Deck 17: Markov Processes
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/41
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 17: Markov Processes
1
Steady state probabilities are independent of initial state.
True
2
The sum of the probabilities in a transition matrix equals the number of rows in the matrix.
True
3
Transition probabilities are conditional probabilities.
True
4
For Markov processes having the memoryless property,the prior states of the system must be considered in order to predict the future behavior of the system.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
If a Markov chain has at least one absorbing state,steady-state probabilities cannot be calculated.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
A state,i,is an absorbing state if,when i = j,pij = 1.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
A state i is a transient state if there exists a state j that is reachable from i,but the state i is not reachable from state j.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
State j is an absorbing state if pij = 1.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
A state i is an absorbing state if pii = 0.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
If an absorbing state exists,then the probability that a unit will ultimately move into the absorbing state is given by the steady state probability.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
The fundamental matrix is used to calculate the probability of the process moving into each absorbing state.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
All entries in a matrix of transition probabilities sum to 1.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Markov processes use historical probabilities.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
All Markov chain transition matrices have the same number of rows as columns.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
All Markov chains have steady-state probabilities.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
A Markov chain cannot consist of all absorbing states.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
A unique matrix of transition probabilities should be developed for each customer.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
The probability that the system is in state 2 in the 5th period is π5(2).

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
All entries in a row of a matrix of transition probabilities sum to 1.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
When absorbing states are present,each row of the transition matrix corresponding to an absorbing state will have a single 1 and all other probabilities will be 0.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Where is a fundamental matrix,N,used? How is N computed?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
At steady state
A)π1(n+1)> π1(n)
B)π1 = π2
C)π1 + π2 ≥ 1
D)π1(n+1)= π1
A)π1(n+1)> π1(n)
B)π1 = π2
C)π1 + π2 ≥ 1
D)π1(n+1)= π1

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Give two examples of how Markov analysis can aid decision making.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Absorbing state probabilities are the same as
A)steady state probabilities.
B)transition probabilities.
C)fundamental probabilities.
D)None of the alternatives is true.
A)steady state probabilities.
B)transition probabilities.
C)fundamental probabilities.
D)None of the alternatives is true.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
In Markov analysis,we are concerned with the probability that the
A)state is part of a system.
B)system is in a particular state at a given time.
C)time has reached a steady state.
D)transition will occur.
A)state is part of a system.
B)system is in a particular state at a given time.
C)time has reached a steady state.
D)transition will occur.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
If the probability of making a transition from a state is 0,then that state is called a(n)
A)steady state.
B)final state.
C)origin state.
D)absorbing state.
A)steady state.
B)final state.
C)origin state.
D)absorbing state.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
A transition probability describes
A)the probability of a success in repeated,independent trials.
B)the probability a system in a particular state now will be in a specific state next period.
C)the probability of reaching an absorbing state.
D)None of the alternatives is correct.
A)the probability of a success in repeated,independent trials.
B)the probability a system in a particular state now will be in a specific state next period.
C)the probability of reaching an absorbing state.
D)None of the alternatives is correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Accounts receivable have been grouped into the following states:
State 1: Paid
State 2: Bad debt
State 3: 0-30 days old
State 4: 31-60 days old
Sixty percent of all new bills are paid before they are 30 days old.The remainder of these go to state 4.Seventy percent of all 30 day old bills are paid before they become 60 days old.If not paid,they are permanently classified as bad debts.
a.Set up the one month Markov transition matrix.
b.What is the probability that an account in state 3 will be paid?
State 1: Paid
State 2: Bad debt
State 3: 0-30 days old
State 4: 31-60 days old
Sixty percent of all new bills are paid before they are 30 days old.The remainder of these go to state 4.Seventy percent of all 30 day old bills are paid before they become 60 days old.If not paid,they are permanently classified as bad debts.
a.Set up the one month Markov transition matrix.
b.What is the probability that an account in state 3 will be paid?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Henry,a persistent salesman,calls North's Hardware Store once a week hoping to speak with the store's buying agent,Shirley.If Shirley does not accept Henry's call this week,the probability she will do the same next week is .35.On the other hand,if she accepts Henry's call this week,the probability she will not do so next week is .20.
a.Construct the transition matrix for this problem.
b.How many times per year can Henry expect to talk to Shirley?
c.What is the probability Shirley will accept Henry's next two calls if she does not accept his call this week?
d.What is the probability of Shirley accepting exactly one of Henry's next two calls if she accepts his call this week?
a.Construct the transition matrix for this problem.
b.How many times per year can Henry expect to talk to Shirley?
c.What is the probability Shirley will accept Henry's next two calls if she does not accept his call this week?
d.What is the probability of Shirley accepting exactly one of Henry's next two calls if she accepts his call this week?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
A recent study done by an economist for the Small Business Administration investigated failures of small business.Failures were either classified as due to poor financing,poor management,or a poor product.The failure rates differed for new businesses (under one year old)versus established businesses (over one year old. )
As the result of the economist's study,the following probabilities were determined.For new businesses the probability of failure due to financing was .15,due to management .20,and due to product .05.The corresponding probabilities for established businesses were .10,.06,and .03 respectively.
a.
Determine a five-state Markov Chain transition matrix with states for new,established,and each of the three failure states.Write it in the form of I,O,R,and Q submatrices.
b.Determine the probability that a new business will survive during the next three years.
c.What proportion of new businesses eventually fail due to:
(1)poor financing? (2)poor management? (3)poor product?
As the result of the economist's study,the following probabilities were determined.For new businesses the probability of failure due to financing was .15,due to management .20,and due to product .05.The corresponding probabilities for established businesses were .10,.06,and .03 respectively.
a.
Determine a five-state Markov Chain transition matrix with states for new,established,and each of the three failure states.Write it in the form of I,O,R,and Q submatrices.
b.Determine the probability that a new business will survive during the next three years.
c.What proportion of new businesses eventually fail due to:
(1)poor financing? (2)poor management? (3)poor product?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Analysis of a Markov process
A)describes future behavior of the system.
B)optimizes the system.
C)leads to higher order decision making.
D)All of the alternatives are true.
A)describes future behavior of the system.
B)optimizes the system.
C)leads to higher order decision making.
D)All of the alternatives are true.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
The probability of reaching an absorbing state is given by the
A)R matrix.
B)NR matrix.
C)Q matrix.
D)(I − Q)−1 matrix
A)R matrix.
B)NR matrix.
C)Q matrix.
D)(I − Q)−1 matrix

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
The probability of going from state 1 in period 2 to state 4 in period 3 is
A)p12
B)p23
C)p14
D)p43
A)p12
B)p23
C)p14
D)p43

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
What assumptions are necessary for a Markov process to have stationary transition probabilities?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Rent-To-Keep rents household furnishings by the month.At the end of a rental month a customer can: a)rent the item for another month,b)buy the item,or c)return the item.The matrix below describes the month-to-month transition probabilities for 32-inch stereo televisions the shop stocks.
What is the probability that a customer who rented a TV this month will eventually buy it?
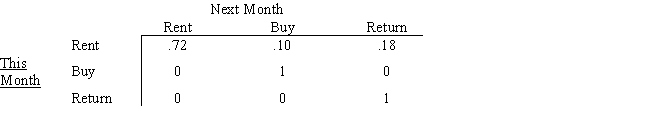
What is the probability that a customer who rented a TV this month will eventually buy it?
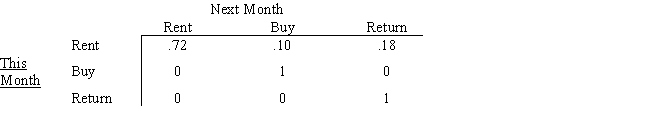

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
For a situation with weekly dining at either an Italian or Mexican restaurant,
A)the weekly visit is the trial and the restaurant is the state.
B)the weekly visit is the state and the restaurant is the trial.
C)the weekly visit is the trend and the restaurant is the transition.
D)the weekly visit is the transition and the restaurant is the trend.
A)the weekly visit is the trial and the restaurant is the state.
B)the weekly visit is the state and the restaurant is the trial.
C)the weekly visit is the trend and the restaurant is the transition.
D)the weekly visit is the transition and the restaurant is the trend.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
The probability that a system is in a particular state after a large number of periods is
A)independent of the beginning state of the system.
B)dependent on the beginning state of the system.
C)equal to one half.
D)the same for every ending system.
A)independent of the beginning state of the system.
B)dependent on the beginning state of the system.
C)equal to one half.
D)the same for every ending system.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
On any particular day an individual can take one of two routes to work.Route A has a 25% chance of being congested,whereas route B has a 40% chance of being congested.
The probability of the individual taking a particular route depends on his previous day's experience.If one day he takes route A and it is not congested,he will take route A again the next day with probability .8.If it is congested,he will take route B the next day with probability .7.
On the other hand,if on a day he takes route B and it is not congested,he will take route B again the next day with probability .9.Similarly if route B is congested,he will take route A the next day with probability .6.
a.Construct the transition matrix for this problem.(HINT: There are 4 states corresponding to the route taken and the congestion.The transition probabilities are products of the independent probabilities of congestion and next day choice. )
b.What is the long-run proportion of time that route A is taken?
The probability of the individual taking a particular route depends on his previous day's experience.If one day he takes route A and it is not congested,he will take route A again the next day with probability .8.If it is congested,he will take route B the next day with probability .7.
On the other hand,if on a day he takes route B and it is not congested,he will take route B again the next day with probability .9.Similarly if route B is congested,he will take route A the next day with probability .6.
a.Construct the transition matrix for this problem.(HINT: There are 4 states corresponding to the route taken and the congestion.The transition probabilities are products of the independent probabilities of congestion and next day choice. )
b.What is the long-run proportion of time that route A is taken?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
Why is a computer necessary for some Markov analyses?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Explain the concept of memorylessness.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
Discuss three types of information provided by analysis of a Markov process.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 41 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








