Deck 4: B: probability and Probability Distributions
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/157
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 4: B: probability and Probability Distributions
1
Political Opinions Narrative
A political scientist asked a group of people how they felt about two political policy statements. Each person was to respond either A (agree), N (neutral), or D (disagree) to each policy statement.
Refer to Political Opinions Narrative. Assuming each response combination in the sample space is equally likely, what is the probability the person being interviewed agrees with at least one of the two policy statements?
A political scientist asked a group of people how they felt about two political policy statements. Each person was to respond either A (agree), N (neutral), or D (disagree) to each policy statement.
Refer to Political Opinions Narrative. Assuming each response combination in the sample space is equally likely, what is the probability the person being interviewed agrees with at least one of the two policy statements?
5/9 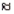 0.556
0.556
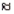 0.556
0.556 2
Job Applicants Narrative
Five applicants apply for two jobs. Applicants A and B are male; applicants C, D, and E are female. The personnel officer selects two applicants at random to fill the two jobs.
Refer to Job Applicants Narrative. If the two jobs are different, and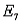 denotes the collection of outcomes where the successful job applicants include exactly one female, what is P(
denotes the collection of outcomes where the successful job applicants include exactly one female, what is P( 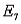 )?
)?
NAR: Job Applicants Narrative
Five applicants apply for two jobs. Applicants A and B are male; applicants C, D, and E are female. The personnel officer selects two applicants at random to fill the two jobs.
Refer to Job Applicants Narrative. If the two jobs are different, and
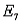 denotes the collection of outcomes where the successful job applicants include exactly one female, what is P(
denotes the collection of outcomes where the successful job applicants include exactly one female, what is P( 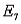 )?
)?NAR: Job Applicants Narrative
P( 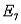 ) = 12/20 = 0.6
) = 12/20 = 0.6
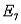 ) = 12/20 = 0.6
) = 12/20 = 0.6 3
Political Opinions Narrative
A political scientist asked a group of people how they felt about two political policy statements. Each person was to respond either A (agree), N (neutral), or D (disagree) to each policy statement.
Refer to Political Opinions Narrative. Assuming each response combination in the sample space is equally likely, what is the probability the person being interviewed agrees with exactly one of the two political policy statements?
A political scientist asked a group of people how they felt about two political policy statements. Each person was to respond either A (agree), N (neutral), or D (disagree) to each policy statement.
Refer to Political Opinions Narrative. Assuming each response combination in the sample space is equally likely, what is the probability the person being interviewed agrees with exactly one of the two political policy statements?
4/9 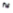 0.444
0.444
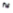 0.444
0.444 4
Job Applicants Narrative
Five applicants apply for two jobs. Applicants A and B are male; applicants C, D, and E are female. The personnel officer selects two applicants at random to fill the two jobs.
Refer to Job Applicants Narrative. If the two jobs are different, and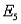 denotes the collection of outcomes where the successful job applicants include at least one female, what is P(
denotes the collection of outcomes where the successful job applicants include at least one female, what is P( 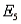 )?
)?
Five applicants apply for two jobs. Applicants A and B are male; applicants C, D, and E are female. The personnel officer selects two applicants at random to fill the two jobs.
Refer to Job Applicants Narrative. If the two jobs are different, and
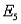 denotes the collection of outcomes where the successful job applicants include at least one female, what is P(
denotes the collection of outcomes where the successful job applicants include at least one female, what is P( 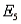 )?
)?
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
Coffee Brands Narrative
A food company plans to conduct an experiment to compare its brand of coffee with that of two competitors. A single person is hired to taste each of three brands of coffee, which are unmarked except for identifying symbols, A, B, and C.
Refer to Coffee Brands Narrative. Define the experiment.
A food company plans to conduct an experiment to compare its brand of coffee with that of two competitors. A single person is hired to taste each of three brands of coffee, which are unmarked except for identifying symbols, A, B, and C.
Refer to Coffee Brands Narrative. Define the experiment.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Job Applicants Narrative
Five applicants apply for two jobs. Applicants A and B are male; applicants C, D, and E are female. The personnel officer selects two applicants at random to fill the two jobs.
Refer to Job Applicants Narrative. If the two jobs are different, and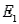 denotes the collection of outcomes where the successful job applicants include at least one male, what is P(
denotes the collection of outcomes where the successful job applicants include at least one male, what is P( 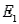 )?
)?
Five applicants apply for two jobs. Applicants A and B are male; applicants C, D, and E are female. The personnel officer selects two applicants at random to fill the two jobs.
Refer to Job Applicants Narrative. If the two jobs are different, and
 denotes the collection of outcomes where the successful job applicants include at least one male, what is P(
denotes the collection of outcomes where the successful job applicants include at least one male, what is P(  )?
)?
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Driver Education Narrative
Three randomly chosen 14-year-old middle school students who had not yet taken driver's education classes were given the written part of the Manitoba Driver's Exam. Each student was graded as passing (P) or failing (F) the written exam.
Refer to Driver Education Narrative. Assume each combination in the sample space is equally likely. Then, if you knew that at least one student passed the test, what is the probability all three students passed the test?
Three randomly chosen 14-year-old middle school students who had not yet taken driver's education classes were given the written part of the Manitoba Driver's Exam. Each student was graded as passing (P) or failing (F) the written exam.
Refer to Driver Education Narrative. Assume each combination in the sample space is equally likely. Then, if you knew that at least one student passed the test, what is the probability all three students passed the test?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Political Opinions Narrative
A political scientist asked a group of people how they felt about two political policy statements. Each person was to respond either A (agree), N (neutral), or D (disagree) to each policy statement.
Refer to Political Opinions Narrative. Describe the sample space; that is, list all possible response combinations to the two statements.
A political scientist asked a group of people how they felt about two political policy statements. Each person was to respond either A (agree), N (neutral), or D (disagree) to each policy statement.
Refer to Political Opinions Narrative. Describe the sample space; that is, list all possible response combinations to the two statements.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Driver Education Narrative
Three randomly chosen 14-year-old middle school students who had not yet taken driver's education classes were given the written part of the Manitoba Driver's Exam. Each student was graded as passing (P) or failing (F) the written exam.
Maria selected two M&M candies at random from a bowl containing three M&Ms. One was red; one was yellow; and the remaining one was orange. Describe the sample space if the sampling is done with replacement.
Three randomly chosen 14-year-old middle school students who had not yet taken driver's education classes were given the written part of the Manitoba Driver's Exam. Each student was graded as passing (P) or failing (F) the written exam.
Maria selected two M&M candies at random from a bowl containing three M&Ms. One was red; one was yellow; and the remaining one was orange. Describe the sample space if the sampling is done with replacement.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
SALES NARRATIVE
A salesperson either makes a sale (S) or does not make a sale (N) with each of two potential customers. The simple events and their probabilities are given below.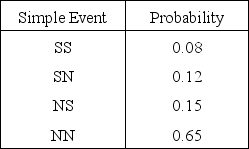
Refer to Sales Narrative. What is the probability that exactly one sale is made?
A salesperson either makes a sale (S) or does not make a sale (N) with each of two potential customers. The simple events and their probabilities are given below.

Refer to Sales Narrative. What is the probability that exactly one sale is made?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Job Applicants Narrative
Five applicants apply for two jobs. Applicants A and B are male; applicants C, D, and E are female. The personnel officer selects two applicants at random to fill the two jobs.
Refer to Job Applicants Narrative. List all possible combinations of the five applicants for the two different jobs.
Five applicants apply for two jobs. Applicants A and B are male; applicants C, D, and E are female. The personnel officer selects two applicants at random to fill the two jobs.
Refer to Job Applicants Narrative. List all possible combinations of the five applicants for the two different jobs.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Job Applicants Narrative
Five applicants apply for two jobs. Applicants A and B are male; applicants C, D, and E are female. The personnel officer selects two applicants at random to fill the two jobs.
A sample space S consists of five simple events with the following probabilities:
P( ) = P(
) = P( 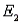 ) = 0.20, P(
) = 0.20, P( 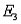 ) = 0.45, and P(
) = 0.45, and P( 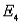 ) = 2P(
) = 2P( 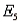 ).
).
a. Find the probabilities for simple events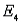 and
and 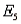 .
.
b. Find the probabilities for these two events: A: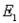 ,
, 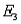 ,
, 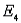 and B:
and B: 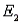 ,
, 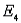 .
.
c. List the simple events that are in either event A or event B or both.
d. List the simple events that are in both event A and event B.
Five applicants apply for two jobs. Applicants A and B are male; applicants C, D, and E are female. The personnel officer selects two applicants at random to fill the two jobs.
A sample space S consists of five simple events with the following probabilities:
P(
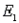 ) = P(
) = P( 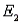 ) = 0.20, P(
) = 0.20, P( 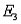 ) = 0.45, and P(
) = 0.45, and P( 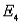 ) = 2P(
) = 2P( 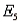 ).
). a. Find the probabilities for simple events
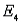 and
and 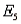 .
. b. Find the probabilities for these two events: A:
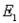 ,
, 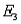 ,
, 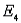 and B:
and B: 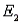 ,
, 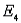 .
. c. List the simple events that are in either event A or event B or both.
d. List the simple events that are in both event A and event B.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
SALES NARRATIVE
A salesperson either makes a sale (S) or does not make a sale (N) with each of two potential customers. The simple events and their probabilities are given below.
Refer to Sales Narrative. What is the probability that exactly two sales were made?
A salesperson either makes a sale (S) or does not make a sale (N) with each of two potential customers. The simple events and their probabilities are given below.

Refer to Sales Narrative. What is the probability that exactly two sales were made?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Job Applicants Narrative
Five applicants apply for two jobs. Applicants A and B are male; applicants C, D, and E are female. The personnel officer selects two applicants at random to fill the two jobs.
Refer to Job Applicants Narrative. If the two jobs are different, and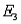 denotes the collection of outcomes where the successful job applicants include exactly one male, what is P(
denotes the collection of outcomes where the successful job applicants include exactly one male, what is P( 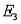 )?
)?
Five applicants apply for two jobs. Applicants A and B are male; applicants C, D, and E are female. The personnel officer selects two applicants at random to fill the two jobs.
Refer to Job Applicants Narrative. If the two jobs are different, and
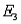 denotes the collection of outcomes where the successful job applicants include exactly one male, what is P(
denotes the collection of outcomes where the successful job applicants include exactly one male, what is P( 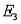 )?
)?
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Driver Education Narrative
Three randomly chosen 14-year-old middle school students who had not yet taken driver's education classes were given the written part of the Manitoba Driver's Exam. Each student was graded as passing (P) or failing (F) the written exam.
Refer to Driver Education Narrative. Describe the sample space; that is, list all possible combinations of the three students' grades.
Three randomly chosen 14-year-old middle school students who had not yet taken driver's education classes were given the written part of the Manitoba Driver's Exam. Each student was graded as passing (P) or failing (F) the written exam.
Refer to Driver Education Narrative. Describe the sample space; that is, list all possible combinations of the three students' grades.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Political Opinions Narrative
A political scientist asked a group of people how they felt about two political policy statements. Each person was to respond either A (agree), N (neutral), or D (disagree) to each policy statement.
Refer to Political Opinions Narrative. Assuming each response combination in the sample space is equally likely, what is the probability the person being interviewed agrees with both of the two political policy statements?
A political scientist asked a group of people how they felt about two political policy statements. Each person was to respond either A (agree), N (neutral), or D (disagree) to each policy statement.
Refer to Political Opinions Narrative. Assuming each response combination in the sample space is equally likely, what is the probability the person being interviewed agrees with both of the two political policy statements?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
SALES NARRATIVE
A salesperson either makes a sale (S) or does not make a sale (N) with each of two potential customers. The simple events and their probabilities are given below.
Refer to Sales Narrative. What is the probability that no sales are made?
A salesperson either makes a sale (S) or does not make a sale (N) with each of two potential customers. The simple events and their probabilities are given below.

Refer to Sales Narrative. What is the probability that no sales are made?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Driver Education Narrative
Three randomly chosen 14-year-old middle school students who had not yet taken driver's education classes were given the written part of the Manitoba Driver's Exam. Each student was graded as passing (P) or failing (F) the written exam.
Refer to Driver Education Narrative. Assuming each combination in the sample space is equally likely, what is the probability that all three students fail?
Three randomly chosen 14-year-old middle school students who had not yet taken driver's education classes were given the written part of the Manitoba Driver's Exam. Each student was graded as passing (P) or failing (F) the written exam.
Refer to Driver Education Narrative. Assuming each combination in the sample space is equally likely, what is the probability that all three students fail?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
SALES NARRATIVE
A salesperson either makes a sale (S) or does not make a sale (N) with each of two potential customers. The simple events and their probabilities are given below.
Refer to Sales Narrative. What is the probability that at least one sale is made?
A salesperson either makes a sale (S) or does not make a sale (N) with each of two potential customers. The simple events and their probabilities are given below.

Refer to Sales Narrative. What is the probability that at least one sale is made?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Driver Education Narrative
Three randomly chosen 14-year-old middle school students who had not yet taken driver's education classes were given the written part of the Manitoba Driver's Exam. Each student was graded as passing (P) or failing (F) the written exam.
Refer to Driver Education Narrative. Assuming each combination in the sample space is equally likely, what is the probability at least one student passes the written test?
Three randomly chosen 14-year-old middle school students who had not yet taken driver's education classes were given the written part of the Manitoba Driver's Exam. Each student was graded as passing (P) or failing (F) the written exam.
Refer to Driver Education Narrative. Assuming each combination in the sample space is equally likely, what is the probability at least one student passes the written test?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
A professor has received a grant to travel to an archaeological dig site. The grant includes funds for three graduate students to accompany the professor. If there are six graduate students available to the professor and all the funds are to be used (i.e., three students will go), how many choices does the professor have?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
An Italian restaurant in Québec City offers a special summer menu in which, for a fixed dinner cost, you can choose from one of two salads, one of three entrees, and one of four desserts. How many different dinners are available?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Smoking Habits of Health Club Members Narrative
A group of 40 people at a health club were classified according to their gender and smoking habits, as shown in the table below. One person is selected at random from that group of 40 people.
Smoking Habits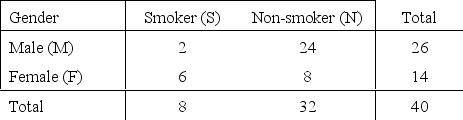
Refer to Smoking Habits of Health Club Members Narrative. What is the probability the person is female and does not smoke?
A group of 40 people at a health club were classified according to their gender and smoking habits, as shown in the table below. One person is selected at random from that group of 40 people.
Smoking Habits

Refer to Smoking Habits of Health Club Members Narrative. What is the probability the person is female and does not smoke?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Smoking Habits of Health Club Members Narrative
A group of 40 people at a health club were classified according to their gender and smoking habits, as shown in the table below. One person is selected at random from that group of 40 people.
Smoking Habits
Refer to Smoking Habits of Health Club Members Narrative. If the person is female, what is the probability she does not smoke?
A group of 40 people at a health club were classified according to their gender and smoking habits, as shown in the table below. One person is selected at random from that group of 40 people.
Smoking Habits

Refer to Smoking Habits of Health Club Members Narrative. If the person is female, what is the probability she does not smoke?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Mall Shopper Narrative
One hundred shoppers at a local shopping mall were categorized by age and gender as shown in the frequency distribution below. One shopper is selected at random from that group of 100 shoppers.
Age Group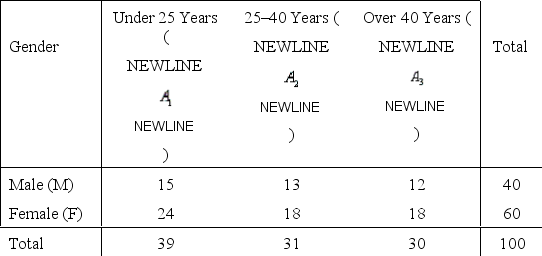
Refer to Mall Shopper Narrative. What is the probability that the randomly selected shopper is under 25 years of age?
One hundred shoppers at a local shopping mall were categorized by age and gender as shown in the frequency distribution below. One shopper is selected at random from that group of 100 shoppers.
Age Group

Refer to Mall Shopper Narrative. What is the probability that the randomly selected shopper is under 25 years of age?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Smoking Habits of Health Club Members Narrative
A group of 40 people at a health club were classified according to their gender and smoking habits, as shown in the table below. One person is selected at random from that group of 40 people.
Smoking Habits
Refer to Smoking Habits of Health Club Members Narrative. What is the probability the person is male?
A group of 40 people at a health club were classified according to their gender and smoking habits, as shown in the table below. One person is selected at random from that group of 40 people.
Smoking Habits

Refer to Smoking Habits of Health Club Members Narrative. What is the probability the person is male?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Smoking Habits of Health Club Members Narrative
A group of 40 people at a health club were classified according to their gender and smoking habits, as shown in the table below. One person is selected at random from that group of 40 people.
Smoking Habits
Refer to Smoking Habits of Health Club Members Narrative. What is the probability the person smokes?
A group of 40 people at a health club were classified according to their gender and smoking habits, as shown in the table below. One person is selected at random from that group of 40 people.
Smoking Habits

Refer to Smoking Habits of Health Club Members Narrative. What is the probability the person smokes?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Mall Shopper Narrative
One hundred shoppers at a local shopping mall were categorized by age and gender as shown in the frequency distribution below. One shopper is selected at random from that group of 100 shoppers.
Age Group
Refer to Mall Shopper Narrative. Convert the frequency table shown above into a probability table.
One hundred shoppers at a local shopping mall were categorized by age and gender as shown in the frequency distribution below. One shopper is selected at random from that group of 100 shoppers.
Age Group

Refer to Mall Shopper Narrative. Convert the frequency table shown above into a probability table.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Smoking Habits of Health Club Members Narrative
A group of 40 people at a health club were classified according to their gender and smoking habits, as shown in the table below. One person is selected at random from that group of 40 people.
Smoking Habits
Refer to Smoking Habits of Health Club Members Narrative. What is the probability the person is female?
A group of 40 people at a health club were classified according to their gender and smoking habits, as shown in the table below. One person is selected at random from that group of 40 people.
Smoking Habits

Refer to Smoking Habits of Health Club Members Narrative. What is the probability the person is female?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
An interior decorator must furnish two offices. Each office must have a desk, a chair, a file cabinet, and two bookcases. At a local office furniture store there are 6 models of desks, 8 models of chairs, 4 models of file cabinets, and 10 models of bookcases, all of which are compatible. (Any desk can be matched with any chair, etc.) How many choices does the decorator have if he wants to select 2 desks, 2 chairs, 2 file cabinets, and 4 bookcases but he doesn't want to select more than one of any model?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Coffee Brands Narrative
A food company plans to conduct an experiment to compare its brand of coffee with that of two competitors. A single person is hired to taste each of three brands of coffee, which are unmarked except for identifying symbols, A, B, and C.
Refer to Coffee Brands Narrative. List the simple events in the sample space S.
A food company plans to conduct an experiment to compare its brand of coffee with that of two competitors. A single person is hired to taste each of three brands of coffee, which are unmarked except for identifying symbols, A, B, and C.
Refer to Coffee Brands Narrative. List the simple events in the sample space S.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Heidi prepares for an exam by studying a list of 15 s. She can solve 9 of them. For the exam, the instructor selects 7 questions at random from the list of 15. What is the probability that Heidi can solve all 7 s on the exam?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
Smoking Habits of Health Club Members Narrative
A group of 40 people at a health club were classified according to their gender and smoking habits, as shown in the table below. One person is selected at random from that group of 40 people.
Smoking Habits
Refer to Smoking Habits of Health Club Members Narrative. If the person is male, what is the probability he smokes?
A group of 40 people at a health club were classified according to their gender and smoking habits, as shown in the table below. One person is selected at random from that group of 40 people.
Smoking Habits

Refer to Smoking Habits of Health Club Members Narrative. If the person is male, what is the probability he smokes?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
Smoking Habits of Health Club Members Narrative
A group of 40 people at a health club were classified according to their gender and smoking habits, as shown in the table below. One person is selected at random from that group of 40 people.
Smoking Habits
Refer to Smoking Habits of Health Club Members Narrative. What is the probability the person does not smoke?
A group of 40 people at a health club were classified according to their gender and smoking habits, as shown in the table below. One person is selected at random from that group of 40 people.
Smoking Habits

Refer to Smoking Habits of Health Club Members Narrative. What is the probability the person does not smoke?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Coffee Brands Narrative
A food company plans to conduct an experiment to compare its brand of coffee with that of two competitors. A single person is hired to taste each of three brands of coffee, which are unmarked except for identifying symbols, A, B, and C.
Refer to Coffee Brands Narrative. If the taster has no ability to distinguish difference in taste among coffees, what is the probability that the taster will rank coffee type C as the most desirable? As the least desirable?
A food company plans to conduct an experiment to compare its brand of coffee with that of two competitors. A single person is hired to taste each of three brands of coffee, which are unmarked except for identifying symbols, A, B, and C.
Refer to Coffee Brands Narrative. If the taster has no ability to distinguish difference in taste among coffees, what is the probability that the taster will rank coffee type C as the most desirable? As the least desirable?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
Smoking Habits of Health Club Members Narrative
A group of 40 people at a health club were classified according to their gender and smoking habits, as shown in the table below. One person is selected at random from that group of 40 people.
Smoking Habits
Refer to Smoking Habits of Health Club Members Narrative. What is the probability the person is male and smokes?
A group of 40 people at a health club were classified according to their gender and smoking habits, as shown in the table below. One person is selected at random from that group of 40 people.
Smoking Habits

Refer to Smoking Habits of Health Club Members Narrative. What is the probability the person is male and smokes?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
How many permutations of 3 colours can be drawn from a group of 20 colours?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
A businessman in Hamilton is preparing an itinerary for a visit to five major cities. Each city will be visited once and only once. The distance travelled, and hence the cost of the trip, will depend on the order in which he plans his route. How many different itineraries (and trip costs) are possible?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
A graduate student has decided she needs a day at the beach. She will need a swimsuit, a pair of sunglasses, and a beach towel for the occasion. If she has two swimsuits, three pairs of sunglasses, and five beach towels, how many different choices does she have?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
How many different combinations of 5 students can be drawn from a class of 25 students?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
Psychological Tests Narrative
A psychologist tests Grade 7 students on basic word association skills and number pattern recognition skills. Let W be the event a student does well on the word association test. Let N be the event a student does well on the number pattern recognition test. A student is selected at random, and the following probabilities are given: P(W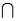 N) = 0.25, P(W
N) = 0.25, P(W 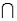
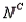 ) = 0.15, P(
) = 0.15, P( 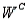
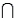 N) = 0.10, and P(
N) = 0.10, and P( 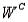
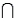
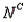 ) = 0.50.
) = 0.50.
Refer to Psychological Tests Narrative. If the randomly selected student does well on the number pattern recognition test, what is the probability he or she will also do well on the word association test?
A psychologist tests Grade 7 students on basic word association skills and number pattern recognition skills. Let W be the event a student does well on the word association test. Let N be the event a student does well on the number pattern recognition test. A student is selected at random, and the following probabilities are given: P(W
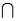 N) = 0.25, P(W
N) = 0.25, P(W 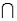
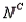 ) = 0.15, P(
) = 0.15, P( 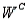
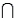 N) = 0.10, and P(
N) = 0.10, and P( 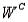
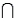
 ) = 0.50.
) = 0.50.Refer to Psychological Tests Narrative. If the randomly selected student does well on the number pattern recognition test, what is the probability he or she will also do well on the word association test?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
Salary of Working Mothers Narrative
A researcher studied the relationship between the salary of a working woman with school-aged children and the number of children she had. The results are shown in the following probability table:
Number of Children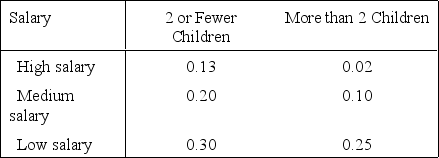 Let A denote the event that a working woman has two or fewer children, and let B denote the event that a working woman has a low salary.
Let A denote the event that a working woman has two or fewer children, and let B denote the event that a working woman has a low salary.
Refer to Salary of Working Mothers Narrative. What is the probability that a working woman either has two or fewer children or has a low salary?
A researcher studied the relationship between the salary of a working woman with school-aged children and the number of children she had. The results are shown in the following probability table:
Number of Children
 Let A denote the event that a working woman has two or fewer children, and let B denote the event that a working woman has a low salary.
Let A denote the event that a working woman has two or fewer children, and let B denote the event that a working woman has a low salary.Refer to Salary of Working Mothers Narrative. What is the probability that a working woman either has two or fewer children or has a low salary?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
Mall Shopper Narrative
One hundred shoppers at a local shopping mall were categorized by age and gender as shown in the frequency distribution below. One shopper is selected at random from that group of 100 shoppers.
Age Group
Refer to Mall Shopper Narrative. What is the probability that the randomly selected shopper is either female or over 40 years of age?
One hundred shoppers at a local shopping mall were categorized by age and gender as shown in the frequency distribution below. One shopper is selected at random from that group of 100 shoppers.
Age Group

Refer to Mall Shopper Narrative. What is the probability that the randomly selected shopper is either female or over 40 years of age?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
Salary of Working Mothers Narrative
A researcher studied the relationship between the salary of a working woman with school-aged children and the number of children she had. The results are shown in the following probability table:
Number of Children Let A denote the event that a working woman has two or fewer children, and let B denote the event that a working woman has a low salary.
Let A denote the event that a working woman has two or fewer children, and let B denote the event that a working woman has a low salary.
Refer to Salary of Working Mothers Narrative. What is the probability that a working woman has a low salary?
A researcher studied the relationship between the salary of a working woman with school-aged children and the number of children she had. The results are shown in the following probability table:
Number of Children
 Let A denote the event that a working woman has two or fewer children, and let B denote the event that a working woman has a low salary.
Let A denote the event that a working woman has two or fewer children, and let B denote the event that a working woman has a low salary.Refer to Salary of Working Mothers Narrative. What is the probability that a working woman has a low salary?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Psychological Tests Narrative
A psychologist tests Grade 7 students on basic word association skills and number pattern recognition skills. Let W be the event a student does well on the word association test. Let N be the event a student does well on the number pattern recognition test. A student is selected at random, and the following probabilities are given: P(W N) = 0.25, P(W
N) = 0.25, P(W 
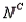 ) = 0.15, P(
) = 0.15, P( 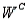
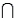 N) = 0.10, and P(
N) = 0.10, and P( 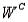
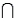
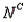 ) = 0.50.
) = 0.50.
Refer to Psychological Tests Narrative. Are the events W and N mutually exclusive? Justify your ANS.
A psychologist tests Grade 7 students on basic word association skills and number pattern recognition skills. Let W be the event a student does well on the word association test. Let N be the event a student does well on the number pattern recognition test. A student is selected at random, and the following probabilities are given: P(W
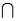 N) = 0.25, P(W
N) = 0.25, P(W 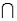
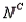 ) = 0.15, P(
) = 0.15, P( 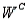
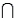 N) = 0.10, and P(
N) = 0.10, and P( 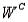
 ) = 0.50.
) = 0.50.Refer to Psychological Tests Narrative. Are the events W and N mutually exclusive? Justify your ANS.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
Mall Shopper Narrative
One hundred shoppers at a local shopping mall were categorized by age and gender as shown in the frequency distribution below. One shopper is selected at random from that group of 100 shoppers.
Age Group
Refer to Mall Shopper Narrative. If the randomly selected shopper is male, what is the probability he is under 25 years of age?
One hundred shoppers at a local shopping mall were categorized by age and gender as shown in the frequency distribution below. One shopper is selected at random from that group of 100 shoppers.
Age Group

Refer to Mall Shopper Narrative. If the randomly selected shopper is male, what is the probability he is under 25 years of age?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
Psychological Tests Narrative
A psychologist tests Grade 7 students on basic word association skills and number pattern recognition skills. Let W be the event a student does well on the word association test. Let N be the event a student does well on the number pattern recognition test. A student is selected at random, and the following probabilities are given: P(W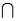 N) = 0.25, P(W
N) = 0.25, P(W 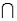
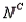 ) = 0.15, P(
) = 0.15, P( 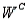
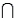 N) = 0.10, and P(
N) = 0.10, and P( 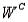
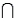
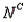 ) = 0.50.
) = 0.50.
Studies have shown a particular television commercial is understood by 25% of Grade 1 students and 80% of Grade 4 students. If a television advertising agency randomly selects one Grade 1 and one Grade 4 student, what is the probability neither child would understand the commercial, assuming the children's reactions are independent?
A psychologist tests Grade 7 students on basic word association skills and number pattern recognition skills. Let W be the event a student does well on the word association test. Let N be the event a student does well on the number pattern recognition test. A student is selected at random, and the following probabilities are given: P(W
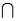 N) = 0.25, P(W
N) = 0.25, P(W 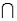
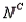 ) = 0.15, P(
) = 0.15, P( 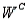
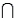 N) = 0.10, and P(
N) = 0.10, and P( 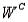
 ) = 0.50.
) = 0.50.Studies have shown a particular television commercial is understood by 25% of Grade 1 students and 80% of Grade 4 students. If a television advertising agency randomly selects one Grade 1 and one Grade 4 student, what is the probability neither child would understand the commercial, assuming the children's reactions are independent?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
Mall Shopper Narrative
One hundred shoppers at a local shopping mall were categorized by age and gender as shown in the frequency distribution below. One shopper is selected at random from that group of 100 shoppers.
Age Group
Refer to Mall Shopper Narrative. If the randomly selected shopper is under 25 years of age, what is the probability that the shopper is male?
One hundred shoppers at a local shopping mall were categorized by age and gender as shown in the frequency distribution below. One shopper is selected at random from that group of 100 shoppers.
Age Group

Refer to Mall Shopper Narrative. If the randomly selected shopper is under 25 years of age, what is the probability that the shopper is male?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
Mall Shopper Narrative
One hundred shoppers at a local shopping mall were categorized by age and gender as shown in the frequency distribution below. One shopper is selected at random from that group of 100 shoppers.
Age Group
Refer to Mall Shopper Narrative. Are the gender of the shopper and the shopper's age independent events? Explain.
One hundred shoppers at a local shopping mall were categorized by age and gender as shown in the frequency distribution below. One shopper is selected at random from that group of 100 shoppers.
Age Group

Refer to Mall Shopper Narrative. Are the gender of the shopper and the shopper's age independent events? Explain.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
Psychological Tests Narrative
A psychologist tests Grade 7 students on basic word association skills and number pattern recognition skills. Let W be the event a student does well on the word association test. Let N be the event a student does well on the number pattern recognition test. A student is selected at random, and the following probabilities are given: P(W N) = 0.25, P(W
N) = 0.25, P(W 
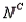 ) = 0.15, P(
) = 0.15, P( 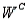
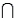 N) = 0.10, and P(
N) = 0.10, and P( 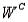
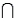
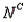 ) = 0.50.
) = 0.50.
Refer to Psychological Tests Narrative. Are the events W and N independent? Explain.
A psychologist tests Grade 7 students on basic word association skills and number pattern recognition skills. Let W be the event a student does well on the word association test. Let N be the event a student does well on the number pattern recognition test. A student is selected at random, and the following probabilities are given: P(W
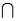 N) = 0.25, P(W
N) = 0.25, P(W 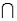
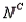 ) = 0.15, P(
) = 0.15, P( 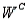
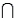 N) = 0.10, and P(
N) = 0.10, and P( 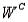
 ) = 0.50.
) = 0.50.Refer to Psychological Tests Narrative. Are the events W and N independent? Explain.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
Salary of Working Mothers Narrative
A researcher studied the relationship between the salary of a working woman with school-aged children and the number of children she had. The results are shown in the following probability table:
Number of Children Let A denote the event that a working woman has two or fewer children, and let B denote the event that a working woman has a low salary.
Let A denote the event that a working woman has two or fewer children, and let B denote the event that a working woman has a low salary.
Refer to Salary of Working Mothers Narrative. What is the probability that a working woman has two or fewer children and has a low salary?
A researcher studied the relationship between the salary of a working woman with school-aged children and the number of children she had. The results are shown in the following probability table:
Number of Children
 Let A denote the event that a working woman has two or fewer children, and let B denote the event that a working woman has a low salary.
Let A denote the event that a working woman has two or fewer children, and let B denote the event that a working woman has a low salary.Refer to Salary of Working Mothers Narrative. What is the probability that a working woman has two or fewer children and has a low salary?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
Psychological Tests Narrative
A psychologist tests Grade 7 students on basic word association skills and number pattern recognition skills. Let W be the event a student does well on the word association test. Let N be the event a student does well on the number pattern recognition test. A student is selected at random, and the following probabilities are given: P(W N) = 0.25, P(W
N) = 0.25, P(W 
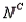 ) = 0.15, P(
) = 0.15, P( 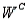
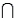 N) = 0.10, and P(
N) = 0.10, and P( 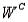
 ) = 0.50.
) = 0.50.
Refer to Psychological Tests Narrative. What is the probability that the randomly selected student does well on the number pattern recognition test?
A psychologist tests Grade 7 students on basic word association skills and number pattern recognition skills. Let W be the event a student does well on the word association test. Let N be the event a student does well on the number pattern recognition test. A student is selected at random, and the following probabilities are given: P(W
 N) = 0.25, P(W
N) = 0.25, P(W 
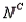 ) = 0.15, P(
) = 0.15, P( 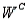
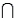 N) = 0.10, and P(
N) = 0.10, and P( 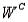
 ) = 0.50.
) = 0.50.Refer to Psychological Tests Narrative. What is the probability that the randomly selected student does well on the number pattern recognition test?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
Mall Shopper Narrative
One hundred shoppers at a local shopping mall were categorized by age and gender as shown in the frequency distribution below. One shopper is selected at random from that group of 100 shoppers.
Age Group
Refer to Mall Shopper Narrative. Are the gender of the shopper and the shopper's age mutually exclusive events? Explain.
One hundred shoppers at a local shopping mall were categorized by age and gender as shown in the frequency distribution below. One shopper is selected at random from that group of 100 shoppers.
Age Group

Refer to Mall Shopper Narrative. Are the gender of the shopper and the shopper's age mutually exclusive events? Explain.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
Psychological Tests Narrative
A psychologist tests Grade 7 students on basic word association skills and number pattern recognition skills. Let W be the event a student does well on the word association test. Let N be the event a student does well on the number pattern recognition test. A student is selected at random, and the following probabilities are given: P(W N) = 0.25, P(W
N) = 0.25, P(W 
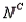 ) = 0.15, P(
) = 0.15, P( 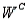
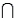 N) = 0.10, and P(
N) = 0.10, and P( 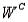
 ) = 0.50.
) = 0.50.
Refer to Psychological Tests Narrative. What is the probability that the randomly selected student does well on the word association test?
A psychologist tests Grade 7 students on basic word association skills and number pattern recognition skills. Let W be the event a student does well on the word association test. Let N be the event a student does well on the number pattern recognition test. A student is selected at random, and the following probabilities are given: P(W
 N) = 0.25, P(W
N) = 0.25, P(W 
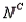 ) = 0.15, P(
) = 0.15, P( 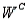
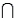 N) = 0.10, and P(
N) = 0.10, and P( 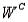
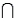
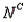 ) = 0.50.
) = 0.50.Refer to Psychological Tests Narrative. What is the probability that the randomly selected student does well on the word association test?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
Salary of Working Mothers Narrative
A researcher studied the relationship between the salary of a working woman with school-aged children and the number of children she had. The results are shown in the following probability table:
Number of Children Let A denote the event that a working woman has two or fewer children, and let B denote the event that a working woman has a low salary.
Let A denote the event that a working woman has two or fewer children, and let B denote the event that a working woman has a low salary.
Refer to Salary of Working Mothers Narrative. What is the probability that a working woman has two or fewer children?
A researcher studied the relationship between the salary of a working woman with school-aged children and the number of children she had. The results are shown in the following probability table:
Number of Children
 Let A denote the event that a working woman has two or fewer children, and let B denote the event that a working woman has a low salary.
Let A denote the event that a working woman has two or fewer children, and let B denote the event that a working woman has a low salary.Refer to Salary of Working Mothers Narrative. What is the probability that a working woman has two or fewer children?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
Psychological Tests Narrative
A psychologist tests Grade 7 students on basic word association skills and number pattern recognition skills. Let W be the event a student does well on the word association test. Let N be the event a student does well on the number pattern recognition test. A student is selected at random, and the following probabilities are given: P(W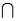 N) = 0.25, P(W
N) = 0.25, P(W 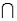
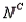 ) = 0.15, P(
) = 0.15, P( 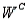
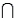 N) = 0.10, and P(
N) = 0.10, and P( 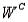
 ) = 0.50.
) = 0.50.
Refer to Psychological Tests Narrative. If the randomly selected student does well on the word association test, what is the probability he or she will also do well on the number pattern recognition test?
A psychologist tests Grade 7 students on basic word association skills and number pattern recognition skills. Let W be the event a student does well on the word association test. Let N be the event a student does well on the number pattern recognition test. A student is selected at random, and the following probabilities are given: P(W
 N) = 0.25, P(W
N) = 0.25, P(W 
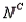 ) = 0.15, P(
) = 0.15, P( 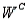
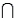 N) = 0.10, and P(
N) = 0.10, and P( 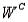
 ) = 0.50.
) = 0.50.Refer to Psychological Tests Narrative. If the randomly selected student does well on the word association test, what is the probability he or she will also do well on the number pattern recognition test?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
Psychological Tests Narrative
A psychologist tests Grade 7 students on basic word association skills and number pattern recognition skills. Let W be the event a student does well on the word association test. Let N be the event a student does well on the number pattern recognition test. A student is selected at random, and the following probabilities are given: P(W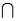 N) = 0.25, P(W
N) = 0.25, P(W 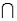
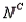 ) = 0.15, P(
) = 0.15, P( 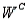
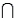 N) = 0.10, and P(
N) = 0.10, and P( 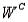
 ) = 0.50.
) = 0.50.
Refer to Psychological Tests Narrative. What is the probability that the randomly selected student does well on at least one of the tests?
A psychologist tests Grade 7 students on basic word association skills and number pattern recognition skills. Let W be the event a student does well on the word association test. Let N be the event a student does well on the number pattern recognition test. A student is selected at random, and the following probabilities are given: P(W
 N) = 0.25, P(W
N) = 0.25, P(W 
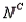 ) = 0.15, P(
) = 0.15, P( 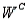
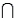 N) = 0.10, and P(
N) = 0.10, and P( 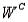
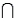
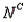 ) = 0.50.
) = 0.50.Refer to Psychological Tests Narrative. What is the probability that the randomly selected student does well on at least one of the tests?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
Mall Shopper Narrative
One hundred shoppers at a local shopping mall were categorized by age and gender as shown in the frequency distribution below. One shopper is selected at random from that group of 100 shoppers.
Age Group
Refer to Mall Shopper Narrative. What is the probability that the randomly selected shopper is male and under 25 years of age?
One hundred shoppers at a local shopping mall were categorized by age and gender as shown in the frequency distribution below. One shopper is selected at random from that group of 100 shoppers.
Age Group

Refer to Mall Shopper Narrative. What is the probability that the randomly selected shopper is male and under 25 years of age?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
Mall Shopper Narrative
One hundred shoppers at a local shopping mall were categorized by age and gender as shown in the frequency distribution below. One shopper is selected at random from that group of 100 shoppers.
Age Group
Refer to Mall Shopper Narrative. If the randomly selected shopper is female, what is the probability that she is 25 to 40 years old?
One hundred shoppers at a local shopping mall were categorized by age and gender as shown in the frequency distribution below. One shopper is selected at random from that group of 100 shoppers.
Age Group

Refer to Mall Shopper Narrative. If the randomly selected shopper is female, what is the probability that she is 25 to 40 years old?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
Mall Shopper Narrative
One hundred shoppers at a local shopping mall were categorized by age and gender as shown in the frequency distribution below. One shopper is selected at random from that group of 100 shoppers.
Age Group
Refer to Mall Shopper Narrative. What is the probability that the randomly selected shopper is male?
One hundred shoppers at a local shopping mall were categorized by age and gender as shown in the frequency distribution below. One shopper is selected at random from that group of 100 shoppers.
Age Group

Refer to Mall Shopper Narrative. What is the probability that the randomly selected shopper is male?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
Late Night Talk Shows Narrative
Let A be the event that a randomly selected person watches the Tonight Show with Jay Leno (event A) and B be the event that a randomly selected person watches the Late Show with David Letterman (event B). It is possible to time-shift a program to a more convenient hour and thus watch both programs. Suppose the following probabilities are given: P(A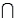 B) = 0.20, P(A
B) = 0.20, P(A 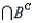 ) = 0.40, P(
) = 0.40, P( 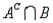 ) = 0.10, and P(
) = 0.10, and P( 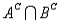 ) = 0.30.
) = 0.30.
Refer to Late Night Talk Shows Narrative. What is the probability that a randomly selected person watches only David Letterman?
Let A be the event that a randomly selected person watches the Tonight Show with Jay Leno (event A) and B be the event that a randomly selected person watches the Late Show with David Letterman (event B). It is possible to time-shift a program to a more convenient hour and thus watch both programs. Suppose the following probabilities are given: P(A
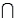 B) = 0.20, P(A
B) = 0.20, P(A 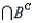 ) = 0.40, P(
) = 0.40, P( 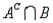 ) = 0.10, and P(
) = 0.10, and P( 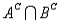 ) = 0.30.
) = 0.30.Refer to Late Night Talk Shows Narrative. What is the probability that a randomly selected person watches only David Letterman?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
Drug Offenders Narrative
Research studies suggest that the likelihood a drug offender will be convicted of a drug offence within two years after treatment for drug abuse may depend on the person's educational level. The proportions of the total number of cases that fall into four education/conviction categories are shown in the table below:
Status within Two Years after Treatment Suppose a single offender is selected from the treatment program. Here are two events of interest:
Suppose a single offender is selected from the treatment program. Here are two events of interest:
A: The offender has 10 or more years of education.
B: The offender is convicted within two years after completion of treatment.
Refer to Drug Offenders Narrative. Find P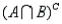 .
.
Research studies suggest that the likelihood a drug offender will be convicted of a drug offence within two years after treatment for drug abuse may depend on the person's educational level. The proportions of the total number of cases that fall into four education/conviction categories are shown in the table below:
Status within Two Years after Treatment
 Suppose a single offender is selected from the treatment program. Here are two events of interest:
Suppose a single offender is selected from the treatment program. Here are two events of interest:A: The offender has 10 or more years of education.
B: The offender is convicted within two years after completion of treatment.
Refer to Drug Offenders Narrative. Find P
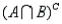 .
.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
Drug Offenders Narrative
Research studies suggest that the likelihood a drug offender will be convicted of a drug offence within two years after treatment for drug abuse may depend on the person's educational level. The proportions of the total number of cases that fall into four education/conviction categories are shown in the table below:
Status within Two Years after Treatment Suppose a single offender is selected from the treatment program. Here are two events of interest:
Suppose a single offender is selected from the treatment program. Here are two events of interest:
A: The offender has 10 or more years of education.
B: The offender is convicted within two years after completion of treatment.
Refer to Drug Offenders Narrative. Find the probability of B given that A has occurred.
Research studies suggest that the likelihood a drug offender will be convicted of a drug offence within two years after treatment for drug abuse may depend on the person's educational level. The proportions of the total number of cases that fall into four education/conviction categories are shown in the table below:
Status within Two Years after Treatment
 Suppose a single offender is selected from the treatment program. Here are two events of interest:
Suppose a single offender is selected from the treatment program. Here are two events of interest:A: The offender has 10 or more years of education.
B: The offender is convicted within two years after completion of treatment.
Refer to Drug Offenders Narrative. Find the probability of B given that A has occurred.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
Drug Offenders Narrative
Research studies suggest that the likelihood a drug offender will be convicted of a drug offence within two years after treatment for drug abuse may depend on the person's educational level. The proportions of the total number of cases that fall into four education/conviction categories are shown in the table below:
Status within Two Years after Treatment Suppose a single offender is selected from the treatment program. Here are two events of interest:
Suppose a single offender is selected from the treatment program. Here are two events of interest:
A: The offender has 10 or more years of education.
B: The offender is convicted within two years after completion of treatment.
Refer to Drug Offenders Narrative. Are events A and B independent? Explain.
Research studies suggest that the likelihood a drug offender will be convicted of a drug offence within two years after treatment for drug abuse may depend on the person's educational level. The proportions of the total number of cases that fall into four education/conviction categories are shown in the table below:
Status within Two Years after Treatment
 Suppose a single offender is selected from the treatment program. Here are two events of interest:
Suppose a single offender is selected from the treatment program. Here are two events of interest:A: The offender has 10 or more years of education.
B: The offender is convicted within two years after completion of treatment.
Refer to Drug Offenders Narrative. Are events A and B independent? Explain.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
Drug Offenders Narrative
Research studies suggest that the likelihood a drug offender will be convicted of a drug offence within two years after treatment for drug abuse may depend on the person's educational level. The proportions of the total number of cases that fall into four education/conviction categories are shown in the table below:
Status within Two Years after Treatment Suppose a single offender is selected from the treatment program. Here are two events of interest:
Suppose a single offender is selected from the treatment program. Here are two events of interest:
A: The offender has 10 or more years of education.
B: The offender is convicted within two years after completion of treatment.
Refer to Drug Offenders Narrative. Find P(A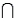 B).
B).
Research studies suggest that the likelihood a drug offender will be convicted of a drug offence within two years after treatment for drug abuse may depend on the person's educational level. The proportions of the total number of cases that fall into four education/conviction categories are shown in the table below:
Status within Two Years after Treatment
 Suppose a single offender is selected from the treatment program. Here are two events of interest:
Suppose a single offender is selected from the treatment program. Here are two events of interest:A: The offender has 10 or more years of education.
B: The offender is convicted within two years after completion of treatment.
Refer to Drug Offenders Narrative. Find P(A
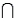 B).
B).
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
Late Night Talk Shows Narrative
Let A be the event that a randomly selected person watches the Tonight Show with Jay Leno (event A) and B be the event that a randomly selected person watches the Late Show with David Letterman (event B). It is possible to time-shift a program to a more convenient hour and thus watch both programs. Suppose the following probabilities are given: P(A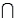 B) = 0.20, P(A
B) = 0.20, P(A 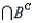 ) = 0.40, P(
) = 0.40, P( 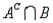 ) = 0.10, and P(
) = 0.10, and P( 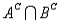 ) = 0.30.
) = 0.30.
Refer to Late Night Talk Shows Narrative. What is the probability that a randomly selected person watches both shows?
Let A be the event that a randomly selected person watches the Tonight Show with Jay Leno (event A) and B be the event that a randomly selected person watches the Late Show with David Letterman (event B). It is possible to time-shift a program to a more convenient hour and thus watch both programs. Suppose the following probabilities are given: P(A
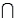 B) = 0.20, P(A
B) = 0.20, P(A 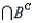 ) = 0.40, P(
) = 0.40, P( 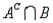 ) = 0.10, and P(
) = 0.10, and P( 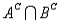 ) = 0.30.
) = 0.30.Refer to Late Night Talk Shows Narrative. What is the probability that a randomly selected person watches both shows?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
Drug Offenders Narrative
Research studies suggest that the likelihood a drug offender will be convicted of a drug offence within two years after treatment for drug abuse may depend on the person's educational level. The proportions of the total number of cases that fall into four education/conviction categories are shown in the table below:
Status within Two Years after Treatment Suppose a single offender is selected from the treatment program. Here are two events of interest:
Suppose a single offender is selected from the treatment program. Here are two events of interest:
A: The offender has 10 or more years of education.
B: The offender is convicted within two years after completion of treatment.
Refer to Drug Offenders Narrative. Find the probability of A given that B has occurred.
Research studies suggest that the likelihood a drug offender will be convicted of a drug offence within two years after treatment for drug abuse may depend on the person's educational level. The proportions of the total number of cases that fall into four education/conviction categories are shown in the table below:
Status within Two Years after Treatment
 Suppose a single offender is selected from the treatment program. Here are two events of interest:
Suppose a single offender is selected from the treatment program. Here are two events of interest:A: The offender has 10 or more years of education.
B: The offender is convicted within two years after completion of treatment.
Refer to Drug Offenders Narrative. Find the probability of A given that B has occurred.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
Drug Offenders Narrative
Research studies suggest that the likelihood a drug offender will be convicted of a drug offence within two years after treatment for drug abuse may depend on the person's educational level. The proportions of the total number of cases that fall into four education/conviction categories are shown in the table below:
Status within Two Years after Treatment Suppose a single offender is selected from the treatment program. Here are two events of interest:
Suppose a single offender is selected from the treatment program. Here are two events of interest:
A: The offender has 10 or more years of education.
B: The offender is convicted within two years after completion of treatment.
Refer to Drug Offenders Narrative. Find P(B).
Research studies suggest that the likelihood a drug offender will be convicted of a drug offence within two years after treatment for drug abuse may depend on the person's educational level. The proportions of the total number of cases that fall into four education/conviction categories are shown in the table below:
Status within Two Years after Treatment
 Suppose a single offender is selected from the treatment program. Here are two events of interest:
Suppose a single offender is selected from the treatment program. Here are two events of interest:A: The offender has 10 or more years of education.
B: The offender is convicted within two years after completion of treatment.
Refer to Drug Offenders Narrative. Find P(B).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
Drug Offenders Narrative
Research studies suggest that the likelihood a drug offender will be convicted of a drug offence within two years after treatment for drug abuse may depend on the person's educational level. The proportions of the total number of cases that fall into four education/conviction categories are shown in the table below:
Status within Two Years after Treatment Suppose a single offender is selected from the treatment program. Here are two events of interest:
Suppose a single offender is selected from the treatment program. Here are two events of interest:
A: The offender has 10 or more years of education.
B: The offender is convicted within two years after completion of treatment.
Refer to Drug Offenders Narrative. Find P(A).
Research studies suggest that the likelihood a drug offender will be convicted of a drug offence within two years after treatment for drug abuse may depend on the person's educational level. The proportions of the total number of cases that fall into four education/conviction categories are shown in the table below:
Status within Two Years after Treatment
 Suppose a single offender is selected from the treatment program. Here are two events of interest:
Suppose a single offender is selected from the treatment program. Here are two events of interest:A: The offender has 10 or more years of education.
B: The offender is convicted within two years after completion of treatment.
Refer to Drug Offenders Narrative. Find P(A).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
Drug Offenders Narrative
Research studies suggest that the likelihood a drug offender will be convicted of a drug offence within two years after treatment for drug abuse may depend on the person's educational level. The proportions of the total number of cases that fall into four education/conviction categories are shown in the table below:
Status within Two Years after Treatment Suppose a single offender is selected from the treatment program. Here are two events of interest:
Suppose a single offender is selected from the treatment program. Here are two events of interest:
A: The offender has 10 or more years of education.
B: The offender is convicted within two years after completion of treatment.
Refer to Drug Offenders Narrative. Find P(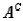 ).
).
Research studies suggest that the likelihood a drug offender will be convicted of a drug offence within two years after treatment for drug abuse may depend on the person's educational level. The proportions of the total number of cases that fall into four education/conviction categories are shown in the table below:
Status within Two Years after Treatment
 Suppose a single offender is selected from the treatment program. Here are two events of interest:
Suppose a single offender is selected from the treatment program. Here are two events of interest:A: The offender has 10 or more years of education.
B: The offender is convicted within two years after completion of treatment.
Refer to Drug Offenders Narrative. Find P(
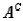 ).
).
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
Late Night Talk Shows Narrative
Let A be the event that a randomly selected person watches the Tonight Show with Jay Leno (event A) and B be the event that a randomly selected person watches the Late Show with David Letterman (event B). It is possible to time-shift a program to a more convenient hour and thus watch both programs. Suppose the following probabilities are given: P(A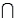 B) = 0.20, P(A
B) = 0.20, P(A 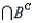 ) = 0.40, P(
) = 0.40, P( 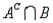 ) = 0.10, and P(
) = 0.10, and P( 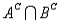 ) = 0.30.
) = 0.30.
Refer to Late Night Talk Shows Narrative. What is the probability that a randomly selected person watches only Jay Leno?
Let A be the event that a randomly selected person watches the Tonight Show with Jay Leno (event A) and B be the event that a randomly selected person watches the Late Show with David Letterman (event B). It is possible to time-shift a program to a more convenient hour and thus watch both programs. Suppose the following probabilities are given: P(A
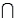 B) = 0.20, P(A
B) = 0.20, P(A 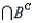 ) = 0.40, P(
) = 0.40, P( 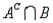 ) = 0.10, and P(
) = 0.10, and P( 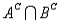 ) = 0.30.
) = 0.30.Refer to Late Night Talk Shows Narrative. What is the probability that a randomly selected person watches only Jay Leno?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
Salary of Working Mothers Narrative
A researcher studied the relationship between the salary of a working woman with school-aged children and the number of children she had. The results are shown in the following probability table:
Number of Children Let A denote the event that a working woman has two or fewer children, and let B denote the event that a working woman has a low salary.
Let A denote the event that a working woman has two or fewer children, and let B denote the event that a working woman has a low salary.
Refer to Salary of Working Mothers Narrative. If a working woman has two or fewer children, what is the probability that she has a low salary?
A researcher studied the relationship between the salary of a working woman with school-aged children and the number of children she had. The results are shown in the following probability table:
Number of Children
 Let A denote the event that a working woman has two or fewer children, and let B denote the event that a working woman has a low salary.
Let A denote the event that a working woman has two or fewer children, and let B denote the event that a working woman has a low salary.Refer to Salary of Working Mothers Narrative. If a working woman has two or fewer children, what is the probability that she has a low salary?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
Drug Offenders Narrative
Research studies suggest that the likelihood a drug offender will be convicted of a drug offence within two years after treatment for drug abuse may depend on the person's educational level. The proportions of the total number of cases that fall into four education/conviction categories are shown in the table below:
Status within Two Years after Treatment Suppose a single offender is selected from the treatment program. Here are two events of interest:
Suppose a single offender is selected from the treatment program. Here are two events of interest:
A: The offender has 10 or more years of education.
B: The offender is convicted within two years after completion of treatment.
A missile designed to destroy enemy satellites has a 0.80 chance of destroying its target. If the government tests three missiles by firing them at a target, what is the probability all three fail to destroy the target? (Assume the missiles perform independently.)
Research studies suggest that the likelihood a drug offender will be convicted of a drug offence within two years after treatment for drug abuse may depend on the person's educational level. The proportions of the total number of cases that fall into four education/conviction categories are shown in the table below:
Status within Two Years after Treatment
 Suppose a single offender is selected from the treatment program. Here are two events of interest:
Suppose a single offender is selected from the treatment program. Here are two events of interest:A: The offender has 10 or more years of education.
B: The offender is convicted within two years after completion of treatment.
A missile designed to destroy enemy satellites has a 0.80 chance of destroying its target. If the government tests three missiles by firing them at a target, what is the probability all three fail to destroy the target? (Assume the missiles perform independently.)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
Late Night Talk Shows Narrative
Let A be the event that a randomly selected person watches the Tonight Show with Jay Leno (event A) and B be the event that a randomly selected person watches the Late Show with David Letterman (event B). It is possible to time-shift a program to a more convenient hour and thus watch both programs. Suppose the following probabilities are given: P(A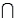 B) = 0.20, P(A
B) = 0.20, P(A 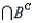 ) = 0.40, P(
) = 0.40, P( 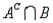 ) = 0.10, and P(
) = 0.10, and P( 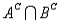 ) = 0.30.
) = 0.30.
Refer to Late Night Talk Shows Narrative. What is the probability that a randomly selected person watches Jay Leno?
Let A be the event that a randomly selected person watches the Tonight Show with Jay Leno (event A) and B be the event that a randomly selected person watches the Late Show with David Letterman (event B). It is possible to time-shift a program to a more convenient hour and thus watch both programs. Suppose the following probabilities are given: P(A
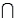 B) = 0.20, P(A
B) = 0.20, P(A 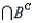 ) = 0.40, P(
) = 0.40, P( 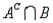 ) = 0.10, and P(
) = 0.10, and P( 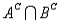 ) = 0.30.
) = 0.30.Refer to Late Night Talk Shows Narrative. What is the probability that a randomly selected person watches Jay Leno?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
Salary of Working Mothers Narrative
A researcher studied the relationship between the salary of a working woman with school-aged children and the number of children she had. The results are shown in the following probability table:
Number of Children Let A denote the event that a working woman has two or fewer children, and let B denote the event that a working woman has a low salary.
Let A denote the event that a working woman has two or fewer children, and let B denote the event that a working woman has a low salary.
Refer to Salary of Working Mothers Narrative. From this information, can one conclude that the salary of a working woman with school-aged children and the number of children she has are independent events? Explain.
A researcher studied the relationship between the salary of a working woman with school-aged children and the number of children she had. The results are shown in the following probability table:
Number of Children
 Let A denote the event that a working woman has two or fewer children, and let B denote the event that a working woman has a low salary.
Let A denote the event that a working woman has two or fewer children, and let B denote the event that a working woman has a low salary.Refer to Salary of Working Mothers Narrative. From this information, can one conclude that the salary of a working woman with school-aged children and the number of children she has are independent events? Explain.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
Late Night Talk Shows Narrative
Let A be the event that a randomly selected person watches the Tonight Show with Jay Leno (event A) and B be the event that a randomly selected person watches the Late Show with David Letterman (event B). It is possible to time-shift a program to a more convenient hour and thus watch both programs. Suppose the following probabilities are given: P(A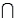 B) = 0.20, P(A
B) = 0.20, P(A 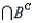 ) = 0.40, P(
) = 0.40, P( 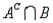 ) = 0.10, and P(
) = 0.10, and P( 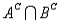 ) = 0.30.
) = 0.30.
Refer to Late Night Talk Shows Narrative. If we know a person watches Jay Leno, what is the probability he or she also watches David Letterman?
Let A be the event that a randomly selected person watches the Tonight Show with Jay Leno (event A) and B be the event that a randomly selected person watches the Late Show with David Letterman (event B). It is possible to time-shift a program to a more convenient hour and thus watch both programs. Suppose the following probabilities are given: P(A
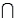 B) = 0.20, P(A
B) = 0.20, P(A 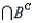 ) = 0.40, P(
) = 0.40, P( 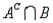 ) = 0.10, and P(
) = 0.10, and P( 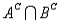 ) = 0.30.
) = 0.30.Refer to Late Night Talk Shows Narrative. If we know a person watches Jay Leno, what is the probability he or she also watches David Letterman?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
Salary of Working Mothers Narrative
A researcher studied the relationship between the salary of a working woman with school-aged children and the number of children she had. The results are shown in the following probability table:
Number of Children Let A denote the event that a working woman has two or fewer children, and let B denote the event that a working woman has a low salary.
Let A denote the event that a working woman has two or fewer children, and let B denote the event that a working woman has a low salary.
Refer to Salary of Working Mothers Narrative. If a working woman has a low salary, what is the probability that she has two or fewer children?
A researcher studied the relationship between the salary of a working woman with school-aged children and the number of children she had. The results are shown in the following probability table:
Number of Children
 Let A denote the event that a working woman has two or fewer children, and let B denote the event that a working woman has a low salary.
Let A denote the event that a working woman has two or fewer children, and let B denote the event that a working woman has a low salary.Refer to Salary of Working Mothers Narrative. If a working woman has a low salary, what is the probability that she has two or fewer children?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
Late Night Talk Shows Narrative
Let A be the event that a randomly selected person watches the Tonight Show with Jay Leno (event A) and B be the event that a randomly selected person watches the Late Show with David Letterman (event B). It is possible to time-shift a program to a more convenient hour and thus watch both programs. Suppose the following probabilities are given: P(A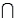 B) = 0.20, P(A
B) = 0.20, P(A 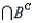 ) = 0.40, P(
) = 0.40, P( 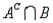 ) = 0.10, and P(
) = 0.10, and P( 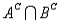 ) = 0.30.
) = 0.30.
Refer to Late Night Talk Shows Narrative. What is the probability that a randomly selected person watches David Letterman?
Let A be the event that a randomly selected person watches the Tonight Show with Jay Leno (event A) and B be the event that a randomly selected person watches the Late Show with David Letterman (event B). It is possible to time-shift a program to a more convenient hour and thus watch both programs. Suppose the following probabilities are given: P(A
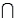 B) = 0.20, P(A
B) = 0.20, P(A 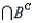 ) = 0.40, P(
) = 0.40, P( 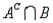 ) = 0.10, and P(
) = 0.10, and P( 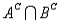 ) = 0.30.
) = 0.30.Refer to Late Night Talk Shows Narrative. What is the probability that a randomly selected person watches David Letterman?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
Drug Offenders Narrative
Research studies suggest that the likelihood a drug offender will be convicted of a drug offence within two years after treatment for drug abuse may depend on the person's educational level. The proportions of the total number of cases that fall into four education/conviction categories are shown in the table below:
Status within Two Years after Treatment Suppose a single offender is selected from the treatment program. Here are two events of interest:
Suppose a single offender is selected from the treatment program. Here are two events of interest:
A: The offender has 10 or more years of education.
B: The offender is convicted within two years after completion of treatment.
Refer to Drug Offenders Narrative. Find P(A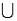 B).
B).
Research studies suggest that the likelihood a drug offender will be convicted of a drug offence within two years after treatment for drug abuse may depend on the person's educational level. The proportions of the total number of cases that fall into four education/conviction categories are shown in the table below:
Status within Two Years after Treatment
 Suppose a single offender is selected from the treatment program. Here are two events of interest:
Suppose a single offender is selected from the treatment program. Here are two events of interest:A: The offender has 10 or more years of education.
B: The offender is convicted within two years after completion of treatment.
Refer to Drug Offenders Narrative. Find P(A
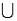 B).
B).
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
Drug Offenders Narrative
Research studies suggest that the likelihood a drug offender will be convicted of a drug offence within two years after treatment for drug abuse may depend on the person's educational level. The proportions of the total number of cases that fall into four education/conviction categories are shown in the table below:
Status within Two Years after Treatment Suppose a single offender is selected from the treatment program. Here are two events of interest:
Suppose a single offender is selected from the treatment program. Here are two events of interest:
A: The offender has 10 or more years of education.
B: The offender is convicted within two years after completion of treatment.
Refer to Drug Offenders Narrative. Find P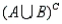 .
.
Research studies suggest that the likelihood a drug offender will be convicted of a drug offence within two years after treatment for drug abuse may depend on the person's educational level. The proportions of the total number of cases that fall into four education/conviction categories are shown in the table below:
Status within Two Years after Treatment
 Suppose a single offender is selected from the treatment program. Here are two events of interest:
Suppose a single offender is selected from the treatment program. Here are two events of interest:A: The offender has 10 or more years of education.
B: The offender is convicted within two years after completion of treatment.
Refer to Drug Offenders Narrative. Find P
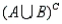 .
.
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 157 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








