Deck 22: Operational Decision-Making Tools: Simulation
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/84
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 22: Operational Decision-Making Tools: Simulation
1
An operations plan is an input into the sales and operations planning process.
False
2
Overtime and undertime are common strategies for adjusting demand.
False
3
One of several strategies for managing demand is to shift it into other time periods using incentives, sales promotions, and advertising.
True
4
Most companies use mixed strategies for managing demand.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
Aggregate planning involves the process of determining the timing and quantity of production for an individual item over an intermediate time frame.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Inventory holding costs are an important consideration for the level production strategy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
A chase strategy involves hiring and firing workers so that production trails demand.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
A mixed strategy for adjusting capacity is simpler and easier to implement than any pure strategy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
The level strategy for adjusting capacity is only appropriate when there is no variation in demand.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Sales and operations planning is an aggregate planning process that determines the capacity needed to meet immediate demand.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
An aggregate operations plan specifies the production quantities for an entire product family or product line.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
An economic strategy for adjusting demand can include adjusting capacity or managing demand.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
When demand fluctuations are extreme using overtime and undertime is a feasible strategy for adjusting capacity.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Financial constraints are one of the major inputs of the sales and operations planning process.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Implementing a companywide game plan for allocating resources addresses the long-standing battle between operations and finance.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
With a pure strategy for aggregate planning only one capacity variable is changed.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Subcontracting is a feasible alternative for adjusting capacity provided the supplier can reliably meet quality and time requirements.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
The transportation method is used for aggregate planning when the strategy for adjusting capacity is hiring and firing workers.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
A chase demand strategy is one of several alternatives available for managing demand.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
One objective of sales and operations planning is to develop a companywide game plan to satisfy production.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Most companies use mixed strategies for production planning.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Disaggregation is the process of breaking a sales and operations plan into more detailed plans.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
All of the following are inputs to the aggregate production planning process except
A) demand forecasts.
B) financial constraints.
C) sales plans.
D) capacity constraints.
A) demand forecasts.
B) financial constraints.
C) sales plans.
D) capacity constraints.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Sharing information and synchronizing production across the supply chain is known as disaggregation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Which of the following is an output of sales and operations planning?
A) company policies
B) demand forecasts
C) operations plans
D) capacity constraints
A) company policies
B) demand forecasts
C) operations plans
D) capacity constraints

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Problems associated with using a part-time workers strategy for adjusting capacity include all of the following except
A) high turnover.
B) accelerated training requirements.
C) scheduling difficulties.
D) high retirement costs.
A) high turnover.
B) accelerated training requirements.
C) scheduling difficulties.
D) high retirement costs.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
The primary cost associated with the level production strategy is the cost of
A) holding inventory.
B) hiring and firing workers.
C) overtime.
D) outsourcing (subcontracting).
A) holding inventory.
B) hiring and firing workers.
C) overtime.
D) outsourcing (subcontracting).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
The term aggregate planning reflects the fact that plans are developed for ___________, rather than _____________.
A) product families, individual products
B) product lines, product families
C) competitor products, product families
D) competitor products, individual products
A) product families, individual products
B) product lines, product families
C) competitor products, product families
D) competitor products, individual products

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Strategies for proactive demand management would not include
A) shifting demand into other time periods.
B) offering products or services with countercyclical demand patterns.
C) partnering with suppliers to reduce information distortion along the supply chain.
D) using subcontracting to meet unexpected high demand levels.
A) shifting demand into other time periods.
B) offering products or services with countercyclical demand patterns.
C) partnering with suppliers to reduce information distortion along the supply chain.
D) using subcontracting to meet unexpected high demand levels.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
Which of the following is not a strategy for adjusting capacity?
A) level production
B) subcontracting
C) backordering
D) product substitution
A) level production
B) subcontracting
C) backordering
D) product substitution

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Shifting demand into other time periods can be accomplished through
A) Advertising
B) Sales promotions
C) Incentives
D) All of these answer choices are correct.
A) Advertising
B) Sales promotions
C) Incentives
D) All of these answer choices are correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Adjusting available capacity by hiring and firing workers to match demand is an example of a(n) ________ strategy.
A) level production
B) chase demand
C) mixed production.
D) optimal production.
A) level production
B) chase demand
C) mixed production.
D) optimal production.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
The following information relates to a company's aggregate production planning activities: 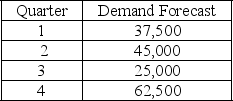 Beginning Workforce = 125 workers
Beginning Workforce = 125 workers
Production per Employee = 500 units per quarter
Hiring Cost = $750 per worker
Firing Cost = $1,500 per worker
Inventory Carrying Cost = $10 per unit per quarter
If a chase demand strategy is used then the number of workers hired at the start of quarter 4 is
A) 0
B) 15
C) 75
D) 125
 Beginning Workforce = 125 workers
Beginning Workforce = 125 workersProduction per Employee = 500 units per quarter
Hiring Cost = $750 per worker
Firing Cost = $1,500 per worker
Inventory Carrying Cost = $10 per unit per quarter
If a chase demand strategy is used then the number of workers hired at the start of quarter 4 is
A) 0
B) 15
C) 75
D) 125

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
Revenue management seeks to maximize profit from time-sensitive products and services.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Sales and operations planning is an aggregate planning process for a(n)______________ time horizon.
A) short-term
B) intermediate
C) long-term
D) infinite
A) short-term
B) intermediate
C) long-term
D) infinite

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
The following information relates to a company's aggregate production planning activities: 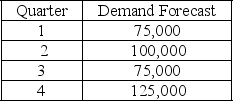 Beginning Workforce = 35 workers
Beginning Workforce = 35 workers
Production per Employee = 1,250 units per quarter
Hiring Cost = $500 per worker
Firing Cost = $1,000 per worker
Inventory Carrying Cost = $20 per unit per quarter
If a chase demand strategy is used then the number of workers hired at the start of quarter 2 is
A) 10
B) 20
C) 35
D) 80
 Beginning Workforce = 35 workers
Beginning Workforce = 35 workersProduction per Employee = 1,250 units per quarter
Hiring Cost = $500 per worker
Firing Cost = $1,000 per worker
Inventory Carrying Cost = $20 per unit per quarter
If a chase demand strategy is used then the number of workers hired at the start of quarter 2 is
A) 10
B) 20
C) 35
D) 80

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Which of the following is not a strategy for managing demand?
A) Shifting demand into other time periods.
B) Create demand for idle resources.
C) Redirecting demand to a competitor.
D) Partnering with suppliers to minimize information distortion.
A) Shifting demand into other time periods.
B) Create demand for idle resources.
C) Redirecting demand to a competitor.
D) Partnering with suppliers to minimize information distortion.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
The most effective aggregate planning strategy depends on
A) the demand distribution
B) the competitive position
C) the firm's cost structure
D) All of these answer choices are correct.
A) the demand distribution
B) the competitive position
C) the firm's cost structure
D) All of these answer choices are correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
Which of the following is an objective to sales and operations planning?
A) Develop an economic strategy for meeting demand.
B) Develop a marketing strategy for meeting demand.
C) Develop an operations strategy for meeting demand.
D) None of these answer choices is correct.
A) Develop an economic strategy for meeting demand.
B) Develop a marketing strategy for meeting demand.
C) Develop an operations strategy for meeting demand.
D) None of these answer choices is correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
The following information relates to a company's aggregate production planning activities: 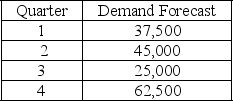 Beginning Workforce = 125 workers
Beginning Workforce = 125 workers
Production per Employee = 500 units per quarter
Hiring Cost = $750 per worker
Firing Cost = $1,500 per worker
Inventory Carrying Cost = $10 per unit per quarter
If a chase demand strategy is used the number of workers fired at the start of quarter 3 is
A) 0
B) 40
C) 50
D) 75
 Beginning Workforce = 125 workers
Beginning Workforce = 125 workersProduction per Employee = 500 units per quarter
Hiring Cost = $750 per worker
Firing Cost = $1,500 per worker
Inventory Carrying Cost = $10 per unit per quarter
If a chase demand strategy is used the number of workers fired at the start of quarter 3 is
A) 0
B) 40
C) 50
D) 75

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
The following information relates to a company's aggregate production planning activities: 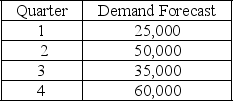 Beginning Workforce = 50 workers
Beginning Workforce = 50 workers
Production per Employee = 250 units per quarter
Hiring Cost = $1000 per worker
Firing Cost = $1,500 per worker
Inventory Carrying Cost = $15 per unit per quarter
If a level production strategy is used then the number of workers required is
A) 125
B) 170
C) 250
D) 325
 Beginning Workforce = 50 workers
Beginning Workforce = 50 workersProduction per Employee = 250 units per quarter
Hiring Cost = $1000 per worker
Firing Cost = $1,500 per worker
Inventory Carrying Cost = $15 per unit per quarter
If a level production strategy is used then the number of workers required is
A) 125
B) 170
C) 250
D) 325

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
The following information relates to a company's aggregate production planning activities: 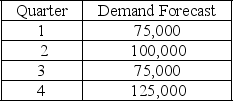 Beginning Workforce = 35 workers
Beginning Workforce = 35 workers
Production per Employee = 1,250 units per quarter
Hiring Cost = $500 per worker
Firing Cost = $1,000 per worker
Inventory Carrying Cost = $20 per unit per quarter
If a chase demand strategy is used then the total firing cost for the plan is
A) $10,000
B) $15,000
C) $20,000
D) $25,000
 Beginning Workforce = 35 workers
Beginning Workforce = 35 workersProduction per Employee = 1,250 units per quarter
Hiring Cost = $500 per worker
Firing Cost = $1,000 per worker
Inventory Carrying Cost = $20 per unit per quarter
If a chase demand strategy is used then the total firing cost for the plan is
A) $10,000
B) $15,000
C) $20,000
D) $25,000

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
The following information relates to a company's aggregate production planning activities: 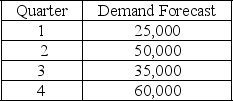 Beginning Workforce = 50 workers
Beginning Workforce = 50 workers
Production per Employee = 250 units per quarter
Hiring Cost = $1000 per worker
Firing Cost = $1,500 per worker
Inventory Carrying Cost = $15 per unit per quarter
If a chase demand strategy is used then the number of workers hired at the start of quarter 2 is
A) 0
B) 50
C) 100
D) 200
 Beginning Workforce = 50 workers
Beginning Workforce = 50 workersProduction per Employee = 250 units per quarter
Hiring Cost = $1000 per worker
Firing Cost = $1,500 per worker
Inventory Carrying Cost = $15 per unit per quarter
If a chase demand strategy is used then the number of workers hired at the start of quarter 2 is
A) 0
B) 50
C) 100
D) 200

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
A company is developing a linear programming model for its aggregate production plan. If It = units in inventory at the end of period t, Pt = units produced in period t, and Dt = demand in period t, then the company's demand constraint to ensure that demand is met in quarter 3 is
A) D3 = I2 - I3 + P3
B) D3 = I3 + P3
C) D3 = I3 - I2 + P3
D) D3 = I2 - I3 + P2
A) D3 = I2 - I3 + P3
B) D3 = I3 + P3
C) D3 = I3 - I2 + P3
D) D3 = I2 - I3 + P2

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
The following information relates to a company's aggregate production planning activities: 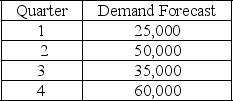 Beginning Workforce = 50 workers
Beginning Workforce = 50 workers
Production per Employee = 250 units per quarter
Hiring Cost = $1000 per worker
Firing Cost = $1,500 per worker
Inventory Carrying Cost = $15 per unit per quarter
If a level production strategy is used then the required output per quarter is
A) 60,000 units.
B) 42,500 units.
C) 35,000 units.
D) 25,000 units.
 Beginning Workforce = 50 workers
Beginning Workforce = 50 workersProduction per Employee = 250 units per quarter
Hiring Cost = $1000 per worker
Firing Cost = $1,500 per worker
Inventory Carrying Cost = $15 per unit per quarter
If a level production strategy is used then the required output per quarter is
A) 60,000 units.
B) 42,500 units.
C) 35,000 units.
D) 25,000 units.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
The following information relates to a company's aggregate production planning activities: 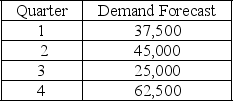 Beginning Workforce = 125 workers
Beginning Workforce = 125 workers
Production per Employee = 500 units per quarter
Hiring Cost = $750 per worker
Firing Cost = $1,500 per worker
Inventory Carrying Cost = $10 per unit per quarter
If a level production strategy is used the total cost of the production plan (hiring cost, firing cost, and inventory cost) is
A) $60,000
B) $275,000
C) $335,000
D) $610,000
 Beginning Workforce = 125 workers
Beginning Workforce = 125 workersProduction per Employee = 500 units per quarter
Hiring Cost = $750 per worker
Firing Cost = $1,500 per worker
Inventory Carrying Cost = $10 per unit per quarter
If a level production strategy is used the total cost of the production plan (hiring cost, firing cost, and inventory cost) is
A) $60,000
B) $275,000
C) $335,000
D) $610,000

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
The following information relates to a company's aggregate production planning activities: 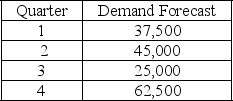 Beginning Workforce = 125 workers
Beginning Workforce = 125 workers
Production per Employee = 500 units per quarter
Hiring Cost = $750 per worker
Firing Cost = $1,500 per worker
Inventory Carrying Cost = $10 per unit per quarter
If a level production strategy is used the number of units in inventory at the end of quarter 3 is
A) 0
B) 2,500
C) 5,000
D) 20,000
 Beginning Workforce = 125 workers
Beginning Workforce = 125 workersProduction per Employee = 500 units per quarter
Hiring Cost = $750 per worker
Firing Cost = $1,500 per worker
Inventory Carrying Cost = $10 per unit per quarter
If a level production strategy is used the number of units in inventory at the end of quarter 3 is
A) 0
B) 2,500
C) 5,000
D) 20,000

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
The following information relates to a company's aggregate production planning activities: 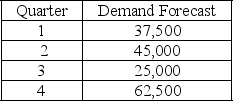 Beginning Workforce = 125 workers
Beginning Workforce = 125 workers
Production per Employee = 500 units per quarter
Hiring Cost = $750 per worker
Firing Cost = $1,500 per worker
Inventory Carrying Cost = $10 per unit per quarter
If a chase demand strategy is used the total hiring and firing costs for the production plan is
A) $67,500
B) $135,000
C) $202,500
D) $337,500
 Beginning Workforce = 125 workers
Beginning Workforce = 125 workersProduction per Employee = 500 units per quarter
Hiring Cost = $750 per worker
Firing Cost = $1,500 per worker
Inventory Carrying Cost = $10 per unit per quarter
If a chase demand strategy is used the total hiring and firing costs for the production plan is
A) $67,500
B) $135,000
C) $202,500
D) $337,500

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
The following information relates to a company's aggregate production planning activities: 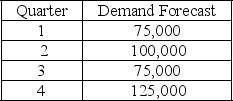 Beginning Workforce = 35 workers
Beginning Workforce = 35 workers
Production per Employee = 1,250 units per quarter
Hiring Cost = $500 per worker
Firing Cost = $1,000 per worker
Inventory Carrying Cost = $20 per unit per quarter
If a level production strategy is used then the cost of the level production plan (inventory costs plus hiring and firing costs) is
A) $20,000
B) $645,000
C) $1,250,000
D) $1,270,000
 Beginning Workforce = 35 workers
Beginning Workforce = 35 workersProduction per Employee = 1,250 units per quarter
Hiring Cost = $500 per worker
Firing Cost = $1,000 per worker
Inventory Carrying Cost = $20 per unit per quarter
If a level production strategy is used then the cost of the level production plan (inventory costs plus hiring and firing costs) is
A) $20,000
B) $645,000
C) $1,250,000
D) $1,270,000

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
The following information relates to a company's aggregate production planning activities: 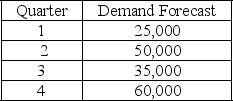 Beginning Workforce = 50 workers
Beginning Workforce = 50 workers
Production per Employee = 250 units per quarter
Hiring Cost = $1000 per worker
Firing Cost = $1,500 per worker
Inventory Carrying Cost = $15 per unit per quarter
If a chase demand strategy is used then the total hiring and firing cost of the plan is
A) $340,000
B) $250,000
C) $125,000
D) $90,000
 Beginning Workforce = 50 workers
Beginning Workforce = 50 workersProduction per Employee = 250 units per quarter
Hiring Cost = $1000 per worker
Firing Cost = $1,500 per worker
Inventory Carrying Cost = $15 per unit per quarter
If a chase demand strategy is used then the total hiring and firing cost of the plan is
A) $340,000
B) $250,000
C) $125,000
D) $90,000

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
The following information relates to a company's aggregate production planning activities: 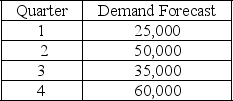 Beginning Workforce = 50 workers
Beginning Workforce = 50 workers
Production per Employee = 250 units per quarter
Hiring Cost = $1000 per worker
Firing Cost = $1,500 per worker
Inventory Carrying Cost = $15 per unit per quarter
If a level production strategy is used then the inventory at the end of quarter 3 is
A) 0
B) 5,000
C) 10,000
D) 17,500
 Beginning Workforce = 50 workers
Beginning Workforce = 50 workersProduction per Employee = 250 units per quarter
Hiring Cost = $1000 per worker
Firing Cost = $1,500 per worker
Inventory Carrying Cost = $15 per unit per quarter
If a level production strategy is used then the inventory at the end of quarter 3 is
A) 0
B) 5,000
C) 10,000
D) 17,500

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
The following information relates to a company's aggregate production planning activities: 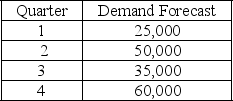 Beginning Workforce = 50 workers
Beginning Workforce = 50 workers
Production per Employee = 250 units per quarter
Hiring Cost = $1000 per worker
Firing Cost = $1,500 per worker
Inventory Carrying Cost = $15 per unit per quarter
If a level production strategy is used then the total cost of the plan (hiring cost, firing cost and inventory carrying cost) is
A) $120,000
B) $377,500
C) $675,000
D) $795,000
 Beginning Workforce = 50 workers
Beginning Workforce = 50 workersProduction per Employee = 250 units per quarter
Hiring Cost = $1000 per worker
Firing Cost = $1,500 per worker
Inventory Carrying Cost = $15 per unit per quarter
If a level production strategy is used then the total cost of the plan (hiring cost, firing cost and inventory carrying cost) is
A) $120,000
B) $377,500
C) $675,000
D) $795,000

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
A company is developing a linear programming model for its aggregate production plan. If Wt = workforce size for period t, Ht = number of workers hired for period t, and Ft = number of workers fired for period t, then the company's workforce constraint for period 2 is
A) W2 = W1 + F2 - H2
B) W2 = H2 - F2
C) W2 = W1 + H2 - F2
D) W2 = H2 - F2 - W1
A) W2 = W1 + F2 - H2
B) W2 = H2 - F2
C) W2 = W1 + H2 - F2
D) W2 = H2 - F2 - W1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
A company is developing a linear programming model for its aggregate production plan. If It = units in inventory at the end of period t, Pt = units produced in period t, and Dt = demand in period t, then the company's demand constraint to ensure that demand is met in quarter 2 is
A) D2 = I2 - I1 + P2
B) D2 = I1 + P2
C) D2 = I2 + I1 + P2
D) D2 = I1 + P2 - I2
A) D2 = I2 - I1 + P2
B) D2 = I1 + P2
C) D2 = I2 + I1 + P2
D) D2 = I1 + P2 - I2

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
The following information relates to a company's aggregate production planning activities: 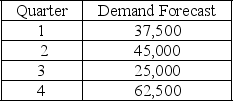 Beginning Workforce = 125 workers
Beginning Workforce = 125 workers
Production per Employee = 500 units per quarter
Hiring Cost = $750 per worker
Firing Cost = $1,500 per worker
Inventory Carrying Cost = $10 per unit per quarter
If a level production strategy is used the number of units to produce each quarter is
A) 42,500
B) 85,000
C) 62,500
D) 37,500
 Beginning Workforce = 125 workers
Beginning Workforce = 125 workersProduction per Employee = 500 units per quarter
Hiring Cost = $750 per worker
Firing Cost = $1,500 per worker
Inventory Carrying Cost = $10 per unit per quarter
If a level production strategy is used the number of units to produce each quarter is
A) 42,500
B) 85,000
C) 62,500
D) 37,500

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
The following information relates to a company's aggregate production planning activities: 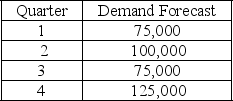 Beginning Workforce = 35 workers
Beginning Workforce = 35 workers
Production per Employee = 1,250 units per quarter
Hiring Cost = $500 per worker
Firing Cost = $1,000 per worker
Inventory Carrying Cost = $20 per unit per quarter
If a level production strategy is used then the inventory at the end of quarter 3 is
A) 18,750
B) 12,500
C) 25,650
D) 31,250
 Beginning Workforce = 35 workers
Beginning Workforce = 35 workersProduction per Employee = 1,250 units per quarter
Hiring Cost = $500 per worker
Firing Cost = $1,000 per worker
Inventory Carrying Cost = $20 per unit per quarter
If a level production strategy is used then the inventory at the end of quarter 3 is
A) 18,750
B) 12,500
C) 25,650
D) 31,250

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
The following information relates to a company's aggregate production planning activities: 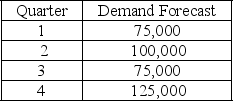 Beginning Workforce = 35 workers
Beginning Workforce = 35 workers
Production per Employee = 1,250 units per quarter
Hiring Cost = $500 per worker
Firing Cost = $1,000 per worker
Inventory Carrying Cost = $20 per unit per quarter
If a level production strategy is used then the number of workers required for the plan is
A) 35
B) 75
C) 100
D) 125
 Beginning Workforce = 35 workers
Beginning Workforce = 35 workersProduction per Employee = 1,250 units per quarter
Hiring Cost = $500 per worker
Firing Cost = $1,000 per worker
Inventory Carrying Cost = $20 per unit per quarter
If a level production strategy is used then the number of workers required for the plan is
A) 35
B) 75
C) 100
D) 125

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
The following information relates to a company's aggregate production planning activities: 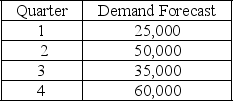 Beginning Workforce = 50 workers
Beginning Workforce = 50 workers
Production per Employee = 250 units per quarter
Hiring Cost = $1000 per worker
Firing Cost = $1,500 per worker
Inventory Carrying Cost = $15 per unit per quarter
If a chase demand strategy is used then the number of workers fired at the start of quarter 3 is
A) 0
B) 50
C) 60
D) 100
 Beginning Workforce = 50 workers
Beginning Workforce = 50 workersProduction per Employee = 250 units per quarter
Hiring Cost = $1000 per worker
Firing Cost = $1,500 per worker
Inventory Carrying Cost = $15 per unit per quarter
If a chase demand strategy is used then the number of workers fired at the start of quarter 3 is
A) 0
B) 50
C) 60
D) 100

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
The following information relates to a company's aggregate production planning activities: 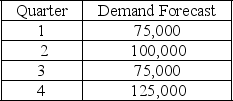 Beginning Workforce = 35 workers
Beginning Workforce = 35 workers
Production per Employee = 1,250 units per quarter
Hiring Cost = $500 per worker
Firing Cost = $1,000 per worker
Inventory Carrying Cost = $20 per unit per quarter
If a level production strategy is used then the required quarterly output is
A) 75,000
B) 87,350
C) 93,750
D) 125,000
 Beginning Workforce = 35 workers
Beginning Workforce = 35 workersProduction per Employee = 1,250 units per quarter
Hiring Cost = $500 per worker
Firing Cost = $1,000 per worker
Inventory Carrying Cost = $20 per unit per quarter
If a level production strategy is used then the required quarterly output is
A) 75,000
B) 87,350
C) 93,750
D) 125,000

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
The following information relates to a company's aggregate production planning activities: 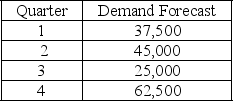 Beginning Workforce = 125 workers
Beginning Workforce = 125 workers
Production per Employee = 500 units per quarter
Hiring Cost = $750 per worker
Firing Cost = $1,500 per worker
Inventory Carrying Cost = $10 per unit per quarter
If a level production strategy is used the number of workers required each quarter is
A) 50
B) 75
C) 85
D) 125
 Beginning Workforce = 125 workers
Beginning Workforce = 125 workersProduction per Employee = 500 units per quarter
Hiring Cost = $750 per worker
Firing Cost = $1,500 per worker
Inventory Carrying Cost = $10 per unit per quarter
If a level production strategy is used the number of workers required each quarter is
A) 50
B) 75
C) 85
D) 125

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
A bagel company bakes a specialty bagel that it sells by the dozen every day. These specialty bagels can only be baked early in the morning before the store opens for business. The company estimates that the daily demand (in dozens) for its specialty bagel is distributed as follows: 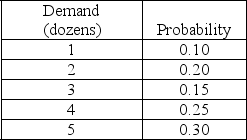 Specialty bagels are sold by the dozen only at a cost of $9.00 per dozen. The cost to make one bagel is $0.50. Leftover specialty bagels are sold by the dozen the next day for a 50% discount. The optimal number of specialty bagels that should be baked tomorrow (in dozens) is
Specialty bagels are sold by the dozen only at a cost of $9.00 per dozen. The cost to make one bagel is $0.50. Leftover specialty bagels are sold by the dozen the next day for a 50% discount. The optimal number of specialty bagels that should be baked tomorrow (in dozens) is
A) 5 dozen.
B) 4 dozen.
C) 3 dozen.
D) 2 dozen.
 Specialty bagels are sold by the dozen only at a cost of $9.00 per dozen. The cost to make one bagel is $0.50. Leftover specialty bagels are sold by the dozen the next day for a 50% discount. The optimal number of specialty bagels that should be baked tomorrow (in dozens) is
Specialty bagels are sold by the dozen only at a cost of $9.00 per dozen. The cost to make one bagel is $0.50. Leftover specialty bagels are sold by the dozen the next day for a 50% discount. The optimal number of specialty bagels that should be baked tomorrow (in dozens) isA) 5 dozen.
B) 4 dozen.
C) 3 dozen.
D) 2 dozen.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
A company is developing a linear programming model for its aggregate production plan. Each worker can produce 500 units per quarter. If Wt = workforce size in period t and Pt = number of units produced in period t, then the production constraint for period 3 is
A) W3 = 500P3
B) P3 = W3 - 500
C) P3 = 500W3
D) P3 = W3/500
A) W3 = 500P3
B) P3 = W3 - 500
C) P3 = 500W3
D) P3 = W3/500

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
Given the information below, the number of available-to-promise units in period 1 is 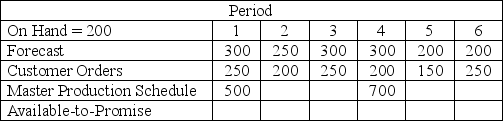
A) 700
B) 500
C) 250
D) 0

A) 700
B) 500
C) 250
D) 0

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
A bagel company bakes a specialty bagel that it sells by the dozen every day. These specialty bagels can only be baked early in the morning before the store opens for business. The company estimates that the daily demand (in dozens) for its specialty bagel is distributed as follows: 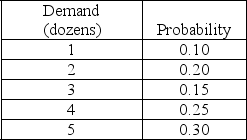 Specialty bagels are sold by the dozen only at a cost of $9.00 per dozen. The cost to make one bagel is $0.50. Leftover specialty bagels are sold by the dozen the next day for a 50% discount. The bagel company's cost of overestimating demand, Co, is
Specialty bagels are sold by the dozen only at a cost of $9.00 per dozen. The cost to make one bagel is $0.50. Leftover specialty bagels are sold by the dozen the next day for a 50% discount. The bagel company's cost of overestimating demand, Co, is
A) $1.50
B) $3.00
C) $4.50
D) $6.00
 Specialty bagels are sold by the dozen only at a cost of $9.00 per dozen. The cost to make one bagel is $0.50. Leftover specialty bagels are sold by the dozen the next day for a 50% discount. The bagel company's cost of overestimating demand, Co, is
Specialty bagels are sold by the dozen only at a cost of $9.00 per dozen. The cost to make one bagel is $0.50. Leftover specialty bagels are sold by the dozen the next day for a 50% discount. The bagel company's cost of overestimating demand, Co, isA) $1.50
B) $3.00
C) $4.50
D) $6.00

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
The search decision rule (SDR) is an algorithm that
A) solves a set of four quadratic equations.
B) finds the minimum cost for combinations of different workforce levels and production rates.
C) uses regression analysis to improve the consistency of production planning decisions.
D) requires that a linear cost function be used.
A) solves a set of four quadratic equations.
B) finds the minimum cost for combinations of different workforce levels and production rates.
C) uses regression analysis to improve the consistency of production planning decisions.
D) requires that a linear cost function be used.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
An optimizing technique originally developed for aggregate planning in the paint factory is the
A) linear decision rule.
B) search decision rule.
C) management coefficients model.
D) transportation technique.
A) linear decision rule.
B) search decision rule.
C) management coefficients model.
D) transportation technique.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
Yield management can be used to address all of the following problems except
A) overbooking.
B) portioning demand into fare classes.
C) single order quantities.
D) backorders.
A) overbooking.
B) portioning demand into fare classes.
C) single order quantities.
D) backorders.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
Given the information below, the number of available-to-promise units in period 4 is 
A) 500
B) 100
C) 200
D) 350

A) 500
B) 100
C) 200
D) 350

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
Which of the following is not a characteristic of aggregate planning for services?
A) labor is usually the most constraining resource for services
B) service capacity must be provided at the appropriate place and time
C) demand for services is easy to predict
D) capacity for services is difficult to predict
A) labor is usually the most constraining resource for services
B) service capacity must be provided at the appropriate place and time
C) demand for services is easy to predict
D) capacity for services is difficult to predict

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
The difference between planned production and customer orders is known as
A) the master production schedule.
B) available-to-promise.
C) capable-to-promise.
D) the disaggregate plan.
A) the master production schedule.
B) available-to-promise.
C) capable-to-promise.
D) the disaggregate plan.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
A company is developing a linear programming model for its aggregate production plan. If Wt = workforce size for period t, Ht = number of workers hired for period t, and Ft = number of workers fired for period t, then the company's workforce constraint for period 4 is
A) W4 = W3 - H4 + F4
B) W4 = W3 + H4 - F4
C) W4 = W3 + H3 - F3
D) W4 = W3 + H4
A) W4 = W3 - H4 + F4
B) W4 = W3 + H4 - F4
C) W4 = W3 + H3 - F3
D) W4 = W3 + H4

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
A hot dog vendor must decide on Monday how many hot dogs to have available for the coming Saturday's football game. Each hot dog costs the vendor $3.00 and is sold for $5.00. After the game any unsold hot dogs are discounted and sold to the university cafeteria for $1.75. The vendor believes that the demand for hot dogs follows the probability distribution shown below: 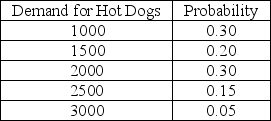 The vendor's cost of underestimating demand, Cu, is
The vendor's cost of underestimating demand, Cu, is
A) $3.00
B) $1.75
C) $2.00
D) $3.25
 The vendor's cost of underestimating demand, Cu, is
The vendor's cost of underestimating demand, Cu, isA) $3.00
B) $1.75
C) $2.00
D) $3.25

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
In capacity planning, the feasibility of the sales and operations production plan is verified by a
A) resource requirements plan.
B) rough-cut capacity plan.
C) capacity requirements plan.
D) master production schedule.
A) resource requirements plan.
B) rough-cut capacity plan.
C) capacity requirements plan.
D) master production schedule.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
Given the information below, the number of available-to-promise units in period 6 is 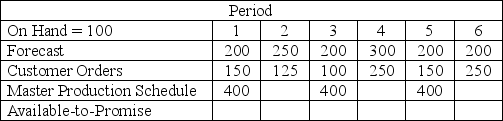
A) 400
B) 150
C) 50
D) 0

A) 400
B) 150
C) 50
D) 0

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
Given the information below, the number of available-to-promise units in period 4 is 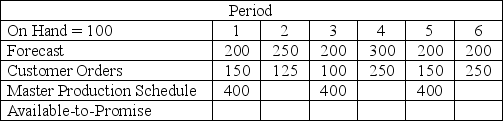
A) 400
B) 150
C) 50
D) 0

A) 400
B) 150
C) 50
D) 0

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
Given the information below, the number of available-to-promise units in period 2 is 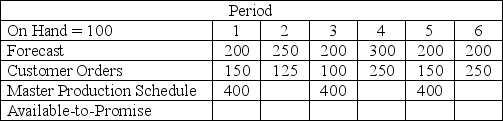
A) 400
B) 150
C) 50
D) 0

A) 400
B) 150
C) 50
D) 0

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
A hot dog vendor must decide on Monday how many hot dogs to have available for the coming Saturday's football game. Each hot dog costs the vendor $3.00 and is sold for $5.00. After the game any unsold hot dogs are discounted and sold to the university cafeteria for $1.75. The vendor believes that the demand for hot dogs follows the probability distribution shown below: 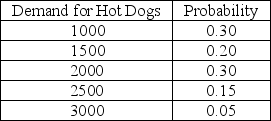 The vendor's cost of overestimating demand, Co, is
The vendor's cost of overestimating demand, Co, is
A) $5.00
B) $3.00
C) $1.75
D) $1.25
 The vendor's cost of overestimating demand, Co, is
The vendor's cost of overestimating demand, Co, isA) $5.00
B) $3.00
C) $1.75
D) $1.25

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
A hot dog vendor must decide on Monday how many hot dogs to have available for the coming Saturday's football game. Each hot dog costs the vendor $3.00 and is sold for $5.00. After the game any unsold hot dogs are discounted and sold to the university cafeteria for $1.75. The vendor believes that the demand for hot dogs follows the probability distribution shown below: 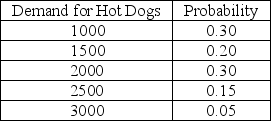 The optimal number of hot dogs the vendor should order for next Saturday's game is
The optimal number of hot dogs the vendor should order for next Saturday's game is
A) 1000
B) 1500
C) 2000
D) 3000
 The optimal number of hot dogs the vendor should order for next Saturday's game is
The optimal number of hot dogs the vendor should order for next Saturday's game isA) 1000
B) 1500
C) 2000
D) 3000

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
The process of breaking an aggregate plan into more detailed plans is referred to as
A) collaborative planning.
B) hierarchical planning.
C) disaggregation.
D) rough-cut planning.
A) collaborative planning.
B) hierarchical planning.
C) disaggregation.
D) rough-cut planning.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
A bagel company bakes a specialty bagel that it sells by the dozen every day. These specialty bagels can only be baked early in the morning before the store opens for business. The company estimates that the daily demand (in dozens) for its specialty bagel is distributed as follows: 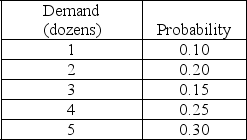 Specialty bagels are sold by the dozen only at a cost of $9.00 per dozen. The cost to bake each bagel is $0.50. Leftover specialty bagels are sold by the dozen the next day for a 50% discount. The bagel company's cost of underestimating demand, Cu, is
Specialty bagels are sold by the dozen only at a cost of $9.00 per dozen. The cost to bake each bagel is $0.50. Leftover specialty bagels are sold by the dozen the next day for a 50% discount. The bagel company's cost of underestimating demand, Cu, is
A) $9.00
B) $6.00
C) $4.50
D) $3.00
 Specialty bagels are sold by the dozen only at a cost of $9.00 per dozen. The cost to bake each bagel is $0.50. Leftover specialty bagels are sold by the dozen the next day for a 50% discount. The bagel company's cost of underestimating demand, Cu, is
Specialty bagels are sold by the dozen only at a cost of $9.00 per dozen. The cost to bake each bagel is $0.50. Leftover specialty bagels are sold by the dozen the next day for a 50% discount. The bagel company's cost of underestimating demand, Cu, isA) $9.00
B) $6.00
C) $4.50
D) $3.00

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 84 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








