Deck 21: The Euro
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/148
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 21: The Euro
1
If nations are members of a currency union that has certain characteristics to deliver the highest net benefit, the union is known as:
A) a floating exchange system.
B) an optimum currency area.
C) the exchange-rate mechanism.
D) an optimum peg.
A) a floating exchange system.
B) an optimum currency area.
C) the exchange-rate mechanism.
D) an optimum peg.
B
2
The European Monetary Union was formed in 1992 to explore issues regarding currency union under the ________ treaty.
A) Versailles
B) Paris
C) Berlin
D) Maastricht
A) Versailles
B) Paris
C) Berlin
D) Maastricht
D
3
Which of the following countries is a member of the Eurozone?
A) Sweden
B) Finland
C) Norway
D) Switzerland
A) Sweden
B) Finland
C) Norway
D) Switzerland
B
4
The common currency area in Europe is called the:
A) common market.
B) Eurozone.
C) euromark.
D) European Union.
A) common market.
B) Eurozone.
C) euromark.
D) European Union.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
The Eurozone is an example of a:
A) common market.
B) currency area.
C) free-trade area.
D) customs union.
A) common market.
B) currency area.
C) free-trade area.
D) customs union.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
The nations of the European Union currently number _____, since _____ joined in 2013.
A) 50; France and Germany
B) 28; Croatia
C) 150; Turkey and Greece
D) 13; Mexico and Canada
A) 50; France and Germany
B) 28; Croatia
C) 150; Turkey and Greece
D) 13; Mexico and Canada

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
The Maastricht Treaty, signed in 1992, initiated:
A) European political integration.
B) an economic and monetary union that featured a common currency.
C) an alliance of nations who opposed environmental harms from trade.
D) an agreement for free flow of labor and other resources across borders.
A) European political integration.
B) an economic and monetary union that featured a common currency.
C) an alliance of nations who opposed environmental harms from trade.
D) an agreement for free flow of labor and other resources across borders.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
In terms of importance, what place does the advent of the euro hold in economic history?
A) It is an important innovation in the evolution of fixed exchange rates.
B) It is an interesting experiment from which we can learn lessons.
C) It is a bold experiment, affecting hundreds of millions of people in one of the most prosperous economic regions.
D) In the grand scheme of things, the euro is less important than the fixed exchange rate scheme devised in Bretton Woods, New Hampshire.
A) It is an important innovation in the evolution of fixed exchange rates.
B) It is an interesting experiment from which we can learn lessons.
C) It is a bold experiment, affecting hundreds of millions of people in one of the most prosperous economic regions.
D) In the grand scheme of things, the euro is less important than the fixed exchange rate scheme devised in Bretton Woods, New Hampshire.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
An optimum currency union refers to the decision by a country to:
A) join a monetary union that best serves its self-interest.
B) join a free trade area.
C) dollarize its economy.
D) eliminate tariffs.
A) join a monetary union that best serves its self-interest.
B) join a free trade area.
C) dollarize its economy.
D) eliminate tariffs.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Which of the following is the same as a currency union?
A) a monetary union
B) a currency pact
C) a monetary pact
D) a monetary area
A) a monetary union
B) a currency pact
C) a monetary pact
D) a monetary area

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Which of the following is the LEAST common?
A) free trade areas
B) currency unions
C) currency crises
D) nominal anchors
A) free trade areas
B) currency unions
C) currency crises
D) nominal anchors

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Which of the following countries is NOT a member of the Eurozone?
A) Germany
B) Ireland
C) Spain
D) Poland
A) Germany
B) Ireland
C) Spain
D) Poland

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
In 1999, the Eurozone was:
A) formed by all European countries to reduce tariffs.
B) formed by 11 countries to adopt a new currency.
C) formed by 21 countries to allow labor migration between countries.
D) renamed the World Trade Organization.
A) formed by all European countries to reduce tariffs.
B) formed by 11 countries to adopt a new currency.
C) formed by 21 countries to allow labor migration between countries.
D) renamed the World Trade Organization.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
A currency union is:
A) a trade agreement between countries.
B) a customs union between countries.
C) when countries abandon their domestic currency and adopt a common currency.
D) a free trade area.
A) a trade agreement between countries.
B) a customs union between countries.
C) when countries abandon their domestic currency and adopt a common currency.
D) a free trade area.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Qualifying for admission to the Eurozone requires a nation to:
A) petition for membership with the European parliament.
B) demonstrate a commitment to democratic principles and take an antiterrorist stance.
C) peg its exchange rates to the euro and demonstrate fiscal responsibility for a length of time.
D) join the IMF and the UN, and be recommended by other members.
A) petition for membership with the European parliament.
B) demonstrate a commitment to democratic principles and take an antiterrorist stance.
C) peg its exchange rates to the euro and demonstrate fiscal responsibility for a length of time.
D) join the IMF and the UN, and be recommended by other members.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
The decision by a nation to join a currency union is based on:
A) the size of the nation's GDP.
B) the diversification of its industry and population.
C) the cost of designing, printing, and managing a national currency.
D) the costs of abandoning a national currency versus the benefits of a common currency.
A) the size of the nation's GDP.
B) the diversification of its industry and population.
C) the cost of designing, printing, and managing a national currency.
D) the costs of abandoning a national currency versus the benefits of a common currency.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Originally considered by economist Robert Mundell, decades later, in 2001, Europe adopted a new common currency now known as:
A) the euroyen, ¥.
B) the eurodollar, $.
C) the europa, .
D) the euro, €.
A) the euroyen, ¥.
B) the eurodollar, $.
C) the europa, .
D) the euro, €.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
The country that did NOT opt out of the currency union is:
A) United Kingdom.
B) Sweden.
C) Denmark.
D) Italy.
A) United Kingdom.
B) Sweden.
C) Denmark.
D) Italy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
As of 2016, the European Union was composed of ______ countries.
A) 12
B) 15
C) 28
D) 22
A) 12
B) 15
C) 28
D) 22

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
The idea of a currency union was initially proposed by:
A) John Maynard Keynes.
B) Paul Samuelson.
C) Robert Mundell.
D) Alan Greenspan.
A) John Maynard Keynes.
B) Paul Samuelson.
C) Robert Mundell.
D) Alan Greenspan.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
(Figure: Shocks and Integration) Using the graph, which of the following has the highest degree of market integration with the other countries? 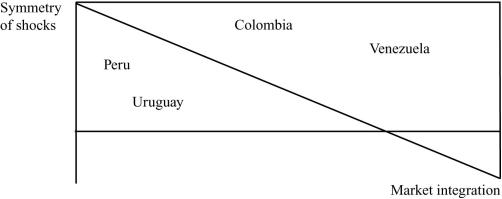
A) Peru and Colombia
B) Peru and Uruguay
C) Venezuela and Uruguay
D) Venezuela

A) Peru and Colombia
B) Peru and Uruguay
C) Venezuela and Uruguay
D) Venezuela

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Which of the following countries is part of the ERM but NOT part of the Eurozone?
A) France
B) Italy
C) Spain
D) Denmark
A) France
B) Italy
C) Spain
D) Denmark

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
The economic costs of forming a currency union will be lower whenever:
A) labor market integration is lower.
B) labor market integration is higher.
C) labor markets are not integrated.
D) wage rigidities are present.
A) labor market integration is lower.
B) labor market integration is higher.
C) labor markets are not integrated.
D) wage rigidities are present.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Higher costs result from a currency union when:
A) nations are economically dissimilar so that demand shocks affect each economy asymmetrically.
B) nations are economically similar so that demand shocks affect each economy symmetrically.
C) there is intense competition between the economies.
D) the currency is pegged to the U.S. dollar.
A) nations are economically dissimilar so that demand shocks affect each economy asymmetrically.
B) nations are economically similar so that demand shocks affect each economy symmetrically.
C) there is intense competition between the economies.
D) the currency is pegged to the U.S. dollar.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Which of the following cases is an OCA that is NOT preferred by a home country?
A) The home country faces symmetric shocks with the other country.
B) The labor market is well integrated, allowing for migration.
C) The home country faces asymmetric shocks with the other country.
D) The home economy is well integrated with the other country, carrying out vast amounts of trade.
A) The home country faces symmetric shocks with the other country.
B) The labor market is well integrated, allowing for migration.
C) The home country faces asymmetric shocks with the other country.
D) The home economy is well integrated with the other country, carrying out vast amounts of trade.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
(Figure: Shocks and Integration) Suppose that policymakers in Colombia, Peru, and Uruguay care only about being able to use policy in response to shocks? Using the graph, which of the following is most likely to join a currency area with the other countries? 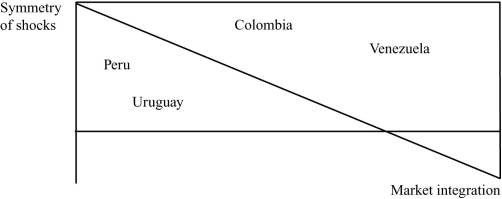
A) Colombia
B) Peru
C) Uruguay
D) Peru and Colombia

A) Colombia
B) Peru
C) Uruguay
D) Peru and Colombia

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Adopting a common currency implies all of the following, EXCEPT that:
A) each region will lose its monetary autonomy.
B) a common interest rate will be set.
C) each region will retain its monetary authority.
D) a common monetary policy will be set by the central bank.
A) each region will lose its monetary autonomy.
B) a common interest rate will be set.
C) each region will retain its monetary authority.
D) a common monetary policy will be set by the central bank.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Which would be easier to reverse? For Denmark, which now pegs its national currency to the euro, to choose monetary autonomy and abandon its peg, or for Italy to switch back from the euro to the lira?
A) Italy, because all it has to do is cash euros for lire
B) Italy, because it can change over to an electronic payments system
C) Denmark, because it would only have to return all the euros in its treasury
D) Denmark, because it would not have to change its currency, accounting structure, nor reprint domestic currency
A) Italy, because all it has to do is cash euros for lire
B) Italy, because it can change over to an electronic payments system
C) Denmark, because it would only have to return all the euros in its treasury
D) Denmark, because it would not have to change its currency, accounting structure, nor reprint domestic currency

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
A nation whose labor market is highly integrated with other nations in a currency union is more ______ to join because ______.
A) unlikely; workers would suffer real wage declines if they have competition from foreign workers
B) unlikely; firms would find it expensive to hire workers if they have to pay in the common currency
C) likely; labor market integration means that when there are asymmetric demand shocks the adjustment can be eased by migration of workers
D) likely; labor force rules and policies can be harmonized more easily
A) unlikely; workers would suffer real wage declines if they have competition from foreign workers
B) unlikely; firms would find it expensive to hire workers if they have to pay in the common currency
C) likely; labor market integration means that when there are asymmetric demand shocks the adjustment can be eased by migration of workers
D) likely; labor force rules and policies can be harmonized more easily

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
Economic benefits to nations in a currency union will be larger whenever:
A) the volume of transactions between the nations is larger and there is a greater degree of economic integration.
B) the volume of transactions is smaller but there is a greater degree of economic integration.
C) trade and financial flows between the nations are erratic.
D) financial integration is lower but cultural integration is higher.
A) the volume of transactions between the nations is larger and there is a greater degree of economic integration.
B) the volume of transactions is smaller but there is a greater degree of economic integration.
C) trade and financial flows between the nations are erratic.
D) financial integration is lower but cultural integration is higher.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Although Denmark currently pegs its krona to the euro successfully, it has not joined the currency union. All of the following are reasons, EXCEPT:
A) with a peg, the Danish monetary authority has the option to exercise control over the exchange rate in the future if needed.
B) Denmark has an additional option to abandon its peg to the euro if required to maintain stability.
C) Denmark has the option to conduct monetary policy if it chooses.
D) if Denmark gave up its krona and adopted the euro, it could always easily go back to the krona if needed to preserve monetary autonomy.
A) with a peg, the Danish monetary authority has the option to exercise control over the exchange rate in the future if needed.
B) Denmark has an additional option to abandon its peg to the euro if required to maintain stability.
C) Denmark has the option to conduct monetary policy if it chooses.
D) if Denmark gave up its krona and adopted the euro, it could always easily go back to the krona if needed to preserve monetary autonomy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
(Figure: Shocks and Integration) The graph shows hypothetical OCA economic criteria for several South American countries. Using the graph, which of the following best satisfy the OCA criteria for forming a monetary union? 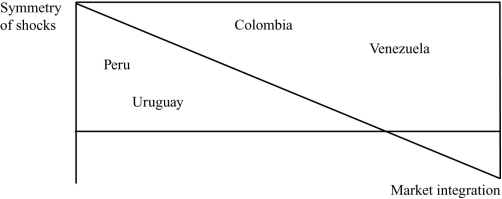
A) Peru and Colombia
B) Peru and Uruguay
C) Venezuela and Uruguay
D) Colombia and Venezuela

A) Peru and Colombia
B) Peru and Uruguay
C) Venezuela and Uruguay
D) Colombia and Venezuela

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
Criteria used to predict the benefits of fixed exchange rates can be applied to benefits from an optimum currency union. Generally, benefits are higher whenever the:
A) home country has balanced trade with its union partners.
B) home country's economy is dissimilar to that of its union partners.
C) home country's economy is similar to that of its union partners and it suffers similar types of economic "shocks."
D) home country has large and growing trade imbalances with its union partners.
A) home country has balanced trade with its union partners.
B) home country's economy is dissimilar to that of its union partners.
C) home country's economy is similar to that of its union partners and it suffers similar types of economic "shocks."
D) home country has large and growing trade imbalances with its union partners.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
Exiting from a peg is relatively ____ compared with exiting from a common currency, which would be ____.
A) difficult; impossible
B) easy; more difficult and costly
C) complex; simple
D) rare; much more common
A) difficult; impossible
B) easy; more difficult and costly
C) complex; simple
D) rare; much more common

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
The decision to form a currency union is similar to the decision to peg; however, the currency union requires:
A) a lower level of commitment and therefore requires a lower net benefit.
B) a higher level of commitment and therefore requires a higher net benefit.
C) more political integration and an agreement to limit trade.
D) the loss of political autonomy and is therefore riskier.
A) a lower level of commitment and therefore requires a lower net benefit.
B) a higher level of commitment and therefore requires a higher net benefit.
C) more political integration and an agreement to limit trade.
D) the loss of political autonomy and is therefore riskier.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
Do the costs of forming a currency union fall or rise as the degree of labor market integration rises among member countries?
A) They will rise because any macroeconomic shock in one country will be transmitted to other members when there is greater labor market integration.
B) They will fall because labor market integration allows labor to move to other member countries when there are negative macroeconomic shocks at home.
C) They will rise because labor market integration allows labor to move to other member countries when there are negative macroeconomic shocks at home.
D) The costs of forming a currency union do not depend at all upon the degree of labor market integration among member countries.
A) They will rise because any macroeconomic shock in one country will be transmitted to other members when there is greater labor market integration.
B) They will fall because labor market integration allows labor to move to other member countries when there are negative macroeconomic shocks at home.
C) They will rise because labor market integration allows labor to move to other member countries when there are negative macroeconomic shocks at home.
D) The costs of forming a currency union do not depend at all upon the degree of labor market integration among member countries.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Larger economic benefits from a currency union occur when:
A) there is intense competition between the economies.
B) market integration is large, yielding efficiency benefits.
C) the central bank acts independently.
D) the currency is pegged to the U.S. dollar.
A) there is intense competition between the economies.
B) market integration is large, yielding efficiency benefits.
C) the central bank acts independently.
D) the currency is pegged to the U.S. dollar.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
As market integration and symmetry between the nations' economies rise, the:
A) net benefits of a currency union fall.
B) OCA becomes less desirable for each nation.
C) political costs of a currency union rise.
D) net benefits of a currency union rise.
A) net benefits of a currency union fall.
B) OCA becomes less desirable for each nation.
C) political costs of a currency union rise.
D) net benefits of a currency union rise.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
Denmark is not a member of the Eurozone but is a member of the ERM. What are the advantages to Denmark of NOT being a member of the Eurozone?
A) There are none. Denmark stubbornly wants to have its own currency (the krone).
B) The Danish central bank loses its monetary autonomy by not joining the Eurozone.
C) There are not very many transactions between Denmark and Eurozone countries, so transaction gains from membership in the Eurozone would be small for Denmark.
D) The ERM allows much more exchange rate flexibility (+/- 15%) than the Eurozone.
A) There are none. Denmark stubbornly wants to have its own currency (the krone).
B) The Danish central bank loses its monetary autonomy by not joining the Eurozone.
C) There are not very many transactions between Denmark and Eurozone countries, so transaction gains from membership in the Eurozone would be small for Denmark.
D) The ERM allows much more exchange rate flexibility (+/- 15%) than the Eurozone.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
The net benefits of entering into an OCA are calculated by:
A) measuring the symmetry between the political structures of the nations.
B) measuring the variability of exchange rates between the nations.
C) comparing the efficiency benefits of market integration versus the costs of abandoning discretionary monetary policy.
D) comparing the trade balances between the nations with growth in GDP for each nation.
A) measuring the symmetry between the political structures of the nations.
B) measuring the variability of exchange rates between the nations.
C) comparing the efficiency benefits of market integration versus the costs of abandoning discretionary monetary policy.
D) comparing the trade balances between the nations with growth in GDP for each nation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
Because of differences in culture and language, it is not surprising that:
A) Eurozone nations are opposed in theory to the currency union but accept it in practice.
B) Eurozone nations tend to be more homogeneous than states in the United States.
C) demand shocks tend to be symmetric, whereas supply shocks are asymmetric.
D) the year-to-year flow of people between states in the United States is larger than the same flow between member nations in the Eurozone.
A) Eurozone nations are opposed in theory to the currency union but accept it in practice.
B) Eurozone nations tend to be more homogeneous than states in the United States.
C) demand shocks tend to be symmetric, whereas supply shocks are asymmetric.
D) the year-to-year flow of people between states in the United States is larger than the same flow between member nations in the Eurozone.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
Having one central bank responsible for managing the common currency and replacing the national monetary authority provides benefits that include all of the following, EXCEPT:
A) independence and the ability to resist political pressure.
B) better performance in keeping inflation stable with no large swings in unemployment.
C) the ability to tailor the supply of money for a variety of economic conditions in the member states.
D) provision of a stable nominal anchor.
A) independence and the ability to resist political pressure.
B) better performance in keeping inflation stable with no large swings in unemployment.
C) the ability to tailor the supply of money for a variety of economic conditions in the member states.
D) provision of a stable nominal anchor.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
If a currency union provides more to its members than a common currency unit, such as fiscal transfers or fiscal federalism, it would make joining that union:
A) less costly.
B) more beneficial.
C) yield higher net benefits.
D) less costly, more beneficial, and yield higher net benefits.
A) less costly.
B) more beneficial.
C) yield higher net benefits.
D) less costly, more beneficial, and yield higher net benefits.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
When nations enter into currency unions, their fiscal affairs continue to be separate. The exception to this situation is whenever a confederation of states has a system:
A) whereby monetary policy is decided by consensus rather than centrally.
B) of government subsidies for firms exporting outside the union.
C) of fiscal mechanisms that permits interstate transfers.
D) of common tax policies and regulatory rule.
A) whereby monetary policy is decided by consensus rather than centrally.
B) of government subsidies for firms exporting outside the union.
C) of fiscal mechanisms that permits interstate transfers.
D) of common tax policies and regulatory rule.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
In the case of a currency union, what is a nominal anchor?
A) It is the weight of the efficiency loss from changing to a common currency.
B) It is an independent value, such as the value of the common currency unit, constraining the ability of a nation to inflate its currency and prices.
C) It is a nominal measure of GDP that is not the same as the measure for real GDP.
D) It links that nation to other members of the currency union and permits no trade or financial relationships outside the union.
A) It is the weight of the efficiency loss from changing to a common currency.
B) It is an independent value, such as the value of the common currency unit, constraining the ability of a nation to inflate its currency and prices.
C) It is a nominal measure of GDP that is not the same as the measure for real GDP.
D) It links that nation to other members of the currency union and permits no trade or financial relationships outside the union.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
The OCA of the European Union falls short of the United States, for each of the following reasons, EXCEPT:
A) labor market integration in the European Union is weaker.
B) goods market integration in the European Union is weaker.
C) fiscal transfers are negligible.
D) the European Union has more asymmetric shocks.
A) labor market integration in the European Union is weaker.
B) goods market integration in the European Union is weaker.
C) fiscal transfers are negligible.
D) the European Union has more asymmetric shocks.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
The advantages of a currency union may extend to political relationships, too. How?
A) Currency unions, unfortunately, create political dissension.
B) Currency unions can be used by the larger nations to grab political power.
C) Currency unions reduce each nation's individual political power.
D) Currency unions enhance each nation's identification with other nations in the currency union.
A) Currency unions, unfortunately, create political dissension.
B) Currency unions can be used by the larger nations to grab political power.
C) Currency unions reduce each nation's individual political power.
D) Currency unions enhance each nation's identification with other nations in the currency union.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
In the Eurozone, labor market integration (including labor mobility) between member nations is:
A) far ahead of the United States.
B) on par with the United States.
C) less than in the United States.
D) structured differently because in the Eurozone workers have better benefits.
A) far ahead of the United States.
B) on par with the United States.
C) less than in the United States.
D) structured differently because in the Eurozone workers have better benefits.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
In the United States, for a $1 fall in state government revenue, the federal government increases transfers by:
A) $2.
B) $1.
C) 30 cents.
D) 15 cents.
A) $2.
B) $1.
C) 30 cents.
D) 15 cents.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
What is meant by the term inflation bias?
A) when policymakers allow exchange rates to continually depreciate and are willing to accept higher rates of inflation
B) when policymakers accept higher rates of inflation and are willing to allow exchange rates to continually depreciate
C) when policy makers use expansionary monetary policy for short-term gain, at the expense of higher inflation in the longer run
D) when fiscal policymakers use deficit financing to stimulate the economy at the expense of higher long-run inflation
A) when policymakers allow exchange rates to continually depreciate and are willing to accept higher rates of inflation
B) when policymakers accept higher rates of inflation and are willing to allow exchange rates to continually depreciate
C) when policy makers use expansionary monetary policy for short-term gain, at the expense of higher inflation in the longer run
D) when fiscal policymakers use deficit financing to stimulate the economy at the expense of higher long-run inflation

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
A currency union would be beneficial to nations with symmetrical demand shocks so that a coordinated monetary policy is possible. Comparing the Eurozone with the United States, the finding is:
A) the Eurozone nations and the U.S. states are markedly different in the correlation between growth rates of GDP.
B) the Eurozone nations and the U.S. states are quite similar in terms of correlation between growth rates of GDP.
C) the Eurozone nations have higher growth rates of GDP in their member states, whereas the United States exhibits lower growth rates.
D) the Eurozone is much more diverse in terms of its growth in GDP.
A) the Eurozone nations and the U.S. states are markedly different in the correlation between growth rates of GDP.
B) the Eurozone nations and the U.S. states are quite similar in terms of correlation between growth rates of GDP.
C) the Eurozone nations have higher growth rates of GDP in their member states, whereas the United States exhibits lower growth rates.
D) the Eurozone is much more diverse in terms of its growth in GDP.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
A key point in the difference between the United States and the European Union as OCAs, is that:
A) the intra-European Union trade is significantly higher than the intrastate trade in the United States.
B) the intra-European Union trade is significantly lower than the intrastate trade in the United States.
C) the intra-European Union labor migration is much higher than the intrastate migration in the United States.
D) in the United States, language creates a significant barrier.
A) the intra-European Union trade is significantly higher than the intrastate trade in the United States.
B) the intra-European Union trade is significantly lower than the intrastate trade in the United States.
C) the intra-European Union labor migration is much higher than the intrastate migration in the United States.
D) in the United States, language creates a significant barrier.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
A variety of indicators such as goods and labor market integration, differing unemployment rates, and the lack of fiscal federalism have prompted most economists to:
A) herald the success of the Eurozone.
B) conclude that the Eurozone has performed better than the United States in nearly every category.
C) conclude that the Eurozone has not been (and is not now) an optimal currency area going back to the 1990s.
D) recommend changes to the new currency to make it more responsive to demand shocks.
A) herald the success of the Eurozone.
B) conclude that the Eurozone has performed better than the United States in nearly every category.
C) conclude that the Eurozone has not been (and is not now) an optimal currency area going back to the 1990s.
D) recommend changes to the new currency to make it more responsive to demand shocks.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
Some nations benefit absolutely from abandoning their monetary policy and control of their currency because:
A) their monetary policy permitted high inflation under pressure from political interests that would not be present under a common currency arrangement.
B) they did not have sufficient currency in their own nation to support a higher GDP.
C) they had a strong currency, which hurt their exports.
D) the central bank would keep the money supply under tight control, which is not good for economic expansion and jobs.
A) their monetary policy permitted high inflation under pressure from political interests that would not be present under a common currency arrangement.
B) they did not have sufficient currency in their own nation to support a higher GDP.
C) they had a strong currency, which hurt their exports.
D) the central bank would keep the money supply under tight control, which is not good for economic expansion and jobs.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
The theory of an OCA sets out benefits to be derived from increased trade. A comparison of the U.S. currency area with that of the Eurozone reveals that:
A) interstate and inter-region trade is roughly equal in both areas.
B) interstate and inter-region trade in the United States is smaller as a percent of gross state product than the same figure for Europe.
C) interstate and inter-region trade in the United States is much larger as a percent of gross state product than the same figure for Europe.
D) trade comparisons are largely irrelevant to the success of a currency union.
A) interstate and inter-region trade is roughly equal in both areas.
B) interstate and inter-region trade in the United States is smaller as a percent of gross state product than the same figure for Europe.
C) interstate and inter-region trade in the United States is much larger as a percent of gross state product than the same figure for Europe.
D) trade comparisons are largely irrelevant to the success of a currency union.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
In comparing the European Union and the United States as OCAs, the authors of the text conclude that there is(are):
A) greater integration of goods markets and greater labor mobility in the United States than in Europe, but about the same symmetry of shocks in the two regions.
B) greater integration of goods markets, greater labor mobility, and greater symmetry of shocks in the United States than in Europe.
C) less integration of goods markets, but greater labor mobility and greater symmetry of shocks in the United States than in Europe.
D) greater integration of goods markets, greater labor mobility, and greater symmetry of shocks in Europe than in the United States.
A) greater integration of goods markets and greater labor mobility in the United States than in Europe, but about the same symmetry of shocks in the two regions.
B) greater integration of goods markets, greater labor mobility, and greater symmetry of shocks in the United States than in Europe.
C) less integration of goods markets, but greater labor mobility and greater symmetry of shocks in the United States than in Europe.
D) greater integration of goods markets, greater labor mobility, and greater symmetry of shocks in Europe than in the United States.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
A key benefit for nations in a politically integrated currency union such as the United States is the existence of fiscal federalism. What is the status of fiscal federalism in the Eurozone?
A) It is almost nonexistent because few fiscal transfers take place.
B) It is thriving and encompasses many aspects of the economy.
C) Most believe it currently lags the United States, but the situation is very fluid and will change soon.
D) Fiscal federalism is a concept that has relevance only in the United States because each Eurozone nation is completely independent.
A) It is almost nonexistent because few fiscal transfers take place.
B) It is thriving and encompasses many aspects of the economy.
C) Most believe it currently lags the United States, but the situation is very fluid and will change soon.
D) Fiscal federalism is a concept that has relevance only in the United States because each Eurozone nation is completely independent.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
A nation joining a currency union must subject itself to the ______ policies of the union, which may or may not conform to its own objectives or economic or political values.
A) fiscal
B) economic
C) monetary
D) accounting
A) fiscal
B) economic
C) monetary
D) accounting

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
The European Union labor markets are different from that of the United States in that:
A) language adds a barrier to free movement of labor in the European Union.
B) there is less labor regulation in the European Union.
C) persistent unemployment exists in member countries in the European Union.
D) language adds a barrier to free movement of labor in the European Union and persistent unemployment exists in member countries in the European Union.
A) language adds a barrier to free movement of labor in the European Union.
B) there is less labor regulation in the European Union.
C) persistent unemployment exists in member countries in the European Union.
D) language adds a barrier to free movement of labor in the European Union and persistent unemployment exists in member countries in the European Union.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
If economic costs outweigh benefits from joining a currency union, a nation may still choose to join because of:
A) political pressure from the large nations.
B) large political benefits.
C) the fear of floating.
D) the ability to limit imports.
A) political pressure from the large nations.
B) large political benefits.
C) the fear of floating.
D) the ability to limit imports.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
After the formation of the European Community (EC), three new nations were admitted in 1973 based on their conformance and compatibility with existing democratic norms, economic stability, and economic development. The nations were:
A) Portugal, Spain, and Finland.
B) Belgium, the Netherlands, and Luxembourg.
C) Denmark, Ireland, and the United Kingdom.
D) Italy, Greece, and Turkey.
A) Portugal, Spain, and Finland.
B) Belgium, the Netherlands, and Luxembourg.
C) Denmark, Ireland, and the United Kingdom.
D) Italy, Greece, and Turkey.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
The earliest beginning of the European Union was the:
A) Maastricht Treaty.
B) Treaty of Rome.
C) Paris Accord.
D) Louvre Accord.
A) Maastricht Treaty.
B) Treaty of Rome.
C) Paris Accord.
D) Louvre Accord.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
The basics of the ERM in the EC provided for:
A) flexible exchange rates and free capital flows.
B) fixed exchange rates based on the U.S. dollar.
C) gradual conversion to a common currency (the euro).
D) fixed exchange rates based on a weighted basket of currencies formula.
A) flexible exchange rates and free capital flows.
B) fixed exchange rates based on the U.S. dollar.
C) gradual conversion to a common currency (the euro).
D) fixed exchange rates based on a weighted basket of currencies formula.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
In spite of less-than-optimal currency area criteria at present in the Eurozone, some believe that the existence of a working currency union will result in:
A) an improvement in the criteria, as the union members are committed to work for more integration.
B) a gradual deterioration of the union, as members seek benefits from having an autonomous monetary policy.
C) tension and a power struggle over which will be the dominant economy in the union.
D) more delay in implementing needed reforms.
A) an improvement in the criteria, as the union members are committed to work for more integration.
B) a gradual deterioration of the union, as members seek benefits from having an autonomous monetary policy.
C) tension and a power struggle over which will be the dominant economy in the union.
D) more delay in implementing needed reforms.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
Some studies find that trade in the Eurozone has risen substantially, but compared with the control group of nations that stayed out, Baldwin finds the effect is:
A) larger (25%) because prices have fallen and trade has increased by much more than the control group.
B) just about the same because the control group is very similar to nations in the Eurozone.
C) somewhat larger (9%) because there has been no measurable price decline within the union or evidence of trade diversion.
D) much smaller (-2%) because trade within the union has been lackluster, whereas trade with the control group has increased dramatically.
A) larger (25%) because prices have fallen and trade has increased by much more than the control group.
B) just about the same because the control group is very similar to nations in the Eurozone.
C) somewhat larger (9%) because there has been no measurable price decline within the union or evidence of trade diversion.
D) much smaller (-2%) because trade within the union has been lackluster, whereas trade with the control group has increased dramatically.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
The Maastricht Treaty of 1991 provided for all of the following, EXCEPT:
A) an enlargement process to include more European nations.
B) a ban on nations opting out of a currency union.
C) a rename of the EC to the European Union.
D) a notion of EU "citizenship."
A) an enlargement process to include more European nations.
B) a ban on nations opting out of a currency union.
C) a rename of the EC to the European Union.
D) a notion of EU "citizenship."

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
If a currency union lowers the cost of trade and therefore promotes increased trade, the Euro-optimists believe that:
A) a currency union at some point will no longer be necessary.
B) at some point the OCA criteria will be satisfied.
C) the benefits of having an independent monetary policy will outweigh the benefits from the currency union.
D) the currency union may never be beneficial to an individual nation, but it does reduce political tension in large regions.
A) a currency union at some point will no longer be necessary.
B) at some point the OCA criteria will be satisfied.
C) the benefits of having an independent monetary policy will outweigh the benefits from the currency union.
D) the currency union may never be beneficial to an individual nation, but it does reduce political tension in large regions.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
In 1979, under the ERM, the member countries were pegged to the ECU, with a ______ band of fluctuation allowed.
A) 2.5%
B) 2.25%
C) 1%
D) 10%
A) 2.5%
B) 2.25%
C) 1%
D) 10%

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
The collapse of the Bretton Woods system of fixed exchange rates during the 1970s prompted the EC to establish its own system. It was called the:
A) Marshall Plan.
B) European Currency Union (ECU).
C) European Monetary System (EMS).
D) lend-lease plan.
A) Marshall Plan.
B) European Currency Union (ECU).
C) European Monetary System (EMS).
D) lend-lease plan.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
Another benefit from entering a currency union that is not optimal would include:
A) the idea that economies interconnected in a currency union with increased trade also develop a symmetry of demand shocks.
B) the reduction of interdependence and an increase in self-sufficiency.
C) the cessation of disagreement over trade protection.
D) the possibility of increasing the currency area.
A) the idea that economies interconnected in a currency union with increased trade also develop a symmetry of demand shocks.
B) the reduction of interdependence and an increase in self-sufficiency.
C) the cessation of disagreement over trade protection.
D) the possibility of increasing the currency area.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
The new European Economic Community, after it changed its name to the European Communities, tackled two issues related to:
A) enlargement (expansion) of the European Communities and economic integration between members.
B) immigration and terrorism.
C) secret Nazi cells and latent communism.
D) unemployment and inflation.
A) enlargement (expansion) of the European Communities and economic integration between members.
B) immigration and terrorism.
C) secret Nazi cells and latent communism.
D) unemployment and inflation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
The Single European Act passed in 1987 sought to:
A) bring former communist nations into the EC.
B) further integrate the European economies to promote trade and economic growth.
C) establish the European nations as sovereign nations with no political ties to the center.
D) impose stiff penalties for violating the exchange rate parities set in the ERM.
A) bring former communist nations into the EC.
B) further integrate the European economies to promote trade and economic growth.
C) establish the European nations as sovereign nations with no political ties to the center.
D) impose stiff penalties for violating the exchange rate parities set in the ERM.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
According to Richard Baldwin, studies indicating massive increases in trade resulting from currency unions are:
A) biased because of use of data from rich countries.
B) generally applicable to the euro.
C) underestimating the impact of the euro on intra-European Union trade.
D) not the result of lowering the transaction costs for trade within the euro area.
A) biased because of use of data from rich countries.
B) generally applicable to the euro.
C) underestimating the impact of the euro on intra-European Union trade.
D) not the result of lowering the transaction costs for trade within the euro area.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
Although Europe is not an OCA, some areas in the European Union would probably meet the criteria. Which of the following would meet them?
A) France, Sweden, and Denmark
B) the former Eastern bloc nations of Yugoslavia, Romania, and Bulgaria
C) the Netherlands, Denmark, and Britain
D) Italy, Germany, Austria, Belgium, the Netherlands, and Luxembourg
A) France, Sweden, and Denmark
B) the former Eastern bloc nations of Yugoslavia, Romania, and Bulgaria
C) the Netherlands, Denmark, and Britain
D) Italy, Germany, Austria, Belgium, the Netherlands, and Luxembourg

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
The idea that nations in a currency union will have fewer trade barriers or other frictions may have the dual effect of:
A) increased integration and more risk of debt default.
B) increased political harmony and less risk of asymmetric shocks.
C) economies of scale and specialization as well as higher risk of asymmetric shocks.
D) economic growth and an increase in environmental degradation.
A) increased integration and more risk of debt default.
B) increased political harmony and less risk of asymmetric shocks.
C) economies of scale and specialization as well as higher risk of asymmetric shocks.
D) economic growth and an increase in environmental degradation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
The original six nations that formed the European Economic Community (EEC) were:
A) Spain, Portugal, Italy, Austria, Germany, and the United Kingdom.
B) France, Bulgaria, Romania, Luxembourg, East Germany, and Russia.
C) Belgium, France, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, and West Germany.
D) Hungary, Austria, Germany, Poland, Belgium, and the United Kingdom.
A) Spain, Portugal, Italy, Austria, Germany, and the United Kingdom.
B) France, Bulgaria, Romania, Luxembourg, East Germany, and Russia.
C) Belgium, France, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, and West Germany.
D) Hungary, Austria, Germany, Poland, Belgium, and the United Kingdom.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
The best estimate of the effect of the euro on trade, according to Richard Baldwin, is a(n):
A) increase of 9%.
B) increase of 235%.
C) fall of 9%.
D) fall of 7%.
A) increase of 9%.
B) increase of 235%.
C) fall of 9%.
D) fall of 7%.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
The impetus to form an administrative body in Europe after World War II to distribute Marshall Plan aid and coordinate trade and other common issues resulted in three organizations:
A) the WTO, the GATT, and the IMF.
B) the European Payments Union, the UN, and the early roots of the European Union.
C) the European Payments Union, the European Coal and Steel Community, and Euratom.
D) the Eastern bloc, the Warsaw Pact, and NATO.
A) the WTO, the GATT, and the IMF.
B) the European Payments Union, the UN, and the early roots of the European Union.
C) the European Payments Union, the European Coal and Steel Community, and Euratom.
D) the Eastern bloc, the Warsaw Pact, and NATO.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
The European Monetary System (EMS) relied on the ______ to maintain fixed rates of exchange, but in 1992, several notable defections from the system created doubt that a monetary union could occur.
A) euro
B) U.S. dollar
C) the European currency unit (ECU)
D) ERM
A) euro
B) U.S. dollar
C) the European currency unit (ECU)
D) ERM

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
Economist Richard Baldwin says the optimism about the Eurozone may be unjustified. His research suggests trade increases in the Eurozone as a result of the currency union:
A) are much larger than previous estimates or forecasts and likely to show future gains.
B) are much smaller than previous estimates or forecasts and unlikely to show future gains.
C) are less stable and subject to wide variations.
D) could be much larger if poor and unstable economies were not in the Eurozone.
A) are much larger than previous estimates or forecasts and likely to show future gains.
B) are much smaller than previous estimates or forecasts and unlikely to show future gains.
C) are less stable and subject to wide variations.
D) could be much larger if poor and unstable economies were not in the Eurozone.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 148 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








