Deck 6: The Supply Curve and the Behavior of Firms
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/182
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 6: The Supply Curve and the Behavior of Firms
1
A competitive market is
A) one in which firms cannot change output levels.
B) any market with several firms in it.
C) a market with a single firm.
D) one in which a single firm cannot influence market price.
E) one in which consumers compete to buy goods and services.
A) one in which firms cannot change output levels.
B) any market with several firms in it.
C) a market with a single firm.
D) one in which a single firm cannot influence market price.
E) one in which consumers compete to buy goods and services.
one in which a single firm cannot influence market price.
2
The main advantage of a corporation over other types of firms is that owners also manage the firm.
False
3
In the pumpkin-growing firm example in the text, land is a fixed factor because
A) it is a physical factor of production.
B) the firm produces a single product.
C) it cannot be varied during the season.
D) it has no close substitutes.
E) the firm is a price-taker.
A) it is a physical factor of production.
B) the firm produces a single product.
C) it cannot be varied during the season.
D) it has no close substitutes.
E) the firm is a price-taker.
it cannot be varied during the season.
4
The owner often also acts as the manager in
A) sole proprietorships.
B) all businesses.
C) corporations.
D) nonprofit firms.
E) government enterprises.
A) sole proprietorships.
B) all businesses.
C) corporations.
D) nonprofit firms.
E) government enterprises.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
A price-taking firm cannot affect its own output price because
A) price is determined by consumers, not producers.
B) market demand is perfectly elastic; that is, even a tiny increase in price results in zero quantity demanded.
C) it is only one firm among many, so the price is determined in the market as a whole.
D) consumer preferences dictate a single price in a competitive market.
E) of government statutes, such as price floors and price ceilings.
A) price is determined by consumers, not producers.
B) market demand is perfectly elastic; that is, even a tiny increase in price results in zero quantity demanded.
C) it is only one firm among many, so the price is determined in the market as a whole.
D) consumer preferences dictate a single price in a competitive market.
E) of government statutes, such as price floors and price ceilings.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Separation of ownership from control is most commonly found in a
A) sole proprietorship.
B) partnership.
C) corporation.
D) nonprofit firm.
E) consortium.
A) sole proprietorship.
B) partnership.
C) corporation.
D) nonprofit firm.
E) consortium.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
A variable factor is the type of input that varies with a firm's output level.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
A firm is one of the terms for a business organization.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
Stock shares are issued by
A) sole proprietorships.
B) partnerships.
C) corporations.
D) nonprofit firms.
E) government enterprises.
A) sole proprietorships.
B) partnerships.
C) corporations.
D) nonprofit firms.
E) government enterprises.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
All types of firms suffer from managerial conflicts.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
A corporation differs from other forms of businesses because it
A) is required to own a seat on a stock exchange.
B) has a lower debt ratio.
C) has no tax liability.
D) is characterized by limited profits.
E) is owned by people who enjoy limited liability.
A) is required to own a seat on a stock exchange.
B) has a lower debt ratio.
C) has no tax liability.
D) is characterized by limited profits.
E) is owned by people who enjoy limited liability.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
In the pumpkin-growing firm example in the text, the firm is a price-taker because
A) the firm does not have the ability to charge whatever price it wants to charge.
B) the firm is not a profit-maximizing firm.
C) price setting is too complicated for an individual firm.
D) the market for pumpkins is a competitive market.
E) it faces no demand.
A) the firm does not have the ability to charge whatever price it wants to charge.
B) the firm is not a profit-maximizing firm.
C) price setting is too complicated for an individual firm.
D) the market for pumpkins is a competitive market.
E) it faces no demand.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Land is commonly considered a fixed factor of production.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Most firms in the United States are sole proprietorships.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
The three basic types of businesses in the United States are
A) enterprises, partnerships, and corporations.
B) partnerships, multinationals, and corporations.
C) partnerships, firms, and sole proprietorships.
D) corporations, households, and sole proprietorships.
E) corporations, sole proprietorships, and partnerships.
A) enterprises, partnerships, and corporations.
B) partnerships, multinationals, and corporations.
C) partnerships, firms, and sole proprietorships.
D) corporations, households, and sole proprietorships.
E) corporations, sole proprietorships, and partnerships.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
A firm is a(n)
A) organization formed to save on income taxes.
B) organization that produces goods and services.
C) entity that produces only services.
D) required organization mandated by government for tax purposes.
E) law representative for small businesses.
A) organization formed to save on income taxes.
B) organization that produces goods and services.
C) entity that produces only services.
D) required organization mandated by government for tax purposes.
E) law representative for small businesses.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Which of the following is an example of a firm?
A) A local government agency
B) A family with four children
C) A grocery store
D) A public school
E) The U.S. Department of Commerce
A) A local government agency
B) A family with four children
C) A grocery store
D) A public school
E) The U.S. Department of Commerce

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
The owner of a sole proprietorship
A) has unlimited liability and is responsible for all debts of the firm.
B) assumes no responsibility for any debt of the firm and enjoys only limited profits.
C) assumes no responsibility for any debt of the firm but also receives no profits
D) has limited liability and shares the responsibility of all debts of the firm with others.
E) has limited liability up to the total value of her or his own personal property.
A) has unlimited liability and is responsible for all debts of the firm.
B) assumes no responsibility for any debt of the firm and enjoys only limited profits.
C) assumes no responsibility for any debt of the firm but also receives no profits
D) has limited liability and shares the responsibility of all debts of the firm with others.
E) has limited liability up to the total value of her or his own personal property.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Which of the following is typically a variable factor of production?
A) Land
B) Equipment
C) Plant
D) Labor
E) Money
A) Land
B) Equipment
C) Plant
D) Labor
E) Money

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Partnerships differ from sole proprietorships because partnerships
A) generate fewer profits than do sole proprietorships.
B) are characterized by unlimited liability and sole proprietorships are not.
C) consist of two or more partners sharing the responsibilities of the firm and sole proprietorships do not.
D) require a written agreement and sole proprietorships do not.
E) require a state charter and sole proprietorships do not.
A) generate fewer profits than do sole proprietorships.
B) are characterized by unlimited liability and sole proprietorships are not.
C) consist of two or more partners sharing the responsibilities of the firm and sole proprietorships do not.
D) require a written agreement and sole proprietorships do not.
E) require a state charter and sole proprietorships do not.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
A monopoly is a price-maker.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
A competitive market is one in which many firms compete for customers and end up charging a common market price.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
In a competitive market, no single consumer or producer can set the market price.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
Which of the following statements is true?
A) Price-taking behavior by competitive firms does not have an analogy in the theory of the consumer.
B) The more competitive a market, the more prices are expected to vary between firms in the market.
C) Buyers and sellers individually set prices.
D) A competitive firm is a price-taker.
E) A competitive firm is a price-maker.
A) Price-taking behavior by competitive firms does not have an analogy in the theory of the consumer.
B) The more competitive a market, the more prices are expected to vary between firms in the market.
C) Buyers and sellers individually set prices.
D) A competitive firm is a price-taker.
E) A competitive firm is a price-maker.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Firms are assumed to maximize
A) inputs.
B) profits.
C) wages.
D) output price.
E) output quantity.
A) inputs.
B) profits.
C) wages.
D) output price.
E) output quantity.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
In economics, the main objective of a firm is to maximize customer satisfaction.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
A firm that considers price as a given and chooses quantity of output accordingly is called a
A) profit-maximizer.
B) quantity-setter.
C) market-taker.
D) monopoly.
E) price-taker.
A) profit-maximizer.
B) quantity-setter.
C) market-taker.
D) monopoly.
E) price-taker.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
A market that includes only a single firm is called a(n)
A) monopsony.
B) monopoly.
C) single-firm market.
D) competitive market.
E) oligopoly.
A) monopsony.
B) monopoly.
C) single-firm market.
D) competitive market.
E) oligopoly.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
In economics, firms are assumed to
A) maximize output prices.
B) minimize output prices.
C) maximize profits.
D) maximize consumer surplus.
E) maximize customer satisfaction.
A) maximize output prices.
B) minimize output prices.
C) maximize profits.
D) maximize consumer surplus.
E) maximize customer satisfaction.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
If total revenue is less than total costs, then
A) economic profits are positive.
B) economic profits are zero.
C) economic profits are negative.
D) a firm breaks even.
E) profits can be positive or negative, depending on other factors.
A) economic profits are positive.
B) economic profits are zero.
C) economic profits are negative.
D) a firm breaks even.
E) profits can be positive or negative, depending on other factors.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
In contrast with a firm in a competitive market, a monopoly is able to control
A) input costs.
B) price.
C) profits.
D) demand.
E) all aspects of its operation.
A) input costs.
B) price.
C) profits.
D) demand.
E) all aspects of its operation.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
By definition, profits are
A) total output minus total inputs.
B) total revenue plus total costs.
C) total revenue minus total costs.
D) total inputs minus total output.
E) total costs minus total revenue.
A) total output minus total inputs.
B) total revenue plus total costs.
C) total revenue minus total costs.
D) total inputs minus total output.
E) total costs minus total revenue.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
If only one firm exists in a market, the firm has no power over the market price.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
A firm in a competitive market can control the price it charges its buyers.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
What is the major characteristic of a competitive market?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
Why is a monopoly a price-maker?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
An individual firm in a competitive market
A) decides, given the market price, how much to produce and sell.
B) has no control over the price or the quantity it produces and sells.
C) takes the market-determined amount it should sell as given, and then, based on this amount, determines what price to charge.
D) decides what price to charge and how much to produce and sell.
E) has control over the price but not the quantity to produce and sell.
A) decides, given the market price, how much to produce and sell.
B) has no control over the price or the quantity it produces and sells.
C) takes the market-determined amount it should sell as given, and then, based on this amount, determines what price to charge.
D) decides what price to charge and how much to produce and sell.
E) has control over the price but not the quantity to produce and sell.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
In a competitive market, price is taken as given by
A) both buyers and sellers.
B) neither buyers nor sellers.
C) buyers only.
D) sellers only.
E) the government.
A) both buyers and sellers.
B) neither buyers nor sellers.
C) buyers only.
D) sellers only.
E) the government.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
Why is an individual firm in a competitive market a price-taker?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
A price-taking firm is one that forces consumers to take whatever price the firm wishes.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
Total revenue always increases if price increases.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
Total costs are
A) variable costs plus average cost.
B) marginal cost plus average cost.
C) fixed costs plus variable costs.
D) marginal cost minus average cost.
E) fixed costs minus variable costs.
A) variable costs plus average cost.
B) marginal cost plus average cost.
C) fixed costs plus variable costs.
D) marginal cost minus average cost.
E) fixed costs minus variable costs.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
Profit maximization is the basic assumption for all types of corporations, but not for sole proprietorships.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
A graph showing how much total output results for any given amount of input is called a(n)
A) labor function.
B) production function.
C) marginal product curve.
D) variable cost curve.
E) earnings schedule.
A) labor function.
B) production function.
C) marginal product curve.
D) variable cost curve.
E) earnings schedule.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Diminishing returns occur when the
A) marginal product of an input is positive.
B) marginal product of an input is zero.
C) marginal product of an input is decreasing.
D) total product of an input is zero.
E) total product of an input is negative.
A) marginal product of an input is positive.
B) marginal product of an input is zero.
C) marginal product of an input is decreasing.
D) total product of an input is zero.
E) total product of an input is negative.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
46
The change in total output that occurs with a one-unit change in labor is called the
A) average productivity of labor.
B) marginal product of labor.
C) total product of labor.
D) marginal benefit of labor.
E) marginal cost of labor.
A) average productivity of labor.
B) marginal product of labor.
C) total product of labor.
D) marginal benefit of labor.
E) marginal cost of labor.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
47
When the production function gets flatter as the quantity of labor increases, we know
A) that marginal product of labor is rising.
B) that marginal product of labor is falling.
C) nothing about the marginal product of labor.
D) that marginal product of labor is zero.
E) that marginal product of labor goes to infinity.
A) that marginal product of labor is rising.
B) that marginal product of labor is falling.
C) nothing about the marginal product of labor.
D) that marginal product of labor is zero.
E) that marginal product of labor goes to infinity.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
48
Total costs include all of the following except
A) equipment purchase price.
B) rent.
C) salaries.
D) output purchase price.
E) materials.
A) equipment purchase price.
B) rent.
C) salaries.
D) output purchase price.
E) materials.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
49
A production function shows the relationship between
A) variable costs and total costs.
B) a fixed input and output.
C) total output and total costs.
D) fixed costs and total costs.
E) a variable input and output.
A) variable costs and total costs.
B) a fixed input and output.
C) total output and total costs.
D) fixed costs and total costs.
E) a variable input and output.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
50
By definition, a profit-maximizing firm is a monopoly.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
51
In 2010, a firm produced 100 units of good X at $1. In 2011, the firm produced 200 units of good X at $0.5. Between 2010 and 2011, the total revenue of producing good X
A) stayed constant
B) increased.
C) might increase, decrease, or stay constant.
D) decreased.
E) was equal to zero.
A) stayed constant
B) increased.
C) might increase, decrease, or stay constant.
D) decreased.
E) was equal to zero.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
52
In moving down along a demand curve, total revenue
A) stays constant.
B) increases.
C) may increase, decrease, or stay constant.
D) decreases.
E) is always equal to zero.
A) stays constant.
B) increases.
C) may increase, decrease, or stay constant.
D) decreases.
E) is always equal to zero.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
53
Refer to Exhibit 6-1. Diminishing returns to labor is illustrated by
A) increasing output.
B) decreasing output.
C) output increasing at a decreasing rate.
D) output increasing at an increasing rate.
E) increasing input.
A) increasing output.
B) decreasing output.
C) output increasing at a decreasing rate.
D) output increasing at an increasing rate.
E) increasing input.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
54
Total revenue is the price of a good times its quantity.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
55
When total product is rising, marginal product
A) must be negative.
B) must be zero.
C) must be positive.
D) can be either negative or positive.
E) must be rising as well.
A) must be negative.
B) must be zero.
C) must be positive.
D) can be either negative or positive.
E) must be rising as well.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
56
When price and quantity sold by a firm are multiplied, the result is called
A) marginal cost.
B) total costs.
C) marginal revenue.
D) average revenue.
E) total revenue.
A) marginal cost.
B) total costs.
C) marginal revenue.
D) average revenue.
E) total revenue.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
57
Production in the short run requires
A) no factor of production.
B) both fixed and variable factors of production.
C) variable factors of production only.
D) fixed factors of production only.
E) the difference between fixed and variable factors of production.
A) no factor of production.
B) both fixed and variable factors of production.
C) variable factors of production only.
D) fixed factors of production only.
E) the difference between fixed and variable factors of production.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
58
Revenue is the only factor that affects profits.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
59
The term diminishing returns to labor means that
A) the wage rate falls as a person takes on more jobs.
B) total output decreases as one more unit of labor is applied to production.
C) the market value of labor decreases as more labor is supplied.
D) increases in output decline as additional units of labor are used in production.
E) the production of labor is becoming less profitable with decreasing real wages.
A) the wage rate falls as a person takes on more jobs.
B) total output decreases as one more unit of labor is applied to production.
C) the market value of labor decreases as more labor is supplied.
D) increases in output decline as additional units of labor are used in production.
E) the production of labor is becoming less profitable with decreasing real wages.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
60
Holding everything else equal, total revenue increases
A) only when quantity increases.
B) only when price increases.
C) whenever total costs increase.
D) when either price or quantity increase.
E) only when both price and quantity increase.
A) only when quantity increases.
B) only when price increases.
C) whenever total costs increase.
D) when either price or quantity increase.
E) only when both price and quantity increase.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
61
The slope of the total cost curve as output increases reflects
A) decreasing marginal benefit.
B) increasing marginal benefit.
C) decreasing marginal cost.
D) increasing marginal cost.
E) increasing variable cost.
A) decreasing marginal benefit.
B) increasing marginal benefit.
C) decreasing marginal cost.
D) increasing marginal cost.
E) increasing variable cost.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
62
A production function is a straight line because of diminishing returns to labor.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
63
Marginal cost begins to increase when
A) total cost falls.
B) total product falls.
C) diminishing returns begin.
D) diminishing returns end.
E) variable inputs are no longer used.
A) total cost falls.
B) total product falls.
C) diminishing returns begin.
D) diminishing returns end.
E) variable inputs are no longer used.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
64
Marginal cost increases with output because
A) capital becomes increasingly difficult to work with as more units of labor utilize it.
B) marginal product increases with output.
C) increasing amounts of input must be used to produce one more unit of output.
D) total costs increase with output.
E) more input must be used to produce more output.
A) capital becomes increasingly difficult to work with as more units of labor utilize it.
B) marginal product increases with output.
C) increasing amounts of input must be used to produce one more unit of output.
D) total costs increase with output.
E) more input must be used to produce more output.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
65
Total costs are the ____ variable and fixed costs.
A) quotient of
B) difference between
C) product of
D) sum of
E) difference between total revenue and the total of
A) quotient of
B) difference between
C) product of
D) sum of
E) difference between total revenue and the total of

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
66
The total cost curve
A) has a positive slope throughout.
B) has a negative slope throughout.
C) is vertical.
D) is horizontal.
E) can have a positive or negative slope throughout.
A) has a positive slope throughout.
B) has a negative slope throughout.
C) is vertical.
D) is horizontal.
E) can have a positive or negative slope throughout.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
67
The slope of the supply curve reflects a(n)
A) increasing variable cost.
B) decreasing variable cost.
C) increasing total cost.
D) increasing marginal cost.
E) decreasing marginal cost.
A) increasing variable cost.
B) decreasing variable cost.
C) increasing total cost.
D) increasing marginal cost.
E) decreasing marginal cost.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
68
When production increases, total costs
A) can increase or decrease in the long run.
B) always increase in the short run.
C) are constant in the long run.
D) can increase or decrease in the short run.
E) become zero.
A) can increase or decrease in the long run.
B) always increase in the short run.
C) are constant in the long run.
D) can increase or decrease in the short run.
E) become zero.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
69
Because marginal cost increases as output increases,
A) marginal product increases at an increasing rate.
B) the total cost curve gets steeper as output increases.
C) the fixed cost curve gets steeper as output increases.
D) the total product curve gets steeper as output increases.
E) the total cost curve becomes horizontal.
A) marginal product increases at an increasing rate.
B) the total cost curve gets steeper as output increases.
C) the fixed cost curve gets steeper as output increases.
D) the total product curve gets steeper as output increases.
E) the total cost curve becomes horizontal.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
70
Marginal cost increases because
A) marginal product decreases.
B) the price of labor decreases.
C) marginal product increases.
D) the price of labor increases.
E) marginal product is constant.
A) marginal product decreases.
B) the price of labor decreases.
C) marginal product increases.
D) the price of labor increases.
E) marginal product is constant.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
71
The change in variable costs that results from producing one more unit of output is called
A) marginal variable cost.
B) average variable cost.
C) total variable cost.
D) marginal cost.
E) marginal product.
A) marginal variable cost.
B) average variable cost.
C) total variable cost.
D) marginal cost.
E) marginal product.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
72
The slope of the production function turns from positive to negative when the marginal product of labor turns from positive to negative.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
73
Because marginal product decreases as input is increased,
A) nothing is implied about how much input is required to produce one more unit of output.
B) it takes decreasing amounts of input to produce one more unit of output.
C) it takes increasing amounts of input to produce one more unit of output.
D) the amount of input it takes to produce one more unit of output does not change.
E) it takes zero input to produce one more unit of output.
A) nothing is implied about how much input is required to produce one more unit of output.
B) it takes decreasing amounts of input to produce one more unit of output.
C) it takes increasing amounts of input to produce one more unit of output.
D) the amount of input it takes to produce one more unit of output does not change.
E) it takes zero input to produce one more unit of output.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
74
Marginal cost is
A) the change in total cost that results from hiring one more unit of labor.
B) total cost divided by total output.
C) the change in total variable cost that results from hiring one more unit of capital.
D) the change in total cost that results from hiring one more unit of capital.
E) the change in total cost that results from increasing output by one unit.
A) the change in total cost that results from hiring one more unit of labor.
B) total cost divided by total output.
C) the change in total variable cost that results from hiring one more unit of capital.
D) the change in total cost that results from hiring one more unit of capital.
E) the change in total cost that results from increasing output by one unit.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
75
When fertilizer yields diminishing returns in the production of potatoes,
A) output increases only if fertilizer input is increased.
B) additional fertilizer causes decreased production.
C) doubling fertilizer input less than doubles output.
D) marginal cost decreases as more fertilizer is added.
E) doubling fertilizer input more than doubles output.
A) output increases only if fertilizer input is increased.
B) additional fertilizer causes decreased production.
C) doubling fertilizer input less than doubles output.
D) marginal cost decreases as more fertilizer is added.
E) doubling fertilizer input more than doubles output.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
76
Variable costs are those that
A) vary with output.
B) are fixed when output changes.
C) decrease when output increases.
D) vary with input.
E) can change even when output is constant.
A) vary with output.
B) are fixed when output changes.
C) decrease when output increases.
D) vary with input.
E) can change even when output is constant.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
77
The slope of the total cost curve is called
A) diminishing returns.
B) marginal cost.
C) marginal product.
D) marginal benefit.
E) total product.
A) diminishing returns.
B) marginal cost.
C) marginal product.
D) marginal benefit.
E) total product.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
78
Variable costs are generally associated with the cost of
A) machinery.
B) loan payments.
C) capital.
D) labor.
E) rental income forgone by not renting facilities to someone else.
A) machinery.
B) loan payments.
C) capital.
D) labor.
E) rental income forgone by not renting facilities to someone else.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
79
Costs that do not vary with output are called
A) total costs.
B) short-run costs.
C) long-run costs.
D) variable costs.
E) fixed costs.
A) total costs.
B) short-run costs.
C) long-run costs.
D) variable costs.
E) fixed costs.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
80
Exhibit 6-2 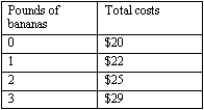
Refer to Exhibit 6-2. The marginal cost of the second pound of bananas is
A) $25.
B) $2.
C) $3.
D) $4.
E) $0.

Refer to Exhibit 6-2. The marginal cost of the second pound of bananas is
A) $25.
B) $2.
C) $3.
D) $4.
E) $0.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 182 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








