Deck 8: Profit Maximization and Competitive Supply
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/149
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 8: Profit Maximization and Competitive Supply
1
Which of following is a key assumption of a perfectly competitive market?
A) Firms can influence market price.
B) Commodities have few sellers.
C) It is difficult for new sellers to enter the market.
D) Each seller has a very small share of the market.
E) none of the above
A) Firms can influence market price.
B) Commodities have few sellers.
C) It is difficult for new sellers to enter the market.
D) Each seller has a very small share of the market.
E) none of the above
D
2
Use the following statements to answer this question:
I) Markets may be highly (but not perfectly) competitive even if there are a few sellers.
II) There is no simple indicator that tells us when markets are highly competitive.
A) I and II are true
B) I is true and II is false
C) I is false and II is true
D) I and II are false
I) Markets may be highly (but not perfectly) competitive even if there are a few sellers.
II) There is no simple indicator that tells us when markets are highly competitive.
A) I and II are true
B) I is true and II is false
C) I is false and II is true
D) I and II are false
A
3
Which of the following costs may provide barriers to entry in a market?
A) High research and development expenditures
B) License fees
C) Sunk costs associated with specialized facilities
D) all of the above
A) High research and development expenditures
B) License fees
C) Sunk costs associated with specialized facilities
D) all of the above
D
4
Owners and managers
A) must be the same people.
B) may be different people with different goals, and in the long run firms that do best are those in which the managers are allowed to pursue their own independent goals.
C) may be different people with different goals, but in the long run firms that do best are those in which the managers pursue the goals of the owners.
D) may be different people with different but exactly complementary goals.
E) may be different people with the same goals.
A) must be the same people.
B) may be different people with different goals, and in the long run firms that do best are those in which the managers are allowed to pursue their own independent goals.
C) may be different people with different goals, but in the long run firms that do best are those in which the managers pursue the goals of the owners.
D) may be different people with different but exactly complementary goals.
E) may be different people with the same goals.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
A few sellers may behave as if they operate in a perfectly competitive market if the market demand is:
A) highly inelastic.
B) very elastic.
C) unitary elastic.
D) composed of many small buyers.
A) highly inelastic.
B) very elastic.
C) unitary elastic.
D) composed of many small buyers.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
The authors note that the goal of maximizing the market value of the firm may be more appropriate than maximizing short-run profits because:
A) the market value of the firm is based on long-run profits.
B) managers will not focus on increasing short-run profits at the expense of long-run profits.
C) this would more closely align the interests of owners and managers.
D) all of the above
A) the market value of the firm is based on long-run profits.
B) managers will not focus on increasing short-run profits at the expense of long-run profits.
C) this would more closely align the interests of owners and managers.
D) all of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
If managers do not choose to maximize profit, but pursue some other goal such as revenue maximization or growth,
A) they are more likely to become takeover targets of profit-maximizing firms.
B) they are less likely to be replaced by stockholders.
C) they are less likely to be replaced by the board of directors.
D) they are more likely to have higher profit than if they had pursued that policy explicitly.
E) their companies are more likely to survive in the long run.
A) they are more likely to become takeover targets of profit-maximizing firms.
B) they are less likely to be replaced by stockholders.
C) they are less likely to be replaced by the board of directors.
D) they are more likely to have higher profit than if they had pursued that policy explicitly.
E) their companies are more likely to survive in the long run.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Which of following is an example of a homogeneous product?
A) Gasoline
B) Copper
C) Personal computers
D) Winter parkas
E) both A and B
A) Gasoline
B) Copper
C) Personal computers
D) Winter parkas
E) both A and B

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
An association of businesses that are jointly owned and operated by members for mutual benefit is a:
A) condominium.
B) corporation.
C) cooperative.
D) joint tenancy.
A) condominium.
B) corporation.
C) cooperative.
D) joint tenancy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
A price taker is
A) a firm that accepts different prices from different customers.
B) a consumer who accepts different prices from different firms.
C) a perfectly competitive firm.
D) a firm that cannot influence the market price.
E) both C and D
A) a firm that accepts different prices from different customers.
B) a consumer who accepts different prices from different firms.
C) a perfectly competitive firm.
D) a firm that cannot influence the market price.
E) both C and D

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
If any of the assumptions of perfect competition are violated,
A) supply-and-demand analysis cannot be used to study the industry.
B) graphs with flat demand curves cannot be used to study the firm.
C) graphs with downward-sloping demand curves cannot be used to study the firm.
D) there may still be enough competition in the industry to make the model of perfect competition usable.
E) one must use the monopoly model instead.
A) supply-and-demand analysis cannot be used to study the industry.
B) graphs with flat demand curves cannot be used to study the firm.
C) graphs with downward-sloping demand curves cannot be used to study the firm.
D) there may still be enough competition in the industry to make the model of perfect competition usable.
E) one must use the monopoly model instead.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
The "perfect information" assumption of perfect competition includes all of the following except one. Which one?
A) Consumers know their preferences.
B) Consumers know their income levels.
C) Consumers know the prices available.
D) Consumers can anticipate price changes.
E) Firms know their costs, prices and technology.
A) Consumers know their preferences.
B) Consumers know their income levels.
C) Consumers know the prices available.
D) Consumers can anticipate price changes.
E) Firms know their costs, prices and technology.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Several years ago, Alcoa was effectively the sole seller of aluminum because the firm owned nearly all of the aluminum ore reserves in the world. This market was not perfectly competitive because this situation violated the:
A) price-taking assumption.
B) homogeneous product assumption.
C) free entry assumption.
D) A and B are correct.
E) A and C are correct.
A) price-taking assumption.
B) homogeneous product assumption.
C) free entry assumption.
D) A and B are correct.
E) A and C are correct.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Which of the following statements identifies a key difference between condominiums and cooperative housing?
A) Condos tends to be less expensive.
B) Condo owners are not responsible for maintaining the common spaces in the building.
C) Co-op owners have more control over who can move into their building.
D) Co-op owners generally commit less time to the building governance.
A) Condos tends to be less expensive.
B) Condo owners are not responsible for maintaining the common spaces in the building.
C) Co-op owners have more control over who can move into their building.
D) Co-op owners generally commit less time to the building governance.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
In many rural areas, electric generation and distribution utilities were initially set up as cooperatives in which the electricity customers were member-owners. Like most cooperatives, the objective of these firms was to:
A) maximize profits for the member-owners.
B) maximize total revenue that could be redistributed to the member-owners.
C) operate at zero profit in order to provide low electricity prices for the member-owners.
D) minimize the costs of production.
A) maximize profits for the member-owners.
B) maximize total revenue that could be redistributed to the member-owners.
C) operate at zero profit in order to provide low electricity prices for the member-owners.
D) minimize the costs of production.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
What do cooperative firms do if they make a profit?
A) Cooperatives never earn profits, so this issue does not occur.
B) Cooperatives must pay their profits to the federal governments as a windfall profit tax.
C) Cooperatives must keep half of the profits and return the other half to their members.
D) Cooperatives generally return the profits to their members as a dividend.
A) Cooperatives never earn profits, so this issue does not occur.
B) Cooperatives must pay their profits to the federal governments as a windfall profit tax.
C) Cooperatives must keep half of the profits and return the other half to their members.
D) Cooperatives generally return the profits to their members as a dividend.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Revenue is equal to
A) price times quantity.
B) price times quantity minus total cost.
C) price times quantity minus average cost.
D) price times quantity minus marginal cost.
E) expenditure on production of output.
A) price times quantity.
B) price times quantity minus total cost.
C) price times quantity minus average cost.
D) price times quantity minus marginal cost.
E) expenditure on production of output.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
The textbook for your class was not produced in a perfectly competitive industry because
A) there are so few firms in the industry that market shares are not small, and firms' decisions have an impact on market price.
B) upper-division microeconomics texts are not all alike.
C) it is not costless to enter or exit the textbook industry.
D) of all of the above reasons.
A) there are so few firms in the industry that market shares are not small, and firms' decisions have an impact on market price.
B) upper-division microeconomics texts are not all alike.
C) it is not costless to enter or exit the textbook industry.
D) of all of the above reasons.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Use the following statements to answer this question:
I) Markets that have only a few sellers cannot be highly competitive.
II) Markets with many sellers are always perfectly competitive.
A) I and II are true.
B) I is true and II is false.
C) II is true and I is false.
D) I and II are false.
I) Markets that have only a few sellers cannot be highly competitive.
II) Markets with many sellers are always perfectly competitive.
A) I and II are true.
B) I is true and II is false.
C) II is true and I is false.
D) I and II are false.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Firms often use patent rights as a:
A) barrier to exit.
B) barrier to entry.
C) way to achieve perfect competition.
D) none of the above
A) barrier to exit.
B) barrier to entry.
C) way to achieve perfect competition.
D) none of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Suppose the state legislature in your state imposes a state licensing fee of $100 per year to be paid by all firms that file state tax revenue reports. This new business tax:
A) increases marginal cost.
B) decreases marginal cost.
C) increases marginal revenue.
D) decreases marginal revenue.
E) none of the above
A) increases marginal cost.
B) decreases marginal cost.
C) increases marginal revenue.
D) decreases marginal revenue.
E) none of the above

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Suppose we plot the total revenue curve with quantity on the horizontal axis and revenue on the vertical axis (as in Figure 8.1 in the book). Under price-taking behavior, the total revenue curve should be:
A) an inverted U-shaped curve (first increasing and then decreasing).
B) a U-shaped curve (first decreasing and then increasing).
C) a horizontal line with vertical axis intercept equal to the market price.
D) a straight line from the origin with slope equal to the market price.
A) an inverted U-shaped curve (first increasing and then decreasing).
B) a U-shaped curve (first decreasing and then increasing).
C) a horizontal line with vertical axis intercept equal to the market price.
D) a straight line from the origin with slope equal to the market price.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
The perfectly competitive firm's marginal revenue curve is
A) exactly the same as the marginal cost curve.
B) downward-sloping, at twice the (negative) slope of the market demand curve.
C) vertical.
D) horizontal.
E) upward-sloping.
A) exactly the same as the marginal cost curve.
B) downward-sloping, at twice the (negative) slope of the market demand curve.
C) vertical.
D) horizontal.
E) upward-sloping.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
If current output is less than the profit-maximizing output, which must be true?
A) Total revenue is less than total cost.
B) Average revenue is less than average cost.
C) Average revenue is greater than average cost.
D) Marginal revenue is less than marginal cost.
E) Marginal revenue is greater than marginal cost.
A) Total revenue is less than total cost.
B) Average revenue is less than average cost.
C) Average revenue is greater than average cost.
D) Marginal revenue is less than marginal cost.
E) Marginal revenue is greater than marginal cost.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
At the profit-maximizing level of output, what is relationship between the total revenue (TR) and total cost (TC) curves?
A) They must intersect, with TC cutting TR from below.
B) They must intersect, with TC cutting TR from above.
C) They must be tangent to each other.
D) They cannot be tangent to each other.
E) They must have the same slope.
A) They must intersect, with TC cutting TR from below.
B) They must intersect, with TC cutting TR from above.
C) They must be tangent to each other.
D) They cannot be tangent to each other.
E) They must have the same slope.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
The following table contains information for a price taking competitive firm. Complete the table and determine the profit maximizing level of output (round your answer to the nearest whole number).
Total Marginal Fixed Average Total Average Marginal
Output Cost Cost Cost Cost Revenue Revenue Revenue
0 25
1 35
2 30
3 45
4 185
5 57
6 120 240
Total Marginal Fixed Average Total Average Marginal
Output Cost Cost Cost Cost Revenue Revenue Revenue
0 25
1 35
2 30
3 45
4 185
5 57
6 120 240

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
The demand curve facing a perfectly competitive firm is
A) the same as the market demand curve.
B) downward-sloping and less flat than the market demand curve.
C) downward-sloping and more flat than the market demand curve.
D) perfectly horizontal.
E) perfectly vertical.
A) the same as the market demand curve.
B) downward-sloping and less flat than the market demand curve.
C) downward-sloping and more flat than the market demand curve.
D) perfectly horizontal.
E) perfectly vertical.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Marginal profit is negative when:
A) marginal revenue is negative.
B) total cost exceeds total revenue.
C) output exceeds the profit-maximizing level.
D) profit is negative.
A) marginal revenue is negative.
B) total cost exceeds total revenue.
C) output exceeds the profit-maximizing level.
D) profit is negative.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
The following table contains information for a price taking competitive firm. Complete the table and determine the profit maximizing level of output (round your answer to the nearest whole number).
Total Marginal Fixed Average Total Average Marginal
Output Cost Cost Cost Cost Revenue Revenue Revenue
0 5 0
1 7 10
2 11 20
3 17 30
4 27 40
5 41 50
6 61 60
Total Marginal Fixed Average Total Average Marginal
Output Cost Cost Cost Cost Revenue Revenue Revenue
0 5 0
1 7 10
2 11 20
3 17 30
4 27 40
5 41 50
6 61 60

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
A firm maximizes profit by operating at the level of output where
A) average revenue equals average cost.
B) average revenue equals average variable cost.
C) total costs are minimized.
D) marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
E) marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost by the greatest amount.
A) average revenue equals average cost.
B) average revenue equals average variable cost.
C) total costs are minimized.
D) marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
E) marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost by the greatest amount.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
When the TR and TC curves have the same slope,
A) they are the furthest from each other.
B) they are closest to each other.
C) they intersect each other.
D) profit is negative.
E) profit is zero.
A) they are the furthest from each other.
B) they are closest to each other.
C) they intersect each other.
D) profit is negative.
E) profit is zero.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
The demand curve facing a perfectly competitive firm is
A) the same as its average revenue curve, but not the same as its marginal revenue curve.
B) the same as its average revenue curve and its marginal revenue curve.
C) the same as its marginal revenue curve, but not its average revenue curve.
D) not the same as either its marginal revenue curve or its average revenue curve.
E) not defined in terms of average or marginal revenue.
A) the same as its average revenue curve, but not the same as its marginal revenue curve.
B) the same as its average revenue curve and its marginal revenue curve.
C) the same as its marginal revenue curve, but not its average revenue curve.
D) not the same as either its marginal revenue curve or its average revenue curve.
E) not defined in terms of average or marginal revenue.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
Suppose your firm operates in a perfectly competitive market and decides to double its output. How does this affect the firm's marginal profit?
A) Marginal revenue and marginal cost increase
B) Marginal revenue increases but marginal cost remains the same
C) Marginal cost may change but marginal revenue remains the same
D) Marginal revenue and marginal cost decrease
A) Marginal revenue and marginal cost increase
B) Marginal revenue increases but marginal cost remains the same
C) Marginal cost may change but marginal revenue remains the same
D) Marginal revenue and marginal cost decrease

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
Marginal revenue, graphically, is
A) the slope of a line from the origin to a point on the total revenue curve.
B) the slope of a line from the origin to the end of the total revenue curve.
C) the slope of the total revenue curve at a given point.
D) the vertical intercept of a line tangent to the total revenue curve at a given point.
E) the horizontal intercept of a line tangent to the total revenue curve at a given point.
A) the slope of a line from the origin to a point on the total revenue curve.
B) the slope of a line from the origin to the end of the total revenue curve.
C) the slope of the total revenue curve at a given point.
D) the vertical intercept of a line tangent to the total revenue curve at a given point.
E) the horizontal intercept of a line tangent to the total revenue curve at a given point.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
If the market price for a competitive firm's output doubles then
A) the profit maximizing output will double
B) the marginal revenue doubles
C) at the new profit maximizing output, price has increased more than marginal cost
D) at the new profit maximizing output, price has risen more than marginal revenue
E) competitive firms will earn an economic profit in the long-run.
A) the profit maximizing output will double
B) the marginal revenue doubles
C) at the new profit maximizing output, price has increased more than marginal cost
D) at the new profit maximizing output, price has risen more than marginal revenue
E) competitive firms will earn an economic profit in the long-run.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
Because of the relationship between a perfectly competitive firm's demand curve and its marginal revenue curve, the profit maximization condition for the firm can be written as
A) P = MR.
B) P = AVC.
C) AR = MR.
D) P = MC.
E) P = AC.
A) P = MR.
B) P = AVC.
C) AR = MR.
D) P = MC.
E) P = AC.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
The amount of output that a firm decides to sell has no effect on the market price in a competitive industry because
A) the market price is determined (through regulation) by the government
B) the firm supplies a different good than its rivals
C) the firm's output is a small fraction of the entire industry's output
D) the short run market price is determined solely by the firm's technology
E) the demand curve for the industry's output is downward sloping
A) the market price is determined (through regulation) by the government
B) the firm supplies a different good than its rivals
C) the firm's output is a small fraction of the entire industry's output
D) the short run market price is determined solely by the firm's technology
E) the demand curve for the industry's output is downward sloping

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
At the profit-maximizing level of output, marginal profit
A) is also maximized.
B) is zero.
C) is positive.
D) is increasing.
E) may be positive, negative or zero.
A) is also maximized.
B) is zero.
C) is positive.
D) is increasing.
E) may be positive, negative or zero.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
If current output is less than the profit-maximizing output, then the next unit produced
A) will decrease profit.
B) will increase cost more than it increases revenue.
C) will increase revenue more than it increases cost.
D) will increase revenue without increasing cost.
E) may or may not increase profit.
A) will decrease profit.
B) will increase cost more than it increases revenue.
C) will increase revenue more than it increases cost.
D) will increase revenue without increasing cost.
E) may or may not increase profit.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
Marginal profit is equal to
A) marginal revenue minus marginal cost.
B) marginal revenue plus marginal cost.
C) marginal cost minus marginal revenue.
D) marginal revenue times marginal cost.
E) marginal revenue divided by marginal cost.
A) marginal revenue minus marginal cost.
B) marginal revenue plus marginal cost.
C) marginal cost minus marginal revenue.
D) marginal revenue times marginal cost.
E) marginal revenue divided by marginal cost.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
Consider the following diagram where a perfectly competitive firm faces a price of $40. 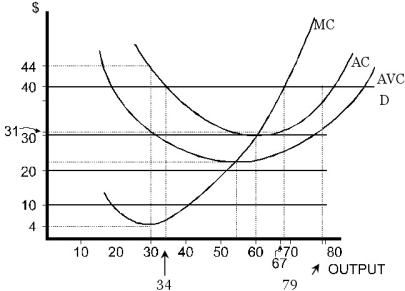 Figure 8.1
Figure 8.1
Refer to Figure 8.1. The profit-maximizing output is
A) 30.
B) 54.
C) 60.
D) 67.
E) 79.
 Figure 8.1
Figure 8.1Refer to Figure 8.1. The profit-maximizing output is
A) 30.
B) 54.
C) 60.
D) 67.
E) 79.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
In the short run, a perfectly competitive firm earning positive economic profit is
A) on the downward-sloping portion of its ATC.
B) at the minimum of its ATC.
C) on the upward-sloping portion of its ATC.
D) above its ATC.
E) below its ATC.
A) on the downward-sloping portion of its ATC.
B) at the minimum of its ATC.
C) on the upward-sloping portion of its ATC.
D) above its ATC.
E) below its ATC.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
Consider the following diagram where a perfectly competitive firm faces a price of $40.  Figure 8.1
Figure 8.1
Refer to Figure 8.1. At the profit-maximizing level of output,
A) AVC is minimized.
B) ATC is minimized.
C) MC is minimized.
D) total cost is minimized.
E) no costs are minimized.
 Figure 8.1
Figure 8.1Refer to Figure 8.1. At the profit-maximizing level of output,
A) AVC is minimized.
B) ATC is minimized.
C) MC is minimized.
D) total cost is minimized.
E) no costs are minimized.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
If a competitive firm has a U-shaped marginal cost curve then
A) the profit maximizing output will always generate positive economic profit.
B) the profit maximizing output will always generate positive producer surplus.
C) the profit maximizing output is found where MC = MR and MC is decreasing.
D) the profit maximizing output is found where MC = MR and MC is constant.
E) the profit maximizing output is found where MC = MR and MC is increasing.
A) the profit maximizing output will always generate positive economic profit.
B) the profit maximizing output will always generate positive producer surplus.
C) the profit maximizing output is found where MC = MR and MC is decreasing.
D) the profit maximizing output is found where MC = MR and MC is constant.
E) the profit maximizing output is found where MC = MR and MC is increasing.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
If price is between AVC and ATC, the best and most practical thing for a perfectly competitive firm to do is
A) raise prices.
B) lower prices to gain revenue from extra volume.
C) shut down immediately, but not liquidate the business.
D) shut down immediately and liquidate the business.
E) continue operating, but plan to go out of business.
A) raise prices.
B) lower prices to gain revenue from extra volume.
C) shut down immediately, but not liquidate the business.
D) shut down immediately and liquidate the business.
E) continue operating, but plan to go out of business.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
Bette's Breakfast, a perfectly competitive eatery, sells its "Breakfast Special" (the only item on the menu) for $5.00. The costs of waiters, cooks, power, food etc. average out to $3.95 per meal; the costs of the lease, insurance and other such expenses average out to $1.25 per meal. Bette should
A) close her doors immediately.
B) continue producing in the short and long run.
C) continue producing in the short run, but plan to go out of business in the long run.
D) raise her prices above the perfectly competitive level.
E) lower her output.
A) close her doors immediately.
B) continue producing in the short and long run.
C) continue producing in the short run, but plan to go out of business in the long run.
D) raise her prices above the perfectly competitive level.
E) lower her output.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
If a competitive firm's marginal cost curve is U-shaped then
A) its short run supply curve is U-shaped too
B) its short run supply curve is the downward-sloping portion of the marginal cost curve
C) its short run supply curve is the upward-sloping portion of the marginal cost curve
D) its short run supply curve is the upward-sloping portion of the marginal cost curve that lies above the short run average variable cost curve
E) its short run supply curve is the upward-sloping portion of the marginal cost curve that lies above the short run average total cost curve
A) its short run supply curve is U-shaped too
B) its short run supply curve is the downward-sloping portion of the marginal cost curve
C) its short run supply curve is the upward-sloping portion of the marginal cost curve
D) its short run supply curve is the upward-sloping portion of the marginal cost curve that lies above the short run average variable cost curve
E) its short run supply curve is the upward-sloping portion of the marginal cost curve that lies above the short run average total cost curve

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
Consider the following diagram where a perfectly competitive firm faces a price of $40.  Figure 8.1
Figure 8.1
Refer to Figure 8.1. The firm earns zero profit at what output?
A) 0.
B) 34 and 79.
C) 54.
D) 60.
E) 67.
 Figure 8.1
Figure 8.1Refer to Figure 8.1. The firm earns zero profit at what output?
A) 0.
B) 34 and 79.
C) 54.
D) 60.
E) 67.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
Average cost for the firm in Table 8.1
A) cannot be determined from the information given.
B) is upward-sloping for all output values shown.
C) is constant for all output values shown.
D) is downward-sloping for all output values shown.
E) is U-shaped.
A) cannot be determined from the information given.
B) is upward-sloping for all output values shown.
C) is constant for all output values shown.
D) is downward-sloping for all output values shown.
E) is U-shaped.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
That Table 8.1 shows a short-run situation is evident from
A) the linear marginal revenue function.
B) the constant price.
C) the increasing marginal cost.
D) the presence of positive costs at Q = 0.
E) the absence of marginal values at Q = 0.
A) the linear marginal revenue function.
B) the constant price.
C) the increasing marginal cost.
D) the presence of positive costs at Q = 0.
E) the absence of marginal values at Q = 0.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
If a graph of a perfectly competitive firm shows that the MR = MC point occurs where MR is above AVC but below ATC,
A) the firm is earning negative profit, and will shut down rather than produce that level of output.
B) the firm is earning negative profit, but will continue to produce where MR = MC in the short run.
C) the firm is still earning positive profit, as long as variable costs are covered.
D) the firm is covering explicit, but not implicit, costs.
E) the firm can cover all of fixed costs but only a portion of variable costs.
A) the firm is earning negative profit, and will shut down rather than produce that level of output.
B) the firm is earning negative profit, but will continue to produce where MR = MC in the short run.
C) the firm is still earning positive profit, as long as variable costs are covered.
D) the firm is covering explicit, but not implicit, costs.
E) the firm can cover all of fixed costs but only a portion of variable costs.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
Consider the following diagram where a perfectly competitive firm faces a price of $40.  Figure 8.1
Figure 8.1
Refer to Figure 8.1. At 67 units of output, profit is
A) maximized and zero.
B) maximized and negative.
C) maximized and positive.
D) not maximized, and zero.
E) not maximized, and negative.
 Figure 8.1
Figure 8.1Refer to Figure 8.1. At 67 units of output, profit is
A) maximized and zero.
B) maximized and negative.
C) maximized and positive.
D) not maximized, and zero.
E) not maximized, and negative.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
The total revenue graph consistent with Table 8.1 is
A) linear and upward-sloping.
B) linear and horizontal.
C) linear and vertical.
D) linear and downward-sloping.
E) concave downwards.
A) linear and upward-sloping.
B) linear and horizontal.
C) linear and vertical.
D) linear and downward-sloping.
E) concave downwards.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
Consider the following diagram where a perfectly competitive firm faces a price of $40.  Figure 8.1
Figure 8.1
Refer to Figure 8.1. At the profit-maximizing level of output, AVC is
A) $22.
B) $26.
C) $30.
D) $32.
E) $40.
 Figure 8.1
Figure 8.1Refer to Figure 8.1. At the profit-maximizing level of output, AVC is
A) $22.
B) $26.
C) $30.
D) $32.
E) $40.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
Consider the following diagram where a perfectly competitive firm faces a price of $40.  Figure 8.1
Figure 8.1
Refer to Figure 8.1. At the profit-maximizing level of output, total profit is
A) -$120.
B) $0.
C) $432.
D) $600.
E) $603.
 Figure 8.1
Figure 8.1Refer to Figure 8.1. At the profit-maximizing level of output, total profit is
A) -$120.
B) $0.
C) $432.
D) $600.
E) $603.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
Table 8.1
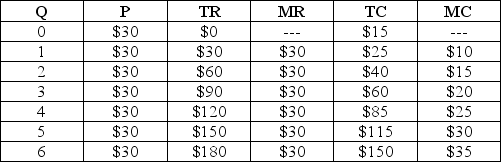
Refer to Table 8.1. That the firm is perfectly competitive is evident from its
A) increasing marginal cost.
B) increasing total cost.
C) zero economic profits.
D) constant marginal revenue.
E) absence of marginal values at Q = 0.

Refer to Table 8.1. That the firm is perfectly competitive is evident from its
A) increasing marginal cost.
B) increasing total cost.
C) zero economic profits.
D) constant marginal revenue.
E) absence of marginal values at Q = 0.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
Consider the following diagram where a perfectly competitive firm faces a price of $40.  Figure 8.1
Figure 8.1
Refer to Figure 8.1. At the profit-maximizing level of output, ATC is
A) $26.
B) $30.
C) $31.
D) $40.
E) $44.
 Figure 8.1
Figure 8.1Refer to Figure 8.1. At the profit-maximizing level of output, ATC is
A) $26.
B) $30.
C) $31.
D) $40.
E) $44.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
Table 8.1

Refer to Table 8.1. The maximum profit available to the firm is
A) $20.
B) $30.
C) $35.
D) $155.
E) $180.

Refer to Table 8.1. The maximum profit available to the firm is
A) $20.
B) $30.
C) $35.
D) $155.
E) $180.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
Consider the following diagram where a perfectly competitive firm faces a price of $40.  Figure 8.1
Figure 8.1
Refer to Figure 8.1. At the profit-maximizing level of output, total revenue is
A) $1200.
B) $2160.
C) $2400.
D) $2680.
E) $3160.
 Figure 8.1
Figure 8.1Refer to Figure 8.1. At the profit-maximizing level of output, total revenue is
A) $1200.
B) $2160.
C) $2400.
D) $2680.
E) $3160.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
An improvement in technology would result in
A) upward shifts of MC and reductions in output.
B) upward shifts of MC and increases in output.
C) downward shifts of MC and reductions in output.
D) downward shifts of MC and increases in output.
E) increased quality of the good, but little change in MC.
A) upward shifts of MC and reductions in output.
B) upward shifts of MC and increases in output.
C) downward shifts of MC and reductions in output.
D) downward shifts of MC and increases in output.
E) increased quality of the good, but little change in MC.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
A firm never operates
A) at the minimum of its ATC curve.
B) at the minimum of its AVC curve.
C) on the downward-sloping portion of its ATC curve.
D) on the downward-sloping portion of its AVC curve.
E) on its long-run marginal cost curve.
A) at the minimum of its ATC curve.
B) at the minimum of its AVC curve.
C) on the downward-sloping portion of its ATC curve.
D) on the downward-sloping portion of its AVC curve.
E) on its long-run marginal cost curve.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
Laura's internet services has the following short-run cost curve: C(q, K) = 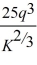
+ rK where q is Laura's output level, K is the number of servers she leases and r is the lease rate of servers. Laura's short-run marginal cost function is: MC(q, K) =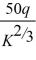
. Currently, Laura leases 8 servers, the lease rate of servers is $15, and Laura can sell all the output she produces for $500. Find Laura's short-run profit maximizing level of output. Calculate Laura's profits. If the lease rate of internet servers rise to $20, how does Laura's optimal output and profits change?
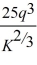
+ rK where q is Laura's output level, K is the number of servers she leases and r is the lease rate of servers. Laura's short-run marginal cost function is: MC(q, K) =
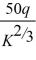
. Currently, Laura leases 8 servers, the lease rate of servers is $15, and Laura can sell all the output she produces for $500. Find Laura's short-run profit maximizing level of output. Calculate Laura's profits. If the lease rate of internet servers rise to $20, how does Laura's optimal output and profits change?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
Scenario 8.1:
Two soft-drink firms, Fizzle & Sizzle, operate on a river. Fizzle is farther upstream, and gets cleaner water, so its cost of purifying water for use in the soft drinks is lower than Sizzle's by $500,000 yearly.
Refer to the information in Scenario 8.1. If Fizzle and Sizzle sell the same output at the same price and are otherwise identical, Fizzle's profit will be
A) higher than Sizzle's by $500,000 yearly.
B) higher than Sizzle's by just less than $500,000 yearly.
C) zero in the long run, and Sizzle will be out of business.
D) the same as Sizzle's, because Fizzle must be assigned an implicit cost of $500,000 yearly for economic rent.
E) the same as Sizzle's, because Sizzle will move to a more advantageous location in order to compete.
Two soft-drink firms, Fizzle & Sizzle, operate on a river. Fizzle is farther upstream, and gets cleaner water, so its cost of purifying water for use in the soft drinks is lower than Sizzle's by $500,000 yearly.
Refer to the information in Scenario 8.1. If Fizzle and Sizzle sell the same output at the same price and are otherwise identical, Fizzle's profit will be
A) higher than Sizzle's by $500,000 yearly.
B) higher than Sizzle's by just less than $500,000 yearly.
C) zero in the long run, and Sizzle will be out of business.
D) the same as Sizzle's, because Fizzle must be assigned an implicit cost of $500,000 yearly for economic rent.
E) the same as Sizzle's, because Sizzle will move to a more advantageous location in order to compete.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
Suppose a technological innovation shifts the marginal cost curve downward. Which one of the following cost curves does NOT shift?
A) Firm's short-run supply curve
B) Average total cost curve
C) Average variable cost curve
D) Average fixed cost curve
A) Firm's short-run supply curve
B) Average total cost curve
C) Average variable cost curve
D) Average fixed cost curve

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
Conigan Box Company produces cardboard boxes that are sold in bundles of 1000 boxes. The market is highly competitive, with boxes currently selling for $100 per thousand. Conigan's total and marginal cost curves are:
TC = 3,000,000 + 0.001Q2
MC = 0.002Q
where Q is measured in thousand box bundles per year.
a. Calculate Conigan's profit maximizing quantity. Is the firm earning a profit?
b. Analyze Conigan's position in terms of the shutdown condition. Should Conigan operate or shut down in the shortrun?
TC = 3,000,000 + 0.001Q2
MC = 0.002Q
where Q is measured in thousand box bundles per year.
a. Calculate Conigan's profit maximizing quantity. Is the firm earning a profit?
b. Analyze Conigan's position in terms of the shutdown condition. Should Conigan operate or shut down in the shortrun?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
When the price faced by a competitive firm was $5, the firm produced nothing in the short run. However, when the price rose to $10, the firm produced 100 tons of output. From this we can infer that
A) the firm's marginal cost curve must be flat.
B) the firm's marginal costs of production never fall below $5.
C) the firm's average cost of production was less than $10.
D) the firm's total cost of producing 100 tons is less than $1000.
E) the minimum value of the firm's average variable cost lies between $5 and $10.
A) the firm's marginal cost curve must be flat.
B) the firm's marginal costs of production never fall below $5.
C) the firm's average cost of production was less than $10.
D) the firm's total cost of producing 100 tons is less than $1000.
E) the minimum value of the firm's average variable cost lies between $5 and $10.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
Scenario 8.1:
Two soft-drink firms, Fizzle & Sizzle, operate on a river. Fizzle is farther upstream, and gets cleaner water, so its cost of purifying water for use in the soft drinks is lower than Sizzle's by $500,000 yearly.
According to Scenario 8.1, Fizzle and Sizzle
A) would be perfectly competitive if their purification costs were equal; otherwise, not.
B) would be perfectly competitive if it costs Fizzle $500,000 yearly to keep that land.
C) may or may not be perfect competitors, but their position on the river has nothing to do with it.
D) cannot be perfect competitors because they are not identical firms.
Two soft-drink firms, Fizzle & Sizzle, operate on a river. Fizzle is farther upstream, and gets cleaner water, so its cost of purifying water for use in the soft drinks is lower than Sizzle's by $500,000 yearly.
According to Scenario 8.1, Fizzle and Sizzle
A) would be perfectly competitive if their purification costs were equal; otherwise, not.
B) would be perfectly competitive if it costs Fizzle $500,000 yearly to keep that land.
C) may or may not be perfect competitors, but their position on the river has nothing to do with it.
D) cannot be perfect competitors because they are not identical firms.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
Spacely Sprockets' short-run cost curve is: C(q, K) = 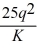
+ 15K, where q is the number of Sprockets produced and K is the number of robot hours Spacely hires. Currently, Spacely hires 10 robot hours per period. The short-run marginal cost curve is: MC(q, K) = 50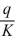
. If Spacely receives $250 for every sprocket he produces, what is his profit maximizing output level? Calculate Spacely's profits.
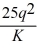
+ 15K, where q is the number of Sprockets produced and K is the number of robot hours Spacely hires. Currently, Spacely hires 10 robot hours per period. The short-run marginal cost curve is: MC(q, K) = 50
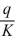
. If Spacely receives $250 for every sprocket he produces, what is his profit maximizing output level? Calculate Spacely's profits.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
In the short run, a perfectly competitive firm earning negative economic profit
A) is on the downward-sloping portion of its AVC.
B) is at the minimum of its AVC.
C) is on the upward-sloping portion of its AVC.
D) is not operating on its AVC.
E) can be at any point on its AVC.
A) is on the downward-sloping portion of its AVC.
B) is at the minimum of its AVC.
C) is on the upward-sloping portion of its AVC.
D) is not operating on its AVC.
E) can be at any point on its AVC.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
Suppose your firm has a U-shaped average variable cost curve and operates in a perfectly competitive market. If you produce where the product price (marginal revenue) equals average variable cost (on the upward sloping portion of the AVC curve), then your output will:
A) exceed the profit-maximizing level of output.
B) be smaller than the profit-maximizing level of output.
C) equal the profit-maximizing level of output.
D) generate zero economic profits.
A) exceed the profit-maximizing level of output.
B) be smaller than the profit-maximizing level of output.
C) equal the profit-maximizing level of output.
D) generate zero economic profits.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
Higher input prices result in
A) upward shifts of MC and reductions in output.
B) upward shifts of MC and increases in output.
C) downward shifts of MC and reductions in output.
D) downward shifts of MC and increases in output.
E) increased demand for the good the input is used for.
A) upward shifts of MC and reductions in output.
B) upward shifts of MC and increases in output.
C) downward shifts of MC and reductions in output.
D) downward shifts of MC and increases in output.
E) increased demand for the good the input is used for.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
The table below lists the short-run costs for One Guy's Pizza. If One Guy's can sell all the output they produce for $12 per unit, how much should One Guy's produce to maximize profits? Does One Guy's Pizza earn an economic profit in the short-run?
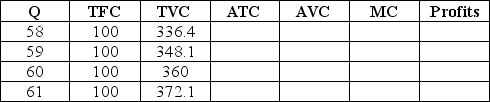


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
Use the following statements to answer this question:
I) The firm's decision to produce zero output when the price is less than the average variable cost of production is known as the shutdown rule.
II) The firm's supply decision is to generate zero output for all prices below the minimum AVC.
A) I and II are true.
B) I is true and II is false.
C) II is true and I is false.
D) I and II are false.
I) The firm's decision to produce zero output when the price is less than the average variable cost of production is known as the shutdown rule.
II) The firm's supply decision is to generate zero output for all prices below the minimum AVC.
A) I and II are true.
B) I is true and II is false.
C) II is true and I is false.
D) I and II are false.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
Suppose a plant manager ignores some implicit marginal costs of production so that the perceived MC curve is below the actual MC curve. What is the likely outcome from this error?
A) Firm produces less than optimal quantity and earns lower profits
B) Firm produces less than optimal quantity and earns higher profits
C) Firm produces more than optimal quantity and earns lower profits
D) Firm produces more than optimal quantity and earns higher profits
A) Firm produces less than optimal quantity and earns lower profits
B) Firm produces less than optimal quantity and earns higher profits
C) Firm produces more than optimal quantity and earns lower profits
D) Firm produces more than optimal quantity and earns higher profits

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
Homer's Boat Manufacturing cost function is: C(q) = 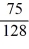
q4 + 10,240. The marginal cost function is: MC(q) =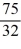
q3. If Homer can sell all the boats he produces for $1,200, what is his optimal output? Calculate Homer's profit or loss.
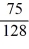
q4 + 10,240. The marginal cost function is: MC(q) =
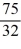
q3. If Homer can sell all the boats he produces for $1,200, what is his optimal output? Calculate Homer's profit or loss.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
In the short run, a perfectly competitive profit maximizing firm that has not shut down
A) is operating on the downward-sloping portion of its AVC curve.
B) is operating at the minimum of its AVC curve.
C) is operating on the upward-sloping portion of its AVC curve.
D) is not operating on its AVC curve.
E) can be at any point on its AVC curve.
A) is operating on the downward-sloping portion of its AVC curve.
B) is operating at the minimum of its AVC curve.
C) is operating on the upward-sloping portion of its AVC curve.
D) is not operating on its AVC curve.
E) can be at any point on its AVC curve.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
An industry analyst observes that in response to a small increase in price, a competitive firm's output sometimes rises a little and sometimes a lot. The best explanation for this finding is that
A) the firm's marginal cost curve is random.
B) the firm's marginal cost curve has a very small positive slope.
C) the firm's marginal cost has a very large positive slope.
D) the firm's marginal cost curve is horizontal for some ranges of output and rises in steps.
E) the firm's marginal cost curve is downward sloping.
A) the firm's marginal cost curve is random.
B) the firm's marginal cost curve has a very small positive slope.
C) the firm's marginal cost has a very large positive slope.
D) the firm's marginal cost curve is horizontal for some ranges of output and rises in steps.
E) the firm's marginal cost curve is downward sloping.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
In the short run, a perfectly competitive firm earning negative economic profit is
A) on the downward-sloping portion of its ATC curve.
B) at the minimum of its ATC curve.
C) on the upward-sloping portion of its ATC curve.
D) above its ATC curve.
A) on the downward-sloping portion of its ATC curve.
B) at the minimum of its ATC curve.
C) on the upward-sloping portion of its ATC curve.
D) above its ATC curve.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
The supply curve for a competitive firm is
A) its entire MC curve.
B) the upward-sloping portion of its MC curve.
C) its MC curve above the minimum point of the AVC curve.
D) its MC curve above the minimum point of the ATC curve.
E) its MR curve.
A) its entire MC curve.
B) the upward-sloping portion of its MC curve.
C) its MC curve above the minimum point of the AVC curve.
D) its MC curve above the minimum point of the ATC curve.
E) its MR curve.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
Ronny's Pizza House is a profit maximizing firm in a perfectly competitive local restaurant market, and their optimal output is 80 pizzas per day. The local government imposes a new tax of $250 per year on all restaurants that operate in the city. How does this affect Ronny's profit maximizing decisions?
A) No impact on the restaurant's decisions
B) Ronny's will remain in business but will definitely produce less pizza
C) Ronny's will definitely shut down
D) Ronny's decision depends on the circumstances -- if their profits are larger than $250 per year, then the tax does not impact output; otherwise, Ronny's Pizza House will shut down.
A) No impact on the restaurant's decisions
B) Ronny's will remain in business but will definitely produce less pizza
C) Ronny's will definitely shut down
D) Ronny's decision depends on the circumstances -- if their profits are larger than $250 per year, then the tax does not impact output; otherwise, Ronny's Pizza House will shut down.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 149 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








