Deck 34: Electromagnetic Fields and Waves
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/52
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 34: Electromagnetic Fields and Waves
1
The magnetic field of an electromagnetic wave has a peak value of 5.0 × 10-10 T. What is the intensity of the wave? (c = 3.0 x 108 m/s, c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A, ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)
A) 1.0 × 10-13 W/m2
B) 1.5 × 10-5 W/m2
C) 3.0 × 10-5 W/m2
D) 2.0 × 10-13 W/m2
E) 7.5 × 105 W/m2
A) 1.0 × 10-13 W/m2
B) 1.5 × 10-5 W/m2
C) 3.0 × 10-5 W/m2
D) 2.0 × 10-13 W/m2
E) 7.5 × 105 W/m2
3.0 × 10-5 W/m2
2
An electromagnetic wave is propagating towards the west. At a certain moment the direction of the magnetic field vector associated with this wave points vertically up. The direction of the electric field vector of this wave is
A) horizontal and pointing south.
B) vertical and pointing down.
C) horizontal and pointing north.
D) vertical and pointing up.
E) horizontal and pointing east.
A) horizontal and pointing south.
B) vertical and pointing down.
C) horizontal and pointing north.
D) vertical and pointing up.
E) horizontal and pointing east.
horizontal and pointing south.
3
The magnitude of the Poynting vector of a planar electromagnetic wave has an average value of 0.939 W/m2. The wave is incident upon a rectangular area, 1.5 m by 2.0 m, at right angles. How much total electromagnetic energy falls on the area during 1.0 minute? (c = 3.0 x 108 m/s, μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A, ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)
A) 170 J
B) 210 J
C) 250 J
D) 300 J
E) 340 J
A) 170 J
B) 210 J
C) 250 J
D) 300 J
E) 340 J
170 J
4
An electromagnetic wave propagates along the +y direction as shown in the figure. If the electric field at the origin is along the +z direction, what is the direction of the magnetic field? 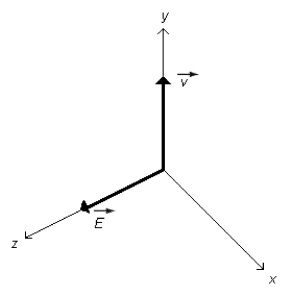
A) +z
B) -z
C) +y
D) +x
E) -x

A) +z
B) -z
C) +y
D) +x
E) -x

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 52 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
The magnitude of the magnetic field at point P for a certain electromagnetic wave is 2.12 μT. What is the magnitude of the electric field for that wave at P? (c = 3.0 x 108 m/s)
A) 636 N/C
B) 745 N/C
C) 5.23 µN/C
D) 6.36 µN/C
E) 7.45 µN/C
A) 636 N/C
B) 745 N/C
C) 5.23 µN/C
D) 6.36 µN/C
E) 7.45 µN/C

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 52 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
The magnitude of the electric field at a point P for a certain electromagnetic wave is 570 N/C. What is the magnitude of the magnetic field for that wave at P? (c = 3.0 x 108 m/s)
A) 2.91 µT
B) 1.90 µT
C) 1.10 µT
D) 1.41 µT
E) 2.41 µT
A) 2.91 µT
B) 1.90 µT
C) 1.10 µT
D) 1.41 µT
E) 2.41 µT

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 52 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
The y component of the electric field of an electromagnetic wave traveling in the +x direction through vacuum obeys the equation Ey = (375 N/C) cos[kx - (2.20 × 1014 rad/s)t]. What is the wavelength of this electromagnetic wave? (c = 3.0 x 108 m/s)
A) 0.272 µm
B) 1.36 µm
C) 2.72 µm
D) 8.57 µm
E) 17.1 µm
A) 0.272 µm
B) 1.36 µm
C) 2.72 µm
D) 8.57 µm
E) 17.1 µm

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 52 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
When an electromagnetic wave falls on a white, perfectly reflecting surface, it exerts a force F on that surface. If the surface is now painted a perfectly absorbing black, what will be the force that the same wave will exert on the surface?
A) 4F
B) 2F
C) F
D) F/2
E) F/4
A) 4F
B) 2F
C) F
D) F/2
E) F/4

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 52 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
A planar electromagnetic wave is propagating in the +x direction. At a certain point P and at a given instant, the electric field of the wave is given by  = (0.082 V/m)
= (0.082 V/m) 
. What is the Poynting vector at the point P at that instant? (c = 3.0 x 108 m/s, μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A, ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)
A) 18 µW/m2
B) -18 µW/m2
C) 9.0 µW/m2
D) -9.0 µW/m2
E) -18 µW/m2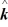
 = (0.082 V/m)
= (0.082 V/m) 
. What is the Poynting vector at the point P at that instant? (c = 3.0 x 108 m/s, μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A, ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)
A) 18 µW/m2

B) -18 µW/m2

C) 9.0 µW/m2

D) -9.0 µW/m2

E) -18 µW/m2

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 52 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
The energy per unit volume in an electromagnetic wave is
A) equally divided between the electric and magnetic fields.
B) mostly in the electric field.
C) mostly in the magnetic field.
D) all in the electric field.
E) all in the magnetic field.
A) equally divided between the electric and magnetic fields.
B) mostly in the electric field.
C) mostly in the magnetic field.
D) all in the electric field.
E) all in the magnetic field.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 52 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
A capacitor is hooked up to a resistor and an AC voltage source as shown in the figure. The output of the source is given by V(t) = V0 sin ωt. The plates of the capacitor are disks of radius R. Point P is directly between the two plates, equidistant from them and a distance R/2 from the center axis. At point P 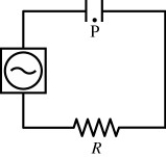
A) there is no magnetic field because there is no charge moving between the plates.
B) there is a constant magnetic field.
C) there is a time-varying magnetic field.

A) there is no magnetic field because there is no charge moving between the plates.
B) there is a constant magnetic field.
C) there is a time-varying magnetic field.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 52 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Given that the wavelengths of visible light range from 400 nm to 700 nm, what is the highest frequency of visible light? (c = 3.0 x 108 m/s)
A) 3.1 × 108 Hz
B) 7.5 × 1014 Hz
C) 2.3 × 1020 Hz
D) 4.3 × 1014 Hz
E) 5.0 × 108 Hz
A) 3.1 × 108 Hz
B) 7.5 × 1014 Hz
C) 2.3 × 1020 Hz
D) 4.3 × 1014 Hz
E) 5.0 × 108 Hz

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 52 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
If the electric field and magnetic field of an electromagnetic wave are given by E = E0 sin(kx - ωt) and B = B0 sin(kx - ωt), and if the value of E0 is 51 µV/m, what is the value of B0? (c = 3.0 x 108 m/s)
A) 1.7 × 1014 T
B) 1.7 × 103 T
C) 1.7 × 10-14 T
D) 1.7 × 104 T
E) 1.7 × 10-13 T
A) 1.7 × 1014 T
B) 1.7 × 103 T
C) 1.7 × 10-14 T
D) 1.7 × 104 T
E) 1.7 × 10-13 T

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 52 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
The y-component of the electric field of an electromagnetic wave traveling in the +x direction through vacuum obeys the equation Ey = (375 N/C) cos[kx - (2.20 × 1014 rad/s)t]. (c = 3.0 x 108 m/s)
(a) What is the largest that the x-component of the wave can be?
(b) What is the largest that the z-component of the wave can be?
(a) What is the largest that the x-component of the wave can be?
(b) What is the largest that the z-component of the wave can be?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 52 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
A planar electromagnetic wave is propagating in the +x direction. At a certain point P and at a given instant, the electric field of the wave is given by 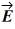 = (0.082 V/m)
= (0.082 V/m) 
. What is the magnetic vector of the wave at the point P at that instant? (c = 3.0 x 108 m/s)
A) 0.27 nT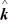
B) -0.27 nT
C) 0.27 nT
D) 6.8 nT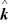
E) -6.8 nT
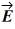 = (0.082 V/m)
= (0.082 V/m) 
. What is the magnetic vector of the wave at the point P at that instant? (c = 3.0 x 108 m/s)
A) 0.27 nT
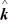
B) -0.27 nT

C) 0.27 nT

D) 6.8 nT
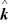
E) -6.8 nT


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 52 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
If the magnetic field of an electromagnetic wave is in the +x-direction and the electric field of the wave is in the +y-direction, the wave is traveling in the
A) xy-plane.
B) +z-direction.
C) -z-direction.
D) -x-direction.
E) -y-direction.
A) xy-plane.
B) +z-direction.
C) -z-direction.
D) -x-direction.
E) -y-direction.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 52 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
The magnitude of the Poynting vector of a planar electromagnetic wave has an average value of 0.724 W/m2. What is the maximum value of the magnetic field in the wave? (c = 3.0 x 108 m/s, μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A, ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)
A) 77.9 nT
B) 55.1 nT
C) 38.9 nT
D) 108 nT
E) 156 nT
A) 77.9 nT
B) 55.1 nT
C) 38.9 nT
D) 108 nT
E) 156 nT

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 52 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
If an electromagnetic wave has components Ey = E0 sin(kx - ωt) and Bz = B0 sin(kx - ωt), in what direction is it traveling?
A) -x
B) +x
C) +y
D) -y
E) +z
A) -x
B) +x
C) +y
D) -y
E) +z

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 52 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
In an electromagnetic wave, the electric and magnetic fields are oriented such that they are
A) parallel to one another and perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation.
B) parallel to one another and parallel to the direction of wave propagation.
C) perpendicular to one another and perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation.
D) perpendicular to one another and parallel to the direction of wave propagation.
A) parallel to one another and perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation.
B) parallel to one another and parallel to the direction of wave propagation.
C) perpendicular to one another and perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation.
D) perpendicular to one another and parallel to the direction of wave propagation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 52 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
If the z-component of the magnetic field of an electromagnetic wave traveling in the +x direction through vacuum obeys the equation Bz(x, t) = (1.25 μT) cos[(3800 m-1)x - (1.14 × 10-12 rad/s)t], what is the largest that the y component of the electric field can be? (c = 3.0 x 108 m/s)
A) 375 N/C
B) 4.17 × 10-15 N/C
C) 3.75 × 108 N/C
D) 4.17 × 10-9 N/C
E) 1.25 × 106 N/C
A) 375 N/C
B) 4.17 × 10-15 N/C
C) 3.75 × 108 N/C
D) 4.17 × 10-9 N/C
E) 1.25 × 106 N/C

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 52 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
A microwave oven operates with sinusoidal microwaves at a frequency of 2400 MHz. The height of the oven cavity is 25 cm and the base measures 30 cm by 30 cm. Assume that microwave energy is generated uniformly on the upper surface of the cavity and propagates directly downward toward the base. The base is lined with a material that completely absorbs microwave energy. The total microwave energy content of the cavity is 0.50 µJ. What is the power output of the oven? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A, ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)
A) 0.50 kW
B) 0.55 kW
C) 0.60 kW
D) 0.65 kW
E) 0.70 kW
A) 0.50 kW
B) 0.55 kW
C) 0.60 kW
D) 0.65 kW
E) 0.70 kW

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 52 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
A sinusoidal electromagnetic wave in vacuum delivers energy at an average rate of 5.00 µW/m2. What are the amplitudes of the electric and magnetic fields of this wave? (c = 3.0 x 108 m/s, μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A, ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 52 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
If the intensity of an electromagnetic wave is 80 MW/m2, what is the amplitude of the magnetic field of this wave? (c = 3.0 x 108 m/s, μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A, ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)
A) 0.82 mT
B) 0.33 µT
C) 10 T
D) 14 T
E) 0.58 mT
A) 0.82 mT
B) 0.33 µT
C) 10 T
D) 14 T
E) 0.58 mT

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 52 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
An 800-kHz radio signal is detected at a point 4.5 km distant from a transmitter tower. The electric field amplitude of the signal at that point is 0.63 V/m. Assume that the signal power is radiated uniformly in all directions and that radio waves incident upon the ground are completely absorbed. What is the magnetic field amplitude of the signal at that point? (c = 3.0 x 108 m/s, μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A, ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)
A) 2.1 nT
B) 1.7 nT
C) 1.3 nT
D) 2.5 nT
E) 2.9 nT
A) 2.1 nT
B) 1.7 nT
C) 1.3 nT
D) 2.5 nT
E) 2.9 nT

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 52 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
A laser with a power of 1.0 mW has a beam radius of 1.0 mm. What is the peak value of the electric field in that beam? (c = 3.0 x 108 m/s, μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A, ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)
A) 490 V/m
B) 840 V/m
C) 65 V/m
D) 120 V/m
E) 22 V/m
A) 490 V/m
B) 840 V/m
C) 65 V/m
D) 120 V/m
E) 22 V/m

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 52 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
A microwave oven operates with sinusoidal microwaves at a frequency of 2400 MHz. The height of the oven cavity is 25 cm and the base measures 30 cm by 30 cm. Assume that microwave energy is generated uniformly on the upper surface of the cavity and propagates directly downward toward the base. The base is lined with a material that completely absorbs microwave energy. The total microwave energy content of the cavity is 0.50 µJ. What is the amplitude of the electric field? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A, ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)
A) 1600 V/m
B) 1900 V/m
C) 2200 V/m
D) 2500 V/m
E) 2800 V/m
A) 1600 V/m
B) 1900 V/m
C) 2200 V/m
D) 2500 V/m
E) 2800 V/m

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 52 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
Near the earth the intensity of radiation from the sun is 1.35 kW/m2. What volume of space in this region contains 1.0 J of electromagnetic energy? (c = 3.0 x 108 m/s, μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A, ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)
A) 4.5 x 10-6 m3
B) 3300 m3
C) 7.4 x 10-4 m3
D) 1400 m3
E) 220,000 m3
A) 4.5 x 10-6 m3
B) 3300 m3
C) 7.4 x 10-4 m3
D) 1400 m3
E) 220,000 m3

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 52 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
An 800-kHz radio signal is detected at a point 8.5 km distant from a transmitter tower. The electric field amplitude of the signal at that point is 0.90 V/m. Assume that the signal power is radiated uniformly in all directions and that radio waves incident upon the ground are completely absorbed. What is the average electromagnetic energy density at that point? (c = 3.0 x 108 m/s, μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A, ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)
A) 3.6 pJ/m3
B) 5.1 pJ/m3
C) 7.2 pJ/m3
D) 10 pJ/m3
E) 14 pJ/m3
A) 3.6 pJ/m3
B) 5.1 pJ/m3
C) 7.2 pJ/m3
D) 10 pJ/m3
E) 14 pJ/m3

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 52 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
The intensity of solar radiation near the earth is 1.4 kW/m2. What force is exerted by solar radiation impinging normally on a 5.0 m2 perfectly reflecting panel of an artificial satellite orbiting the earth?
(c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A, ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)
A) 14 kN
B) 94 µN
C) 140 µN
D) 23 µN
E) 47 µN
(c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A, ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)
A) 14 kN
B) 94 µN
C) 140 µN
D) 23 µN
E) 47 µN

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 52 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
A microwave oven operates with sinusoidal microwaves at a frequency of 2400 MHz. The height of the oven cavity is 25 cm and the base measures 30 cm by 30 cm. Assume that microwave energy is generated uniformly on the upper surface of the cavity and propagates directly downward toward the base. The base is lined with a material that completely absorbs microwave energy. The total microwave energy content of the cavity is 0.50 µJ. What is the intensity of the microwave beam? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A, ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)
A) 5.2 kW/m2
B) 5.7 kW/m2
C) 6.2 kW/m2
D) 6.7 kW/m2
E) 7.2 kW/m2
A) 5.2 kW/m2
B) 5.7 kW/m2
C) 6.2 kW/m2
D) 6.7 kW/m2
E) 7.2 kW/m2

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 52 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
The average intensity of the sunlight in Miami, Florida, is 1.04 kW/m2. For surfaces on which the light is all absorbed, what is the average value of the radiation pressure due to this sunlight in Miami?
(c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A, ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)
A) 2.28 µPa
B) 1.73 µPa
C) 6.93 µPa
D) 3.47 µPa
E) 9.78 µPa
(c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A, ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)
A) 2.28 µPa
B) 1.73 µPa
C) 6.93 µPa
D) 3.47 µPa
E) 9.78 µPa

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 52 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
28) A sinusoidal electromagnetic wave is propagating in vacuum. At a given point P and at a particular time, the electric field is in the +x direction and the magnetic field is in the -y direction.
(a) What is the direction of propagation of the wave?
(b) If the intensity of the wave at point P is 0.36 W/m2, what is the electric field amplitude at that point? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A, ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)
(a) What is the direction of propagation of the wave?
(b) If the intensity of the wave at point P is 0.36 W/m2, what is the electric field amplitude at that point? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A, ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 52 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
A very small source of light that radiates uniformly in all directions produces an electric field amplitude of 2.96 V/m at a point 33.0 m from the source. What is the power output from the source?
(c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A, ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)
(c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A, ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 52 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
A 7.5 × 1014 Hz laser emits a 7.7-μs pulse, 5.0 mm in diameter, with a beam energy density of 0.51 J/m3. What is the amplitude of the electric field of the emitted waves? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A, ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)
A) 340 kV/m
B) 480 kV/m
C) 240 kV/m
D) 150 kV/m
E) 120 kV/m
A) 340 kV/m
B) 480 kV/m
C) 240 kV/m
D) 150 kV/m
E) 120 kV/m

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 52 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
If a beam of electromagnetic radiation has an intensity of 120 W/m2, what is the maximum value of the electric field? (c = 3.0 x 108 m/s, μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A, ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)
A) 1.5 kV/m
B) 1.0 µT
C) 1.0 µV/m
D) 0.30 kV/m
E) 0.0032 V/m
A) 1.5 kV/m
B) 1.0 µT
C) 1.0 µV/m
D) 0.30 kV/m
E) 0.0032 V/m

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 52 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
A radiometer has two square vanes (each measuring 1.0 cm by 1.0 cm), attached to a light horizontal cross arm, and pivoted about a vertical axis through the center, as shown in the figure. The center of each vane is 6.0 cm from the axis. One vane is silvered and it reflects all radiant energy incident upon it. The other vane is blackened and it absorbs all incident radiant energy. An electromagnetic wave with an intensity of 0.30 kW/m2 is incident normally upon the vanes. What is the electromagnetic power absorbed by the blackened vane? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A, ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2) 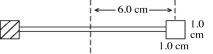
A) 0.030 W
B) 0.040 W
C) 0.050 W
D) 0.060 W
E) 0.090 W

A) 0.030 W
B) 0.040 W
C) 0.050 W
D) 0.060 W
E) 0.090 W

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 52 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
An electromagnetic wave has a peak electric field of 3.0 kV/m. What is the intensity of the wave? (c = 3.0 x 108 m/s, μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A, ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)
A) 24 kW/m2
B) 12 kW/m2
C) 8.0 kW/m2
D) 4.0 kW/m2
A) 24 kW/m2
B) 12 kW/m2
C) 8.0 kW/m2
D) 4.0 kW/m2

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 52 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
The total electromagnetic power emitted by the sun is 3.8 × 1026 W. What is the radiation pressure on a totally absorbing satellite at the orbit of Mercury, which has an orbital radius of 5.8 × 1010 m?
(c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A, ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)
A) 30 µPa
B) 0.30 µPa
C) 0.030 µPa
D) 300 µPa
E) 3.0 µPa
(c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A, ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)
A) 30 µPa
B) 0.30 µPa
C) 0.030 µPa
D) 300 µPa
E) 3.0 µPa

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 52 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
An 800-kHz radio signal is detected at a point 2.7 km distant from a transmitter tower. The electric field amplitude of the signal at that point is 0.36 V/m. Assume that the signal power is radiated uniformly in all directions and that radio waves incident upon the ground are completely absorbed. What is the intensity of the radio signal at that point? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A, ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)
A) 170 µW/m2
B) 240 µW/m2
C) 340 µW/m2
D) 120 µW/m2
E) 86 µW/m2
A) 170 µW/m2
B) 240 µW/m2
C) 340 µW/m2
D) 120 µW/m2
E) 86 µW/m2

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 52 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
An 800-kHz radio signal is detected at a point 9.1 km distant from a transmitter tower. The electric field amplitude of the signal at that point is 0.440 V/m. Assume that the signal power is radiated uniformly in all directions and that radio waves incident upon the ground are completely absorbed. What is the average total power radiated by the transmitter? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A, ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)
A) 0.27 MW
B) 0.32 MW
C) 0.38 MW
D) 0.45 MW
E) 0.50 MW
A) 0.27 MW
B) 0.32 MW
C) 0.38 MW
D) 0.45 MW
E) 0.50 MW

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 52 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
The following are positioned in sequence: A source of a beam of natural light of intensity I0; three ideal polarizers A, B, and C; and an observer. Polarizer axis angles are measured clockwise from the vertical, from the perspective of the observer. The axis angle of polarizer A is set at 0° (vertical), and the axis angle of polarizer C is set at 50°. Polarizer B is set so that the beam intensity is zero at the observer. Which of the following pairs of angles are possible axis angle settings of polarizer B?
A) 40° and 90°
B) 40° and 130°
C) 40° and 140°
D) 90° and 130°
E) 90° and 140°
A) 40° and 90°
B) 40° and 130°
C) 40° and 140°
D) 90° and 130°
E) 90° and 140°

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 52 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
A radiometer has two square vanes (1.0 cm by 1.0 cm), attached to a light horizontal cross arm, and pivoted about a vertical axis through the center, as shown in the figure. The center of each vane is 6.0 cm from the axis. One vane is silvered and it reflects all radiant energy incident upon it. The other vane is blackened and it absorbs all incident radiant energy. An electromagnetic wave with an intensity of 0.30 kW/m2 is incident normally upon the vanes. What is the torque due to radiation pressure on the vane assembly about the vertical axis? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A, ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2) 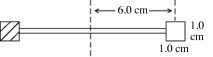
A) 2.4 × 10-12 N ∙ m
B) 6.0 × 10-12 N ∙ m
C) 1.2 × 10-11 N ∙ m
D) 1.8 × 10-11 N ∙ m
E) 2.4 × 10-11 N ∙ m

A) 2.4 × 10-12 N ∙ m
B) 6.0 × 10-12 N ∙ m
C) 1.2 × 10-11 N ∙ m
D) 1.8 × 10-11 N ∙ m
E) 2.4 × 10-11 N ∙ m

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 52 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
A microwave oven operates with sinusoidal microwaves at a frequency of 2400 MHz. The height of the oven cavity is 25 cm and the base measures 30 cm by 30 cm. Assume that microwave energy is generated uniformly on the upper surface of the cavity and propagates directly downward toward the base. The base is lined with a material that completely absorbs microwave energy. The total microwave energy content of the cavity is 0.50 µJ. What magnitude force does the microwave beam exert on the base of the oven? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A, ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)
A) 1.6 µN
B) 2.0 µN
C) 2.5 µN
D) 3.0 µN
E) 3.5 µN
A) 1.6 µN
B) 2.0 µN
C) 2.5 µN
D) 3.0 µN
E) 3.5 µN

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 52 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
A radiometer has two square vanes (1.0 cm by 1.0 cm), attached to a light horizontal cross arm, and pivoted about a vertical axis through the center, as shown in the figure. The center of each vane is 6.0 cm from the axis. One vane is silvered and it reflects all radiant energy incident upon it. The other vane is blackened and it absorbs all incident radiant energy. An electromagnetic wave with an intensity of 0.30 kW/m2 is incident normally upon the vanes. What is the radiation pressure on the blackened vane? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A, ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2) 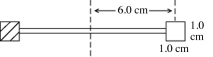
A) 1.0 × 10-10 Pa
B) 1.0 × 10-9 Pa
C) 1.0 × 10-8 Pa
D) 1.0 × 10-7 Pa
E) 1.0 × 10-6 Pa

A) 1.0 × 10-10 Pa
B) 1.0 × 10-9 Pa
C) 1.0 × 10-8 Pa
D) 1.0 × 10-7 Pa
E) 1.0 × 10-6 Pa

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 52 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
A totally absorbing surface having an area of 7.7 cm2 faces a small source of sinusoidal electromagnetic radiation that is 2.4 m away. At the surface, the electric field amplitude of the radiation is 84 V/m. (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A, ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)
(a) What is the radiation pressure exerted on the surface?
(b) What is the total power output of the source, if it is assumed to radiate uniformly in all directions?
(a) What is the radiation pressure exerted on the surface?
(b) What is the total power output of the source, if it is assumed to radiate uniformly in all directions?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 52 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
A 22.0-kg mirror with a surface area of 1.0 m2 and a 98% reflectivity is bombarded by light of average intensity 770.0 W/m2 at an angle of 30.0∘ to the normal of its surface. If the light has a duration of 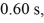 how much does the velocity of the mirror change during that time? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A, ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)
how much does the velocity of the mirror change during that time? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A, ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)
A) 120 nm/s
B) 4.2 nm/s
C) 3.6 nm/s
D) 2.1 nm/s
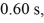 how much does the velocity of the mirror change during that time? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A, ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)
how much does the velocity of the mirror change during that time? (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A, ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)A) 120 nm/s
B) 4.2 nm/s
C) 3.6 nm/s
D) 2.1 nm/s

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 52 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
A laser beam has a wavelength of 633 nm and a power of 0.500 mW spread uniformly over a circle 1.20 mm in diameter. This beam falls perpendicularly on a perfectly reflecting piece of paper having twice the diameter of the laser beam and a mass of 1.50 mg. (c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, μ0 = 4π × 10-7 T ∙ m/A, ε0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ∙ m2)
(a) What are the amplitudes of the electric and magnetic fields in this laser beam?
(b) What acceleration does the laser beam give to the paper?
(a) What are the amplitudes of the electric and magnetic fields in this laser beam?
(b) What acceleration does the laser beam give to the paper?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 52 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
Unpolarized light passes through three polarizing filters. The first one is oriented with a horizontal transmission axis, the second filter has its transmission axis 25.7° from the horizontal, and the third one has a vertical transmission axis. What percent of the light gets through this combination of filters?
A) 7.6%
B) 92.4%
C) 50.0%
D) 0.00%
A) 7.6%
B) 92.4%
C) 50.0%
D) 0.00%

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 52 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
Unpolarized light is incident upon two polarization filters that do not have their transmission axes aligned. If 18% of the light passes through this combination of filters, what is the angle between the transmission axes of the filters?
A) 53°
B) 73°
C) 85°
D) 80°
A) 53°
B) 73°
C) 85°
D) 80°

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 52 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
Light of intensity I0 and polarized horizontally passes through three polarizes. The first and third polarizing axes are horizontal, but the second one is oriented 20.0° to the horizontal. In terms of I0, what is the intensity of the light that passes through the set of polarizers?
A) 0.780I0
B) 0.180I0
C) 0.442I0
D) 0.883I0
A) 0.780I0
B) 0.180I0
C) 0.442I0
D) 0.883I0

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 52 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
In the figure, the orientation of the transmission axis for each of three polarizing sheets is labeled relative to the vertical direction. A beam of light, polarized in the vertical direction, is incident on the first polarized with an intensity of 1000 W/m2. What is the intensity of the beam after it has passed through the three polarizing sheets when θ1 = 30°, θ2 = 30° and θ3 =60°? 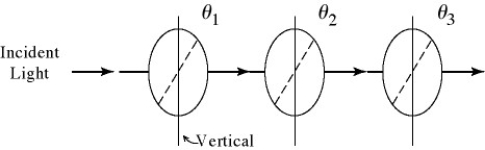
A) 141 W/m2
B) 316 W/m2
C) 433 W/m2
D) 563 W/m2
E) 188 W/m2

A) 141 W/m2
B) 316 W/m2
C) 433 W/m2
D) 563 W/m2
E) 188 W/m2

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 52 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
Polarized light passes through a polarizer. If the electric vector of the polarized light is horizontal what, in terms of the initial intensity I0, is the intensity of the light that passes through a polarizer if the polarizer is tilted 22.5° from the horizontal?
A) 0.854I0
B) 0.147I0
C) 0.191I0
D) 0.011I0
A) 0.854I0
B) 0.147I0
C) 0.191I0
D) 0.011I0

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 52 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








