Deck 19: Electrochemistry
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/122
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 19: Electrochemistry
1
When the following equation is balanced with the lowest whole number coefficients,the coefficients are: Cu(s)+ H+(aq)+ NO3-(aq)→ NO(g)+ H2O(l)+ Cu2+(aq)
A)1,2,1,1,1,1
B)3,2,1,1,1,3
C)3,2,4,2,4,3
D)1,8,2,2,4,1
E)3,8,2,2,4,3
A)1,2,1,1,1,1
B)3,2,1,1,1,3
C)3,2,4,2,4,3
D)1,8,2,2,4,1
E)3,8,2,2,4,3
3,8,2,2,4,3
2
When the following redox equation is balanced with the smallest whole number coefficients,what is the coefficient for nitrogen dioxide? I2(s)+ HNO3(aq)→ HIO3(aq)+ NO2(g)+ H2O(l)
A)1
B)2
C)4
D)5
E)10
A)1
B)2
C)4
D)5
E)10
10
3
What is the oxidizing agent in the (unbalanced)reaction? Cu(s)+ H+(aq)+ NO3-(aq)→ NO(g)+ H2O(l)+ Cu2+(aq)
A)Cu
B)H+
C)NO3-
D)NO
E)Cu2+
A)Cu
B)H+
C)NO3-
D)NO
E)Cu2+
NO3-
4
Which statement is correct?
A)The cathode is the electrode where the oxidation takes place.
B)The cathode is the electrode where the reduction takes place.
C)Both oxidation and reduction make take place at the cathode,depending on the cell.
D)The cathode is always positive.
E)The anode is always negative.
A)The cathode is the electrode where the oxidation takes place.
B)The cathode is the electrode where the reduction takes place.
C)Both oxidation and reduction make take place at the cathode,depending on the cell.
D)The cathode is always positive.
E)The anode is always negative.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
If a substance is reduced,it must undergo a
A)gain of electrons.
B)loss of oxygen.
C)gain of hydrogen.
D)loss of electrons.
E)gain of oxygen.
A)gain of electrons.
B)loss of oxygen.
C)gain of hydrogen.
D)loss of electrons.
E)gain of oxygen.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
When the following redox equation is balanced with the smallest whole number coefficients,what is the coefficient of Zn(s)? Zn(s)+ ReO4-(aq)→ Re(s)+ Zn2+(aq) (acidic solution)
A)2
B)7
C)8
D)16
E)None of these choices is correct.
A)2
B)7
C)8
D)16
E)None of these choices is correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Complete and balance the following redox equation.When properly balanced using the smallest whole-number coefficients,the coefficient of S is H2S + HNO3 → S + NO + H2O (acidic solution)
A)1.
B)2.
C)3.
D)5.
E)6.
A)1.
B)2.
C)3.
D)5.
E)6.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Consider the following balanced redox reaction. 3CuO(s)+ 2NH3(aq)→ N2(g)+ 3H2O(l)+ 3Cu(s)
Which of the following statements is true?
A)CuO(s)is the oxidizing agent and copper is reduced.
B)CuO(s)is the oxidizing agent and copper is oxidized.
C)CuO(s)is the reducing agent and copper is oxidized.
D)CuO(s)is the reducing agent and copper is reduced.
E)CuO(s)is the oxidizing agent and N2(g)is the reducing agent.
Which of the following statements is true?
A)CuO(s)is the oxidizing agent and copper is reduced.
B)CuO(s)is the oxidizing agent and copper is oxidized.
C)CuO(s)is the reducing agent and copper is oxidized.
D)CuO(s)is the reducing agent and copper is reduced.
E)CuO(s)is the oxidizing agent and N2(g)is the reducing agent.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
When the following redox equation is balanced using the smallest whole-number coefficients,what is the coefficient of NO2? Sn + HNO3 → SnO2 + NO2 + H2O (acidic solution)
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
E)5
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
E)5

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Consider the following redox equation. Mn(OH)2(s)+ MnO4-(aq)→ MnO42-(aq) (basic solution)
When the equation is balanced with the smallest whole number coefficients,what is the coefficient for OH-(aq)and on which side of the equation is OH-(aq)present?
A)4,reactant side
B)4,product side
C)6,reactant side
D)6,product side
E)8,reactant side
When the equation is balanced with the smallest whole number coefficients,what is the coefficient for OH-(aq)and on which side of the equation is OH-(aq)present?
A)4,reactant side
B)4,product side
C)6,reactant side
D)6,product side
E)8,reactant side

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
When the following redox equation is balanced with the smallest whole number coefficients,the coefficient for the hydrogen sulfate ion will be ______. Al(s)+ HSO4-(aq)+ OH-(aq)→ Al2O3(s)+ S2-(aq)+ H2O(l)
A)1
B)3
C)4
D)6
E)8
A)1
B)3
C)4
D)6
E)8

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Which is not a redox reaction?
A)Al(OH)4-(aq)+ 4H+(aq)→ Al3+(aq)+ 4H2O(l)
B)C6H12O6(s)+ 6O2(g)→ 6CO2(g)+ 6H2O(l)
C)Na6FeCl8(s)+ 2Na(l)→ 8NaCl(s)+ Fe(s)
D)2H2O2(aq)→ 2H2O(l)+ O2(g)
E)CO2(g)+ H2(g)→ CO(g)+ H2O(g)
A)Al(OH)4-(aq)+ 4H+(aq)→ Al3+(aq)+ 4H2O(l)
B)C6H12O6(s)+ 6O2(g)→ 6CO2(g)+ 6H2O(l)
C)Na6FeCl8(s)+ 2Na(l)→ 8NaCl(s)+ Fe(s)
D)2H2O2(aq)→ 2H2O(l)+ O2(g)
E)CO2(g)+ H2(g)→ CO(g)+ H2O(g)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Complete and balance the following redox equation using the set of smallest whole numbers coefficients.What is the sum of the coefficients? HI + HNO3 → I2 + NO (acidic solution)
A)5
B)7
C)14
D)17
E)None of these choices is correct.
A)5
B)7
C)14
D)17
E)None of these choices is correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
What is the name given to the apparatus where oxidation occurs in a cell where electricity flows?
A)Cathode
B)Electrode
C)Galvanic cell
D)Anode
E)Voltaic cell
A)Cathode
B)Electrode
C)Galvanic cell
D)Anode
E)Voltaic cell

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
When the following redox equation is balanced with the smallest whole number coefficients,what is the coefficient of Sn(OH)3-? Bi(OH)3(s)+ Sn(OH)3-(aq)→ Sn(OH)62-(aq)+ Bi(s) (basic solution)
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)6
E)12
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)6
E)12

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Consider the following balanced redox reaction. Mn2+(aq)+ S2O82-(aq)+ 2H2O(l)→ MnO2(s)+ 4H+(aq)+ 2SO42-(aq)
Which of the following statements is true?
A)Mn2+(aq)is the oxidizing agent and is reduced.
B)Mn2+ (aq)is the oxidizing agent and is oxidized.
C)Mn2+ (aq)is the reducing agent and is oxidized.
D)Mn2+ (aq)is the reducing agent and is reduced.
E)Manganese does not change its oxidation number in this reaction.
Which of the following statements is true?
A)Mn2+(aq)is the oxidizing agent and is reduced.
B)Mn2+ (aq)is the oxidizing agent and is oxidized.
C)Mn2+ (aq)is the reducing agent and is oxidized.
D)Mn2+ (aq)is the reducing agent and is reduced.
E)Manganese does not change its oxidation number in this reaction.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Consider the reaction CuO(s)+ H2(g)→ Cu(s)+ H2O(l)
In this reaction,which substances are the oxidizing agent and reducing agent,
Respectively?
A)CuO and H2
B)H2 and CuO
C)CuO and Cu
D)H2O and H2
E)Cu and H2O
In this reaction,which substances are the oxidizing agent and reducing agent,
Respectively?
A)CuO and H2
B)H2 and CuO
C)CuO and Cu
D)H2O and H2
E)Cu and H2O

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
When the following redox equation is balanced with the smallest whole number coefficients,what is the coefficient of Sb3+(aq)? BrO3-(aq)+ Sb3+(aq)→ Br-(aq)+ Sb5+(aq) (acidic solution)
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
E)6
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4
E)6

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Complete and balance the following redox equation.Now sum the coefficients of all species in the balanced equation.(Remember to add the coefficients that are equal to one,and to add the coefficients of any species added to the equation.)The sum of the smallest whole number coefficients is Bi(OH)3 + SnO22- → Bi + SnO32- (basic solution)
A)32
B)25
C)16
D)13
E)4
A)32
B)25
C)16
D)13
E)4

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
What is the name given to the experimental apparatus for generating electricity through the use of a spontaneous reaction?
A)Electrolytic cell
B)Galvanic cell
C)Redox cell
D)Cathode
E)Anode
A)Electrolytic cell
B)Galvanic cell
C)Redox cell
D)Cathode
E)Anode

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
The redox reaction of peroxydisulfate with iodide has been used for many years as part of the iodine clock reaction.If E°cell = 1.587 V and E° of the cathode half-cell is 0.536 V, what is E° of the anode half-cell?
S2O82-(aq)+ 2H+ + 2I-(aq)→ 2HSO4-(aq)+ I2(aq)
A)-1.051 V
B)-2.123 V
C)1.051 V
D)2.123 V
E)None of these choices is correct.
S2O82-(aq)+ 2H+ + 2I-(aq)→ 2HSO4-(aq)+ I2(aq)
A)-1.051 V
B)-2.123 V
C)1.051 V
D)2.123 V
E)None of these choices is correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
What is E°cell for a galvanic cell represented by the combination of the following half-reactions? 2Hg2+(aq)+ 2e-
 Hg22+(aq)E°= 0.92V
Hg22+(aq)E°= 0.92V
Cr3+(aq)+ 3e- Cr(s)E°= -0.74V
3e- Cr(s)E°= -0.74V
A)-0.18 V
B)0.18 V
C)1.28 V
D)1.66 V
E)2.12 V
 Hg22+(aq)E°= 0.92V
Hg22+(aq)E°= 0.92VCr3+(aq)+
 3e- Cr(s)E°= -0.74V
3e- Cr(s)E°= -0.74VA)-0.18 V
B)0.18 V
C)1.28 V
D)1.66 V
E)2.12 V

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
What is E°cell for the following reaction? 2Fe2+(aq)+ Cd2+(aq)→ 2Fe3+(aq)+ Cd(s)
Fe3+(aq)+ e- →Fe2+ (aq)E° = 0.77 V
Cd2+(aq)+ 2e- → Cd(s)E° = -0.40 V
A)-0.37 V
B)0.37 V
C)-1.17 V
D)1.17 V
E)None of these choices is correct
Fe3+(aq)+ e- →Fe2+ (aq)E° = 0.77 V
Cd2+(aq)+ 2e- → Cd(s)E° = -0.40 V
A)-0.37 V
B)0.37 V
C)-1.17 V
D)1.17 V
E)None of these choices is correct

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
What is E°cell for the following reaction? 2Au(s)+ 3Ca2+(aq)→ 2Au3+(aq)+ 3Ca(s)
Au3+(aq)+ 3e- → Au(s)E° = 1.50 V
Ca2+ (aq)+ 2e- → Ca(s)E° = -2.87 V
A)-4.37 V
B)-1.37 V
C)-11.6 V
D)1.37 V
E)4.37 V
Au3+(aq)+ 3e- → Au(s)E° = 1.50 V
Ca2+ (aq)+ 2e- → Ca(s)E° = -2.87 V
A)-4.37 V
B)-1.37 V
C)-11.6 V
D)1.37 V
E)4.37 V

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Which is incorrect?
A)At equilibrium,Ecell = 0.
B)E > 0 for a spontaneous process.
C)E = 0 for a spontaneous process.
D)ΔG < 0 for a spontaneous process.
E)ΔG = 0 at equilibrium.
A)At equilibrium,Ecell = 0.
B)E > 0 for a spontaneous process.
C)E = 0 for a spontaneous process.
D)ΔG < 0 for a spontaneous process.
E)ΔG = 0 at equilibrium.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Which is the correct cell notation for the following reaction? Au3+(aq)+ Al(s)→ Al3+(aq)+ Au(s)
A)Al3+(aq)|Al(s)||Au3+(aq)|Au(s)
B)Al(s)|Al3+(aq)||Au3+(aq)|Au(s)
C)Al3+(aq)|Au3+(aq)||Al(s)|Au(s)
D)Al3+(aq)|Au(s)||Au3+(aq)|Al(s)
E)Au(s)|Al(s)||Au3+(aq)|Al3+(aq)
A)Al3+(aq)|Al(s)||Au3+(aq)|Au(s)
B)Al(s)|Al3+(aq)||Au3+(aq)|Au(s)
C)Al3+(aq)|Au3+(aq)||Al(s)|Au(s)
D)Al3+(aq)|Au(s)||Au3+(aq)|Al(s)
E)Au(s)|Al(s)||Au3+(aq)|Al3+(aq)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
What is the purpose of a salt bridge in an electrochemical cell?
A)A salt bridge provides electrical contact between the electrodes that make up the cell.
B)A salt bridge carries electrons between the cathode and anode.
C)A salt bridge insulates the two electrodes.
D)A salt bridge allows the electrolyte solution to siphon from one side of the cell to the other so the levels remain equal.
E)A salt bridge allows electrolyte to flow from one half-cell to the other in order to maintain electroneutrality.
A)A salt bridge provides electrical contact between the electrodes that make up the cell.
B)A salt bridge carries electrons between the cathode and anode.
C)A salt bridge insulates the two electrodes.
D)A salt bridge allows the electrolyte solution to siphon from one side of the cell to the other so the levels remain equal.
E)A salt bridge allows electrolyte to flow from one half-cell to the other in order to maintain electroneutrality.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
What is the name given to the apparatus where reduction occurs in a cell where electricity flows?
A)Cathode
B)Electrode
C)Galvanic cell
D)Anode
E)Voltaic cell
A)Cathode
B)Electrode
C)Galvanic cell
D)Anode
E)Voltaic cell

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
If E° for X + e- → Y is larger than E° for A + 2e- → B,then in a spontaneous process under standard-state conditions,
A)X will oxidize A.
B)Y will oxidize A.
C)Y will reduce A.
D)B will oxidize X.
E)B will reduce X.
A)X will oxidize A.
B)Y will oxidize A.
C)Y will reduce A.
D)B will oxidize X.
E)B will reduce X.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
A voltaic cell is prepared using copper and silver.Its cell notation is shown below. Cu(s)| Cu2+(aq)|| Ag+(aq)| Ag(s)
Which reaction occurs at the cathode?
A)Cu(s)→ Cu2+(aq)+ 2e-
B)Cu2+(aq)+ 2e- → Cu(s)
C)Ag(s)→ Ag+(aq)+ e-
D)Ag+(aq)+ e- → Ag(s)
E)Cu(s)+ 2Ag+(aq)→ Cu2+(aq)+ 2Ag(s)
Which reaction occurs at the cathode?
A)Cu(s)→ Cu2+(aq)+ 2e-
B)Cu2+(aq)+ 2e- → Cu(s)
C)Ag(s)→ Ag+(aq)+ e-
D)Ag+(aq)+ e- → Ag(s)
E)Cu(s)+ 2Ag+(aq)→ Cu2+(aq)+ 2Ag(s)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
A voltaic cell prepared using aluminum and nickel has the following cell notation. Al(s)| Al3+(aq)|| Ni2+(aq)| Ni(s)
Which reaction occurs at the anode?
A)Al(s)→ Al3+(aq)+ 3e-
B)Al3+(aq)+ 3e- → Al(s)
C)Ni(s)→ Ni2+(aq)+ 2e-
D)Ni2+(aq)+ 2e- → Ni(s)
E)Ni(s)+ Ni2+(aq)→ Al(s)+ Al3+(aq)
Which reaction occurs at the anode?
A)Al(s)→ Al3+(aq)+ 3e-
B)Al3+(aq)+ 3e- → Al(s)
C)Ni(s)→ Ni2+(aq)+ 2e-
D)Ni2+(aq)+ 2e- → Ni(s)
E)Ni(s)+ Ni2+(aq)→ Al(s)+ Al3+(aq)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
What is E°cell for the following reaction? 2 Ag(s)+ Sn2+(aq)→ 2 Ag+(aq)+ Sn(s)
Ag+(aq)+ e- → Ag(s)E° = 0.80 V
Sn4+(aq)+ 2e? →Sn2+(aq)E° = 0.13 V
Sn2+(aq)+ 2e- → Sn(s)E° = -0.14 V
A)+0.94 V
B)-0.94 V
C)+0.67 V
D)-0.67 V
E)+1.34 V
Ag+(aq)+ e- → Ag(s)E° = 0.80 V
Sn4+(aq)+ 2e? →Sn2+(aq)E° = 0.13 V
Sn2+(aq)+ 2e- → Sn(s)E° = -0.14 V
A)+0.94 V
B)-0.94 V
C)+0.67 V
D)-0.67 V
E)+1.34 V

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
What is E°cell for a galvanic cell represented by the combination of the following half-reactions? ClO4-(aq)+ 8 H+(aq)+8e-
 Cl-(aq)+4H2O(l)E° = 1.389V
Cl-(aq)+4H2O(l)E° = 1.389V
VO2+(aq)+ 2H+(aq)+e-
 VO+(aq)+H2O(l)E° = 0.991V
VO+(aq)+H2O(l)E° = 0.991V
A)-0.398 V
B)-2.380 V
C)0.398 V
D)2.380 V
E)6.539 V
 Cl-(aq)+4H2O(l)E° = 1.389V
Cl-(aq)+4H2O(l)E° = 1.389VVO2+(aq)+ 2H+(aq)+e-
 VO+(aq)+H2O(l)E° = 0.991V
VO+(aq)+H2O(l)E° = 0.991VA)-0.398 V
B)-2.380 V
C)0.398 V
D)2.380 V
E)6.539 V

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
Based on the data presented below,which is the strongest oxidizing agent? [PtCl4]2-(aq)+ 2e-
![<strong>Based on the data presented below,which is the strongest oxidizing agent? [PtCl<sub>4</sub>]<sup>2-</sup>(aq)+ 2e<sup>-</sup> <sup> </sup> Pt(s)+ 4Cl<sup>-</sup>(aq)E° = 0.755V RuO<sub>4</sub>(s)+ 8H<sup>+</sup>(aq)+ 8e<sup>-</sup> Ru(s)+ 4H<sub>2</sub>O(l)E° = 1.038V FeO<sub>4</sub><sup>2-</sup>(aq)+ 8H<sup>+</sup>(aq)+ 3e<sup>-</sup> Fe<sup>3+</sup>(aq)+4H<sub>2</sub>O(l)E° = 2.07 V H<sub>4</sub>XeO<sub>6</sub>(aq)+ 2H<sup>+</sup>(aq)+ 2e<sup>-</sup> XeO<sub>3</sub>(aq)+3H<sub>2</sub>O(l)E° = 2.42 V</strong> A)[PtCl<sub>4</sub>]<sup>2-</sup>(aq) B)RuO<sub>4</sub>(s) C)HFeO<sub>4</sub><sup>-</sup>(aq) D)H<sub>4</sub>XeO<sub>6</sub>(aq) E)Cl<sup>-</sup>(aq)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6485/11eab46b_9c88_4d12_a889_b53b00109f06_TB6485_11.jpg) Pt(s)+ 4Cl-(aq)E° = 0.755V
Pt(s)+ 4Cl-(aq)E° = 0.755V
RuO4(s)+ 8H+(aq)+ 8e-![<strong>Based on the data presented below,which is the strongest oxidizing agent? [PtCl<sub>4</sub>]<sup>2-</sup>(aq)+ 2e<sup>-</sup> <sup> </sup> Pt(s)+ 4Cl<sup>-</sup>(aq)E° = 0.755V RuO<sub>4</sub>(s)+ 8H<sup>+</sup>(aq)+ 8e<sup>-</sup> Ru(s)+ 4H<sub>2</sub>O(l)E° = 1.038V FeO<sub>4</sub><sup>2-</sup>(aq)+ 8H<sup>+</sup>(aq)+ 3e<sup>-</sup> Fe<sup>3+</sup>(aq)+4H<sub>2</sub>O(l)E° = 2.07 V H<sub>4</sub>XeO<sub>6</sub>(aq)+ 2H<sup>+</sup>(aq)+ 2e<sup>-</sup> XeO<sub>3</sub>(aq)+3H<sub>2</sub>O(l)E° = 2.42 V</strong> A)[PtCl<sub>4</sub>]<sup>2-</sup>(aq) B)RuO<sub>4</sub>(s) C)HFeO<sub>4</sub><sup>-</sup>(aq) D)H<sub>4</sub>XeO<sub>6</sub>(aq) E)Cl<sup>-</sup>(aq)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6485/11eab46b_9c88_7423_a889_4fc9dc310489_TB6485_11.jpg) Ru(s)+ 4H2O(l)E° = 1.038V
Ru(s)+ 4H2O(l)E° = 1.038V
FeO42-(aq)+ 8H+(aq)+ 3e-![<strong>Based on the data presented below,which is the strongest oxidizing agent? [PtCl<sub>4</sub>]<sup>2-</sup>(aq)+ 2e<sup>-</sup> <sup> </sup> Pt(s)+ 4Cl<sup>-</sup>(aq)E° = 0.755V RuO<sub>4</sub>(s)+ 8H<sup>+</sup>(aq)+ 8e<sup>-</sup> Ru(s)+ 4H<sub>2</sub>O(l)E° = 1.038V FeO<sub>4</sub><sup>2-</sup>(aq)+ 8H<sup>+</sup>(aq)+ 3e<sup>-</sup> Fe<sup>3+</sup>(aq)+4H<sub>2</sub>O(l)E° = 2.07 V H<sub>4</sub>XeO<sub>6</sub>(aq)+ 2H<sup>+</sup>(aq)+ 2e<sup>-</sup> XeO<sub>3</sub>(aq)+3H<sub>2</sub>O(l)E° = 2.42 V</strong> A)[PtCl<sub>4</sub>]<sup>2-</sup>(aq) B)RuO<sub>4</sub>(s) C)HFeO<sub>4</sub><sup>-</sup>(aq) D)H<sub>4</sub>XeO<sub>6</sub>(aq) E)Cl<sup>-</sup>(aq)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6485/11eab46b_9c88_7424_a889_a759138c4604_TB6485_11.jpg) Fe3+(aq)+4H2O(l)E° = 2.07 V
Fe3+(aq)+4H2O(l)E° = 2.07 V
H4XeO6(aq)+ 2H+(aq)+ 2e-![<strong>Based on the data presented below,which is the strongest oxidizing agent? [PtCl<sub>4</sub>]<sup>2-</sup>(aq)+ 2e<sup>-</sup> <sup> </sup> Pt(s)+ 4Cl<sup>-</sup>(aq)E° = 0.755V RuO<sub>4</sub>(s)+ 8H<sup>+</sup>(aq)+ 8e<sup>-</sup> Ru(s)+ 4H<sub>2</sub>O(l)E° = 1.038V FeO<sub>4</sub><sup>2-</sup>(aq)+ 8H<sup>+</sup>(aq)+ 3e<sup>-</sup> Fe<sup>3+</sup>(aq)+4H<sub>2</sub>O(l)E° = 2.07 V H<sub>4</sub>XeO<sub>6</sub>(aq)+ 2H<sup>+</sup>(aq)+ 2e<sup>-</sup> XeO<sub>3</sub>(aq)+3H<sub>2</sub>O(l)E° = 2.42 V</strong> A)[PtCl<sub>4</sub>]<sup>2-</sup>(aq) B)RuO<sub>4</sub>(s) C)HFeO<sub>4</sub><sup>-</sup>(aq) D)H<sub>4</sub>XeO<sub>6</sub>(aq) E)Cl<sup>-</sup>(aq)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6485/11eab46b_9c88_7425_a889_55be93414ba6_TB6485_11.jpg) XeO3(aq)+3H2O(l)E° = 2.42 V
XeO3(aq)+3H2O(l)E° = 2.42 V
A)[PtCl4]2-(aq)
B)RuO4(s)
C)HFeO4-(aq)
D)H4XeO6(aq)
E)Cl-(aq)
![<strong>Based on the data presented below,which is the strongest oxidizing agent? [PtCl<sub>4</sub>]<sup>2-</sup>(aq)+ 2e<sup>-</sup> <sup> </sup> Pt(s)+ 4Cl<sup>-</sup>(aq)E° = 0.755V RuO<sub>4</sub>(s)+ 8H<sup>+</sup>(aq)+ 8e<sup>-</sup> Ru(s)+ 4H<sub>2</sub>O(l)E° = 1.038V FeO<sub>4</sub><sup>2-</sup>(aq)+ 8H<sup>+</sup>(aq)+ 3e<sup>-</sup> Fe<sup>3+</sup>(aq)+4H<sub>2</sub>O(l)E° = 2.07 V H<sub>4</sub>XeO<sub>6</sub>(aq)+ 2H<sup>+</sup>(aq)+ 2e<sup>-</sup> XeO<sub>3</sub>(aq)+3H<sub>2</sub>O(l)E° = 2.42 V</strong> A)[PtCl<sub>4</sub>]<sup>2-</sup>(aq) B)RuO<sub>4</sub>(s) C)HFeO<sub>4</sub><sup>-</sup>(aq) D)H<sub>4</sub>XeO<sub>6</sub>(aq) E)Cl<sup>-</sup>(aq)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6485/11eab46b_9c88_4d12_a889_b53b00109f06_TB6485_11.jpg) Pt(s)+ 4Cl-(aq)E° = 0.755V
Pt(s)+ 4Cl-(aq)E° = 0.755VRuO4(s)+ 8H+(aq)+ 8e-
![<strong>Based on the data presented below,which is the strongest oxidizing agent? [PtCl<sub>4</sub>]<sup>2-</sup>(aq)+ 2e<sup>-</sup> <sup> </sup> Pt(s)+ 4Cl<sup>-</sup>(aq)E° = 0.755V RuO<sub>4</sub>(s)+ 8H<sup>+</sup>(aq)+ 8e<sup>-</sup> Ru(s)+ 4H<sub>2</sub>O(l)E° = 1.038V FeO<sub>4</sub><sup>2-</sup>(aq)+ 8H<sup>+</sup>(aq)+ 3e<sup>-</sup> Fe<sup>3+</sup>(aq)+4H<sub>2</sub>O(l)E° = 2.07 V H<sub>4</sub>XeO<sub>6</sub>(aq)+ 2H<sup>+</sup>(aq)+ 2e<sup>-</sup> XeO<sub>3</sub>(aq)+3H<sub>2</sub>O(l)E° = 2.42 V</strong> A)[PtCl<sub>4</sub>]<sup>2-</sup>(aq) B)RuO<sub>4</sub>(s) C)HFeO<sub>4</sub><sup>-</sup>(aq) D)H<sub>4</sub>XeO<sub>6</sub>(aq) E)Cl<sup>-</sup>(aq)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6485/11eab46b_9c88_7423_a889_4fc9dc310489_TB6485_11.jpg) Ru(s)+ 4H2O(l)E° = 1.038V
Ru(s)+ 4H2O(l)E° = 1.038VFeO42-(aq)+ 8H+(aq)+ 3e-
![<strong>Based on the data presented below,which is the strongest oxidizing agent? [PtCl<sub>4</sub>]<sup>2-</sup>(aq)+ 2e<sup>-</sup> <sup> </sup> Pt(s)+ 4Cl<sup>-</sup>(aq)E° = 0.755V RuO<sub>4</sub>(s)+ 8H<sup>+</sup>(aq)+ 8e<sup>-</sup> Ru(s)+ 4H<sub>2</sub>O(l)E° = 1.038V FeO<sub>4</sub><sup>2-</sup>(aq)+ 8H<sup>+</sup>(aq)+ 3e<sup>-</sup> Fe<sup>3+</sup>(aq)+4H<sub>2</sub>O(l)E° = 2.07 V H<sub>4</sub>XeO<sub>6</sub>(aq)+ 2H<sup>+</sup>(aq)+ 2e<sup>-</sup> XeO<sub>3</sub>(aq)+3H<sub>2</sub>O(l)E° = 2.42 V</strong> A)[PtCl<sub>4</sub>]<sup>2-</sup>(aq) B)RuO<sub>4</sub>(s) C)HFeO<sub>4</sub><sup>-</sup>(aq) D)H<sub>4</sub>XeO<sub>6</sub>(aq) E)Cl<sup>-</sup>(aq)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6485/11eab46b_9c88_7424_a889_a759138c4604_TB6485_11.jpg) Fe3+(aq)+4H2O(l)E° = 2.07 V
Fe3+(aq)+4H2O(l)E° = 2.07 VH4XeO6(aq)+ 2H+(aq)+ 2e-
![<strong>Based on the data presented below,which is the strongest oxidizing agent? [PtCl<sub>4</sub>]<sup>2-</sup>(aq)+ 2e<sup>-</sup> <sup> </sup> Pt(s)+ 4Cl<sup>-</sup>(aq)E° = 0.755V RuO<sub>4</sub>(s)+ 8H<sup>+</sup>(aq)+ 8e<sup>-</sup> Ru(s)+ 4H<sub>2</sub>O(l)E° = 1.038V FeO<sub>4</sub><sup>2-</sup>(aq)+ 8H<sup>+</sup>(aq)+ 3e<sup>-</sup> Fe<sup>3+</sup>(aq)+4H<sub>2</sub>O(l)E° = 2.07 V H<sub>4</sub>XeO<sub>6</sub>(aq)+ 2H<sup>+</sup>(aq)+ 2e<sup>-</sup> XeO<sub>3</sub>(aq)+3H<sub>2</sub>O(l)E° = 2.42 V</strong> A)[PtCl<sub>4</sub>]<sup>2-</sup>(aq) B)RuO<sub>4</sub>(s) C)HFeO<sub>4</sub><sup>-</sup>(aq) D)H<sub>4</sub>XeO<sub>6</sub>(aq) E)Cl<sup>-</sup>(aq)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6485/11eab46b_9c88_7425_a889_55be93414ba6_TB6485_11.jpg) XeO3(aq)+3H2O(l)E° = 2.42 V
XeO3(aq)+3H2O(l)E° = 2.42 VA)[PtCl4]2-(aq)
B)RuO4(s)
C)HFeO4-(aq)
D)H4XeO6(aq)
E)Cl-(aq)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
A cell can be prepared from copper and tin.What is the E°cell for the galvanic cell that forms from the following half-reactions? Cu2+(aq)+ 2e-  Cu(s)E° = 0.34V
Cu(s)E° = 0.34V
Sn4+(aq)+ 2e- Sn2+(aq)E° = 0.13V
Sn2+(aq)E° = 0.13V
A)0.47 V
B)0.21 V
C)-0.21 V
D)-0.47 V
E)0.42 V
 Cu(s)E° = 0.34V
Cu(s)E° = 0.34VSn4+(aq)+ 2e-
 Sn2+(aq)E° = 0.13V
Sn2+(aq)E° = 0.13VA)0.47 V
B)0.21 V
C)-0.21 V
D)-0.47 V
E)0.42 V

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
What is E°cell for the following reaction? Al(s)+ 3Ag+(aq)→ Al3+(aq)+ 3Ag(s)
Al3+(aq)+ 3e- →Al(s)E° = -1.66 V
Ag+(aq)+ e- →Ag(s)E° = 0.80 V
A)-2.46 V
B)0.86 V
C)-0.86 V
D)2.46 V
E)4.06 V
Al3+(aq)+ 3e- →Al(s)E° = -1.66 V
Ag+(aq)+ e- →Ag(s)E° = 0.80 V
A)-2.46 V
B)0.86 V
C)-0.86 V
D)2.46 V
E)4.06 V

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
What is meant by SHE?
A)Shared half electrodes
B)Shifting half of the electricity
C)Standard hydrogen electrode
D)Small helium electrode
E)Standard Hg electrode
A)Shared half electrodes
B)Shifting half of the electricity
C)Standard hydrogen electrode
D)Small helium electrode
E)Standard Hg electrode

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
The voltaic cell composed of Co(s),Co2+(aq),Cu(s),and Cu2+(aq)has E°cell = 0.62 V.If E° of the cathode half-cell is 0.34 V,what is E° of the anode half-cell? Cu2+(aq)+ Co(s)→ Cu(s)+ Co2+(aq)
A)-0.28 V
B)-0.96 V
C)0.28 V
D)0.96 V
E)0.21 V
A)-0.28 V
B)-0.96 V
C)0.28 V
D)0.96 V
E)0.21 V

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
A certain electrochemical cell has for its cell reaction: Zn + HgO → ZnO + Hg
Which is the half-reaction occurring at the anode?
A)HgO + 2e- → Hg + O2-
B)Zn2++ 2e- → Zn
C)Zn → Zn2+ + 2e-
D)ZnO + 2e- → Zn
Which is the half-reaction occurring at the anode?
A)HgO + 2e- → Hg + O2-
B)Zn2++ 2e- → Zn
C)Zn → Zn2+ + 2e-
D)ZnO + 2e- → Zn

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
What is the name given to the apparatus that connects the two solutions by a conducting medium through which the cations and anions can move from one half-cell to the other?
A)Cathode
B)Electrode
C)Galvanic cell
D)Salt bridge
E)Fuel cell
A)Cathode
B)Electrode
C)Galvanic cell
D)Salt bridge
E)Fuel cell

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
What is the equilibrium constant at 25°C for the following reaction? (R = 8.314 J/K • mol,F = 96,500 C • mol-1)
2Cr(s)+ 3Pb2+(aq) 3Pb(s)+2Cr3+(aq)E°cell = 0.61V
3Pb(s)+2Cr3+(aq)E°cell = 0.61V
A)4.1 × 1020
B)8.2 × 1030
C)3.3 × 1051
D)6.7 × 1061
E)> 9.9 × 1099
2Cr(s)+ 3Pb2+(aq)
 3Pb(s)+2Cr3+(aq)E°cell = 0.61V
3Pb(s)+2Cr3+(aq)E°cell = 0.61VA)4.1 × 1020
B)8.2 × 1030
C)3.3 × 1051
D)6.7 × 1061
E)> 9.9 × 1099

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
Consider the reaction in the lead-acid cell Pb(s)+ PbO2(s)+ 2H2SO4(aq)→ 2PbSO4(aq)+ 2H2O(l)
For which E°cell = 2.04 V at 298 K.ΔG° for this reaction is
A)-3.94 × 105 kJ/mol.
B)-3.94 × 102 kJ/mol.
C)-1.97 × 105 kJ/mol.
D)-7.87 × 102 kJ/mol.
E)-7.87 × 105 kJ/mol.
For which E°cell = 2.04 V at 298 K.ΔG° for this reaction is
A)-3.94 × 105 kJ/mol.
B)-3.94 × 102 kJ/mol.
C)-1.97 × 105 kJ/mol.
D)-7.87 × 102 kJ/mol.
E)-7.87 × 105 kJ/mol.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
Consider the reaction of iodine with manganese dioxide. 3I2(s)+ 2MnO2(s)+ 8OH-(aq)  6I-(aq)+ 2MnO4-(aq)+ 4H2O(l)
6I-(aq)+ 2MnO4-(aq)+ 4H2O(l)
The equilibrium constant for the overall reaction is 8.3 × 10-7.What is E°cell for the reaction at 25°C? (R = 8.314 J/K • mol,F = 96,500 C • mol-1)
A)-0.36 V
B)-0.18 V
C)-0.12 V
D)-0.060 V
E)+0.12 V
 6I-(aq)+ 2MnO4-(aq)+ 4H2O(l)
6I-(aq)+ 2MnO4-(aq)+ 4H2O(l)The equilibrium constant for the overall reaction is 8.3 × 10-7.What is E°cell for the reaction at 25°C? (R = 8.314 J/K • mol,F = 96,500 C • mol-1)
A)-0.36 V
B)-0.18 V
C)-0.12 V
D)-0.060 V
E)+0.12 V

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
What is E°cell for the reaction of nickel(II)ions with cadmium metal at 25°C? (R = 8.314 J/K • mol,F = 96,500 C • mol-1)
Ni2+(aq)+ Cd(s) Cd2+(aq)+ Ni(s)K = 1.17 × 105
Cd2+(aq)+ Ni(s)K = 1.17 × 105
A)0.0750 V
B)0.100 V
C)0.120 V
D)0.150 V
E)0.300 V
Ni2+(aq)+ Cd(s)
 Cd2+(aq)+ Ni(s)K = 1.17 × 105
Cd2+(aq)+ Ni(s)K = 1.17 × 105A)0.0750 V
B)0.100 V
C)0.120 V
D)0.150 V
E)0.300 V

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
What is ΔG° for the following reaction? (F = 96,500 C • mol-1) I2(s)+ 2Br-(aq)→ 2I-(aq)+ Br2(l)
Given:
I2(s) (aq)+ 2e- → 2I-(aq)E°= 0.53 V
Br2(l)+ 2e- → 2Br-(aq)E° = 1.07 V
A)+104 kJ/mol
B)-104 kJ/mol
C)+309 kJ/mol
D)+52 kJ/mol
E)-52 kJ/mol
Given:
I2(s) (aq)+ 2e- → 2I-(aq)E°= 0.53 V
Br2(l)+ 2e- → 2Br-(aq)E° = 1.07 V
A)+104 kJ/mol
B)-104 kJ/mol
C)+309 kJ/mol
D)+52 kJ/mol
E)-52 kJ/mol

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
What is ΔG° at 298 K for the following reaction? (F = 96,500 C • mol-1) 2Cr3+(aq)+ 6Hg(l)→ 2Cr(s)+ 3Hg22+(aq)E°cell = 1.59V
A)-921 kJ/mol
B)-767 kJ/mol
C)-460 kJ/mol
D)-307 kJ/mol
E)-1840 kJ/mol
A)-921 kJ/mol
B)-767 kJ/mol
C)-460 kJ/mol
D)-307 kJ/mol
E)-1840 kJ/mol

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
A voltaic cell consists of a Mn/Mn2+ electrode (E° = -1.18 V)and a Fe/Fe2+ electrode (E° = -0.44 V).Calculate [Fe2+] if [Mn2+] = 0.050 M and Ecell = 0.78 V at 25°C.
A)0.040 M
B)0.24 M
C)1.1 M
D)1.8 M
E)None of these choices is correct.
A)0.040 M
B)0.24 M
C)1.1 M
D)1.8 M
E)None of these choices is correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
What is the equilibrium constant at 25°C for the following reaction? (R = 8.314 J/K • mol,F = 96,500 C • mol-1)
Sn2+(aq)+ Fe(s) Sn(s)+ Fe2+(aq)E°cell = 0.30V
Sn(s)+ Fe2+(aq)E°cell = 0.30V
A)1.2 × 105
B)1.4 × 1010
C)8.6 × 10-6
D)7.1 × 10-11
E)2.3 × 1023
Sn2+(aq)+ Fe(s)
 Sn(s)+ Fe2+(aq)E°cell = 0.30V
Sn(s)+ Fe2+(aq)E°cell = 0.30VA)1.2 × 105
B)1.4 × 1010
C)8.6 × 10-6
D)7.1 × 10-11
E)2.3 × 1023

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
Given the following standard reduction potentials, Ag+(aq)+ e- → Ag(s)E° = +0.80 V
AgCN(s)+ e- → Ag(s)+ CN-(aq)E° = -0.01 V
Calculate the solubility product of AgCN at 25°C.
A)4.3 × 10-14
B)2.3 × 1013
C)2.1 × 10-14
D)5.1 × 1013
E)None of these choices is correct.
AgCN(s)+ e- → Ag(s)+ CN-(aq)E° = -0.01 V
Calculate the solubility product of AgCN at 25°C.
A)4.3 × 10-14
B)2.3 × 1013
C)2.1 × 10-14
D)5.1 × 1013
E)None of these choices is correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
What is ΔG° at 200°C for the following reaction? (F = 96,500 C • mol-1) 2Na(l)+ FeCl2(s)  2NaCl(s)+ Fe(s)E°cell = 2.35 V
2NaCl(s)+ Fe(s)E°cell = 2.35 V
A)454 kJ/mol
B)-454 kJ/mol
C)907 kJ/mol
D)-907 kJ/mol
E)227 kJ/mol
 2NaCl(s)+ Fe(s)E°cell = 2.35 V
2NaCl(s)+ Fe(s)E°cell = 2.35 VA)454 kJ/mol
B)-454 kJ/mol
C)907 kJ/mol
D)-907 kJ/mol
E)227 kJ/mol

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
Which metals may be oxidized by H+ under standard-state conditions? Ag+(aq)+ e- →Ag(s)E° = 0.80 V
Cu2+ (aq)+ 2e- →Cu(s)E° = 0.34 V
Sn2+(aq)+ 2e- →Sn(s)E° = -0.14 V
Zn2+(aq)+ 2e- →Zn(s)E° = -0.76 V
A)Ag,Cu,Sn,and Zn
B)Ag and Cu
C)Sn and Cu
D)Zn and Cu
E)Zn and Sn
Cu2+ (aq)+ 2e- →Cu(s)E° = 0.34 V
Sn2+(aq)+ 2e- →Sn(s)E° = -0.14 V
Zn2+(aq)+ 2e- →Zn(s)E° = -0.76 V
A)Ag,Cu,Sn,and Zn
B)Ag and Cu
C)Sn and Cu
D)Zn and Cu
E)Zn and Sn

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
What is the cell potential at 25°C for the following reaction if [Zn2+] = 1.0 × 10-4 M and [Sn2+] = 0.20 M ? (R = 8.314 J/K • mol,F = 96,500 C • mol-1) Zn2+(aq)+ Sn(s)→ Zn(s)+ Sn2+(aq)E°cell = -0.62 V
A)-0.62 V
B)+0.52 V
C)-0.52 V
D)-0.72 V
E)+0.72 V
A)-0.62 V
B)+0.52 V
C)-0.52 V
D)-0.72 V
E)+0.72 V

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
Based on the data presented below,which is the strongest reducing agent? PbI2(s)+ 2e-  Pb(s)+2I-(aq)E° = -0.365 V
Pb(s)+2I-(aq)E° = -0.365 V
Ca2+(aq)+ 2e- Ca(s)E° = -2.868 V
Ca(s)E° = -2.868 V
Pt2+(aq)+ 2e- Pt(s)E° = 1.18 V
Pt(s)E° = 1.18 V
Br2(l)+ 2e- 2Br-(aq)E° = 1.066 V
2Br-(aq)E° = 1.066 V
A)Pb(s)
B)Ca(s)
C)Pt(s)
D)Br-(aq)
E)Pt2+(aq)
 Pb(s)+2I-(aq)E° = -0.365 V
Pb(s)+2I-(aq)E° = -0.365 VCa2+(aq)+ 2e-
 Ca(s)E° = -2.868 V
Ca(s)E° = -2.868 VPt2+(aq)+ 2e-
 Pt(s)E° = 1.18 V
Pt(s)E° = 1.18 VBr2(l)+ 2e-
 2Br-(aq)E° = 1.066 V
2Br-(aq)E° = 1.066 VA)Pb(s)
B)Ca(s)
C)Pt(s)
D)Br-(aq)
E)Pt2+(aq)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
Which equation is correct?
A)E°cell = E°anode - E°cathode
B)E°cell = E°cathode + E°anode
C)E°cell = E°cathode - E°anode
D)E°cell = E°cathode / E°anode
A)E°cell = E°anode - E°cathode
B)E°cell = E°cathode + E°anode
C)E°cell = E°cathode - E°anode
D)E°cell = E°cathode / E°anode

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
Based on the data presented below,which is the strongest reducing agent? E°(V)
Al3+ + 3e- → Al(s)-1.66
AgBr(s)+ e- → Ag(s)+Br- +0.07
Sn4+ + 2e- → Sn2+ +0.14
Fe3+ + e- → Fe2+ +0.77
A)Fe3+
B)Fe2+
C)Br-
D)Al3+
E)Al(s)
Al3+ + 3e- → Al(s)-1.66
AgBr(s)+ e- → Ag(s)+Br- +0.07
Sn4+ + 2e- → Sn2+ +0.14
Fe3+ + e- → Fe2+ +0.77
A)Fe3+
B)Fe2+
C)Br-
D)Al3+
E)Al(s)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
Which equation is correct?
A)E = -(RT/nF)lnK
B)E° = (RT/nF)lnK
C)E° = (RT/nF)lnQ
D)E = -(RT/nF)lnQ
E)E = E° + lnQ
A)E = -(RT/nF)lnK
B)E° = (RT/nF)lnK
C)E° = (RT/nF)lnQ
D)E = -(RT/nF)lnQ
E)E = E° + lnQ

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
What is E°cell for the following reaction,and is it spontaneous or nonspontaneous under standard-state conditions? 2Fe3+(aq)+ 2H2O(l)→ H2O2(aq)+ 2H+(aq)+ 2Fe2+(aq)
Given:
H2O2(aq)+ 2H+(aq)+ 2e-
 2H2O(l)E° = 1.77V
2H2O(l)E° = 1.77V
Fe3+(aq)+ e- Fe2+(aq)E° = 0.77V
Fe2+(aq)E° = 0.77V
A)E°cell = -1.00 V,nonspontaneous
B)E°cell = -1.00 V,spontaneous
C)E°cell = 1.00 V,nonspontaneous
D)E°cell = 1.00 V,spontaneous
E)E°cell = -0.23 V,nonspontaneous
Given:
H2O2(aq)+ 2H+(aq)+ 2e-
 2H2O(l)E° = 1.77V
2H2O(l)E° = 1.77VFe3+(aq)+ e-
 Fe2+(aq)E° = 0.77V
Fe2+(aq)E° = 0.77VA)E°cell = -1.00 V,nonspontaneous
B)E°cell = -1.00 V,spontaneous
C)E°cell = 1.00 V,nonspontaneous
D)E°cell = 1.00 V,spontaneous
E)E°cell = -0.23 V,nonspontaneous

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
Based on the data presented below,which is the strongest oxidizing agent? Half-Reaction E°(V)
Al3++ 3e- → Al(s)-1.66
AgBr(s)+ e- → Ag(s)+ Br- +0.07
Sn4++ 2e- → Sn2+ +0.14
Fe3++ e- → Fe2+ +0.77
A)Fe3+
B)Fe2+
C)Br-
D)Al3+
E)Al(s)
Al3++ 3e- → Al(s)-1.66
AgBr(s)+ e- → Ag(s)+ Br- +0.07
Sn4++ 2e- → Sn2+ +0.14
Fe3++ e- → Fe2+ +0.77
A)Fe3+
B)Fe2+
C)Br-
D)Al3+
E)Al(s)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
If ΔG° of the following reaction is -110 kJ/mol,what is E°cell? (F = 96,500 C • mol-1) A3+(aq)+ 3B(s)→ A(s)+ 3B+(aq)
A)+0.38 V
B)-0.09 V
C)-0.38 V
D)+0.00038 V
E)+0.09 V
A)+0.38 V
B)-0.09 V
C)-0.38 V
D)+0.00038 V
E)+0.09 V

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
What is ΔG° for the reaction of iron(II)ions with one mole of permanganate ions? (F = 96,500 C • mol-1)
MnO4-(aq)+ 8H+(aq)+ 5e- Mn2+(aq)+4H2O(l)E° = 1.51V
Mn2+(aq)+4H2O(l)E° = 1.51V
Fe3+(aq)+ e- Fe2+(aq)E° = 0.77V
A)-71.4 kJ
B)-286 kJ
C)-357 kJ
D)-428 kJ
E)None of these choices is correct.
MnO4-(aq)+ 8H+(aq)+ 5e-
 Mn2+(aq)+4H2O(l)E° = 1.51V
Mn2+(aq)+4H2O(l)E° = 1.51VFe3+(aq)+ e- Fe2+(aq)E° = 0.77V
A)-71.4 kJ
B)-286 kJ
C)-357 kJ
D)-428 kJ
E)None of these choices is correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
Which is the half-reaction at the cathode in a lead storage battery?
A)Pb(s)+ PbO2(s)+ 4H+(aq)+ 2SO42-(aq)→ 2PbSO4(s)+ 2H2O(l)
B)PbO2(s)+ 4H+(aq)+ 2SO42-(aq)+ 2e- → PbSO4(s)+ 2H2O(l)
C)Pb(s)+ SO42-(aq)→ PbSO4(s)+ 2e-
D)Pb(s)→ Pb(s)+ 2e-
E)H2(g)→ 2H+(aq)+ 2e-
A)Pb(s)+ PbO2(s)+ 4H+(aq)+ 2SO42-(aq)→ 2PbSO4(s)+ 2H2O(l)
B)PbO2(s)+ 4H+(aq)+ 2SO42-(aq)+ 2e- → PbSO4(s)+ 2H2O(l)
C)Pb(s)+ SO42-(aq)→ PbSO4(s)+ 2e-
D)Pb(s)→ Pb(s)+ 2e-
E)H2(g)→ 2H+(aq)+ 2e-

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
What mass of Cu may be deposited from a Cu2+ solution during electrolysis by a current of 3.00 A for 10.0 hours?
A)63.6 g Cu
B)35.6 g Cu
C)6.4 g Cu
D)3.6 g Cu
E)71.2 g Cu
A)63.6 g Cu
B)35.6 g Cu
C)6.4 g Cu
D)3.6 g Cu
E)71.2 g Cu

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
Which is the half-reaction at the anode in a lead storage battery?
A)Pb(s)+ PbO2(s)+ 4H+(aq)+ 2SO42-(aq)→ 2PbSO4(s)+ 2H2O(l)
B)PbO2(s)+ 4H+(aq)+ 2SO42-(aq)+ 2e- → PbSO4(s)+ 2H2O(l)
C)Pb(s)+ SO42-(aq)→ PbSO4(s)+ 2e-
D)Pb(s)→ Pb(s)+ 2e-
E)H2(g)→ 2H+(aq)+ 2e-
A)Pb(s)+ PbO2(s)+ 4H+(aq)+ 2SO42-(aq)→ 2PbSO4(s)+ 2H2O(l)
B)PbO2(s)+ 4H+(aq)+ 2SO42-(aq)+ 2e- → PbSO4(s)+ 2H2O(l)
C)Pb(s)+ SO42-(aq)→ PbSO4(s)+ 2e-
D)Pb(s)→ Pb(s)+ 2e-
E)H2(g)→ 2H+(aq)+ 2e-

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
How much charge must pass through an electrolytic cell to reduce 0.44 mol Ca2+ ion to calcium metal?
A)1.9 ×105 C
B)8.5 ×104 C
C)2.1 ×104 C
D)4.3 ×104 C
E)0.88 C
A)1.9 ×105 C
B)8.5 ×104 C
C)2.1 ×104 C
D)4.3 ×104 C
E)0.88 C

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
How many minutes would be required to electroplate 25.0 g of chromium by passing a constant current of 4.80 A through a solution containing CrCl3?
A)483 min
B)161 min
C)322 min
D)2.01 × 104 min
E)1.11 × 104 min
A)483 min
B)161 min
C)322 min
D)2.01 × 104 min
E)1.11 × 104 min

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
What quantity of charge is required to cause reduction of 0.20 mole of Cr3+ to Cr?
A)0.60 C
B)3.0 C
C)1.9 × 104 C
D)5.8 × 104 C
E)9.7 × 104 C
A)0.60 C
B)3.0 C
C)1.9 × 104 C
D)5.8 × 104 C
E)9.7 × 104 C

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
Which,if any,of the following metals would be capable of acting as a sacrificial anode when used with iron pipe? 
A)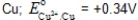
B)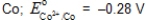
C)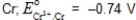
D)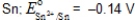
E)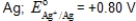

A)
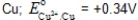
B)
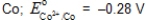
C)
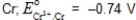
D)
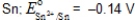
E)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
What mass of nickel may be electroplated by passing a constant current of 7.2 A through a solution of NiSO4 for 90.0 min?
A)0.20 g Ni
B)0.40 g Ni
C)12 g Ni
D)24 g Ni
E)47 g Ni
A)0.20 g Ni
B)0.40 g Ni
C)12 g Ni
D)24 g Ni
E)47 g Ni

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
Which metal is not capable of acting as a sacrificial anode when used with iron pipe? 
A)
B)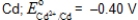
C)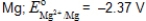
D)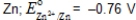
E)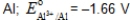
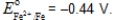
A)
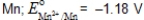
B)
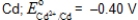
C)
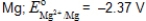
D)
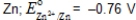
E)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
A metal object is to be gold-plated by an electrolytic procedure using aqueous AuCl3 electrolyte.How much gold may be deposited in 3.0 min by a constant current of 10.A?
A)6.2 × 10-3 mol
B)9.3 × 10-3 mol
C)1.8 × 10-2 mol
D)3.5 × 10-5 mol
E)1.6 × 102 mol
A)6.2 × 10-3 mol
B)9.3 × 10-3 mol
C)1.8 × 10-2 mol
D)3.5 × 10-5 mol
E)1.6 × 102 mol

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
How many faradays are transferred in an electrolytic cell when a current of 2.0 A flows for 12 hours? (1 faraday = 96,500 C)
A)24 faradays
B)8.6 × 104 faradays
C)0.90 faradays
D)6.2 × 10-3 faradays
E)1.1 faradays
A)24 faradays
B)8.6 × 104 faradays
C)0.90 faradays
D)6.2 × 10-3 faradays
E)1.1 faradays

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
Predict the products obtained from the electrolysis of a 1 M AlBr3 solution. Note that 2H2O(l)+ 2e- → H2(g)+2OH-(aq),E° = -0.83 V
O2(g)+ 4H+(aq)+ 4e- → 2H2O(l),E° = +1.23 V
Br2(l)+ 2e- → 2Br-(aq)E° = +1.08 V,and
Al3+(aq)+ 3e- → Al(s)E° = -1.66 V
A)Al and Br2
B)Al and O2
C)H2 and O2
D)H2 and Br2
E)Al and H2
O2(g)+ 4H+(aq)+ 4e- → 2H2O(l),E° = +1.23 V
Br2(l)+ 2e- → 2Br-(aq)E° = +1.08 V,and
Al3+(aq)+ 3e- → Al(s)E° = -1.66 V
A)Al and Br2
B)Al and O2
C)H2 and O2
D)H2 and Br2
E)Al and H2

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
A voltaic cell consists of a Hg/Hg22+ electrode (E°= 0.85 V)and a Sn/Sn2+ electrode (E°= -0.14 V).Calculate [Sn2+] if [Hg22+] = 0.24 M and Ecell = 1.04 V at 25°C.
A)0.00010 M
B)0.00070 M
C)0.0049 M
D)0.030 M
E)0.050 M
A)0.00010 M
B)0.00070 M
C)0.0049 M
D)0.030 M
E)0.050 M

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
A voltaic cell consists of an Au/Au3+ electrode (E° = 1.50 V)and a Cu/ Cu2+ electrode (E° = 0.34 V).Calculate [Au3+] if [Cu2+] = 1.20 M and Ecell = 1.15 V at 25°C.
A)0.0010 M
B)0.0020 M
C)0.010 M
D)0.020 M
E)0.41 M
A)0.0010 M
B)0.0020 M
C)0.010 M
D)0.020 M
E)0.41 M

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
Which is the Nernst equation?
A)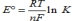
B)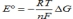
C)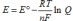
D)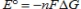
E)None of these statements is correct.
A)
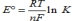
B)
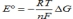
C)
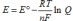
D)
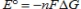
E)None of these statements is correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
A voltaic cell consists of a Cd/Cd2+ electrode (E° = -0.40 V)and a Fe/Fe2+ electrode (E° = -0.44 V).If Ecell = 0 and the temperature is 25°C,what is the ratio [Fe2+]/[Cd2+]?
A)2.3 × 101
B)1.0 × 101
C)1.0
D)1.0 × 10-1
E)5.0 × 10-2
A)2.3 × 101
B)1.0 × 101
C)1.0
D)1.0 × 10-1
E)5.0 × 10-2

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
Which one of the following statements relating to the glass electrode is correct?
A)The glass electrode detects hydrogen gas.
B)The glass of a glass electrode serves to conduct electrons.
C)When pH is measured,only a single electrode,the glass electrode,need be used.
D)The potential of the glass electrode varies linearly with the pH of the solution.
E)None of these statements is correct.
A)The glass electrode detects hydrogen gas.
B)The glass of a glass electrode serves to conduct electrons.
C)When pH is measured,only a single electrode,the glass electrode,need be used.
D)The potential of the glass electrode varies linearly with the pH of the solution.
E)None of these statements is correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
What is the minimum voltage required for the electrolysis of 1.0 M NaCl in neutral solution? 2H2O + 2Cl- (1.0 M)→ H2(1 atm)+ Cl2(1 atm)+ 2OH-(1 × 10-7 M)
Note that
2H2O(l)+ 2e- → H2(g)+2OH-(aq),E° = -0.83 V,
2H2O(l)+ 2e- → H2(g)+2OH-(aq),E = -0.41 V([OH-] = 1 × 10-7M),
O2(g)+ 4H+(aq)+ 4e- →2H2O(l),E° = +1.23 V,
Cl2(g)+ 2e- → 2Cl-(aq)E° = +1.36 V,and
Na+(aq)+ e- → Na(s)E° = -2.71 V
A)2.19 V
B)1.77 V
C)0.41 V
D)-0.41 V
E)-1.78 V
Note that
2H2O(l)+ 2e- → H2(g)+2OH-(aq),E° = -0.83 V,
2H2O(l)+ 2e- → H2(g)+2OH-(aq),E = -0.41 V([OH-] = 1 × 10-7M),
O2(g)+ 4H+(aq)+ 4e- →2H2O(l),E° = +1.23 V,
Cl2(g)+ 2e- → 2Cl-(aq)E° = +1.36 V,and
Na+(aq)+ e- → Na(s)E° = -2.71 V
A)2.19 V
B)1.77 V
C)0.41 V
D)-0.41 V
E)-1.78 V

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
What is the half-reaction that occurs at the cathode during the electrolysis of an aqueous sodium iodide solution? Half-Reaction E° (V)
2H2O(l)+ 2e- → H2(g)+2OH-(aq)-0.83
O2(g)+ 4H+(aq)+ 4e- →2H2O(l)+1.23
Na+(aq)+ e- → Na(s)-2.71
I2(s)+ 2e- → 2I-(aq)+0.53
A)Na+ + e- →
B)O2(g)+ 4H+(aq)+ 4e- → 2H2O(l)
C)2H2O + 2e- → H2 + 2OH-
D)I2 + 2e- → 2I-
E)2I- → I2 + 2e-
2H2O(l)+ 2e- → H2(g)+2OH-(aq)-0.83
O2(g)+ 4H+(aq)+ 4e- →2H2O(l)+1.23
Na+(aq)+ e- → Na(s)-2.71
I2(s)+ 2e- → 2I-(aq)+0.53
A)Na+ + e- →
B)O2(g)+ 4H+(aq)+ 4e- → 2H2O(l)
C)2H2O + 2e- → H2 + 2OH-
D)I2 + 2e- → 2I-
E)2I- → I2 + 2e-

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
What mass of oxygen gas is produced in the electrolysis of water,for every gram of hydrogen gas formed? Reaction: 2H2O(l)→ 2H2(g)+ O2(g)
A)32 g O2
B)16 g O2
C)64 g O2
D)20 g O2
E)8 g O2
A)32 g O2
B)16 g O2
C)64 g O2
D)20 g O2
E)8 g O2

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 122 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








