Deck 10: Standard Costs for Control: Direct Material and Direct Labour
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/105
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 10: Standard Costs for Control: Direct Material and Direct Labour
1
A control system comprises
A) a predetermined or standard performance level.
B) a measure of actual performance.
C) a comparison between standard and actual performance.
D) All of the given answers
A) a predetermined or standard performance level.
B) a measure of actual performance.
C) a comparison between standard and actual performance.
D) All of the given answers
D
2
A cost variance is
A) the difference between the cost of a product and its selling price.
B) a measure of risk.
C) the difference between the actual cost and the standard cost.
D) the difference between actual costs in two successive time periods.
A) the difference between the cost of a product and its selling price.
B) a measure of risk.
C) the difference between the actual cost and the standard cost.
D) the difference between actual costs in two successive time periods.
C
3
Which of the following statements is/are true?
A) The standard cost per unit of materials is used to calculate a materials price variance.
B) The standard cost per unit of materials is used to calculate a materials usage variance.
C) The standard cost per unit of materials cannot be determined until the end of the period.
D) The standard cost per unit of materials is used to calculate a materials price variance AND the standard cost per unit of materials is used to calculate a materials usage variance.
A) The standard cost per unit of materials is used to calculate a materials price variance.
B) The standard cost per unit of materials is used to calculate a materials usage variance.
C) The standard cost per unit of materials cannot be determined until the end of the period.
D) The standard cost per unit of materials is used to calculate a materials price variance AND the standard cost per unit of materials is used to calculate a materials usage variance.
D
4
An unfavourable labour efficiency variance indicates that
A) standard hours exceed actual hours.
B) actual hours exceed standard hours.
C) standard rate times standard hours exceeds actual rate times actual hours.
D) actual rate exceeds standard rate.
A) standard hours exceed actual hours.
B) actual hours exceed standard hours.
C) standard rate times standard hours exceeds actual rate times actual hours.
D) actual rate exceeds standard rate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
Given the following information, calculate the direct labour rate variance. 
A) $17 250 (U)
B) $20 700 (U)
C) $21 000 (F)
D) $20 700 (F)

A) $17 250 (U)
B) $20 700 (U)
C) $21 000 (F)
D) $20 700 (F)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
A labour efficiency variance is shown by
A) (AR) (AR).
B) SR (AH - SH).
C) (AH - SH).
D) AH (AR - SR).
A) (AR) (AR).
B) SR (AH - SH).
C) (AH - SH).
D) AH (AR - SR).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Given the following information, calculate the materials price variance: 
A) $2800 (F)
B) $2800 (U)
C) $6000 (U)
D) $6000 (F)

A) $2800 (F)
B) $2800 (U)
C) $6000 (U)
D) $6000 (F)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
A standard that assumes a production process is as efficient as practical under normal operating conditions is
A) a perfection standard.
B) an attainable standard.
C) an average standard.
D) an operating standard.
A) a perfection standard.
B) an attainable standard.
C) an average standard.
D) an operating standard.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Which department typically is responsible for an unfavourable materials price variance?
A) Purchasing
B) Engineering
C) Production
D) Receiving
A) Purchasing
B) Engineering
C) Production
D) Receiving

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
A labour rate variance is shown by
A) AH (AR - SR).
B) (AH - SH),
C) (AH - SH) (AR - SR),
D) AR (AH - SH),
A) AH (AR - SR).
B) (AH - SH),
C) (AH - SH) (AR - SR),
D) AR (AH - SH),

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Which of the following statements is false concerning the two ways to set standards?
A) Time and motion studies are part of the task analysis method.
B) The usefulness of the historical data analysis method is reduced by changes in production methods.
C) The task analysis method is future oriented rather than past oriented.
D) The task analysis method and the analysis of historical data method cannot be used together.
A) Time and motion studies are part of the task analysis method.
B) The usefulness of the historical data analysis method is reduced by changes in production methods.
C) The task analysis method is future oriented rather than past oriented.
D) The task analysis method and the analysis of historical data method cannot be used together.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Which of the following statements is/are true?
A) Many service organisations cannot use standard costing because their services are non-repetitive.
B) Practical standards are also known as attainable standards.
C) Practical standards incorporate a certain amount of inefficiency, such as that caused by an occasional machine breakdown.
D) All of the given answers
A) Many service organisations cannot use standard costing because their services are non-repetitive.
B) Practical standards are also known as attainable standards.
C) Practical standards incorporate a certain amount of inefficiency, such as that caused by an occasional machine breakdown.
D) All of the given answers

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
A material quantity variance is shown by
A) SP (AQ - SQ).
B) (SQ) (AQ).
C) (AQ - SQ).
D) (AQ - SQ) (AP - SP).
A) SP (AQ - SQ).
B) (SQ) (AQ).
C) (AQ - SQ).
D) (AQ - SQ) (AP - SP).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Which of the following are methods for setting standards?
A) Historical data analysis and cost analysis
B) Task analysis and analysis of historical data
C) Budgetary analysis and data analysis
D) Cost analysis and budgetary analysis
A) Historical data analysis and cost analysis
B) Task analysis and analysis of historical data
C) Budgetary analysis and data analysis
D) Cost analysis and budgetary analysis

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Legacy Company Ltd has determined that 1 unit of its product requires 1.5 hours of direct labour in the assembly department and 1 hour in the finishing department. Assemblers are paid $8.00 per hour and finishers are paid $9.00 per hour. Determine the standard labour cost of one unit.
A) $22.50
B) $17.00
C) $20.00
D) $21.00
A) $22.50
B) $17.00
C) $20.00
D) $21.00

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
A standard cost is
A) the actual cost of a unit of production.
B) a budget for the production of one unit of a product or service.
C) useful in calculating equivalent units.
D) the average cost within the industry.
A) the actual cost of a unit of production.
B) a budget for the production of one unit of a product or service.
C) useful in calculating equivalent units.
D) the average cost within the industry.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
A material price variance is shown by
A) AP(PQ - SQ).
B) (AP - SP).
C) PQ (AP - SP).
D) (PQ - SQ) (AP - SP).
A) AP(PQ - SQ).
B) (AP - SP).
C) PQ (AP - SP).
D) (PQ - SQ) (AP - SP).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
Which of the following statements is false regarding perfection standards?
A) They are attained only under optimum operating conditions.
B) These standards assume peak efficiency, lowest input prices and best quality materials attainable.
C) These standards motivate some employees to achieve the lowest cost possible.
D) The benefits of these standards have been proven and are irrefutable.
A) They are attained only under optimum operating conditions.
B) These standards assume peak efficiency, lowest input prices and best quality materials attainable.
C) These standards motivate some employees to achieve the lowest cost possible.
D) The benefits of these standards have been proven and are irrefutable.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Which of the following statements about perfection standards is false?
A) Some managers believe that perfection standards encourage a higher level of performance.
B) Some managers believe that perfection standards discourage workers who may then not perform as well.
C) Some managers believe that perfection standards will encourage workers to sacrifice quality in order to achieve the quantity standard.
D) Perfection standards are generally accepted by managers as the best type of standard.
A) Some managers believe that perfection standards encourage a higher level of performance.
B) Some managers believe that perfection standards discourage workers who may then not perform as well.
C) Some managers believe that perfection standards will encourage workers to sacrifice quality in order to achieve the quantity standard.
D) Perfection standards are generally accepted by managers as the best type of standard.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Which of the following statements is/are true?
A) The standard direct labour hours per unit of output are used to calculate a labour rate variance.
B) The standard direct labour hours per unit of output are used to calculate a labour efficiency variance.
C) The standard direct labour hours per unit of output cannot be determined until the end of the period.
D) All of the given answers.
A) The standard direct labour hours per unit of output are used to calculate a labour rate variance.
B) The standard direct labour hours per unit of output are used to calculate a labour efficiency variance.
C) The standard direct labour hours per unit of output cannot be determined until the end of the period.
D) All of the given answers.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Management by exception is best defined as
A) controlling actions of subordinates through acceptance by them of management techniques.
B) investigating unfavourable variances.
C) devoting management time to follow up only on significant variances.
D) controlling costs so that non-zero variances are quite exceptional.
A) controlling actions of subordinates through acceptance by them of management techniques.
B) investigating unfavourable variances.
C) devoting management time to follow up only on significant variances.
D) controlling costs so that non-zero variances are quite exceptional.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
The following data relates to QA firm.
Cost standards:
Actual results:
7800 units were produced.
Calculate the labour efficiency variance.
A) $8000 (F)
B) $8000 (U)
C) $8250 (U)
D) $8250 (F)
Cost standards:

Actual results:
7800 units were produced.

Calculate the labour efficiency variance.
A) $8000 (F)
B) $8000 (U)
C) $8250 (U)
D) $8250 (F)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
The following data relates to QA firm:
Cost standards:
Actual results:
7800 units were produced.
Calculate the direct material price variance, based on the quantity of materials purchased.
A) $2310 (F)
B) $2310 (U)
C) $2500 (U)
D) $2500 (F)
Cost standards:

Actual results:
7800 units were produced.

Calculate the direct material price variance, based on the quantity of materials purchased.
A) $2310 (F)
B) $2310 (U)
C) $2500 (U)
D) $2500 (F)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
The following data relates to QA firm.
Cost standards:
Actual results:
7800 units were produced.
Calculate the direct labour rate variance.
A) $8010 (F)
B) $8000 (U)
C) $8020 (F)
D) $7800 (F)
Cost standards:

Actual results:
7800 units were produced.

Calculate the direct labour rate variance.
A) $8010 (F)
B) $8000 (U)
C) $8020 (F)
D) $7800 (F)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Twister Pty Ltd has set direct labour standards of 3 hours per unit and $5 per hour. During the month 2900 hours at a total cost of $17 400 were used to produce 1000 units. Determine the direct labour efficiency variance.
A) $100 (F)
B) $100 (U)
C) $500 (F)
D) $500 (U)
A) $100 (F)
B) $100 (U)
C) $500 (F)
D) $500 (U)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
When considering the significance of cost variances, managers should not consider
A) relative size of the variances.
B) recurring variances.
C) the trends of the variances.
D) favourable or unfavourable status of the variances.
A) relative size of the variances.
B) recurring variances.
C) the trends of the variances.
D) favourable or unfavourable status of the variances.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
What is the most viable rule of thumb for choosing variances that should be investigated?
A) Greater than $10 000 or greater than 10 per cent of standard cost
B) Greater than 50 per cent of standard
C) Never investigate favourable variances
D) Always investigate unfavourable variances
A) Greater than $10 000 or greater than 10 per cent of standard cost
B) Greater than 50 per cent of standard
C) Never investigate favourable variances
D) Always investigate unfavourable variances

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
The following data relates to QA firm.
Cost standards:
Actual results:
7800 units were produced.
Calculate the direct material quantity variance.
A) $750 (F)
B) $800 (F)
C) $750 (U)
D) $780 (F)
Cost standards:

Actual results:
7800 units were produced.

Calculate the direct material quantity variance.
A) $750 (F)
B) $800 (F)
C) $750 (U)
D) $780 (F)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Cultco Company Ltd has set the following direct material standards per unit of product: 2.5 kg @ $3.00 per kg; $7.50 per unit. During April, actual direct material purchased and used amounted to 8000 kg at a cost of $3.10 per kg. Actual production amounted to 3000 units. Determine Cultco's direct material quantity variance.
A) $2300 (U)
B) $1500 (U)
C) $800 (U)
D) $500 (U)
A) $2300 (U)
B) $1500 (U)
C) $800 (U)
D) $500 (U)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
Which of the following statements regarding standard costing is/are true?
A) Standard costing is useful in diagnosing organisational performance.
B) Standard costing is useful in performance appraisal.
C) Standard costing is useful in determining employee pay bonuses.
D) All of the given answers.
A) Standard costing is useful in diagnosing organisational performance.
B) Standard costing is useful in performance appraisal.
C) Standard costing is useful in determining employee pay bonuses.
D) All of the given answers.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Cultco Company Ltd has set the following direct material standards per unit of product: 2.5 kg @ $3.00 per kg; $7.50 per unit. During April, actual direct material purchased and used amounted to 8000 kg at a cost of $3.10 per kg. Actual production amounted to 3000 units. Determine Cultco's direct material price variance.
A) $1500 (U)
B) $800 (U)
C) $750 (U)
D) $500 (U)
A) $1500 (U)
B) $800 (U)
C) $750 (U)
D) $500 (U)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Twister Pty Ltd has set direct labour standards of 3 hours per unit and $5 per hour. During the month 2900 hours at a total cost of $17 400 were used to produce 1000 units. Determine the total direct labour variance.
A) $2400 (F)
B) $2900 (F)
C) $2900 (U)
D) $2400 (U)
A) $2400 (F)
B) $2900 (F)
C) $2900 (U)
D) $2400 (U)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
I Wear Optometry determined the following variances had occurred during the month of September: 
The company made 1600 pairs of eyeglasses during the month using 2000 direct labour hours. The standard wage rate per hour is $14.50. Determine the standard wages for September's output.
A) $22 750
B) $34 800
C) $29 000
D) $23 200

The company made 1600 pairs of eyeglasses during the month using 2000 direct labour hours. The standard wage rate per hour is $14.50. Determine the standard wages for September's output.
A) $22 750
B) $34 800
C) $29 000
D) $23 200

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
I Wear Optometry determined the following variances had occurred during the month of September: 
The company made 1600 pairs of eyeglasses during the month using 2000 direct labour hours. The standard wage rate per hour is $14.50. What is the number of standard hours allowed for one pair of eyeglasses?
A) 1 hour
B) 1600 hours
C) 1 hour 15 minutes
D) Insufficient data to determine

The company made 1600 pairs of eyeglasses during the month using 2000 direct labour hours. The standard wage rate per hour is $14.50. What is the number of standard hours allowed for one pair of eyeglasses?
A) 1 hour
B) 1600 hours
C) 1 hour 15 minutes
D) Insufficient data to determine

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Cultco Company Ltd has set the following direct material standards per unit of product: 2.5 kg @ $3.00 per kg; $7.50 per unit. During April, actual direct material purchased and used amounted to 8000 kg at a cost of $3.10 per kg. Actual production amounted to 3000 units. Determine the total material variance.
A) $2300 (U)
B) $11 500 (U)
C) $800 (U)
D) $750 (U)
A) $2300 (U)
B) $11 500 (U)
C) $800 (U)
D) $750 (U)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
The following data relates to QA firm.
Cost standards:
Actual results:
7800 units were produced.
Calculate the direct material price variance, based on the quantity of materials purchased.
A) $2310 (U)
B) $2500 (U)
C) $2500 (F)
D) $2000 (U)
Cost standards:

Actual results:
7800 units were produced.

Calculate the direct material price variance, based on the quantity of materials purchased.
A) $2310 (U)
B) $2500 (U)
C) $2500 (F)
D) $2000 (U)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
The manager generally responsible for the direct material price variance is the
A) sales manager.
B) production supervisor.
C) purchasing manager.
D) personnel manager.
A) sales manager.
B) production supervisor.
C) purchasing manager.
D) personnel manager.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
A direct labour efficiency variance cannot be caused by
A) producing fewer finished units than originally planned.
B) poor quality raw materials.
C) employee inefficiency.
D) an out-of-date labour time standard.
A) producing fewer finished units than originally planned.
B) poor quality raw materials.
C) employee inefficiency.
D) an out-of-date labour time standard.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
Which of the following statements regarding variances is/are true?
The actions that create a favourable direct material price variance
I) can result in an unfavourable direct material quantity variance
Ii) are likely to create an unfavourable direct labour rate variance
Iii) can result in an unfavourable direct labour efficiency variance
A) i
B) i and ii
C) i and iii
D) ii and iii
The actions that create a favourable direct material price variance
I) can result in an unfavourable direct material quantity variance
Ii) are likely to create an unfavourable direct labour rate variance
Iii) can result in an unfavourable direct labour efficiency variance
A) i
B) i and ii
C) i and iii
D) ii and iii

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Twister Pty Ltd has set direct labour standards of 3 hours per unit and $5 per hour. During the month 2900 hours at a total cost of $17 400 were used to produce 1000 units. Determine the direct labour price variance.
A) $2400 (U)
B) $2400 (F)
C) $2900 (U)
D) $2900 (F)
A) $2400 (U)
B) $2400 (F)
C) $2900 (U)
D) $2900 (F)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
The production supervisor generally does not influence the
A) direct material quantity variance.
B) direct labour rate variance.
C) direct labour efficiency variance.
D) direct material price variance.
A) direct material quantity variance.
B) direct labour rate variance.
C) direct labour efficiency variance.
D) direct material price variance.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
Which of the following statements is true with regard to variances requiring investigation?
I) Favourable variances do not need to be investigated.
Ii) Large variances should be investigated.
Iii) Consistent trends in variances should be investigated.
A) i
B) ii
C) i and ii
D) ii and iii
I) Favourable variances do not need to be investigated.
Ii) Large variances should be investigated.
Iii) Consistent trends in variances should be investigated.
A) i
B) ii
C) i and ii
D) ii and iii

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
Flexer Company Ltd has set the following standards for the production of one unit of product. Normal production each month is 500 units. 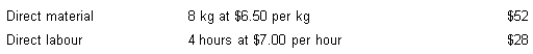
During June, actual production amounted to 420 units. All direct material was purchased and used this month. Actual cost amounted to:
Determine the standard direct labour hours allowed for June production.
A) 2000 hours
B) 1720 hours
C) 420 hours
D) 1680 hours
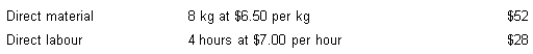
During June, actual production amounted to 420 units. All direct material was purchased and used this month. Actual cost amounted to:

Determine the standard direct labour hours allowed for June production.
A) 2000 hours
B) 1720 hours
C) 420 hours
D) 1680 hours

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
Flexer Company Ltd has set the following standards for the production of one unit of product. Normal production each month is 500 units. 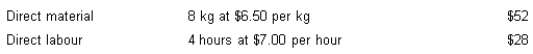
During June, actual production amounted to 420 units. All direct material was purchased and used this month. Actual cost amounted to:
Determine the direct material quantity variance for June production.
A) $35 (U)
B) $875 (U)
C) $910 (U)
D) $875 (F)
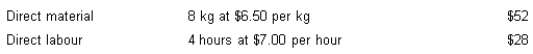
During June, actual production amounted to 420 units. All direct material was purchased and used this month. Actual cost amounted to:

Determine the direct material quantity variance for June production.
A) $35 (U)
B) $875 (U)
C) $910 (U)
D) $875 (F)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Which of the following statements is/are false?
A) All favourable variances represent the costs of producing efficiently.
B) Favourable variances (after closing to cost of goods sold) cause cost of goods sold to be lower.
C) Significant favourable variances do not need to be investigated by managers.
D) All favourable variances represent the costs of producing efficiently AND significant favourable variances do not need to be investigated by managers.
A) All favourable variances represent the costs of producing efficiently.
B) Favourable variances (after closing to cost of goods sold) cause cost of goods sold to be lower.
C) Significant favourable variances do not need to be investigated by managers.
D) All favourable variances represent the costs of producing efficiently AND significant favourable variances do not need to be investigated by managers.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
A company using a standard costing system uses an actual quantity of 520 direct labour hours at an actual cost of $5.90 per hour. The direct labour hours quantity allowed was 500 hours at a standard cost of $6.00 per hour. What is the cost of direct labour that would appear in work in process inventory?
A) $3068
B) $3120
C) $2950
D) $3000
A) $3068
B) $3120
C) $2950
D) $3000

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
Which of the following statements is false?
A) Standard cost systems use budgeted costs of direct material and direct labour.
B) Variances provide a means of performance evaluation and rewards for employees.
C) A standard costing system is usually more expensive than an actual costing system.
D) Variances provide motivation for employees to adhere to standards.
A) Standard cost systems use budgeted costs of direct material and direct labour.
B) Variances provide a means of performance evaluation and rewards for employees.
C) A standard costing system is usually more expensive than an actual costing system.
D) Variances provide motivation for employees to adhere to standards.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
If Company XYZ purchased 30 000 kg of brass metal at an actual price of $7.10 per kg (standard price is $7.00 per kg), the entry to the direct material price variance should be
A) $3000 debit.
B) $3000 credit.
C) $1500 debit.
D) $1500 credit.
A) $3000 debit.
B) $3000 credit.
C) $1500 debit.
D) $1500 credit.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
Which of the following statements is false?
A) Unfavourable variances represent the costs of producing inefficiently.
B) Unfavourable variances (after closing to cost of goods sold) cause cost of goods sold to be higher.
C) Unfavourable variances are recorded as a credit entry.
D) Significant unfavourable variances should be investigated by managers.
A) Unfavourable variances represent the costs of producing inefficiently.
B) Unfavourable variances (after closing to cost of goods sold) cause cost of goods sold to be higher.
C) Unfavourable variances are recorded as a credit entry.
D) Significant unfavourable variances should be investigated by managers.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
Flexer Company Ltd has set the following standards for the production of one unit of product. Normal production each month is 500 units. 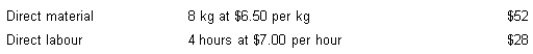
During June, actual production amounted to 420 units. All direct material was purchased and used this month. Actual cost amounted to:
Determine the direct material price for June production.
A) $875 (U)
B) $840 (F)
C) $840 (U)
D) $875 (F)
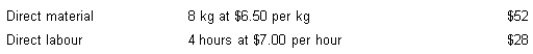
During June, actual production amounted to 420 units. All direct material was purchased and used this month. Actual cost amounted to:

Determine the direct material price for June production.
A) $875 (U)
B) $840 (F)
C) $840 (U)
D) $875 (F)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
Flexer Company Ltd has set the following standards for the production of one unit of product. Normal production each month is 500 units. 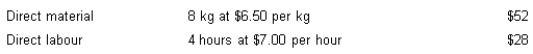
During June, actual production amounted to 420 units. All direct material was purchased and used this month. Actual cost amounted to:
Determine the direct labour rate variance for June production.
A) $280 (U)
B) $172 (U)
C) $200 (U)
D) $168 (U)
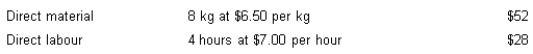
During June, actual production amounted to 420 units. All direct material was purchased and used this month. Actual cost amounted to:

Determine the direct labour rate variance for June production.
A) $280 (U)
B) $172 (U)
C) $200 (U)
D) $168 (U)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
Flexer Company Ltd has set the following standards for the production of one unit of product. Normal production each month is 500 units. 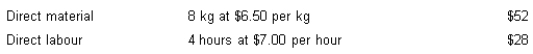
During June, actual production amounted to 420 units. All direct material was purchased and used this month. Actual cost amounted to:
Determine the standard material quantity allowed for June production.
A) 4000 kg
B) 8 kg
C) 3360 kg
D) 3500 kg
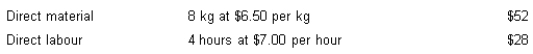
During June, actual production amounted to 420 units. All direct material was purchased and used this month. Actual cost amounted to:

Determine the standard material quantity allowed for June production.
A) 4000 kg
B) 8 kg
C) 3360 kg
D) 3500 kg

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
Which of the following journal entries correctly represents the recording of an unfavourable material price variance?
A) Direct material debit, materials price variance and accounts payable credit.
B) Direct material and materials price variance debit, accounts payable credit.
C) Direct material debit, work in process and accounts payable credit.
D) Direct materials debit, accounts payable credit.
A) Direct material debit, materials price variance and accounts payable credit.
B) Direct material and materials price variance debit, accounts payable credit.
C) Direct material debit, work in process and accounts payable credit.
D) Direct materials debit, accounts payable credit.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
A firm's purchasing manager bought poor quality material at a large saving. Because of the lower quality of material, more scrap was produced and because of the extra labour hours required an additional employee had to be hired to assist in the cutting operation. Assuming only the facts given, what variance(s) would result?
A) Favourable material price
B) Favourable material price; unfavourable material quantity; unfavourable labour efficiency
C) Favourable material price; unfavourable material quantity; unfavourable labour efficiency; unfavourable labour rate
D) Favourable material price; unfavourable labour efficiency
A) Favourable material price
B) Favourable material price; unfavourable material quantity; unfavourable labour efficiency
C) Favourable material price; unfavourable material quantity; unfavourable labour efficiency; unfavourable labour rate
D) Favourable material price; unfavourable labour efficiency

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
A favourable labour rate variance leads to a
A) credit to the labour rate variance account.
B) debit to the labour rate variance account.
C) larger than standard debit to work in process.
D) None of the given answers
A) credit to the labour rate variance account.
B) debit to the labour rate variance account.
C) larger than standard debit to work in process.
D) None of the given answers

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
Which of the following statements is/are true?
A) Variances are temporary accounts.
B) Variance accounts may be closed to cost of goods sold.
C) Favourable variances are recorded as a credit entry.
D) All of the given answers.
A) Variances are temporary accounts.
B) Variance accounts may be closed to cost of goods sold.
C) Favourable variances are recorded as a credit entry.
D) All of the given answers.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
Which of the following statements is false?
A) Standard costs are used for product costing.
B) Standard costs provide a benchmark against which actual costs can be compared.
C) Standard costs are actual costs.
D) Standard costs are used for control.
A) Standard costs are used for product costing.
B) Standard costs provide a benchmark against which actual costs can be compared.
C) Standard costs are actual costs.
D) Standard costs are used for control.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
Flexer Company Ltd has set the following standards for the production of one unit of product. Normal production each month is 500 units. 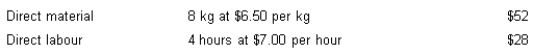
During June, actual production amounted to 420 units. All direct material was purchased and used this month. Actual cost amounted to:
Determine the direct labour efficiency variance for June production.
A) $452 (U)
B) $172 (U)
C) $280 (U)
D) $284 (F)
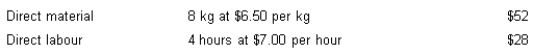
During June, actual production amounted to 420 units. All direct material was purchased and used this month. Actual cost amounted to:

Determine the direct labour efficiency variance for June production.
A) $452 (U)
B) $172 (U)
C) $280 (U)
D) $284 (F)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
A company using a standard costing system uses an actual quantity of 1100 kg of material at an actual cost of $1.20 per kg. The standard quantity allowed was 1000 kg at a standard cost of $1.00 per kg. After the goods are completed and transferred from work in process inventory, what is the cost of direct material that would appear in finished goods inventory?
A) $1000
B) $1100
C) $1200
D) $1320
A) $1000
B) $1100
C) $1200
D) $1320

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
Under a standard costing system
A) standard costs are entered into the work in process and finished goods inventory account.
B) actual costs are entered into work in process inventory account while standard costs are entered into the finished goods account.
C) the raw material inventory account is based on standard quantities and standard cost.
D) actual costs are entered into raw material and work in process inventory account.
A) standard costs are entered into the work in process and finished goods inventory account.
B) actual costs are entered into work in process inventory account while standard costs are entered into the finished goods account.
C) the raw material inventory account is based on standard quantities and standard cost.
D) actual costs are entered into raw material and work in process inventory account.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
Jay Bole is in the process of developing a standard for the labour cost of one unit of Product X. According to the design manual, it takes a skilled worker 30 minutes to produce one unit of Product X when the workshop is operating at peak condition. However, Product X is quite complex and even a skilled worker operating in high efficiency often needs another 5 minutes to adjust the tools, re-oil the machine and rework some aspects of the product. A skilled worker is paid $30 per hour, while the company pays 20 per cent on-costs on top of this.
Jay decides to develop a perfection standard. The standard labour cost for one unit of Product X is
A) $15.
B) $17.50.
C) $18.
D) $21.
Jay decides to develop a perfection standard. The standard labour cost for one unit of Product X is
A) $15.
B) $17.50.
C) $18.
D) $21.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
Dexter Surgical Tools has set the following perfection direct labour standard: 0.5 hours at $20 per hour, for each unit of Tool #11. The company plans to produce 1200 units of Tool #11 in July; however, the actual production was 1000 units and only 900 units were actually sold. The actual labour cost for July was $22 per hour.
If Dexter Surgical Tools decides to use a practical standard instead of the perfection standard, the labour efficiency variance is likely to
A) remain unchanged.
B) increase.
C) decrease.
D) not enough information.
If Dexter Surgical Tools decides to use a practical standard instead of the perfection standard, the labour efficiency variance is likely to
A) remain unchanged.
B) increase.
C) decrease.
D) not enough information.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
When developing a perfection standard for direct labour, a manager should include which of the following?
I Labour on-costs
Ii Occasional inefficiencies and machine breakdowns
Iii A minimal acceptable idle time
A) i
B) i and ii
C) iii
D) i and iii
I Labour on-costs
Ii Occasional inefficiencies and machine breakdowns
Iii A minimal acceptable idle time
A) i
B) i and ii
C) iii
D) i and iii

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
Jasmine Morron is examining a statistical control chart on the recent cost report of her manufacturing company. Jasmine is focusing on one specific process, the labour efficiency variance of polishing. She determines that the critical values for this process are $1000. The labour efficiency variances for the last 6 months were all favourable: $500F (July), $600F (August), $750F (September), $880F (October), $900F (November) and $990F (December). Jasmine decides not to investigate these variances. Do you agree with her decision?
A) Yes, because all the variances are below the critical value.
B) Yes, because all the variances are below the critical value and are favourable.
C) No, because there is a trend of the variances increasing steadily over time.
D) No, she should investigate the variances in November and December because they are both within 10% of the critical value.
A) Yes, because all the variances are below the critical value.
B) Yes, because all the variances are below the critical value and are favourable.
C) No, because there is a trend of the variances increasing steadily over time.
D) No, she should investigate the variances in November and December because they are both within 10% of the critical value.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
Selected data about a firm's materials follows. 
What amount would be debited to materials account for the purchase of material?
A) $780
B) $750
C) $720
D) $810

What amount would be debited to materials account for the purchase of material?
A) $780
B) $750
C) $720
D) $810

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
Which of the following could not be an explanation of the labour efficiency variance for a firm whose variances for the period included an unfavourable material price variance and a favourable labour efficiency variance?
A) Standards are out of date.
B) If the unfavourable material price variance was due to better quality materials being purchased, this in turn could lead to less waste of materials.
C) A timesaving improvement to the material-handling techniques has not yet been incorporated into the standard.
D) Deliberate inefficiency.
A) Standards are out of date.
B) If the unfavourable material price variance was due to better quality materials being purchased, this in turn could lead to less waste of materials.
C) A timesaving improvement to the material-handling techniques has not yet been incorporated into the standard.
D) Deliberate inefficiency.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
Selected data about a firm's materials follows. 
What amount would be debited to work in process account for materials used?
A) $660
B) $630
C) $600
D) None of the given answers

What amount would be debited to work in process account for materials used?
A) $660
B) $630
C) $600
D) None of the given answers

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
When using the statistical control chart to investigate variances
A) managers should only investigate variances that are beyond the critical value.
B) managers should only investigate variances that are fall below the critical value over a number of consecutive periods.
C) any variances that go beyond the critical values are likely to be the result of random events such as employee illness.
D) managers should estimate the critical values by averaging the variances over a number of periods.
A) managers should only investigate variances that are beyond the critical value.
B) managers should only investigate variances that are fall below the critical value over a number of consecutive periods.
C) any variances that go beyond the critical values are likely to be the result of random events such as employee illness.
D) managers should estimate the critical values by averaging the variances over a number of periods.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
When material price variances are recognised at the time of material purchase, direct materials used are
A) credited to the materials account at standard cost.
B) debited to the work in process account at actual prices.
C) credited to the materials account at actual cost.
D) debited to the materials account at standard cost.
A) credited to the materials account at standard cost.
B) debited to the work in process account at actual prices.
C) credited to the materials account at actual cost.
D) debited to the materials account at standard cost.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
For a particular period a firm worked a larger number of overtime hours than planned in order to complete a larger than usual number of job orders. The jobs were all completed within the standard time allowed for each job. Assuming only the facts given, what variance(s) would result from these facts?
A) Unfavourable labour rate; unfavourable labour efficiency
B) Unfavourable labour efficiency; unfavourable material quantity variance
C) Unfavourable labour rate; unfavourable labour efficiency; unfavourable material quantity
D) None of the given answers
A) Unfavourable labour rate; unfavourable labour efficiency
B) Unfavourable labour efficiency; unfavourable material quantity variance
C) Unfavourable labour rate; unfavourable labour efficiency; unfavourable material quantity
D) None of the given answers

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
Jasmine Morron is examining a statistical control chart on the recent cost report of her manufacturing company. Jasmine is focusing on one specific process, the labour efficiency variance of polishing. She determines that the critical values for this process are $1000. Which of the following statements is correct?
A) Jasmine should investigate only unfavourable variances that are larger than $1000.
B) Any variances of less than $1000 are likely to be the result of random events.
C) Jasmine should investigate unfavourable variances of any size, and favourable variances that are larger than $1000.
D) Jasmine should investigate any variances that are larger than $500.
A) Jasmine should investigate only unfavourable variances that are larger than $1000.
B) Any variances of less than $1000 are likely to be the result of random events.
C) Jasmine should investigate unfavourable variances of any size, and favourable variances that are larger than $1000.
D) Jasmine should investigate any variances that are larger than $500.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
A particular firm with zero material inventory purchased 30 000 kg of material and used 25 000 kg. For control purposes, it is recommended that firms calculate the material price variance at the time of purchase. The variance could alternatively be calculated at the time of usage of that material. Which of the following statements most correctly reflects a comparison of the two methods for this firm?
A) Whether calculated on purchase or usage, both variances will be favourable.
B) Whether calculated on purchase or usage, both variances will be unfavourable.
C) The variance calculated on purchase will be larger than the variance calculated on usage, but in the same direction (favourable/unfavourable).
D) The variance calculated on purchase will be smaller than the variance calculated on usage, but in the same direction (favourable/unfavourable).
A) Whether calculated on purchase or usage, both variances will be favourable.
B) Whether calculated on purchase or usage, both variances will be unfavourable.
C) The variance calculated on purchase will be larger than the variance calculated on usage, but in the same direction (favourable/unfavourable).
D) The variance calculated on purchase will be smaller than the variance calculated on usage, but in the same direction (favourable/unfavourable).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
In which of the following circumstances would it be acceptable to record the material price variance at the time of usage of the materials?
A) Where a fixed contract price is in place for the purchase of materials for a period.
B) Where the purchasing manager is held accountable for all material price variances.
C) Where the purchasing manager has little control over the price paid.
D) Both where a fixed contract price is in place for the purchase of materials for a period AND where the purchasing manager has little control over the price paid.
A) Where a fixed contract price is in place for the purchase of materials for a period.
B) Where the purchasing manager is held accountable for all material price variances.
C) Where the purchasing manager has little control over the price paid.
D) Both where a fixed contract price is in place for the purchase of materials for a period AND where the purchasing manager has little control over the price paid.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
Dexter Surgical Tools has set the following direct labour standard: 0.5 hours at $20 per hour, for each unit of Tool #11. The company plans to produce 1200 units of Tool #11 in July; however, the actual production was 1000 units and only 900 units were actually sold. The actual labour cost for July was $22 per hour.
Which of the following is a likely explanation for the July labour efficiency variance?
A) The standard was set incorrectly.
B) A machine breakdown has resulted in unanticipated inefficiencies.
C) The production level was smaller than expected.
D) Both incorrectly set standards and a machine breakdown are likely explanations.
Which of the following is a likely explanation for the July labour efficiency variance?
A) The standard was set incorrectly.
B) A machine breakdown has resulted in unanticipated inefficiencies.
C) The production level was smaller than expected.
D) Both incorrectly set standards and a machine breakdown are likely explanations.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
A department's budgeted output for a 4-week period was 500 units at a standard cost of $100 per unit. The actual production was 450 units and the firm's ledger revealed actual costs for the month to be $50 200. The standard production cost for the period is
A) $50 000.
B) $50 200.
C) $45 000.
D) insufficient information to determine.
A) $50 000.
B) $50 200.
C) $45 000.
D) insufficient information to determine.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
A material price variance of $5000 (unfavourable) for a period has been calculated. The actual unit price was $9.00. The actual quantity of material used was 6000. The standard quantity of materials was 5000. Calculate the standard unit price for a unit of raw materials for the period (round where necessary).
A) $5.00
B) $8.00
C) $8.17
D) $9.83
A) $5.00
B) $8.00
C) $8.17
D) $9.83

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
Which of the following statements is a definition of standard quantity of direct materials allowed for a period? Standard quantity of direct materials is
A) the number of units of material that should have been used for expected (budgeted) production.
B) the number of units of material that were used for actual production.
C) the number of units of material that should have been used for actual production.
D) the number of units of material required for each unit of production.
A) the number of units of material that should have been used for expected (budgeted) production.
B) the number of units of material that were used for actual production.
C) the number of units of material that should have been used for actual production.
D) the number of units of material required for each unit of production.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
Which of the following statements regarding allowances for spoilage and/or inefficiency is not correct?
A) When allowances are not included within the standards, any inefficiencies are highlighted as unfavourable variances.
B) When allowances are not included within the standards, any inefficiencies are highlighted as favourable variances.
C) Firms would never set standards that included an allowance for spoilage.
D) When allowances are not included within the standards, any inefficiencies are highlighted as favourable variances AND firms would never set standards that included an allowance for spoilage.
A) When allowances are not included within the standards, any inefficiencies are highlighted as unfavourable variances.
B) When allowances are not included within the standards, any inefficiencies are highlighted as favourable variances.
C) Firms would never set standards that included an allowance for spoilage.
D) When allowances are not included within the standards, any inefficiencies are highlighted as favourable variances AND firms would never set standards that included an allowance for spoilage.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
Jay Bole is in the process of developing a standard for the labour cost of one unit of Product X. According to the design manual, it takes a skilled worker 30 minutes to produce one unit of Product X when the workshop is operating at peak condition. However, Product X is quite complex, and even a skilled worker operating in high efficiency often needs another 5 minutes to adjust the tools, re-oil the machine, and rework some aspects of the product. A skilled worker is paid $30 per hour, while the company pays 20 per cent on-costs on top of this.
Jay decides to develop a practical standard. The standard labour cost for one unit of Product X is
A) $15.
B) $17.50.
C) $18.
D) $21.
Jay decides to develop a practical standard. The standard labour cost for one unit of Product X is
A) $15.
B) $17.50.
C) $18.
D) $21.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
Dexter Surgical Tools has set the following direct labour standard: 0.5 hours at $20 per hour, for each unit of Tool #11. The company plans to produce 1200 units of Tool #11 in July; however, the actual production was 1000 units and only 900 units were actually sold. The actual labour cost for July was $22 per hour.
The labour efficiency variance for July was
A) $1200 Favourable.
B) $1200 Unfavourable.
C) $1000 Favourable.
D) $1000 Unfavourable.
The labour efficiency variance for July was
A) $1200 Favourable.
B) $1200 Unfavourable.
C) $1000 Favourable.
D) $1000 Unfavourable.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 105 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








