Deck 8: Large-Sample Estimation
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/187
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 8: Large-Sample Estimation
1
Which of the following best describes an unbiased estimator?
A) any sample statistic used to approximate a population parameter
B) a sample statistic which has an expected value equal to the value of the population parameter
C) a sample statistic whose value is usually less than the value of the population parameter
D) any estimator whose standard error is relatively small
A) any sample statistic used to approximate a population parameter
B) a sample statistic which has an expected value equal to the value of the population parameter
C) a sample statistic whose value is usually less than the value of the population parameter
D) any estimator whose standard error is relatively small
B
2
From a sample of 200 items, 12 items are defective. In this case, what will be the point estimate of the population proportion defective?
A) 0.06
B) 0.12
C) 12
D) 16.67
A) 0.06
B) 0.12
C) 12
D) 16.67
A
3
Which of the following best describes the term "margin of error"?
A) It is the difference between the point estimate and the true value of the population parameter.
B) It is the critical value times the standard error of the estimator.
C) It is the smallest possible sampling error.
D) It is a measurement of the variability of the true value of the population parameter.
A) It is the difference between the point estimate and the true value of the population parameter.
B) It is the critical value times the standard error of the estimator.
C) It is the smallest possible sampling error.
D) It is a measurement of the variability of the true value of the population parameter.
B
4
Which of the following best describes an interval estimate?
A) It is a sampling procedure that matches each unit from population A with a "twin" from population B, so that any sample observation about a unit in population A automatically yields an associated observation about a unit in population B.
B) It is an estimate of a population parameter that is expressed as a range of values within which the unknown but true parameter presumably lies.
C) It is a sample statistic such that the mean of all its possible values equals the population parameter the statistic seeks to estimate.
D) It is the sum of an estimator's squared bias plus its variance.
A) It is a sampling procedure that matches each unit from population A with a "twin" from population B, so that any sample observation about a unit in population A automatically yields an associated observation about a unit in population B.
B) It is an estimate of a population parameter that is expressed as a range of values within which the unknown but true parameter presumably lies.
C) It is a sample statistic such that the mean of all its possible values equals the population parameter the statistic seeks to estimate.
D) It is the sum of an estimator's squared bias plus its variance.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
Which of these options is the best definition of a point estimate?
A) It is the average of the sample values.
B) It is the average of the population values.
C) It is a single value that is the best estimate of an unknown population parameter.
D) It is a single value that is the best estimate of an unknown sample statistic.
A) It is the average of the sample values.
B) It is the average of the population values.
C) It is a single value that is the best estimate of an unknown population parameter.
D) It is a single value that is the best estimate of an unknown sample statistic.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
In developing an interval estimate for a population mean for which the population standard deviation 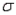 was 8, the interval estimate was 40.52
was 8, the interval estimate was 40.52 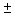 3.24. If
3.24. If 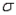 had equalled 16, what would the interval estimate have been?
had equalled 16, what would the interval estimate have been?
A) 40.526.48
B) 40.5211.24
C) 48.5211.24
D) 81.046.48
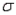 was 8, the interval estimate was 40.52
was 8, the interval estimate was 40.52 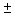 3.24. If
3.24. If 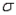 had equalled 16, what would the interval estimate have been?
had equalled 16, what would the interval estimate have been?A) 40.526.48
B) 40.5211.24
C) 48.5211.24
D) 81.046.48

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
A 99% confidence interval estimate for a population mean 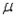 is determined to be 85.58 to 96.62. If the confidence level is reduced to 90%, what happens to the confidence interval for
is determined to be 85.58 to 96.62. If the confidence level is reduced to 90%, what happens to the confidence interval for 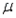 ?
?
A) It becomes wider.
B) It remains the same.
C) It becomes narrower.
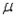 is determined to be 85.58 to 96.62. If the confidence level is reduced to 90%, what happens to the confidence interval for
is determined to be 85.58 to 96.62. If the confidence level is reduced to 90%, what happens to the confidence interval for 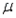 ?
?A) It becomes wider.
B) It remains the same.
C) It becomes narrower.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
After constructing a confidence interval estimate for a population mean, you believe that the interval is useless because it is too wide. In order to correct this , what should you do?
A) increase the population size
B) increase the sample mean
C) increase the confidence coefficient
D) increase the sample size
A) increase the population size
B) increase the sample mean
C) increase the confidence coefficient
D) increase the sample size

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Which of the following must hold before one can make use of the standard normal distribution in order to construct a confidence interval estimate for the population proportion p?
A) and) are both greater than 5, whereis the sample proportion.
B) np and n(1 - p) are both greater than 5.
C) (p +) and (p -) are both greater than 1.
D) The sample size is greater than 5.
A) and) are both greater than 5, whereis the sample proportion.
B) np and n(1 - p) are both greater than 5.
C) (p +) and (p -) are both greater than 1.
D) The sample size is greater than 5.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
What is the type of sample statistic that is used to make inferences about a given type of population parameter?
A) the estimator of that parameter
B) the confidence level of that parameter
C) the confidence interval of that parameter
D) the point estimate of that parameter
A) the estimator of that parameter
B) the confidence level of that parameter
C) the confidence interval of that parameter
D) the point estimate of that parameter

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Whenever a sampled population is normally distributed, or whenever the conditions of the Central Limit Theorem are fulfilled, what may be said of the sample mean 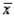 ?
?
A) It is a consistent estimator of the population mean,, because the mean of the sampling distribution of the sample mean equals.
B) It is an efficient estimator of the population mean,, because the mean of the sampling distribution of the sample mean equals.
C) It is an unbiased estimator of the population mean,, because the mean of the sampling distribution of the sample mean equals.
D) It is an efficient estimator of the population mean,, because the mean of the sampling distribution of the sample proportion equals p.
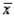 ?
?A) It is a consistent estimator of the population mean,, because the mean of the sampling distribution of the sample mean equals.
B) It is an efficient estimator of the population mean,, because the mean of the sampling distribution of the sample mean equals.
C) It is an unbiased estimator of the population mean,, because the mean of the sampling distribution of the sample mean equals.
D) It is an efficient estimator of the population mean,, because the mean of the sampling distribution of the sample proportion equals p.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Which of these options provides the best interpretation of a 90% confidence interval estimate of the population mean 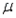 ?
?
A) If we repeatedly draw samples of the same size from the same population, 90% of the values of the sample meanswill result in a confidence interval that includes the population mean.
B) There is a 90% probability that the population meanwill lie between the lower confidence limit (LCL) and the upper confidence limit (UCL).
C) We are 90% confident that we have selected a sample whose range of values does not contain the population mean.
D) We are 90% confident that 10% the values of the sample meanswill result in a confidence interval that includes the population mean.
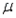 ?
?A) If we repeatedly draw samples of the same size from the same population, 90% of the values of the sample meanswill result in a confidence interval that includes the population mean.
B) There is a 90% probability that the population meanwill lie between the lower confidence limit (LCL) and the upper confidence limit (UCL).
C) We are 90% confident that we have selected a sample whose range of values does not contain the population mean.
D) We are 90% confident that 10% the values of the sample meanswill result in a confidence interval that includes the population mean.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
In order to estimate the average number of kilometres that students living off-campus commute to classes every day, the following statistics were given: n = 50, 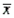 = 5.21, and s = 2.48. Which of the values below would be the best point estimate of the true population mean
= 5.21, and s = 2.48. Which of the values below would be the best point estimate of the true population mean 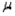 ?
?
A) 1.96
B) 2.10
C) 5.21
D) 7.07
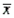 = 5.21, and s = 2.48. Which of the values below would be the best point estimate of the true population mean
= 5.21, and s = 2.48. Which of the values below would be the best point estimate of the true population mean 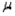 ?
?A) 1.96
B) 2.10
C) 5.21
D) 7.07

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
In developing an interval estimate for a population mean, a sample of 40 observations was used. The interval estimate was 17.25 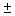 2.42. If the sample size had been 160 instead of 40, what would the interval estimate have been?
2.42. If the sample size had been 160 instead of 40, what would the interval estimate have been?
A) 17.251.21
B) 17.259.68
C) 34.504.82
D) 69.009.68
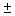 2.42. If the sample size had been 160 instead of 40, what would the interval estimate have been?
2.42. If the sample size had been 160 instead of 40, what would the interval estimate have been?A) 17.251.21
B) 17.259.68
C) 34.504.82
D) 69.009.68

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Which of the following is NOT a part of the formula for constructing a confidence interval estimate of the population proportion?
A) a point estimate of the population proportion
B) the standard error of the sampling distribution of the sample proportion
C) the confidence coefficient
D) the value of the population proportion
A) a point estimate of the population proportion
B) the standard error of the sampling distribution of the sample proportion
C) the confidence coefficient
D) the value of the population proportion

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Why do those who engage in estimation insist on random sampling, rather than convenience sampling or judgment sampling?
A) because random sampling avoids the errors inherent in matched pairs sampling
B) because random sampling avoids the errors inherent in work sampling
C) because random sampling eliminates the systematic error or bias that arises in non-random sampling
A) because random sampling avoids the errors inherent in matched pairs sampling
B) because random sampling avoids the errors inherent in work sampling
C) because random sampling eliminates the systematic error or bias that arises in non-random sampling

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
What would be the lower limit of a confidence interval, at the 95% level of confidence, for the population proportion if a sample of size 100 were to have 30 successes?
A) 0.2102
B) 0.2959
C) 0.3041
D) 0.3898
A) 0.2102
B) 0.2959
C) 0.3041
D) 0.3898

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Which of these statements is NOT a property of the confidence interval estimate of the population mean?
A) Its width narrows when the sample size increases.
B) Its width narrows when the value of the sample mean increases.
C) Its width widens when the confidence level increases.
A) Its width narrows when the sample size increases.
B) Its width narrows when the value of the sample mean increases.
C) Its width widens when the confidence level increases.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
What is a sample statistic such that the mean of all its possible values differs from the population parameter that the statistic seeks to estimate?
A) an efficient estimator
B) an inconsistent estimator
C) a biased estimator
D) a Bayesian estimator
A) an efficient estimator
B) an inconsistent estimator
C) a biased estimator
D) a Bayesian estimator

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Which of the following best defines statistical estimation?
A) a process of inferring the values of unknown population parameters from those of known sample statistics
B) a process of inferring the values of unknown sample statistics from those of known population parameters
C) any procedure that views the parameter being estimated not as a constant, but, just like the estimator, as a random variable
D) a sampling procedure that matches each unit from population A with a "twin" from population B so that any sample observation about a unit in population A automatically yields an associated observation about a unit in population B
A) a process of inferring the values of unknown population parameters from those of known sample statistics
B) a process of inferring the values of unknown sample statistics from those of known population parameters
C) any procedure that views the parameter being estimated not as a constant, but, just like the estimator, as a random variable
D) a sampling procedure that matches each unit from population A with a "twin" from population B so that any sample observation about a unit in population A automatically yields an associated observation about a unit in population B

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
A recent survey indicates that the proportion of season ticket holders for the school hockey team who renew their seats is about 0.80. Using a 95% confidence interval and a margin of error of 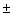 0.025, what is the approximate size of the sample needed to estimate the true proportion who plan to renew their seats?
0.025, what is the approximate size of the sample needed to estimate the true proportion who plan to renew their seats?
A) 689
B) 697
C) 984
D) 1179
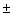 0.025, what is the approximate size of the sample needed to estimate the true proportion who plan to renew their seats?
0.025, what is the approximate size of the sample needed to estimate the true proportion who plan to renew their seats?A) 689
B) 697
C) 984
D) 1179

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
If the population deviation 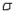 is known and we wish to estimate the population mean
is known and we wish to estimate the population mean 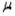 with 90% confidence, what is the appropriate critical z-value to use?
with 90% confidence, what is the appropriate critical z-value to use?
A) 1.28
B) 1.645
C) 1.96
D) 2.33
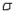 is known and we wish to estimate the population mean
is known and we wish to estimate the population mean 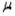 with 90% confidence, what is the appropriate critical z-value to use?
with 90% confidence, what is the appropriate critical z-value to use?A) 1.28
B) 1.645
C) 1.96
D) 2.33

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
If we wish to construct a 95% confidence interval estimate for the difference between two population proportions, what would the confidence level be?
A) 1.96
B) 0.95
C) 0.475
D) 0.05
A) 1.96
B) 0.95
C) 0.475
D) 0.05

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
A random sample of 400 students was surveyed to determine an estimate for the proportion of all students who had attended at least three football games. The estimate revealed that between 0.372 and 0.458 of all students attended. Given this information, which of the following is the approximate value of the confidence coefficient?
A) 0.95
B) 0.92
C) 0.90
D) 0.88
A) 0.95
B) 0.92
C) 0.90
D) 0.88

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
If the population deviation 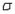 is known and we wish to estimate the population mean
is known and we wish to estimate the population mean 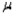 with 95% confidence, which of the following would be the appropriate critical z-value to use?
with 95% confidence, which of the following would be the appropriate critical z-value to use?
A) 1.28
B) 1.645
C) 1.96
D) 2.33
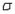 is known and we wish to estimate the population mean
is known and we wish to estimate the population mean 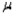 with 95% confidence, which of the following would be the appropriate critical z-value to use?
with 95% confidence, which of the following would be the appropriate critical z-value to use?A) 1.28
B) 1.645
C) 1.96
D) 2.33

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
To what does the term "confidence level" refer?
A) the absolute number of interval estimates that can be expected to contain the actual value of the parameter being estimated when the same procedure of interval construction is used again and again
B) the percentage of interval estimates that can be expected to contain the actual value of the parameter being estimated when the same procedure of interval construction is used again and again
C) the range of values among which an unknown population parameter can presumably be found
D) the sum of an estimator's squared bias plus its variance, which indicates the degree to which it is consistent, efficient, and unbiased
A) the absolute number of interval estimates that can be expected to contain the actual value of the parameter being estimated when the same procedure of interval construction is used again and again
B) the percentage of interval estimates that can be expected to contain the actual value of the parameter being estimated when the same procedure of interval construction is used again and again
C) the range of values among which an unknown population parameter can presumably be found
D) the sum of an estimator's squared bias plus its variance, which indicates the degree to which it is consistent, efficient, and unbiased

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Suppose you wish to estimate the difference between two population means when the population variances are known. Which critical values of z can you use to develop the 90% confidence interval estimate?
A) 2.33
B) 1.96
C) 1.645
D) 1.28
A) 2.33
B) 1.96
C) 1.645
D) 1.28

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
In order to construct a 95% confidence interval estimate for the difference between the means of two normally distributed populations, where the unknown population variances are assumed not to be equal, the following summary statistics were computed from two independent samples: 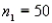 ,
, 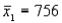 ,
, 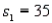 ,
, 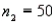 ,
, 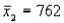 , and
, and 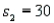 . In this case, what is the upper confidence limit?
. In this case, what is the upper confidence limit?
A) 6.78
B) 18.78
C) 77.3
D) 89.3
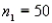 ,
, 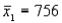 ,
, 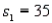 ,
, 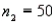 ,
, 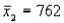 , and
, and 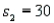 . In this case, what is the upper confidence limit?
. In this case, what is the upper confidence limit?A) 6.78
B) 18.78
C) 77.3
D) 89.3

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
When two independent random samples of sizes 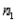 and
and 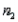 have been selected from populations with means
have been selected from populations with means 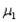 and
and 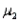 and variances
and variances 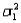 and
and 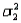 , respectively, which of the following is a property of the sampling distribution of
, respectively, which of the following is a property of the sampling distribution of 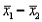 ?
?
A) If the sampled populations are normally distributed, then the sampling distribution ofis exactly normal only whenandare both 30 or more.
B) If the sampled populations are normally distributed, then the sampling distribution ofis exactly normal regardless of the sizes ofand.
C) If the sampled populations are not normally distributed, then the sampling distribution ofis approximately normally distributed regardless of the sizes ofand.
D) If the sampled populations are not normally distributed, then the sampling distribution ofis approximately normally distributed only ifis 30 or more.
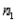 and
and 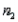 have been selected from populations with means
have been selected from populations with means 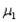 and
and 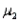 and variances
and variances 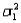 and
and 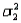 , respectively, which of the following is a property of the sampling distribution of
, respectively, which of the following is a property of the sampling distribution of 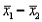 ?
?A) If the sampled populations are normally distributed, then the sampling distribution ofis exactly normal only whenandare both 30 or more.
B) If the sampled populations are normally distributed, then the sampling distribution ofis exactly normal regardless of the sizes ofand.
C) If the sampled populations are not normally distributed, then the sampling distribution ofis approximately normally distributed regardless of the sizes ofand.
D) If the sampled populations are not normally distributed, then the sampling distribution ofis approximately normally distributed only ifis 30 or more.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
In developing a confidence interval estimate for the difference between two population means, which of the following will result from an increase in the size of the sample?
A) a wider confidence interval
B) a narrower confidence interval
C) a smaller critical z-value
D) a larger critical z-value
A) a wider confidence interval
B) a narrower confidence interval
C) a smaller critical z-value
D) a larger critical z-value

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Which of the following are possible options when estimating a population mean 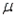 , where the population standard deviation
, where the population standard deviation 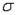 is known?
is known?
A) We may define the limits of an interval estimate ofas.
B) We may define the limits of an interval estimate ofas.
C) We may choose a smaller z-value, construct a narrower confidence interval, and achieve a higher confidence level.
D) We may choose a larger z-value, construct a wider confidence interval, and achieve a lower confidence level.
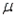 , where the population standard deviation
, where the population standard deviation 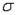 is known?
is known?A) We may define the limits of an interval estimate ofas.
B) We may define the limits of an interval estimate ofas.
C) We may choose a smaller z-value, construct a narrower confidence interval, and achieve a higher confidence level.
D) We may choose a larger z-value, construct a wider confidence interval, and achieve a lower confidence level.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
A 95% confidence interval for the population proportion of professional tennis players who earn more than $2 million a year is found to be between 0.82 and 0.88. What was the approximate sample size used to obtain this information?
A) 545
B) 387
C) 382
D) 233
A) 545
B) 387
C) 382
D) 233

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
What is the z-value needed to construct a 92.5% confidence interval estimate for the difference between two population proportions?
A) 2.58
B) 2.33
C) 1.96
D) 1.78
A) 2.58
B) 2.33
C) 1.96
D) 1.78

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
A statistician wishes to reduce the margin of error associated with a confidence interval estimate for a population proportion p. What does she or he need to do?
A) reduce the confidence level 1 -
B) decrease the sample size n
C) take another sample
D) increase the sample size n
A) reduce the confidence level 1 -
B) decrease the sample size n
C) take another sample
D) increase the sample size n

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
If a 90% confidence interval estimate for the difference between two population proportions is to be constructed, what would the confidence coefficient be?
A) 0.90
B) 0.45
C) 0.10
D) 0.05
A) 0.90
B) 0.45
C) 0.10
D) 0.05

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
What is the z-value needed to construct a 97.8% confidence interval estimate for the difference between two population proportions?
A) 2.29
B) 2.02
C) 1.96
D) 1.65
A) 2.29
B) 2.02
C) 1.96
D) 1.65

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Suppose you wish to estimate the difference between two population means when the population variances are known. Which critical value of z can you use to develop the 99% confidence interval estimate?
A) 2.575
B) 2.325
C) 1.645
D) 1.275
A) 2.575
B) 2.325
C) 1.645
D) 1.275

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
What is the approximate z-value you would use if you wish to construct an 85% upper confidence bound for the population proportion p?
A) 2.33
B) 1.96
C) 1.65
D) 1.04
A) 2.33
B) 1.96
C) 1.65
D) 1.04

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
What is the approximate z-value you would use if you wish to construct an 80% lower confidence bound for the population mean 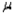 ?
?
A) 0.84
B) 1.28
C) 1.96
D) 2.33
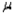 ?
?A) 0.84
B) 1.28
C) 1.96
D) 2.33

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Suppose the population standard deviation equals 10. What is the sample size needed to estimate, with 95% confidence, a population mean within 1.5 units of its true value?
A) 171
B) 121
C) 54
D) 13
A) 171
B) 121
C) 54
D) 13

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
What is the approximate z-value you would use if you wish to construct a 92% lower confidence bound for the difference between population means in the case of large samples?
A) 2.58
B) 1.65
C) 1.41
D) 1.06
A) 2.58
B) 1.65
C) 1.41
D) 1.06

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
What is the approximate z-value you would use if you wish to construct a 98% upper confidence bound for the difference between population proportions?
A) 2.33
B) 2.05
C) 1.65
D) 1.41
A) 2.33
B) 2.05
C) 1.65
D) 1.41

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
An estimator is a random variable calculated from a random sample that provides either a point estimate or an interval estimate for some population parameter.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
The margin of error equals the sum of an estimator's squared bias plus its variance.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
An interval estimate is an interval that provides an upper and a lower bound for a specific population parameter whose value is unknown.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
An unbiased estimator of a population parameter is an estimator whose variance is the same as the actual value of the population variance.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
The error of estimation is the difference between a statistic computed from a sample and the corresponding parameter computed from the population.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
The sample standard deviation, s, is an unbiased estimator of the population standard deviation, 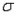 .
.
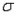 .
.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
A point estimate is a single number that is used as an estimate of a population parameter or population characteristic. It is usually derived from a random sample from the population of interest.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
If the campaign manager of the Conservative Party is interested in estimating the proportion of voters who will support the Conservative Party in the next federal election, the sample proportion, 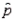 , would be the appropriate point estimate.
, would be the appropriate point estimate.
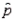 , would be the appropriate point estimate.
, would be the appropriate point estimate.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
A statistic is said to be unbiased if its sampling distribution has the smallest standard error.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
The maximum distance between an estimator and the true value of a parameter is called the margin of error.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
If a store manager is interested in estimating the mean amount spent per customer per visit at her store, the sample mean 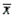 would be the approximate point estimate.
would be the approximate point estimate.
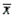 would be the approximate point estimate.
would be the approximate point estimate.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
A sample statistic such that the mean of all its possible values equals the population parameter that the statistic seeks to estimate is an unbiased estimator.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
The error of estimation is the distance between an estimate and the estimated parameter.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
A sample statistic such that the mean of all its possible values differs from the population parameter that the statistic seeks to estimate is a biased estimator.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
Suppose you wish to estimate a population mean 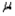 based on a sample of n observations. What sample size is required if you want your estimate to be within 2 standard deviations of
based on a sample of n observations. What sample size is required if you want your estimate to be within 2 standard deviations of 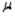 with probability equal to 0.95, if you know the population standard deviation
with probability equal to 0.95, if you know the population standard deviation 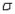 is 12?
is 12?
A) 239
B) 196
C) 139
D) 98
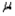 based on a sample of n observations. What sample size is required if you want your estimate to be within 2 standard deviations of
based on a sample of n observations. What sample size is required if you want your estimate to be within 2 standard deviations of 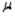 with probability equal to 0.95, if you know the population standard deviation
with probability equal to 0.95, if you know the population standard deviation 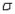 is 12?
is 12?A) 239
B) 196
C) 139
D) 98

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
The process of inferring the values of unknown population parameters from those of known sample statistics is called estimation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
An estimator is unbiased if the mean of its sampling distribution is the population parameter being estimated.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
A point estimate is an estimate of a population parameter, expressed as a single numerical value.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
Increasing the sample size, n, will result in a point estimate that is closer to the true value of the population parameter.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
In developing an interval estimate for the population mean 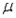 , the population standard deviation
, the population standard deviation 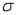 was assumed to be 6. The interval estimate was 45.0
was assumed to be 6. The interval estimate was 45.0 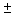 1.5. Had
1.5. Had  equalled 12, the interval estimate would be 90
equalled 12, the interval estimate would be 90 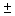 3.
3.
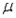 , the population standard deviation
, the population standard deviation 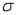 was assumed to be 6. The interval estimate was 45.0
was assumed to be 6. The interval estimate was 45.0 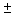 1.5. Had
1.5. Had  equalled 12, the interval estimate would be 90
equalled 12, the interval estimate would be 90 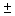 3.
3.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
If a store manager has recently stated that she estimates the mean amount spent per customer per visit to be between $38.75 and $72.23, the numbers $38.75 and $72.23 are considered point estimates for the true population mean.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
Given that n = 49, 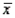 = 75, and
= 75, and 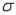 = 7, the lower and upper limits of the 68.26% confidence interval for the population mean
= 7, the lower and upper limits of the 68.26% confidence interval for the population mean 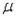 are 74 and 76, respectively.
are 74 and 76, respectively.
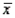 = 75, and
= 75, and 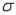 = 7, the lower and upper limits of the 68.26% confidence interval for the population mean
= 7, the lower and upper limits of the 68.26% confidence interval for the population mean 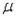 are 74 and 76, respectively.
are 74 and 76, respectively.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
An interval estimate is an estimate of the range for a sample statistic.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
A point estimate is a single value estimate of the value of a population parameter.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
As the sample size increases and other factors remain the same, the width of a confidence interval for a population mean tends to decrease.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
A point estimate is an estimate of the range of a population parameter.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
The margin of error is a half-width of an interval estimate, equal to the difference between the point estimate on the one hand and either the lower or the upper limit of the interval on the other hand.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
In order to construct a confidence interval estimate of the population proportion p, the value of p is needed.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
The unknown parameter of a population is presumed to lie at the centre of the interval that the point estimate and margin of error create.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
The concept of margin of error applies directly when estimating the population mean, 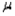 , but is not applicable when estimating the population proportion, p.
, but is not applicable when estimating the population proportion, p.
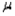 , but is not applicable when estimating the population proportion, p.
, but is not applicable when estimating the population proportion, p.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
The sample proportion 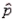 is an unbiased estimator of the population proportion, p.
is an unbiased estimator of the population proportion, p.
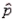 is an unbiased estimator of the population proportion, p.
is an unbiased estimator of the population proportion, p.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
A point estimate of a population parameter will likely be different from the corresponding population value due to the fact that point estimates are subject to sampling error.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
In the formula 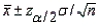 , the
, the 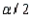 refers to the area in the lower tail or upper tail of the sampling distribution of the sample mean.
refers to the area in the lower tail or upper tail of the sampling distribution of the sample mean.
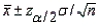 , the
, the 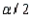 refers to the area in the lower tail or upper tail of the sampling distribution of the sample mean.
refers to the area in the lower tail or upper tail of the sampling distribution of the sample mean.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
The confidence coefficient is the probability that a confidence interval will enclose the estimated parameter.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
A point estimate is subject to sampling error and will almost always be different from the true value of the population parameter.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
Suppose a 95% confidence interval for the mean height of a 12-year-old male in Canada is 137 to 165 cm. It can be said that 95% of 12-year-old males in Canada have height greater than or equal to 137 cm and less than or equal to 165 cm.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
Statisticians routinely construct interval estimates by setting the point estimate as the centre of the interval and then creating a range of other possible values, known as the margin of error, below and above the centre.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
If the population variance is increased and other factors remain the same, the width of a confidence interval for the population mean tends to increase.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 187 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








