Deck 4: Atmospheric Energy and Global Temperatures
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/120
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 4: Atmospheric Energy and Global Temperatures
1
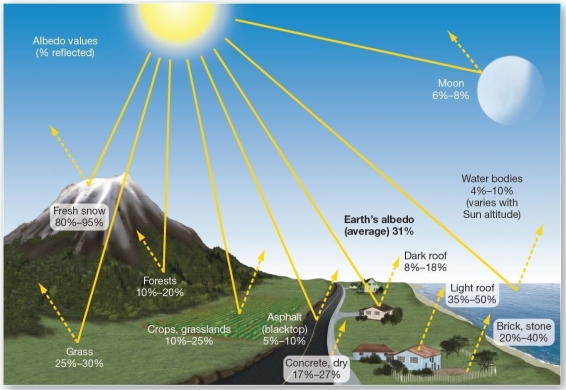 Various albedo values. Which of the following has the lowest albedo?
Various albedo values. Which of the following has the lowest albedo?A)fresh snow
B)croplands
C)light roof
D)forests
E)the Moon
E
2
Because of the process known as the Sun appears above the horizon it has actually risen.
A)transmission;before
B)transmission;after
C)refraction;before
D)refraction;after
E)reflection;before
A)transmission;before
B)transmission;after
C)refraction;before
D)refraction;after
E)reflection;before
C
3
Heat that can be sensed due to the kinetic energy of molecular motion is
A)sensible heat.
B)latent heat.
C)radiation.
D)conduction.
E)convection.
A)sensible heat.
B)latent heat.
C)radiation.
D)conduction.
E)convection.
A
4
Earth's main energy outputs are
A)gamma rays,X-rays,and ultraviolet radiation.
B)ultraviolet radiation and visible radiation.
C)visible and infrared radiation.
D)thermal infrared radiation.
E)microwaves and radio waves.
A)gamma rays,X-rays,and ultraviolet radiation.
B)ultraviolet radiation and visible radiation.
C)visible and infrared radiation.
D)thermal infrared radiation.
E)microwaves and radio waves.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
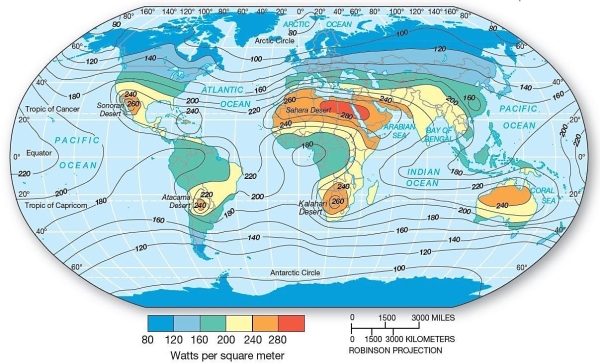 Insolation at Earth's Surface The insolation received at Earth's surface is
Insolation at Earth's Surface The insolation received at Earth's surface isA)usually low at the equator.
B)generally greater at high latitudes because of day length.
C)greatest over low-latitude deserts with their cloudless skies.
D)inadequate to sustain life.
E)highest in the mid-latitudes due to seasonality.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
The assimilation of radiation by molecules of matter is
A)refraction.
B)absorption.
C)reflection.
D)transmission.
E)scattering.
A)refraction.
B)absorption.
C)reflection.
D)transmission.
E)scattering.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
The reflective quality of a surface is known as its
A)conduction.
B)absorption.
C)albedo.
D)scattering.
E)transmission.
A)conduction.
B)absorption.
C)albedo.
D)scattering.
E)transmission.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Which of the following is true of the albedo of water?
A)It changes,depending upon the Sun angle.
B)It is greatest when the Sun is low in the sky.
C)It never changes-albedos are constant values.
D)It is less for frozen water than for liquid water.
E)It is greatest for rough waters.
A)It changes,depending upon the Sun angle.
B)It is greatest when the Sun is low in the sky.
C)It never changes-albedos are constant values.
D)It is less for frozen water than for liquid water.
E)It is greatest for rough waters.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
An image that appears near the horizon when layers of air are at different temperatures and densities is a(n)_ and an example of .
A)reflection;albedo.
B)Rayleigh scatter;albedo.
C)reflection;refraction.
D)mirage;refraction.
E)Mie scatter;refraction.
A)reflection;albedo.
B)Rayleigh scatter;albedo.
C)reflection;refraction.
D)mirage;refraction.
E)Mie scatter;refraction.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
The principle that explains the differential scattering of shorter wavelength radiation and accounts for the Earth's blue sky is
A)Mie scattering.
B)refraction.
C)Rayleigh scattering.
D)transmission.
E)albedo.
A)Mie scattering.
B)refraction.
C)Rayleigh scattering.
D)transmission.
E)albedo.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
If a surface absorbs insolation,
A)its temperature increases.
B)its temperature decreases.
C)its temperature is unaffected.
D)refraction occurs.
E)diffuse radiation occurs.
A)its temperature increases.
B)its temperature decreases.
C)its temperature is unaffected.
D)refraction occurs.
E)diffuse radiation occurs.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Heat always flow from an area of temperature to an area of _ temperature.
A)high;higher
B)lower;higher
C)low;lower
D)moderate;extreme
E)higher;lower
A)high;higher
B)lower;higher
C)low;lower
D)moderate;extreme
E)higher;lower

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Incoming radiation that reaches Earth's surface after scattering is
A)direct insolation.
B)diffuse radiation.
C)direct radiation.
D)indirect insolation.
E)reflective radiation.
A)direct insolation.
B)diffuse radiation.
C)direct radiation.
D)indirect insolation.
E)reflective radiation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Earth's main energy inputs are
A)longwave radiation and ultraviolet light.
B)ultraviolet,visible,and near infrared radiation.
C)near infrared and far infrared (i.e. ,longwave radiation).
D)gamma rays,X-rays,and ultraviolet radiation.
E)microwaves and radio waves.
A)longwave radiation and ultraviolet light.
B)ultraviolet,visible,and near infrared radiation.
C)near infrared and far infrared (i.e. ,longwave radiation).
D)gamma rays,X-rays,and ultraviolet radiation.
E)microwaves and radio waves.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Earth's average overall albedo is
A)10 percent.
B)31 percent.
C)51 percent.
D)69 percent.
E)75 percent.
A)10 percent.
B)31 percent.
C)51 percent.
D)69 percent.
E)75 percent.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
When light passes from one medium to another,resulting in a change in speed and direction of insolation,
A)transmission happens.
B)Rayleigh scattering is the predominant effect.
C)refraction occurs.
D)it is usually not affected physically.
E)albedo increases.
A)transmission happens.
B)Rayleigh scattering is the predominant effect.
C)refraction occurs.
D)it is usually not affected physically.
E)albedo increases.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Scattering caused by atmospheric particles larger than the wavelengths of light is
A)Mie scattering.
B)refraction.
C)Rayleigh scattering.
D)transmission.
E)albedo.
A)Mie scattering.
B)refraction.
C)Rayleigh scattering.
D)transmission.
E)albedo.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
The passage of shortwave and longwave energy through the atmosphere and water is an example of
A)absorption.
B)transmission.
C)refraction.
D)insolation.
E)reflection.
A)absorption.
B)transmission.
C)refraction.
D)insolation.
E)reflection.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
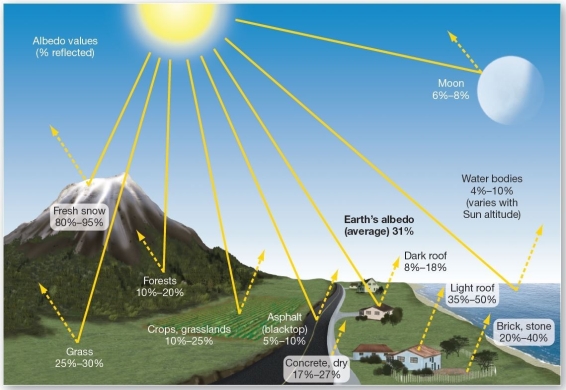 Various albedo values. Which of the following has the highest albedo?
Various albedo values. Which of the following has the highest albedo?A)forests
B)asphalt
C)dry,light sandy soils
D)fresh snow
E)the Moon

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Which two gases are good absorbers of longwave radiation emitted from Earth?
A)oxygen and hydrogen
B)ozone and dust
C)nitrogen and oxygen
D)water vapor and carbon dioxide
E)helium and argon
A)oxygen and hydrogen
B)ozone and dust
C)nitrogen and oxygen
D)water vapor and carbon dioxide
E)helium and argon

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Which of the following is a nonradiative transfer of longwave radiation to the atmosphere?
A)the greenhouse effect
B)latent heat transfer
C)stratospheric ozone radiation
D)conduction from the surface
E)longwave radiation from Earth's surface
A)the greenhouse effect
B)latent heat transfer
C)stratospheric ozone radiation
D)conduction from the surface
E)longwave radiation from Earth's surface

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Which of the following is true relative to the Earth-atmosphere radiation system?
A)Averaged over a year,Earth's surface has an energy surplus.
B)Averaged over a year,Earth's surface has an energy deficit.
C)Averaged over a year,Earth's atmosphere has an energy budget.
D)Averaged over a year,Earth's atmosphere has an energy gain.
E)The Earth's energy is never in balance because surface deficits are greater than atmosphere surpluses.
A)Averaged over a year,Earth's surface has an energy surplus.
B)Averaged over a year,Earth's surface has an energy deficit.
C)Averaged over a year,Earth's atmosphere has an energy budget.
D)Averaged over a year,Earth's atmosphere has an energy gain.
E)The Earth's energy is never in balance because surface deficits are greater than atmosphere surpluses.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Recent studies of jet contrails found that
A)contrails have a very limited effect on the Earth's energy budget.
B)contrails reflect more insolation than trap outgoing radiation from Earth.
C)contrails contribute more to cloud-albedo forcing than cloud-greenhouse forcing.
D)contrails are difficult to distinguish from natural cirrus clouds.
E)contrails contribute more to cloud-greenhouse forcing than cloud-albedo forcing.
A)contrails have a very limited effect on the Earth's energy budget.
B)contrails reflect more insolation than trap outgoing radiation from Earth.
C)contrails contribute more to cloud-albedo forcing than cloud-greenhouse forcing.
D)contrails are difficult to distinguish from natural cirrus clouds.
E)contrails contribute more to cloud-greenhouse forcing than cloud-albedo forcing.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Longwave radiation absorbed by certain atmospheric constituents and re-radiated back to Earth's surface is known as
A)conduction.
B)advection.
C)latent heat.
D)greenhouse heat.
E)counterradiation.
A)conduction.
B)advection.
C)latent heat.
D)greenhouse heat.
E)counterradiation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
The analogy of a greenhouse
A)is completely unrelated to our Earth-atmosphere system,and should never have been used to describe global warming.
B)describes exactly how the Earth-atmosphere system operates.
C)is a useful,but inaccurate model since atmospheric gases do not trap,but absorb heat.
D)incorrectly describes shortwave energy transmission but perfectly encapsulates how longwave terrestrial radiation is trapped.
E)is antiquated and rarely used anymore to describe our Earth-atmosphere system.
A)is completely unrelated to our Earth-atmosphere system,and should never have been used to describe global warming.
B)describes exactly how the Earth-atmosphere system operates.
C)is a useful,but inaccurate model since atmospheric gases do not trap,but absorb heat.
D)incorrectly describes shortwave energy transmission but perfectly encapsulates how longwave terrestrial radiation is trapped.
E)is antiquated and rarely used anymore to describe our Earth-atmosphere system.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
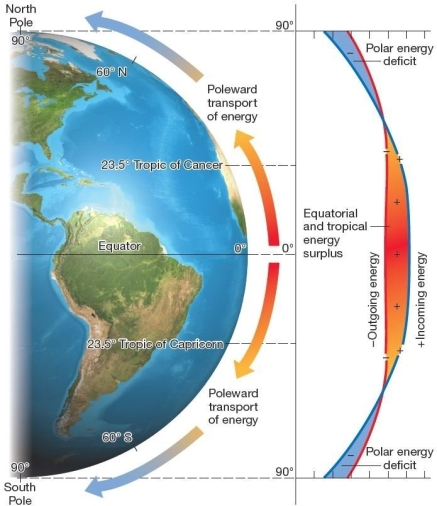
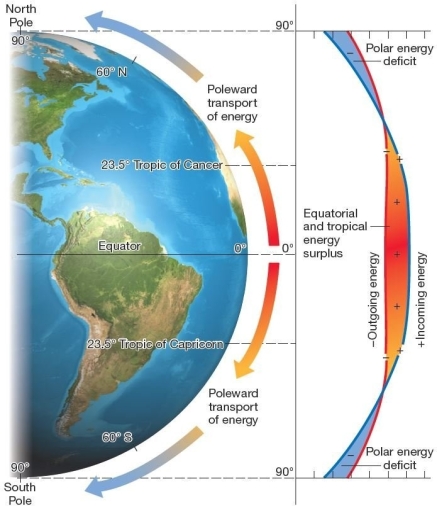 Energy budget by latitude.Low-latitude energy surpluses and high-latitude energy deficits produce the poleward transport of energy and mass in each hemisphere,through atmospheric circulation and ocean currents. Which of the following is true of differences in latitudinal energy?
Energy budget by latitude.Low-latitude energy surpluses and high-latitude energy deficits produce the poleward transport of energy and mass in each hemisphere,through atmospheric circulation and ocean currents. Which of the following is true of differences in latitudinal energy?A)There is an energy balance between energy gains and losses around 36° latitude.
B)There is year-round energy deficit at the Tropic of Capricorn.
C)The equator has an energy balance in the summer,but a deficit in the winter.
D)Energy imbalances between the tropics and the poles are negligible.
E)The greatest energy deficit occurs between the tropics.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Why is a greenhouse an imperfect analogy for how the Earth's atmosphere behaves?
A)A greenhouse allows longwave radiation to escape and mix with the surrounding air,unlike the Earth's atmosphere.
B)The glass of a greenhouse is designed to allow transmission of both longwave and shortwave radiation,whereas certain atmospheric constituents only allow transmission of shortwave radiation.
C)It is exceedingly rare for a greenhouse to contain carbon dioxide like the Earth's atmosphere contains.
D)Passage of longwave radiation to space is delayed by certain atmospheric constituents,but not trapped like an actual greenhouse.
E)A greenhouse is designed to artificially warm an area and has built in ventilation,whereas there is no such ventilation system in the Earth-atmosphere system.
A)A greenhouse allows longwave radiation to escape and mix with the surrounding air,unlike the Earth's atmosphere.
B)The glass of a greenhouse is designed to allow transmission of both longwave and shortwave radiation,whereas certain atmospheric constituents only allow transmission of shortwave radiation.
C)It is exceedingly rare for a greenhouse to contain carbon dioxide like the Earth's atmosphere contains.
D)Passage of longwave radiation to space is delayed by certain atmospheric constituents,but not trapped like an actual greenhouse.
E)A greenhouse is designed to artificially warm an area and has built in ventilation,whereas there is no such ventilation system in the Earth-atmosphere system.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Which of the following is not a reason for the energy surplus between the tropics?
A)high insolation
B)indirect solar radiation
C)consistent daylength
D)little seasonal variations
E)small diurnal and annual insolation differences
A)high insolation
B)indirect solar radiation
C)consistent daylength
D)little seasonal variations
E)small diurnal and annual insolation differences

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Which of the following is correctly matched?
A)conduction - molecule-to-molecule heat transfer
B)advection - strongly vertical mixing
C)radiation - assimilation and conversion of
D)convection - strongly horizontal mixing
E)latent heat - energy that can be sensed
A)conduction - molecule-to-molecule heat transfer
B)advection - strongly vertical mixing
C)radiation - assimilation and conversion of
D)convection - strongly horizontal mixing
E)latent heat - energy that can be sensed

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
An increase in the amount of high altitude,ice crystal (cirrus)clouds would
A)cool the planet in a process called cloud-albedo forcing.
B)warm the planet in a process called cloud-greenhouse forcing.
C)warm the planet in a process called cloud-albedo forcing.
D)cool the planet in a process called cloud-greenhouse forcing.
E)have no effect on the planet's temperature because insolation is constant.
A)cool the planet in a process called cloud-albedo forcing.
B)warm the planet in a process called cloud-greenhouse forcing.
C)warm the planet in a process called cloud-albedo forcing.
D)cool the planet in a process called cloud-greenhouse forcing.
E)have no effect on the planet's temperature because insolation is constant.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
Conduction refers to
A)strong vertical movement of air in the atmosphere.
B)strong horizontal movement of air in the atmosphere.
C)the molecule-to-molecule transfer of heat energy.
D)the behavior of something.
E)heat that can be sensed by humans as temperature.
A)strong vertical movement of air in the atmosphere.
B)strong horizontal movement of air in the atmosphere.
C)the molecule-to-molecule transfer of heat energy.
D)the behavior of something.
E)heat that can be sensed by humans as temperature.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Differential transmissivity of shortwave insolation and longwave terrestrial radiation by various atmospheric gases is better known as
A)global dimming.
B)the greenhouse effect.
C)cloud-albedo forcing.
D)global warming.
E)latent heat transfer.
A)global dimming.
B)the greenhouse effect.
C)cloud-albedo forcing.
D)global warming.
E)latent heat transfer.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
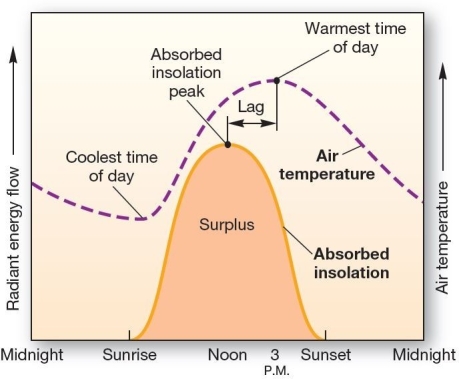 Daily radiation and temperature curves The relationship between insolation and air temperature through the course of day shows
Daily radiation and temperature curves The relationship between insolation and air temperature through the course of day showsA)air temperature reaches a maximum at noon when absorbed insolation also reaches a maximum.
B)air temperature reaches a maximum afternoon,whereas absorbed insolation reaches a maximum at noon.
C)air temperature maximum and minimums are not related to absorbed insolation.
D)air temperature reaches a minimum at midnight when there is no absorbed insolation.
E)air temperature minimum corresponds to maximum insolation absorption.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
Energy gained or lost when a substance changes from one state to another is
A)sensible heat.
B)latent heat.
C)radiation.
D)conduction.
E)convection.
A)sensible heat.
B)latent heat.
C)radiation.
D)conduction.
E)convection.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
A horizontal air current that is generated by temperature-induced density differences is an example of heat transfer by
A)advection.
B)convection.
C)conduction.
D)transmission.
E)diffusion.
A)advection.
B)convection.
C)conduction.
D)transmission.
E)diffusion.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
Which of the following is correctly matched?
A)insolation - shortwave radiation - UV,visible,and near infrared
B)insolation - longwave radiation - thermal infrared radiation
C)terrestrial radiation - shortwave radiation - UV,visible,and near infrared
D)terrestrial radiation - shortwave radiation - thermal infrared radiation
E)both insolation and terrestrial radiation - shortwave radiation - UV,visible,and near infrared
A)insolation - shortwave radiation - UV,visible,and near infrared
B)insolation - longwave radiation - thermal infrared radiation
C)terrestrial radiation - shortwave radiation - UV,visible,and near infrared
D)terrestrial radiation - shortwave radiation - thermal infrared radiation
E)both insolation and terrestrial radiation - shortwave radiation - UV,visible,and near infrared

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
36)  Energy budget by latitude.Low-latitude energy surpluses and high-latitude energy deficits produce the poleward transport of energy and mass in each hemisphere,through atmospheric circulation and ocean currents On the average,which of the following is true regarding the distribution of shortwave and longwave energy at Earth's surface by latitude?
Energy budget by latitude.Low-latitude energy surpluses and high-latitude energy deficits produce the poleward transport of energy and mass in each hemisphere,through atmospheric circulation and ocean currents On the average,which of the following is true regarding the distribution of shortwave and longwave energy at Earth's surface by latitude?
A)The equatorial zone is a region of net deficits.
B)The polar regions are areas of net surpluses.
C)The distribution shows an imbalance of net radiation from equator to poles.
D)More energy is lost than is gained in the equatorial regions.
E)The midlatitudes are the area of the largest surpluses throughout the year.
 Energy budget by latitude.Low-latitude energy surpluses and high-latitude energy deficits produce the poleward transport of energy and mass in each hemisphere,through atmospheric circulation and ocean currents On the average,which of the following is true regarding the distribution of shortwave and longwave energy at Earth's surface by latitude?
Energy budget by latitude.Low-latitude energy surpluses and high-latitude energy deficits produce the poleward transport of energy and mass in each hemisphere,through atmospheric circulation and ocean currents On the average,which of the following is true regarding the distribution of shortwave and longwave energy at Earth's surface by latitude?A)The equatorial zone is a region of net deficits.
B)The polar regions are areas of net surpluses.
C)The distribution shows an imbalance of net radiation from equator to poles.
D)More energy is lost than is gained in the equatorial regions.
E)The midlatitudes are the area of the largest surpluses throughout the year.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
Which of the following is not a reason for the energy deficit in the polar regions?
A)little seasonal variability
B)low sun angle
C)high albedo due to snow and ice
D)up to six months without insolation
E)large diurnal and annual insolation differences
A)little seasonal variability
B)low sun angle
C)high albedo due to snow and ice
D)up to six months without insolation
E)large diurnal and annual insolation differences

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
A stove that circulates heated air to uniformly cook food is an example of heat transfer.
A)conduction
B)convection
C)kinetic
D)latent
E)sensible
A)conduction
B)convection
C)kinetic
D)latent
E)sensible

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
If the amount of low,thick stratus cloud cover increases,the Earth's climates would likely due to increased .
A)cool;absorption
B)cool;reflectivity
C)warm;absorption
D)warm;reflectivity
E)warm;conduction
A)cool;absorption
B)cool;reflectivity
C)warm;absorption
D)warm;reflectivity
E)warm;conduction

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
Longwave radiation (+ LW)arriving at the Earth's surface
A)comes primarily from infrared energy emitted by the atmosphere.
B)comes directly from the Sun.
C)comes from diffuse solar radiation.
D)comes from UV radiation reflected from the bottoms of clouds.
E)encompasses energy primarily in the visible portion of the electromagnetic spectrum.
A)comes primarily from infrared energy emitted by the atmosphere.
B)comes directly from the Sun.
C)comes from diffuse solar radiation.
D)comes from UV radiation reflected from the bottoms of clouds.
E)encompasses energy primarily in the visible portion of the electromagnetic spectrum.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
The best thermometer to use where temperatures drop below -39°C (-38.2°F)is
A)a barometric thermometer.
B)a mercury thermometer.
C)a bulb mounted in direct sunshine.
D)an alcohol thermometer.
E)Aneroid thermometer.
A)a barometric thermometer.
B)a mercury thermometer.
C)a bulb mounted in direct sunshine.
D)an alcohol thermometer.
E)Aneroid thermometer.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
The Celsius scale
A)is used exclusively in the United States.
B)places melting point of ice at 0° and was formerly called centigrade.
C)was developed by the British physicist Lord Kelvin.
D)was developed by Fahrenheit,who also developed the alcohol and mercury thermometers.
E)places melting point of ice at 32° and boiling at 212°.
A)is used exclusively in the United States.
B)places melting point of ice at 0° and was formerly called centigrade.
C)was developed by the British physicist Lord Kelvin.
D)was developed by Fahrenheit,who also developed the alcohol and mercury thermometers.
E)places melting point of ice at 32° and boiling at 212°.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
![<strong> Global latent heat of evaporation.Annual energy dissipated as the latent heat of evaporation (LE)at the surface.Note the highest values over areas with high sea-surface temperatures associated with warm ocean currents-the Gulf Stream off the east coast of North America and the Kuroshio off the east coast of Japan.[Adapted from M.I.Budyko,The Earth's Climate,Past and Future,© 1982 Academic Press.] On land,the highest annual values for latent heat of evaporation (LE)occur</strong> A)near the poles. B)over the subtropics. C)in the tropics. D)in the midlatitudes. E)in continental interiors.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5538/11eab6b6_9b7a_f11b_a5f2_6f71d4385b79_TB5538_00.jpg) Global latent heat of evaporation.Annual energy dissipated as the latent heat of evaporation (LE)at the surface.Note the highest values over areas with high sea-surface temperatures associated with warm ocean currents-the Gulf Stream off the east coast of North America and the Kuroshio off the east coast of Japan.[Adapted from M.I.Budyko,The Earth's Climate,Past and Future,© 1982 Academic Press.] On land,the highest annual values for latent heat of evaporation (LE)occur
Global latent heat of evaporation.Annual energy dissipated as the latent heat of evaporation (LE)at the surface.Note the highest values over areas with high sea-surface temperatures associated with warm ocean currents-the Gulf Stream off the east coast of North America and the Kuroshio off the east coast of Japan.[Adapted from M.I.Budyko,The Earth's Climate,Past and Future,© 1982 Academic Press.] On land,the highest annual values for latent heat of evaporation (LE)occurA)near the poles.
B)over the subtropics.
C)in the tropics.
D)in the midlatitudes.
E)in continental interiors.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
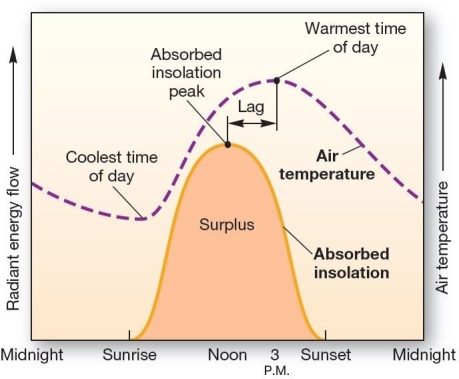 Daily radiation and temperature curves The time of maximum daily temperature occurs
Daily radiation and temperature curves The time of maximum daily temperature occursA)at the same time that maximum absorbed insolation occurs,because that is when maximum energy is available for heating the air.
B)before the time of maximum absorbed insolation,because the residual heat energy left over in the atmosphere from the previous day adds to the energy supplied by insolation.
C)before the time of maximum absorbed insolation occurs,because the thermosphere transfers heat energy to the surface during the early morning hours as the layers in the ionosphere become active.
D)after the time of maximum absorbed insolation,because an energy surplus accumulates in the atmosphere while the Sun is still high in the sky and reaches a peak in mid-afternoon.
E)after the time of maximum absorbed insolation,because the ground starts to reflect heat energy in the late afternoon,and this creates an energy surplus.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
Land surface temperature (LST)is
A)measured using a ground network of at least one station per 250,000 km2 across the globe.
B)often much cooler than air temperature due to vegetation cover.
C)highest in areas with high albedo and dense cloud cover.
D)a measure of the heating of the land surface and is distinct from air temperature.
E)typically much cooler than air temperature.
A)measured using a ground network of at least one station per 250,000 km2 across the globe.
B)often much cooler than air temperature due to vegetation cover.
C)highest in areas with high albedo and dense cloud cover.
D)a measure of the heating of the land surface and is distinct from air temperature.
E)typically much cooler than air temperature.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
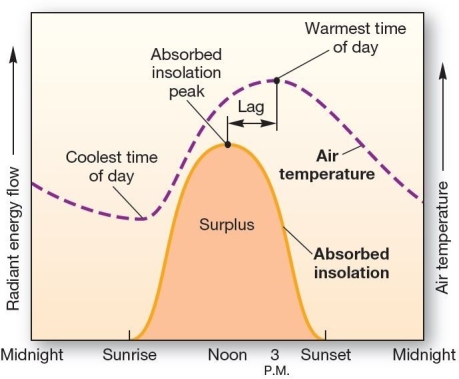 Daily radiation and temperature curves The relationship between the absorbed insolation curve and the air temperature curve on a graph of daily surface energy
Daily radiation and temperature curves The relationship between the absorbed insolation curve and the air temperature curve on a graph of daily surface energyA)exhibits a lag of several hours between the plotted lines.
B)shows little or no relationship between the two variables.
C)shows that peak temperatures occur near noon,whereas peak insolation receipt is at 3:00 or 4:00 P.M.
D)coincides at noon.
E)indicates that absorbed insolation is constant,whereas daily air temperature is not.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
![<strong> Daily radiation budget.Radiation budget on a typical July summer day at a midlatitude location (Matador in southern Saskatchewan,about 51° N).[Based on T.R.Oke,Boundary Layer Climates,© 1978 Methuen & Co.] NET R values,as illustrated for a typically summer day at a midlatitude location,are positive</strong> A)during the night when +LW is at a maximum. B)after dusk due to a lag effect of outgoing infrared radiation. C)during daylight hours,peaking just after noon with the peak of insolation. D)during the daylight hours,peaking just after sunrise. E)around midnight when +SW is the highest.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5538/11eab6b6_9b7a_ca0a_a5f2_8744973c6f00_TB5538_00.jpg) Daily radiation budget.Radiation budget on a typical July summer day at a midlatitude location (Matador in southern Saskatchewan,about 51° N).[Based on T.R.Oke,Boundary Layer Climates,© 1978 Methuen & Co.] NET R values,as illustrated for a typically summer day at a midlatitude location,are positive
Daily radiation budget.Radiation budget on a typical July summer day at a midlatitude location (Matador in southern Saskatchewan,about 51° N).[Based on T.R.Oke,Boundary Layer Climates,© 1978 Methuen & Co.] NET R values,as illustrated for a typically summer day at a midlatitude location,are positiveA)during the night when +LW is at a maximum.
B)after dusk due to a lag effect of outgoing infrared radiation.
C)during daylight hours,peaking just after noon with the peak of insolation.
D)during the daylight hours,peaking just after sunrise.
E)around midnight when +SW is the highest.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
Sensible heat transfer (H)refers to energy transfer between the air and the surface by
A)convection and conduction.
B)evaporation of water.
C)reflection of insolation.
D)ground heating.
E)latent heat of evaporation.
A)convection and conduction.
B)evaporation of water.
C)reflection of insolation.
D)ground heating.
E)latent heat of evaporation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
The science that studies the climate at or near Earth's surface is
A)astronomy.
B)meteorology.
C)micrometeorology.
D)microclimatology.
E)microastronomy.
A)astronomy.
B)meteorology.
C)micrometeorology.
D)microclimatology.
E)microastronomy.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
Net radiation (NET R)refers to
A)the net energy expended for ground heating and cooling.
B)the balance of all radiation incoming and outgoing at Earth's surface.
C)the amount of insolation coming into the surface.
D)the amount of insolation not absorbed at the surface.
E)the sum of outgoing radiation from Earth,averaged over a year.
A)the net energy expended for ground heating and cooling.
B)the balance of all radiation incoming and outgoing at Earth's surface.
C)the amount of insolation coming into the surface.
D)the amount of insolation not absorbed at the surface.
E)the sum of outgoing radiation from Earth,averaged over a year.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
Official temperatures are measured using thermometers placed in shelters that are
A)non-ventilated and black boxes,placed at ground level.
B)placed a few feet above the ground in louvered white boxes.
C)in black boxes placed in direct sunlight for maximum insolation absorption.
D)at ground level,in direct sunlight.
E)in shade or near buildings or other shelters.
A)non-ventilated and black boxes,placed at ground level.
B)placed a few feet above the ground in louvered white boxes.
C)in black boxes placed in direct sunlight for maximum insolation absorption.
D)at ground level,in direct sunlight.
E)in shade or near buildings or other shelters.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
-273°C (-459.67°F)is
A)the same as 273 Kelvin.
B)an average boiling temperature.
C)0 absolute temperature.
D)not possible on any scale.
E)freezing point of water.
A)the same as 273 Kelvin.
B)an average boiling temperature.
C)0 absolute temperature.
D)not possible on any scale.
E)freezing point of water.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
The size of one Kelvin unit is
A)twice as large as one Celsius degree.
B)the same size as one Celsius degree.
C)two times smaller than one Celsius degree.
D)the same size as one Fahrenheit degree.
E)twice as large as one Fahrenheit degree.
A)twice as large as one Celsius degree.
B)the same size as one Celsius degree.
C)two times smaller than one Celsius degree.
D)the same size as one Fahrenheit degree.
E)twice as large as one Fahrenheit degree.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
When water evaporates from a surface,which of the following occurs?
A)Energy is stored within the water.
B)Energy is released to the surface.
C)The surface is warmed.
D)Heat is transferred back and forth between the air and surface.
E)Energy flows into the ground by conduction.
A)Energy is stored within the water.
B)Energy is released to the surface.
C)The surface is warmed.
D)Heat is transferred back and forth between the air and surface.
E)Energy flows into the ground by conduction.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
Temperature is
A)a form of energy.
B)heat,as perceived by humans and other living things.
C)a function of insolation and wind speed.
D)measure of the average kinetic energy of individual molecules in matter.
E)a measure of the amount of heat in a substance.
A)a form of energy.
B)heat,as perceived by humans and other living things.
C)a function of insolation and wind speed.
D)measure of the average kinetic energy of individual molecules in matter.
E)a measure of the amount of heat in a substance.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
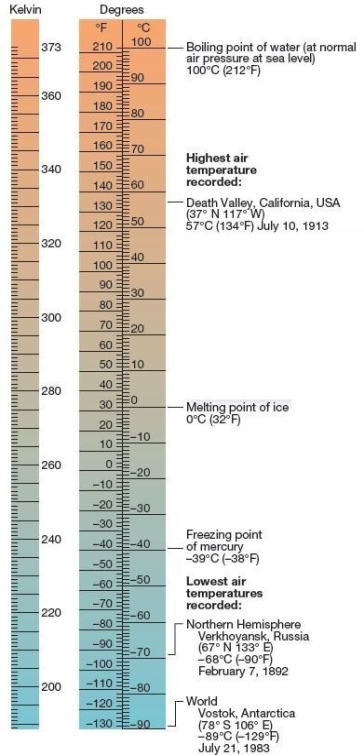 Temperature Scales The Celsius and Fahrenheit scales only coincide at
Temperature Scales The Celsius and Fahrenheit scales only coincide atA)-40°.
B)-273°.
C)0°.
D)212°.
E)10°.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
In the surface energy budget,the term "- SW" represents
A)heat.
B)insolation.
C)reflection.
D)outgoing infrared radiation.
E)NET R.
A)heat.
B)insolation.
C)reflection.
D)outgoing infrared radiation.
E)NET R.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
Which of the following is not true of solar energy?
A)In the U.S. ,the solar energy arriving every 35 minutes is equivalent to the energy produced by fossil fuels in a year.
B)It can provide both heat and electricity.
C)Photovoltaic capacity has not increased in recent years.
D)New solar cell technology makes them suitable for rooftop tiles or shingles.
E)Growth of solar energy in the U.S.has lagged behind that of Europe.
A)In the U.S. ,the solar energy arriving every 35 minutes is equivalent to the energy produced by fossil fuels in a year.
B)It can provide both heat and electricity.
C)Photovoltaic capacity has not increased in recent years.
D)New solar cell technology makes them suitable for rooftop tiles or shingles.
E)Growth of solar energy in the U.S.has lagged behind that of Europe.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
![<strong> Global latent heat of evaporation.Annual energy dissipated as the latent heat of evaporation (LE)at the surface.Note the highest values over areas with high sea-surface temperatures associated with warm ocean currents-the Gulf Stream off the east coast of North America and the Kuroshio off the east coast of Japan.[Adapted from M.I.Budyko,The Earth's Climate,Past and Future,© 1982 Academic Press.] Over the oceans,the highest annual values for latent heat of evaporation (LE)occur</strong> A)near the poles. B)over the subtropics. C)in the tropics. D)in the midlatitudes. E)on the eastern side of continents.](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5538/11eab6b6_9b7a_f11c_a5f2_07936866d5b9_TB5538_00.jpg) Global latent heat of evaporation.Annual energy dissipated as the latent heat of evaporation (LE)at the surface.Note the highest values over areas with high sea-surface temperatures associated with warm ocean currents-the Gulf Stream off the east coast of North America and the Kuroshio off the east coast of Japan.[Adapted from M.I.Budyko,The Earth's Climate,Past and Future,© 1982 Academic Press.] Over the oceans,the highest annual values for latent heat of evaporation (LE)occur
Global latent heat of evaporation.Annual energy dissipated as the latent heat of evaporation (LE)at the surface.Note the highest values over areas with high sea-surface temperatures associated with warm ocean currents-the Gulf Stream off the east coast of North America and the Kuroshio off the east coast of Japan.[Adapted from M.I.Budyko,The Earth's Climate,Past and Future,© 1982 Academic Press.] Over the oceans,the highest annual values for latent heat of evaporation (LE)occurA)near the poles.
B)over the subtropics.
C)in the tropics.
D)in the midlatitudes.
E)on the eastern side of continents.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
The temperature control that includes the heat capacity of a substance is
A)movement.
B)evaporation.
C)cloud cover.
D)specific heat.
E)latitude.
A)movement.
B)evaporation.
C)cloud cover.
D)specific heat.
E)latitude.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
The specific heat of land is than water and,therefore,land heats more than water.
A)higher;slowly
B)higher;quickly
C)lower;slowly
D)lower;quickly
E)equal;evenly
A)higher;slowly
B)higher;quickly
C)lower;slowly
D)lower;quickly
E)equal;evenly

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
The single most important control on temperature is
A)insolation.
B)altitude.
C)distribution of land and water.
D)latitude.
E)cloud cover.
A)insolation.
B)altitude.
C)distribution of land and water.
D)latitude.
E)cloud cover.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
The land-water heating difference that specifically relates to opaqueness is
A)altitude.
B)specific heat.
C)transparency.
D)evaporation.
E)movement.
A)altitude.
B)specific heat.
C)transparency.
D)evaporation.
E)movement.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
If the temperature at the surface of Earth (at sea level)is 100°F,what is the temperature at 2000 feet if the average lapse rate is 3.5°F/1000 feet?
A)93°F
B)96.5°F
C)103.5°F
D)107°F
E)89.5°F
A)93°F
B)96.5°F
C)103.5°F
D)107°F
E)89.5°F

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
Which of the following is true regarding clouds?
A)They increase temperature minimums and temperature maximums.
B)They cover about 15 percent of Earth's surface at any one time.
C)They have a moderating influence on temperatures.
D)They decrease nighttime temperatures and increase daytime temperatures.
E)They have only a negligible effect on temperature and climate.
A)They increase temperature minimums and temperature maximums.
B)They cover about 15 percent of Earth's surface at any one time.
C)They have a moderating influence on temperatures.
D)They decrease nighttime temperatures and increase daytime temperatures.
E)They have only a negligible effect on temperature and climate.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
On average,the illuminated zone in oceans is to a depth of ,but in some oceans may be as deep as .
A)20 m (66 ft);30 m (100 ft)
B)100 m (330 ft);500 m (1,640 ft)
C)60 m (200 ft);300 m (1,000 ft)
D)30 m (100 ft);900 m (3,000 ft)
E)5 m (16.4 ft. );30 m (100 ft)
A)20 m (66 ft);30 m (100 ft)
B)100 m (330 ft);500 m (1,640 ft)
C)60 m (200 ft);300 m (1,000 ft)
D)30 m (100 ft);900 m (3,000 ft)
E)5 m (16.4 ft. );30 m (100 ft)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
If the temperature at the surface of Earth (at sea level)is 40°C,what is the temperature at 2000 m if the normal lapse rate is 6.4°C/1000 m?
A)27.2°C
B)33.6°C
C)46.4°C
D)52.8°C
E)21.8°C
A)27.2°C
B)33.6°C
C)46.4°C
D)52.8°C
E)21.8°C

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
Elevation typically refers to whereas altitude refers to .
A)the height of a point on Earth's surface;the height above Earth's surface
B)the height above Earth's surface;the height of a point on Earth's surface
C)the height of a point on Earth's surface;the latitude at which a location occurs
D)Both elevation and altitude refer to the height above Earth's surface.
E)Both elevation and altitude refer to the height of a point on Earth's surface.
A)the height of a point on Earth's surface;the height above Earth's surface
B)the height above Earth's surface;the height of a point on Earth's surface
C)the height of a point on Earth's surface;the latitude at which a location occurs
D)Both elevation and altitude refer to the height above Earth's surface.
E)Both elevation and altitude refer to the height of a point on Earth's surface.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
Which of the following is true?
A)Northern Hemisphere temperatures are more strongly dominated by continentality than are Southern Hemisphere temperatures.
B)Southern Hemisphere temperatures are more strongly dominated by continentality than are Northern Hemisphere temperatures.
C)The Northern and Southern hemispheres are dominated equally by maritime influences.
D)The Northern and Southern hemispheres are dominated equally by continentality.
E)Continentality does not follow any hemispheric patterns.
A)Northern Hemisphere temperatures are more strongly dominated by continentality than are Southern Hemisphere temperatures.
B)Southern Hemisphere temperatures are more strongly dominated by continentality than are Northern Hemisphere temperatures.
C)The Northern and Southern hemispheres are dominated equally by maritime influences.
D)The Northern and Southern hemispheres are dominated equally by continentality.
E)Continentality does not follow any hemispheric patterns.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
Imagine two hypothetical cities,both located at 12° N latitude.However,one is located near sea level,while the other at an elevation of 4,000 m (13,123 ft)above sea level.Which of the following is likely true?
A)The climates of the two cities are quite similar.
B)Annual temperatures for the city at the lower elevation are lower than those at the city at the higher elevation.
C)The city at the higher elevation has extremely cold winters (similar to those at high latitudes).
D)The city at the higher elevation has average monthly and yearly temperatures lower than the city near sea level.
E)The average annual temperatures for the city at the higher elevation are higher than the city at sea level.
A)The climates of the two cities are quite similar.
B)Annual temperatures for the city at the lower elevation are lower than those at the city at the higher elevation.
C)The city at the higher elevation has extremely cold winters (similar to those at high latitudes).
D)The city at the higher elevation has average monthly and yearly temperatures lower than the city near sea level.
E)The average annual temperatures for the city at the higher elevation are higher than the city at sea level.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
Which of the following is true regarding locations at high elevations?
A)Higher elevations experience higher temperatures during the day because they are closer to the Sun.
B)Higher elevations experience lower average temperatures during both day and night.
C)The density of air increases with increasing elevation creating overall warmer temperatures.
D)Temperatures at night are greater,though lower in the day,at higher elevations.
E)Temperatures increase with altitude and,therefore,are higher at higher elevations.
A)Higher elevations experience higher temperatures during the day because they are closer to the Sun.
B)Higher elevations experience lower average temperatures during both day and night.
C)The density of air increases with increasing elevation creating overall warmer temperatures.
D)Temperatures at night are greater,though lower in the day,at higher elevations.
E)Temperatures increase with altitude and,therefore,are higher at higher elevations.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
How does evaporation affect land-water heating differences?
A)Evaporation tends to increase temperatures over land.
B)Evaporation tends to lower temperatures more over water bodies than over land.
C)Evaporation tends to increase the temperature over water.
D)Evaporation affects land more than ocean surfaces.
E)Evaporation affects the temperature of land surfaces and water bodies the same amount.
A)Evaporation tends to increase temperatures over land.
B)Evaporation tends to lower temperatures more over water bodies than over land.
C)Evaporation tends to increase the temperature over water.
D)Evaporation affects land more than ocean surfaces.
E)Evaporation affects the temperature of land surfaces and water bodies the same amount.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
An estimated percent of all evaporation on Earth is from oceans.
A)22
B)37
C)84
D)76
E)5
A)22
B)37
C)84
D)76
E)5

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
refers to the greater range between maximum and minimum temperatures that occurs in inland areas distant from large bodies of water.
A)The maritime effect
B)Specific heat
C)Heat dome
D)Continentality
E)Opacity
A)The maritime effect
B)Specific heat
C)Heat dome
D)Continentality
E)Opacity

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
The principal controls and influences of temperature patterns include
A)Earth's tilt,rotation,revolution,and sphericity.
B)latitude,altitude,land-water heating differences,cloud cover,and ocean currents.
C)the distance of the Earth from the sun and sunspot activity.
D)the seasons and human activity.
E)latitude and elevation,only.
A)Earth's tilt,rotation,revolution,and sphericity.
B)latitude,altitude,land-water heating differences,cloud cover,and ocean currents.
C)the distance of the Earth from the sun and sunspot activity.
D)the seasons and human activity.
E)latitude and elevation,only.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
During summer,cities located near the coast are than those in the interior at the same latitude,while in the winter they are .
A)warmer;warmer
B)warmer;cooler
C)cooler;warmer
D)cooler;cooler
E)much warmer;much cooler
A)warmer;warmer
B)warmer;cooler
C)cooler;warmer
D)cooler;cooler
E)much warmer;much cooler

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
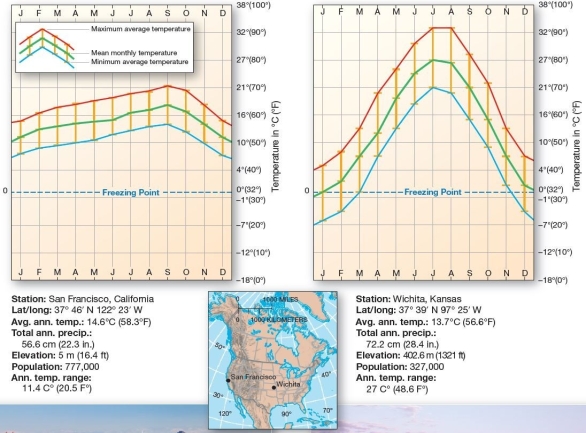 Marine and continental cities-United States San Francisco,CA and Wichita,KS are located at approximately the same latitude.Which of the following is true?
Marine and continental cities-United States San Francisco,CA and Wichita,KS are located at approximately the same latitude.Which of the following is true?A)San Francisco experiences several months with average temperatures below the freezing point.
B)Annual temperature ranges in Wichita are greater than those in San Francisco.
C)Summer temperatures in San Francisco far exceed those of Wichita.
D)Minimum average temperatures in Wichita are consistently lowers than those in San Francisco.
E)On average,December temperatures in San Francisco tend to be lower than those in Wichita.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
During the day,clouds insolation,lowering daily maximum temperatures;at night,clouds longwave energy,thereby raising minimum nighttime temperatures.
A)absorb;reflect
B)scatter;refract
C)reflect;absorb and counterradiate
D)reflect;scatter
E)scatter;absorb and counterradiate
A)absorb;reflect
B)scatter;refract
C)reflect;absorb and counterradiate
D)reflect;scatter
E)scatter;absorb and counterradiate

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
Trondheim,Norway is located at approximately 63° N.Despite its high latitude,it has a relatively moderate annual temperature regime.What likely accounts for this moderation?
A)Trondheim's high degree of continentality.
B)Trondheim's maritime location.
C)The urban heat island of Trondheim.
D)Thick cloud cover in Trondheim traps in longwave radiation.
E)Influence of the subpolar low pressure system.
A)Trondheim's high degree of continentality.
B)Trondheim's maritime location.
C)The urban heat island of Trondheim.
D)Thick cloud cover in Trondheim traps in longwave radiation.
E)Influence of the subpolar low pressure system.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 120 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








