate the hydrogen bonds that form the helix.
E) stack within the interior of the helix.
A) alternate between the outside and the inside of the helix.
B) are found on the outside of the helix spiral.
C) cause only right-handed helices to form.
D) generate the hydrogen bonds that form the helix.
E) stack within the interior of the helix.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
Pauling and Corey's studies of the peptide bond showed that:
A) at pH 7, many different peptide bond conformations are equally probable.
B) peptide bonds are essentially planar, with no rotation about the C-N axis.
C) peptide bonds in proteins are unusual, and unlike those in small model compounds.
D) peptide bond structure is extraordinarily complex.
E) primary structure of all proteins is similar, although the secondary and tertiary structure may differ greatly.
A) at pH 7, many different peptide bond conformations are equally probable.
B) peptide bonds are essentially planar, with no rotation about the C-N axis.
C) peptide bonds in proteins are unusual, and unlike those in small model compounds.
D) peptide bond structure is extraordinarily complex.
E) primary structure of all proteins is similar, although the secondary and tertiary structure may differ greatly.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
In the helix, the hydrogen bonds:
A) are roughly parallel to the axis of the helix.
B) are roughly perpendicular to the axis of the helix.
C) occur mainly between electronegative atoms of the R groups.
D) occur only between some of the amino acids of the helix.
E) occur only near the amino and carboxyl termini of the helix.
A) are roughly parallel to the axis of the helix.
B) are roughly perpendicular to the axis of the helix.
C) occur mainly between electronegative atoms of the R groups.
D) occur only between some of the amino acids of the helix.
E) occur only near the amino and carboxyl termini of the helix.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Which pairs of bonds within a peptide backbone show free rotation around both bonds?
A) C -C and N-C
B) C=O and N-C
C) C=O and N-C
D) N-C and C -C
E) N-C and N-C
A) C -C and N-C
B) C=O and N-C
C) C=O and N-C
D) N-C and C -C
E) N-C and N-C

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Which backbone arrangement BEST represents that of two peptide bonds?
A) C -N-C -C-C -N-C -C
B) C -N-C-C-N-C
C) C-N-C -C -C-N
D) C -C-N-C -C-N
E) C -C -C-N-C -C -C
A) C -N-C -C-C -N-C -C
B) C -N-C-C-N-C
C) C-N-C -C -C-N
D) C -C-N-C -C-N
E) C -C -C-N-C -C -C

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
An helix would be destabilized most by:
A) an electric dipole spanning several peptide bonds throughout the helix.
B) interactions between neighboring Asp and Arg residues.
C) interactions between two adjacent hydrophobic Val residues.
D) the presence of an Arg residue near the carboxyl terminus of the helix.
E) the presence of two Lys residues near the amino terminus of the helix.
A) an electric dipole spanning several peptide bonds throughout the helix.
B) interactions between neighboring Asp and Arg residues.
C) interactions between two adjacent hydrophobic Val residues.
D) the presence of an Arg residue near the carboxyl terminus of the helix.
E) the presence of two Lys residues near the amino terminus of the helix.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Roughly how many amino acids are there in one turn of an helix?
A) 1
B) 2.8
C) 3.6
D) 4.2
E) 10
A) 1
B) 2.8
C) 3.6
D) 4.2
E) 10

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
In an aqueous solution, protein conformation is determined by two major factors. One is the formation of the maximum number of hydrogen bonds. The other is the:
A) formation of the maximum number of hydrophilic interactions.
B) maximization of ionic interactions.
C) minimization of entropy by the formation of a water solvent shell around the protein.
D) placement of hydrophobic amino acid residues within the interior of the protein.
E) placement of polar amino acid residues around the exterior of the protein.
A) formation of the maximum number of hydrophilic interactions.
B) maximization of ionic interactions.
C) minimization of entropy by the formation of a water solvent shell around the protein.
D) placement of hydrophobic amino acid residues within the interior of the protein.
E) placement of polar amino acid residues around the exterior of the protein.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
The major reason that antiparallel -stranded protein structures are more stable than parallel -stranded structures is that the latter:
A) are in a slightly less extended configuration than antiparallel strands.
B) do not have as many disulfide crosslinks between adjacent strands.
C) do not stack in sheets as well as antiparallel strands.
D) have fewer lateral hydrogen bonds than antiparallel strands.
E) have weaker hydrogen bonds laterally between adjacent strands.
A) are in a slightly less extended configuration than antiparallel strands.
B) do not have as many disulfide crosslinks between adjacent strands.
C) do not stack in sheets as well as antiparallel strands.
D) have fewer lateral hydrogen bonds than antiparallel strands.
E) have weaker hydrogen bonds laterally between adjacent strands.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Which statement is NOT an appropriate description for van der Waals interactions?
A) They involve dipole-dipole interactions.
B) Their strength depends on the distance between the two interacting atoms.
C) They are highly specific.
D) An individual van der Waals interaction does not contribute significantly to the stability of a protein.
E) They can involve hydrophobic amino acids.
A) They involve dipole-dipole interactions.
B) Their strength depends on the distance between the two interacting atoms.
C) They are highly specific.
D) An individual van der Waals interaction does not contribute significantly to the stability of a protein.
E) They can involve hydrophobic amino acids.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Which interactions are NOT considered to be "weak" in proteins?
A) hydrogen bonds
B) hydrophobic interactions
C) ionic bonds
D) peptide bonds
E) van der Waals forces
A) hydrogen bonds
B) hydrophobic interactions
C) ionic bonds
D) peptide bonds
E) van der Waals forces

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Thr and/or Leu residues tend to disrupt an helix when they occur next to each other in a protein because:
A) an amino acids like Thr is highly hydrophobic.
B) covalent interactions may occur between the Thr side chains.
C) electrostatic repulsion occurs between the Thr side chains.
D) steric hindrance occurs between the bulky Thr side chains.
E) the R group of Thr can form a hydrogen bond.
A) an amino acids like Thr is highly hydrophobic.
B) covalent interactions may occur between the Thr side chains.
C) electrostatic repulsion occurs between the Thr side chains.
D) steric hindrance occurs between the bulky Thr side chains.
E) the R group of Thr can form a hydrogen bond.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
The MOST important contribution to the stability of a protein's conformation appears to be the:
A) entropy increase from the decrease in ordered water molecules forming a solvent shell around it.
B) maximum entropy increase from ionic interactions between the ionized amino acids in a protein.
C) sum of free energies of formation of many weak interactions among the hundreds of amino acids in a protein.
D) sum of free energies of formation of many weak interactions between its polar amino acids and surrounding water.
E) stabilizing effect of hydrogen bonding between the carbonyl group of one peptide bond and the amino group of another.
A) entropy increase from the decrease in ordered water molecules forming a solvent shell around it.
B) maximum entropy increase from ionic interactions between the ionized amino acids in a protein.
C) sum of free energies of formation of many weak interactions among the hundreds of amino acids in a protein.
D) sum of free energies of formation of many weak interactions between its polar amino acids and surrounding water.
E) stabilizing effect of hydrogen bonding between the carbonyl group of one peptide bond and the amino group of another.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Amino acid residues commonly found in the middle of turn are:
A) Ala and Gly.
B) hydrophobic.
C) Pro and Gly.
D) those with ionized R-groups.
E) two Cys.
A) Ala and Gly.
B) hydrophobic.
C) Pro and Gly.
D) those with ionized R-groups.
E) two Cys.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
A sequence of amino acids in a certain protein is found to be -Ser-Gly-Pro-Gly-. The sequence is most probably part of a(n):
A) antiparallel sheet.
B) parallel sheet.
C) helix.
D) sheet.
E) turn.
A) antiparallel sheet.
B) parallel sheet.
C) helix.
D) sheet.
E) turn.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Which statement about intrinsically disordered proteins is TRUE?
A) They contain small hydrophobic cores.
B) They represent misfolded conformations of cellular proteins.
C) They have no stable three-dimensional structure and therefore have no cellular function.
D) They are responsible for proteostasis.
E) They can interact with multiple protein-binding partners and are central to protein interaction networks.
A) They contain small hydrophobic cores.
B) They represent misfolded conformations of cellular proteins.
C) They have no stable three-dimensional structure and therefore have no cellular function.
D) They are responsible for proteostasis.
E) They can interact with multiple protein-binding partners and are central to protein interaction networks.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
In the diagram below, the plane drawn behind the peptide bond indicates the: 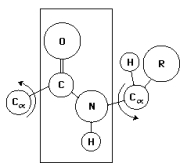
A) absence of rotation around the C-N bond because of its partial double-bond character.
B) plane of rotation around the C -N bond.
C) region of steric hindrance determined by the large C=O group.
D) region of the peptide bond that contributes to a Ramachandran plot.
E) theoretical space between -180 and +180 degrees that can be occupied by the and angles in the peptide bond.

A) absence of rotation around the C-N bond because of its partial double-bond character.
B) plane of rotation around the C -N bond.
C) region of steric hindrance determined by the large C=O group.
D) region of the peptide bond that contributes to a Ramachandran plot.
E) theoretical space between -180 and +180 degrees that can be occupied by the and angles in the peptide bond.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Which residues are MOST likely to be enriched in an intrinsically disordered protein that is soluble in water?
A) Y, K, W
B) E, C, F
C) V, I, L
D) R, K, A
E) H, F, W
A) Y, K, W
B) E, C, F
C) V, I, L
D) R, K, A
E) H, F, W

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Proteins often have regions that can fold and function as an independent entity from the whole protein. These regions are called:
A) domains.
B) oligomers.
C) peptides.
D) sites.
E) subunits.
A) domains.
B) oligomers.
C) peptides.
D) sites.
E) subunits.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
A repeating structural unit in a multimeric protein is known as a(n):
A) domain.
B) motif.
C) oligomer.
D) protomer.
E) subunit.
A) domain.
B) motif.
C) oligomer.
D) protomer.
E) subunit.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
The structural classification of proteins (based on motifs) is based primarily on their:
A) amino-acid sequence.
B) evolutionary relationships.
C) function.
D) secondary structure content and arrangement.
E) subunit content and arrangement.
A) amino-acid sequence.
B) evolutionary relationships.
C) function.
D) secondary structure content and arrangement.
E) subunit content and arrangement.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Experiments on denaturation and renaturation after the reduction and reoxidation of the -S-S- bonds in the enzyme ribonuclease (RNase) have shown that:
A) folding of denatured RNase into the native, active conformation, requires the input of energy in the form of heat.
B) native ribonuclease does not have a unique secondary and tertiary structure.
C) the completely unfolded enzyme, with all -S-S- bonds broken, is still enzymatically active.
D) the enzyme, dissolved in water, is thermodynamically stable relative to the mixture of amino acids whose residues are contained in RNase.
E) the primary sequence of RNase is sufficient to determine its specific secondary and tertiary structure.
A) folding of denatured RNase into the native, active conformation, requires the input of energy in the form of heat.
B) native ribonuclease does not have a unique secondary and tertiary structure.
C) the completely unfolded enzyme, with all -S-S- bonds broken, is still enzymatically active.
D) the enzyme, dissolved in water, is thermodynamically stable relative to the mixture of amino acids whose residues are contained in RNase.
E) the primary sequence of RNase is sufficient to determine its specific secondary and tertiary structure.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Which statement concerning protein domains is TRUE?
A) They are a form of secondary structure.
B) They are examples of structural motifs.
C) They consist of separate polypeptide chains (subunits).
D) They have been found only in prokaryotic proteins.
E) They may retain their correct shape even when separated from the rest of the protein.
A) They are a form of secondary structure.
B) They are examples of structural motifs.
C) They consist of separate polypeptide chains (subunits).
D) They have been found only in prokaryotic proteins.
E) They may retain their correct shape even when separated from the rest of the protein.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Disulfide bonds are more likely to be formed _____ of the cell, due to the _____ environment there.
A) inside; oxidizing
B) inside; reducing
C) outside; oxidizing
D) outside; reducing
E) inside; hydrophobic
A) inside; oxidizing
B) inside; reducing
C) outside; oxidizing
D) outside; reducing
E) inside; hydrophobic

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
A salt bridge would be MOST likely to be found:
A) in the interior of a protein of a bacterium that lives in humans.
B) on the exterior of a protein of a bacterium that lives in humans.
C) in the interior of a protein of a thermophilic archaeal organism.
D) on the exterior of a protein of a thermophilic archaeal organism.
E) A salt bridge would be equally likely to be found in any of these cases.
A) in the interior of a protein of a bacterium that lives in humans.
B) on the exterior of a protein of a bacterium that lives in humans.
C) in the interior of a protein of a thermophilic archaeal organism.
D) on the exterior of a protein of a thermophilic archaeal organism.
E) A salt bridge would be equally likely to be found in any of these cases.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Protein S will fold into its native conformation only when protein Q is also present in the solution. However, protein Q can fold into its native conformation without protein S. Protein Q, therefore, may function as a _____ for protein S.
A) proteasome
B) molecular chaperone
C) protein precursor
D) structural motif
E) supersecondary structural unit
A) proteasome
B) molecular chaperone
C) protein precursor
D) structural motif
E) supersecondary structural unit

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
Which statement is FALSE?
A) Collagen is a protein in which the polypeptides are mainly in the -helix conformation.
B) Disulfide linkages are important for keratin structure.
C) Gly residues are particularly abundant in collagen.
D) Silk fibroin is a protein in which the polypeptide is almost entirely in the conformation.
E) -keratin is a protein in which the polypeptides are mainly in the -helix conformation.
A) Collagen is a protein in which the polypeptides are mainly in the -helix conformation.
B) Disulfide linkages are important for keratin structure.
C) Gly residues are particularly abundant in collagen.
D) Silk fibroin is a protein in which the polypeptide is almost entirely in the conformation.
E) -keratin is a protein in which the polypeptides are mainly in the -helix conformation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Which factor is LEAST likely to result in protein denaturation?
A) altering net charge by changing pH
B) changing the salt concentration
C) disruption of weak interactions by boiling
D) exposure to detergents
E) mixing with organic solvents such as acetone
A) altering net charge by changing pH
B) changing the salt concentration
C) disruption of weak interactions by boiling
D) exposure to detergents
E) mixing with organic solvents such as acetone

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
An average protein will NOT be denatured by:
A) a detergent such as sodium dodecyl sulfate.
B) heating to 90°C.
C) iodoacetic acid.
D) pH 10.
E) urea.
A) a detergent such as sodium dodecyl sulfate.
B) heating to 90°C.
C) iodoacetic acid.
D) pH 10.
E) urea.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
Which factor is NOT known to be involved in the process of assisted folding of proteins?
A) chaperonins
B) disulfide interchange
C) heat shock proteins
D) peptide bond condensation
E) peptide bond isomerization
A) chaperonins
B) disulfide interchange
C) heat shock proteins
D) peptide bond condensation
E) peptide bond isomerization

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
Which group of amino acids would be MOST likely to be found in the core of protein that is folded into a three-dimensional structure and soluble in water?
A) N, Y, and K
B) I, M, and V
C) V, T, and R
D) M, S, and Y
E) F, Y, and W
A) N, Y, and K
B) I, M, and V
C) V, T, and R
D) M, S, and Y
E) F, Y, and W

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Proteostasis is the cellular process by which:
A) proteins are synthesized.
B) proteins are folded.
C) proteins are modified.
D) proteins are degraded.
E) protein levels are maintained.
A) proteins are synthesized.
B) proteins are folded.
C) proteins are modified.
D) proteins are degraded.
E) protein levels are maintained.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
Which statement about oligomeric proteins is FALSE?
A) A subunit may be similar to other proteins.
B) All subunits must be identical.
C) Many have regulatory roles.
D) Some oligomeric proteins can further associate into large fibers.
E) Some subunits may have nonprotein prosthetic groups.
A) A subunit may be similar to other proteins.
B) All subunits must be identical.
C) Many have regulatory roles.
D) Some oligomeric proteins can further associate into large fibers.
E) Some subunits may have nonprotein prosthetic groups.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Proteins in their functional, folded conformation are called _____ proteins.
A) native
B) unique
C) intrinsic
D) inherent
E) natural
A) native
B) unique
C) intrinsic
D) inherent
E) natural

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
Which statement concerning the process of spontaneous folding of proteins is FALSE?
A) It may be an essentially random process.
B) It may be defective in some human diseases.
C) It may involve a gradually decreasing range of conformational species.
D) It may involve initial formation of a highly compact state.
E) It may involve initial formation of local secondary structure.
A) It may be an essentially random process.
B) It may be defective in some human diseases.
C) It may involve a gradually decreasing range of conformational species.
D) It may involve initial formation of a highly compact state.
E) It may involve initial formation of local secondary structure.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
Proteins are classified within families or superfamilies based on similarities in:
A) evolutionary origin.
B) physico-chemical properties.
C) structure and/or function.
D) subcellular location.
E) subunit structure.
A) evolutionary origin.
B) physico-chemical properties.
C) structure and/or function.
D) subcellular location.
E) subunit structure.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Kendrew's studies of the globular myoglobin structure demonstrated that:
A) "corners" between -helical regions invariably lacked proline residue.
B) highly polar or charged amino-acid residues tended to be located interiorally.
C) myoglobin was completely different from hemoglobin, as expected.
D) the structure was very compact, with virtually no internal space available for water.
E) the helix predicted by Pauling and Corey was not found in myoglobin.
A) "corners" between -helical regions invariably lacked proline residue.
B) highly polar or charged amino-acid residues tended to be located interiorally.
C) myoglobin was completely different from hemoglobin, as expected.
D) the structure was very compact, with virtually no internal space available for water.
E) the helix predicted by Pauling and Corey was not found in myoglobin.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
Which method would be BEST to use to monitor protein secondary structure during the titration of a denaturing agent?
A) x-ray crystallography
B) electron microscopy
C) circular dichroism
D) mass spectrometry
E) liquid chromatography
A) x-ray crystallography
B) electron microscopy
C) circular dichroism
D) mass spectrometry
E) liquid chromatography

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
The secondary structure shown below is an example of a(n): 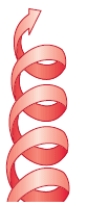
A) parallel sheet.
B) antiparallel sheet.
C) right-handed helix.
D) left-handed helix.
E) turn.

A) parallel sheet.
B) antiparallel sheet.
C) right-handed helix.
D) left-handed helix.
E) turn.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
The dimensions of an helix from a fibrous protein such as keratin differ slightly from an helix from a globular protein. What is the reason for this difference in helical dimensions?
A) An helix from a fibrous protein is left-handed, not right-handed.
B) An helix from a fibrous protein contains mainly hydrophobic residues, elongating the helix.
C) An helix from a fibrous protein contains mainly polar residues, elongating the helix.
D) An helix from a fibrous protein forms a coiled-coil, distorting the helix.
E) An helix from a fibrous protein contains mainly Gly residues for more efficient packing.
A) An helix from a fibrous protein is left-handed, not right-handed.
B) An helix from a fibrous protein contains mainly hydrophobic residues, elongating the helix.
C) An helix from a fibrous protein contains mainly polar residues, elongating the helix.
D) An helix from a fibrous protein forms a coiled-coil, distorting the helix.
E) An helix from a fibrous protein contains mainly Gly residues for more efficient packing.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
As humans age, their connective tissue, rich in collagen, becomes more rigid and brittle. What is the molecular cause of this change?
A) Collagen fibrils change their degree of supercoiling over time.
B) Many older adults have vitamin C deficiencies that result in collagen oxidation.
C) As cells age, a variant of collagen is expressed.
D) Crosslinks between collagen fibrils accumulate over time.
E) UV damage to collagen accumulates over time.
A) Collagen fibrils change their degree of supercoiling over time.
B) Many older adults have vitamin C deficiencies that result in collagen oxidation.
C) As cells age, a variant of collagen is expressed.
D) Crosslinks between collagen fibrils accumulate over time.
E) UV damage to collagen accumulates over time.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
A protein is highly unlikely to have both and angles equal to zero degrees due to:
A) steric hindrance between the side chain and the peptide backbone.
B) polarity differences between adjacent side chains.
C) hydrophobic interactions between adjacent side chains.
D) steric hindrance between adjacent side chains.
E) too few van der Waals contacts for proper folding.
A) steric hindrance between the side chain and the peptide backbone.
B) polarity differences between adjacent side chains.
C) hydrophobic interactions between adjacent side chains.
D) steric hindrance between adjacent side chains.
E) too few van der Waals contacts for proper folding.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
Long-range interactions between residues on a single polypeptide chain could BEST be classified as _____ structure.
A) primary
B) secondary
C) tertiary
D) quaternary
E) globular
A) primary
B) secondary
C) tertiary
D) quaternary
E) globular

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
Which method would NOT increase the strength of a fibrous protein?
A) increasing the number of coiled-coils in the supercomplex
B) increasing the number of Pro residues in the polypeptide
C) increasing the number of Cys residues in the polypeptide
D) placing the protein in an oxidizing environment
E) All of these methods could increase the strength of a fibrous protein.
A) increasing the number of coiled-coils in the supercomplex
B) increasing the number of Pro residues in the polypeptide
C) increasing the number of Cys residues in the polypeptide
D) placing the protein in an oxidizing environment
E) All of these methods could increase the strength of a fibrous protein.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
Interactions between residues on separate polypeptide chains could be best classified as _____ structure.
A) primary
B) secondary
C) tertiary
D) quaternary
E) global
A) primary
B) secondary
C) tertiary
D) quaternary
E) global

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
A _____ protein will often have properties that allow it to be both strong and flexible.
A) macromolecular
B) fibrous
C) globular
D) helical
E) membrane
A) macromolecular
B) fibrous
C) globular
D) helical
E) membrane

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
The secondary structure shown below is an example of a(n): 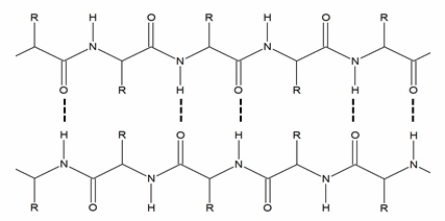
A) parallel sheet.
B) antiparallel sheet.
C) right-handed helix.
D) left-handed helix.
E) turn.

A) parallel sheet.
B) antiparallel sheet.
C) right-handed helix.
D) left-handed helix.
E) turn.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
The difference between the stretching ability of silk and wool fibers, low and high ability to stretch, respectively, is due to their protein components. Which statement CORRECTLY attributes the secondary structure contributions to this stretch ability?
A) Both silk and wool fibers have roughly equal distributions of helices and sheets, but they are arranged in different conformations.
B) Silk is mainly sheets; wool is mainly helices.
C) Silk is mainly helices; wool is mainly sheets.
D) Silk contains mainly barrels; wool contains mainly coiled-coil helices.
E) Silk contains coiled-coil helices; wool contains mainly barrels.
A) Both silk and wool fibers have roughly equal distributions of helices and sheets, but they are arranged in different conformations.
B) Silk is mainly sheets; wool is mainly helices.
C) Silk is mainly helices; wool is mainly sheets.
D) Silk contains mainly barrels; wool contains mainly coiled-coil helices.
E) Silk contains coiled-coil helices; wool contains mainly barrels.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
The _____ secondary structure is formed more readily than other types of secondary structures, most likely due to _____.
A) turn; hydrogen bonds with solvent molecules
B) sheet; R-group contacts
C) sheet; internal hydrogen bonds
D) helix; R-group contacts
E) helix; internal hydrogen helical bonds
A) turn; hydrogen bonds with solvent molecules
B) sheet; R-group contacts
C) sheet; internal hydrogen bonds
D) helix; R-group contacts
E) helix; internal hydrogen helical bonds

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
Which amino acid is MOST likely to be found outside of the highlighted/shaded regions on a Ramachandran plot?
A) Met
B) Cys
C) Ala
D) Gly
E) His
A) Met
B) Cys
C) Ala
D) Gly
E) His

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
Which method would be MOST useful to solve the structure of a small, soluble protein that does not easily form a repeating structure?
A) NMR
B) x-ray crystallography
C) mass spectrometry
D) circular dichroism
E) electron microscopy
A) NMR
B) x-ray crystallography
C) mass spectrometry
D) circular dichroism
E) electron microscopy

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
Using the Ramachandran plot below, identify the secondary structure adopted by an amino acid with phi and psi angles of -90 and 60 degrees, respectively. 
A) right-handed helix
B) left-handed helix
C) sheet
D) twisted sheets
E) Amino acids will not adopt this conformation.

A) right-handed helix
B) left-handed helix
C) sheet
D) twisted sheets
E) Amino acids will not adopt this conformation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
Proline residues are infrequently found in _____ due to their _____.
A) helices; decreased ability to serve as hydrogen-bond donors
B) helices; large positive charge that disrupts the repeating structure
C) sheets; decreased ability to serve as hydrogen-bond donors
D) sheets; large positive charge that disrupts the repeating structure
E) turns; decreased flexibility as an amino acid
A) helices; decreased ability to serve as hydrogen-bond donors
B) helices; large positive charge that disrupts the repeating structure
C) sheets; decreased ability to serve as hydrogen-bond donors
D) sheets; large positive charge that disrupts the repeating structure
E) turns; decreased flexibility as an amino acid

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
Of the following bonds, which have freedom of rotation? I. N - C
II) C - C
III) C - N
IV) R - C
A) All of them
B) II, III, and IV
C) I, II, and IV
D) I, II, and III
E) I and IV
II) C - C
III) C - N
IV) R - C
A) All of them
B) II, III, and IV
C) I, II, and IV
D) I, II, and III
E) I and IV

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
Using the Ramachandran plot below, identify the secondary structure adopted by an amino acid with phi and psi angles of -90 and -180 degrees, respectively. 
A) right-handed helix
B) left-handed helix
C) sheet
D) twisted sheets
E) Amino acids will not adopt this conformation

A) right-handed helix
B) left-handed helix
C) sheet
D) twisted sheets
E) Amino acids will not adopt this conformation

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
Which method would be MOST useful to solve the atomic resolution structure of a protein that happens to easily form a repeating structure?
A) NMR
B) x-ray crystallography
C) mass spectrometry
D) circular dichroism
E) electron microscopy
A) NMR
B) x-ray crystallography
C) mass spectrometry
D) circular dichroism
E) electron microscopy

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
Which peptide could form an amphipathic helix?
A) Nterm-RIFHKVAE-Cterm
B) Nterm-RIHFKMEA-Cterm
C) Nterm-RHKEMVAI-Cterm
D) Nterm-ALIWSQDK-Cterm
E) None of the answers is correct.
A) Nterm-RIFHKVAE-Cterm
B) Nterm-RIHFKMEA-Cterm
C) Nterm-RHKEMVAI-Cterm
D) Nterm-ALIWSQDK-Cterm
E) None of the answers is correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
Which disease is NOT one characterized by or associated with an unfolded protein aggregate?
A) Alzheimer disease
B) diabetes
C) Parkinson disease
D) scurvy
E) All of these diseases are linked to unfolded protein aggregates.
A) Alzheimer disease
B) diabetes
C) Parkinson disease
D) scurvy
E) All of these diseases are linked to unfolded protein aggregates.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
Any given protein is characterized by a unique amino acid sequence (primary structure) and three-dimensional (tertiary) structure. How are these related?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
Describe three of the important features of the -helical polypeptide structure predicted by Pauling and Corey. Provide one or two sentences for each feature.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
Why are glycine and proline often found within a turn?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
Which mutation would be MOST likely to result in amyloid formation?
A) Lys Arg
B) Gln Glu
C) Lys Phe
D) Tyr His
E) Trp Ile
A) Lys Arg
B) Gln Glu
C) Lys Phe
D) Tyr His
E) Trp Ile

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
Pauling and Corey showed that in small peptides, six atoms associated with the peptide bond all lie in a plane. On a dipeptide of two amino acids in trans linkage (side-chains can be shown as -R), which six atoms are part of the planar structure of the peptide bond?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
Provide a brief explanation for the statement "Soluble globular proteins can be distinguished from soluble intrinsically disordered proteins on the basis of their amino acid content."

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
When a polypeptide is in its native conformation, there are weak interactions between its R groups. However, when it is denatured there are similar interactions between the protein groups and water. What then accounts for the greater stability of the native conformation?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
Which statement does NOT describe a feature of the E. coli GroEL/GroES chaperonin system?
A) The conformational changes in GroEL/GroES do not require external energy input.
B) An unfolded protein binds to the hydrophobic surface of the GroEL chamber.
C) Constraining a protein inside the GroEL chamber restricts the conformational space a protein can explore while folding.
D) Constraining a protein inside the GroEL chamber prevents protein aggregation.
E) All of these function in the process of the GroEL/GroES chaperonin.
A) The conformational changes in GroEL/GroES do not require external energy input.
B) An unfolded protein binds to the hydrophobic surface of the GroEL chamber.
C) Constraining a protein inside the GroEL chamber restricts the conformational space a protein can explore while folding.
D) Constraining a protein inside the GroEL chamber prevents protein aggregation.
E) All of these function in the process of the GroEL/GroES chaperonin.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
What is the CORRECT way to classify the protein below according to its secondary-structure elements? 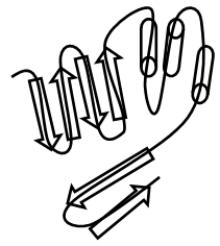
A) all
B) +
C) / 0
D) / /
E) / /

A) all
B) +
C) / 0
D) / /
E) / /

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
Where are the hydrogen bonding typically found between two residues in an helix?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
Name four factors (bonds or other forces) that contribute to stabilizing the native structure of a protein, and describe one condition or reagent that interferes with each type of stabilizing force.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
Intrinsically disordered proteins may:
A) wrap around their targets.
B) have multiple interaction partners.
C) function as molecular "scavengers."
D) lack a hydrophobic core.
E) All of the answers are correct.
A) wrap around their targets.
B) have multiple interaction partners.
C) function as molecular "scavengers."
D) lack a hydrophobic core.
E) All of the answers are correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
The image below plots the denaturation of ribonuclease A as a function of guanidine hydrochloride (GdnHCl) concentration, monitored by circular dichroism. The shape of the curve in the figure supports which statement? 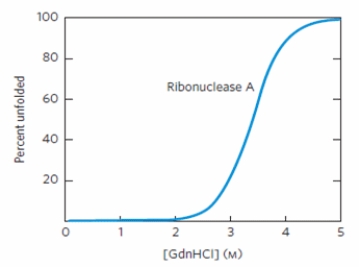
A) The addition of GdnHCl has little effect on protein secondary structure.
B) Increasing temperature causes the protein to become unfolded.
C) Unfolding of this protein is a cooperative process.
D) Ribonuclease A is a heat-stable protein.
E) The peptide bonds of the protein are broken around 3.4 M GdnHCl.

A) The addition of GdnHCl has little effect on protein secondary structure.
B) Increasing temperature causes the protein to become unfolded.
C) Unfolding of this protein is a cooperative process.
D) Ribonuclease A is a heat-stable protein.
E) The peptide bonds of the protein are broken around 3.4 M GdnHCl.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
Describe three of the important features of a sheet polypeptide structure. Provide one or two sentences for each feature.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
Which statement about protein folding is NOT true?
A) Burial of hydrophobic residues requires at least two layers of secondary structure.
B) Generally, helices and sheets are found in different layers of a protein structure.
C) Residues close together in primary structure are often close together in tertiary structure.
D) The conformation is most stable in a right-handed twist.
E) The backbone of a sheet cannot readily hydrogen bond to an adjacent helix.
A) Burial of hydrophobic residues requires at least two layers of secondary structure.
B) Generally, helices and sheets are found in different layers of a protein structure.
C) Residues close together in primary structure are often close together in tertiary structure.
D) The conformation is most stable in a right-handed twist.
E) The backbone of a sheet cannot readily hydrogen bond to an adjacent helix.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
If a protein is not folded correctly or becomes partially unfolded, what could NOT be a consequence?
A) The protein may form an inactive aggregate that leads to disease.
B) The protein may be remodeled by a chaperone.
C) The protein may be degraded by the proteasome.
D) The protein may be refolded.
E) All of these consequences are possible.
A) The protein may form an inactive aggregate that leads to disease.
B) The protein may be remodeled by a chaperone.
C) The protein may be degraded by the proteasome.
D) The protein may be refolded.
E) All of these consequences are possible.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
Which image below shows that there are folding intermediates with substantial stability along nearly every folding pathway? 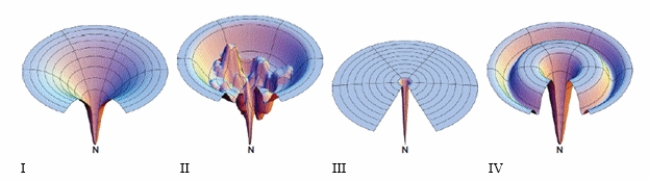
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) None of the answers is correct.

A) I
B) II
C) III
D) IV
E) None of the answers is correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
Which of the images below depict a protein-folding pathway with no stable folding intermediates? 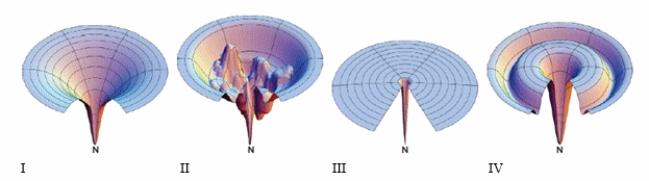
A) I
B) III
C) IV
D) I and III
E) II and IV

A) I
B) III
C) IV
D) I and III
E) II and IV

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
Describe the resonance structure of a peptide bond, and explain why there is no rotation around the C-N bond.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 100 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








