Deck 26: Biomolecules: Amino Acids,peptides,and Proteins
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال
سؤال

فتح الحزمة
قم بالتسجيل لفتح البطاقات في هذه المجموعة!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/45
العب
ملء الشاشة (f)
Deck 26: Biomolecules: Amino Acids,peptides,and Proteins
1
Exhibit 26-1
Refer to the data below to answer the following question(s):
Leucine is an essential amino acid with the systematic name 2-amino-3-methylpentanoic acid.It has pKa1 = 2.36 and pKa2 = 9.60.
Refer to Exhibit 26-1.Show how leucine might be synthesized using the Knowles enantioselective synthesis.
Refer to the data below to answer the following question(s):
Leucine is an essential amino acid with the systematic name 2-amino-3-methylpentanoic acid.It has pKa1 = 2.36 and pKa2 = 9.60.
Refer to Exhibit 26-1.Show how leucine might be synthesized using the Knowles enantioselective synthesis.
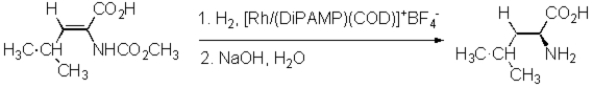
2
Exhibit 26-2
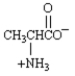
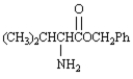
MATCH a structure from the list below to each of the following terms.Place the letter of the structure in the blank to the left of the term which it describes.
_____ an amino acid in its zwitterionic form.
A)
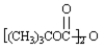
B)
C)
Val−Phe−Leu−Met−Tyr−Pro−Gly−Trp−Cys−Glu
D)
E)
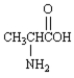
F) Asp−Tyr−Ile−His−Pro−Phe−Arg−Val
G)
apoenzyme
H)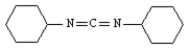
I)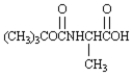
J)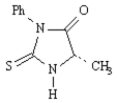
K)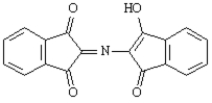
L) Val−Lys−Phe−Gly−Arg−Met−Arg−Phe
M) vitamins
MATCH a structure from the list below to each of the following terms.Place the letter of the structure in the blank to the left of the term which it describes.
_____ an amino acid in its zwitterionic form.
A)
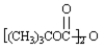
B)

C)
Val−Phe−Leu−Met−Tyr−Pro−Gly−Trp−Cys−Glu
D)

E)

F) Asp−Tyr−Ile−His−Pro−Phe−Arg−Val
G)
apoenzyme
H)
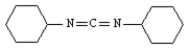
I)

J)

K)

L) Val−Lys−Phe−Gly−Arg−Met−Arg−Phe
M) vitamins

3
Exhibit 26-2
MATCH a structure from the list below to each of the following terms.Place the letter of the structure in the blank to the left of the term which it describes.
_____ a carboxyl-protected amino acid.
A)
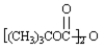
B)

C)
Val−Phe−Leu−Met−Tyr−Pro−Gly−Trp−Cys−Glu
D)

E)

F) Asp−Tyr−Ile−His−Pro−Phe−Arg−Val
G)
apoenzyme
H)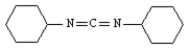
I)
J)
K)
L) Val−Lys−Phe−Gly−Arg−Met−Arg−Phe
M) vitamins
MATCH a structure from the list below to each of the following terms.Place the letter of the structure in the blank to the left of the term which it describes.
_____ a carboxyl-protected amino acid.
A)
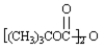
B)

C)
Val−Phe−Leu−Met−Tyr−Pro−Gly−Trp−Cys−Glu
D)

E)

F) Asp−Tyr−Ile−His−Pro−Phe−Arg−Val
G)
apoenzyme
H)
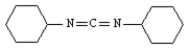
I)

J)

K)

L) Val−Lys−Phe−Gly−Arg−Met−Arg−Phe
M) vitamins

4
Exhibit 26-4
Refer to the data below to answer the following question(s):
Porcine dynorphin is a neuropeptide having 17 amino acid residues.Its structure is shown below.
Tyr−Gly−Gly−Phe−Leu−Arg−Arg−Ile−Arg−Pro−Lys−Leu−Lys−Trp−Asp−Asn−Gln
Refer to Exhibit 26-4.Leu5-enkephalin is a pentapeptide contained as the N-terminal sequence of dynorphin.Write the structure of Leu5-enkephalin using both the three letter and one letter abbreviations for the amino acids.
Refer to the data below to answer the following question(s):
Porcine dynorphin is a neuropeptide having 17 amino acid residues.Its structure is shown below.
Tyr−Gly−Gly−Phe−Leu−Arg−Arg−Ile−Arg−Pro−Lys−Leu−Lys−Trp−Asp−Asn−Gln
Refer to Exhibit 26-4.Leu5-enkephalin is a pentapeptide contained as the N-terminal sequence of dynorphin.Write the structure of Leu5-enkephalin using both the three letter and one letter abbreviations for the amino acids.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 45 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
5
Exhibit 26-1
Refer to the data below to answer the following question(s):
Leucine is an essential amino acid with the systematic name 2-amino-3-methylpentanoic acid.It has pKa1 = 2.36 and pKa2 = 9.60.
Refer to Exhibit 26-1.Draw the structure of the predominant form of leucine at pH = 1.50.
Refer to the data below to answer the following question(s):
Leucine is an essential amino acid with the systematic name 2-amino-3-methylpentanoic acid.It has pKa1 = 2.36 and pKa2 = 9.60.
Refer to Exhibit 26-1.Draw the structure of the predominant form of leucine at pH = 1.50.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 45 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
6
Exhibit 26-2
MATCH a structure from the list below to each of the following terms.Place the letter of the structure in the blank to the left of the term which it describes.
_____ an octapeptide with a C-terminal valine.
A)
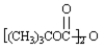
B)

C)
Val−Phe−Leu−Met−Tyr−Pro−Gly−Trp−Cys−Glu
D)

E)

F) Asp−Tyr−Ile−His−Pro−Phe−Arg−Val
G)
apoenzyme
H)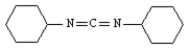
I)
J)
K)
L) Val−Lys−Phe−Gly−Arg−Met−Arg−Phe
M) vitamins
MATCH a structure from the list below to each of the following terms.Place the letter of the structure in the blank to the left of the term which it describes.
_____ an octapeptide with a C-terminal valine.
A)
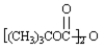
B)

C)
Val−Phe−Leu−Met−Tyr−Pro−Gly−Trp−Cys−Glu
D)

E)

F) Asp−Tyr−Ile−His−Pro−Phe−Arg−Val
G)
apoenzyme
H)
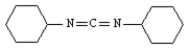
I)

J)

K)

L) Val−Lys−Phe−Gly−Arg−Met−Arg−Phe
M) vitamins

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 45 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
7
Exhibit 26-2
MATCH a structure from the list below to each of the following terms.Place the letter of the structure in the blank to the left of the term which it describes.
_____ a polypeptide which gives four fragments on treatment with chymotrypsin.
A)
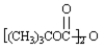
B)

C)
Val−Phe−Leu−Met−Tyr−Pro−Gly−Trp−Cys−Glu
D)

E)

F) Asp−Tyr−Ile−His−Pro−Phe−Arg−Val
G)
apoenzyme
H)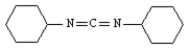
I)
J)
K)
L) Val−Lys−Phe−Gly−Arg−Met−Arg−Phe
M) vitamins
MATCH a structure from the list below to each of the following terms.Place the letter of the structure in the blank to the left of the term which it describes.
_____ a polypeptide which gives four fragments on treatment with chymotrypsin.
A)
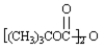
B)

C)
Val−Phe−Leu−Met−Tyr−Pro−Gly−Trp−Cys−Glu
D)

E)

F) Asp−Tyr−Ile−His−Pro−Phe−Arg−Val
G)
apoenzyme
H)
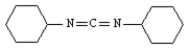
I)

J)

K)

L) Val−Lys−Phe−Gly−Arg−Met−Arg−Phe
M) vitamins

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 45 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
8
Exhibit 26-1
Refer to the data below to answer the following question(s):
Leucine is an essential amino acid with the systematic name 2-amino-3-methylpentanoic acid.It has pKa1 = 2.36 and pKa2 = 9.60.
Refer to Exhibit 26-1.Draw the structure of the predominant form of leucine at pH = 10.00.
Refer to the data below to answer the following question(s):
Leucine is an essential amino acid with the systematic name 2-amino-3-methylpentanoic acid.It has pKa1 = 2.36 and pKa2 = 9.60.
Refer to Exhibit 26-1.Draw the structure of the predominant form of leucine at pH = 10.00.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 45 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
9
The most acidic amino acid is ____.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 45 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
10
Exhibit 26-2
MATCH a structure from the list below to each of the following terms.Place the letter of the structure in the blank to the left of the term which it describes.
_____ the product of an Edman degradation.
A)
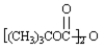
B)

C)
Val−Phe−Leu−Met−Tyr−Pro−Gly−Trp−Cys−Glu
D)

E)

F) Asp−Tyr−Ile−His−Pro−Phe−Arg−Val
G)
apoenzyme
H)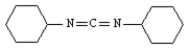
I)
J)
K)
L) Val−Lys−Phe−Gly−Arg−Met−Arg−Phe
M) vitamins
MATCH a structure from the list below to each of the following terms.Place the letter of the structure in the blank to the left of the term which it describes.
_____ the product of an Edman degradation.
A)
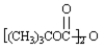
B)

C)
Val−Phe−Leu−Met−Tyr−Pro−Gly−Trp−Cys−Glu
D)

E)

F) Asp−Tyr−Ile−His−Pro−Phe−Arg−Val
G)
apoenzyme
H)
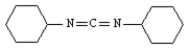
I)

J)

K)

L) Val−Lys−Phe−Gly−Arg−Met−Arg−Phe
M) vitamins

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 45 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
11
Exhibit 26-1
Refer to the data below to answer the following question(s):
Leucine is an essential amino acid with the systematic name 2-amino-3-methylpentanoic acid.It has pKa1 = 2.36 and pKa2 = 9.60.
Refer to Exhibit 26-1.How many possible stereoisomers of leucine are there?
Refer to the data below to answer the following question(s):
Leucine is an essential amino acid with the systematic name 2-amino-3-methylpentanoic acid.It has pKa1 = 2.36 and pKa2 = 9.60.
Refer to Exhibit 26-1.How many possible stereoisomers of leucine are there?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 45 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
12
Exhibit 26-1
Refer to the data below to answer the following question(s):
Leucine is an essential amino acid with the systematic name 2-amino-3-methylpentanoic acid.It has pKa1 = 2.36 and pKa2 = 9.60.
Refer to Exhibit 26-1.Leucine is described as an essential amino acid.What does this mean?
Refer to the data below to answer the following question(s):
Leucine is an essential amino acid with the systematic name 2-amino-3-methylpentanoic acid.It has pKa1 = 2.36 and pKa2 = 9.60.
Refer to Exhibit 26-1.Leucine is described as an essential amino acid.What does this mean?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 45 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
13
Exhibit 26-1
Refer to the data below to answer the following question(s):
Leucine is an essential amino acid with the systematic name 2-amino-3-methylpentanoic acid.It has pKa1 = 2.36 and pKa2 = 9.60.
Refer to Exhibit 26-1.Draw the condensed structure for leucine,and label all chirality centers with an asterisk.
Refer to the data below to answer the following question(s):
Leucine is an essential amino acid with the systematic name 2-amino-3-methylpentanoic acid.It has pKa1 = 2.36 and pKa2 = 9.60.
Refer to Exhibit 26-1.Draw the condensed structure for leucine,and label all chirality centers with an asterisk.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 45 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
14
Exhibit 26-1
Refer to the data below to answer the following question(s):
Leucine is an essential amino acid with the systematic name 2-amino-3-methylpentanoic acid.It has pKa1 = 2.36 and pKa2 = 9.60.
Refer to Exhibit 26-1.Draw a Fischer projection of L-leucine and label the chirality center(s) as R or S.
Refer to the data below to answer the following question(s):
Leucine is an essential amino acid with the systematic name 2-amino-3-methylpentanoic acid.It has pKa1 = 2.36 and pKa2 = 9.60.
Refer to Exhibit 26-1.Draw a Fischer projection of L-leucine and label the chirality center(s) as R or S.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 45 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
15
Exhibit 26-1
Refer to the data below to answer the following question(s):
Leucine is an essential amino acid with the systematic name 2-amino-3-methylpentanoic acid.It has pKa1 = 2.36 and pKa2 = 9.60.
Refer to Exhibit 26-1.Show the alkyl halide you would use to prepare leucine by the amidomalonate method.
Refer to the data below to answer the following question(s):
Leucine is an essential amino acid with the systematic name 2-amino-3-methylpentanoic acid.It has pKa1 = 2.36 and pKa2 = 9.60.
Refer to Exhibit 26-1.Show the alkyl halide you would use to prepare leucine by the amidomalonate method.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 45 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
16
Exhibit 26-1
Refer to the data below to answer the following question(s):
Leucine is an essential amino acid with the systematic name 2-amino-3-methylpentanoic acid.It has pKa1 = 2.36 and pKa2 = 9.60.
Refer to Exhibit 26-1.What is the pI of leucine?
Refer to the data below to answer the following question(s):
Leucine is an essential amino acid with the systematic name 2-amino-3-methylpentanoic acid.It has pKa1 = 2.36 and pKa2 = 9.60.
Refer to Exhibit 26-1.What is the pI of leucine?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 45 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
17
Exhibit 26-2
MATCH a structure from the list below to each of the following terms.Place the letter of the structure in the blank to the left of the term which it describes.
_____ a peptide coupling reagent.
A)
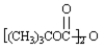
B)

C)
Val−Phe−Leu−Met−Tyr−Pro−Gly−Trp−Cys−Glu
D)

E)

F) Asp−Tyr−Ile−His−Pro−Phe−Arg−Val
G)
apoenzyme
H)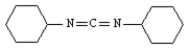
I)
J)
K)
L) Val−Lys−Phe−Gly−Arg−Met−Arg−Phe
M) vitamins
MATCH a structure from the list below to each of the following terms.Place the letter of the structure in the blank to the left of the term which it describes.
_____ a peptide coupling reagent.
A)
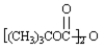
B)

C)
Val−Phe−Leu−Met−Tyr−Pro−Gly−Trp−Cys−Glu
D)

E)

F) Asp−Tyr−Ile−His−Pro−Phe−Arg−Val
G)
apoenzyme
H)
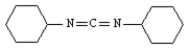
I)

J)

K)

L) Val−Lys−Phe−Gly−Arg−Met−Arg−Phe
M) vitamins

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 45 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
18
The most basic amino acid is _____.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 45 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
19
Define isoelectric point.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 45 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
20
Exhibit 26-2
MATCH a structure from the list below to each of the following terms.Place the letter of the structure in the blank to the left of the term which it describes.
_____ small organic molecules which act as coenzymes.
A)
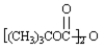
B)

C)
Val−Phe−Leu−Met−Tyr−Pro−Gly−Trp−Cys−Glu
D)

E)

F) Asp−Tyr−Ile−His−Pro−Phe−Arg−Val
G)
apoenzyme
H)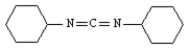
I)
J)
K)
L) Val−Lys−Phe−Gly−Arg−Met−Arg−Phe
M) vitamins
MATCH a structure from the list below to each of the following terms.Place the letter of the structure in the blank to the left of the term which it describes.
_____ small organic molecules which act as coenzymes.
A)
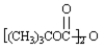
B)

C)
Val−Phe−Leu−Met−Tyr−Pro−Gly−Trp−Cys−Glu
D)

E)

F) Asp−Tyr−Ile−His−Pro−Phe−Arg−Val
G)
apoenzyme
H)
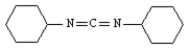
I)

J)

K)

L) Val−Lys−Phe−Gly−Arg−Met−Arg−Phe
M) vitamins

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 45 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
21
Consider the following titration curve for an amino acid. 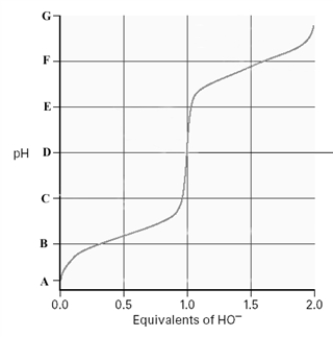 What is the pI of this amino acid?
What is the pI of this amino acid?
A)A
B)B
C)D
D)F
 What is the pI of this amino acid?
What is the pI of this amino acid?A)A
B)B
C)D
D)F

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 45 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
22
Exhibit 26-4
Refer to the data below to answer the following question(s):
Porcine dynorphin is a neuropeptide having 17 amino acid residues.Its structure is shown below.
Tyr−Gly−Gly−Phe−Leu−Arg−Arg−Ile−Arg−Pro−Lys−Leu−Lys−Trp−Asp−Asn−Gln
Refer to Exhibit 26-4.What fragments would result if dynorphin were cleaved by trypsin?
Refer to the data below to answer the following question(s):
Porcine dynorphin is a neuropeptide having 17 amino acid residues.Its structure is shown below.
Tyr−Gly−Gly−Phe−Leu−Arg−Arg−Ile−Arg−Pro−Lys−Leu−Lys−Trp−Asp−Asn−Gln
Refer to Exhibit 26-4.What fragments would result if dynorphin were cleaved by trypsin?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 45 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
23
Draw and name the structure of the tripeptide formed from the following amino acids.Use B as the N-terminal acid and A as the C-terminal end.Atoms other than carbon and hydrogen are labeled. 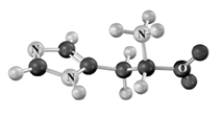
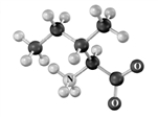
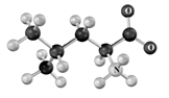 A B C
A B C


 A B C
A B C
فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 45 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
24
What alkyl halide should be used to prepare the following amino acid by the amidomalonate method? Atoms other than carbon and hydrogen are labeled. 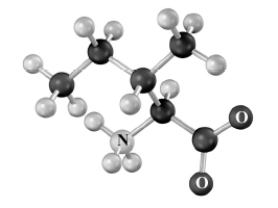


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 45 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
25
Exhibit 26-5
Refer to the data below to answer the following question(s):
The octapeptide saralasin is a specific antagonist of angiotensin II.A derivative of saralasin is used therapeutically as an antihypertensive.Amino acid analysis of saralasin show the presence of the following amino acids:
Ala,Arg,His,Pro,Sar,Tyr,Val,Val
Refer to Exhibit 26-5.Sar is the abbreviation for sarcosine,N-methyl aminoethanoic acid.Draw the structure of sarcosine.
Refer to the data below to answer the following question(s):
The octapeptide saralasin is a specific antagonist of angiotensin II.A derivative of saralasin is used therapeutically as an antihypertensive.Amino acid analysis of saralasin show the presence of the following amino acids:
Ala,Arg,His,Pro,Sar,Tyr,Val,Val
Refer to Exhibit 26-5.Sar is the abbreviation for sarcosine,N-methyl aminoethanoic acid.Draw the structure of sarcosine.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 45 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
26
Consider the following image.  Which level of protein structure is shown here?
Which level of protein structure is shown here?
A)Primary
B)Secondary
C)Tertiary
D)Quaternary
 Which level of protein structure is shown here?
Which level of protein structure is shown here?A)Primary
B)Secondary
C)Tertiary
D)Quaternary

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 45 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
27
The following amino acid: (Atoms other than carbon and hydrogen are labeled. ) 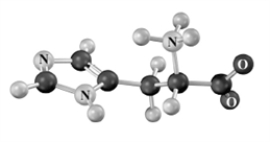
A)has two chirality centers.
B)is classified as secondary α-amino acid.
C)is characterized by three pKas
D)would have a net +1 charge as shown.

A)has two chirality centers.
B)is classified as secondary α-amino acid.
C)is characterized by three pKas
D)would have a net +1 charge as shown.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 45 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
28
Consider the following image. 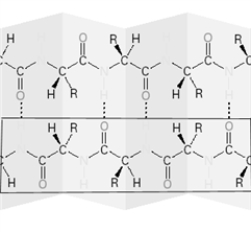 Which level of protein structure is shown in the box?
Which level of protein structure is shown in the box?
A)Primary
B)Secondary
C)Tertiary
D)Quaternary
 Which level of protein structure is shown in the box?
Which level of protein structure is shown in the box?A)Primary
B)Secondary
C)Tertiary
D)Quaternary

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 45 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
29
Show the steps involved in a synthesis of the peptide "F-G-I" using the Merrifield procedure.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 45 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
30
Exhibit 26-4
Refer to the data below to answer the following question(s):
Porcine dynorphin is a neuropeptide having 17 amino acid residues.Its structure is shown below.
Tyr−Gly−Gly−Phe−Leu−Arg−Arg−Ile−Arg−Pro−Lys−Leu−Lys−Trp−Asp−Asn−Gln
Refer to Exhibit 26-4.What fragments would result if dynorphin were cleaved by chymotropsin?
Refer to the data below to answer the following question(s):
Porcine dynorphin is a neuropeptide having 17 amino acid residues.Its structure is shown below.
Tyr−Gly−Gly−Phe−Leu−Arg−Arg−Ile−Arg−Pro−Lys−Leu−Lys−Trp−Asp−Asn−Gln
Refer to Exhibit 26-4.What fragments would result if dynorphin were cleaved by chymotropsin?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 45 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
31
How many different peptides could be produced using one each of the following amino acids? Ala,Gly,His,Cys
A)6
B)16
C)24
D)64
A)6
B)16
C)24
D)64

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 45 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
32
Consider the following titration curve for an amino acid. 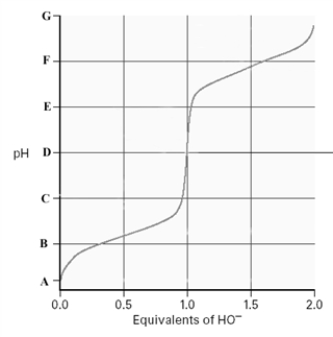 At which of the following "pH" values would the amino acid have a net charge of zero?
At which of the following "pH" values would the amino acid have a net charge of zero?
A)A
B)B
C)D
D)F
 At which of the following "pH" values would the amino acid have a net charge of zero?
At which of the following "pH" values would the amino acid have a net charge of zero?A)A
B)B
C)D
D)F

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 45 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
33
Show how you could prepare the following amino acid starting with the appropriate carboxylic acid.Atoms other than carbon and hydrogen are labeled. 


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 45 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
34
Classify the following amino acid.Atoms other than carbon and hydrogen are labeled. 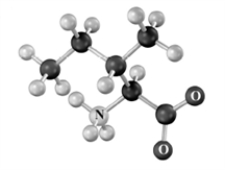
A)acidic
B)basic
C)neutral

A)acidic
B)basic
C)neutral

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 45 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
35
Consider the following image. 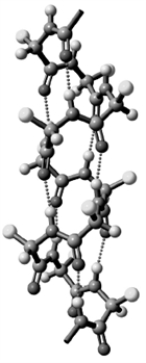 Which level of protein structure is shown here?
Which level of protein structure is shown here?
A)Primary
B)Secondary
C)Tertiary
D)Quaternary
 Which level of protein structure is shown here?
Which level of protein structure is shown here?A)Primary
B)Secondary
C)Tertiary
D)Quaternary

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 45 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
36
Consider the following data for a hypothetical basic amino acid. pKa
3)15
8)22
10)93
What is the pI of this substance?
A)5.68
B)7.04
C)8.22
D)9.58
3)15
8)22
10)93
What is the pI of this substance?
A)5.68
B)7.04
C)8.22
D)9.58

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 45 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
37
Consider the following titration curve for an amino acid. 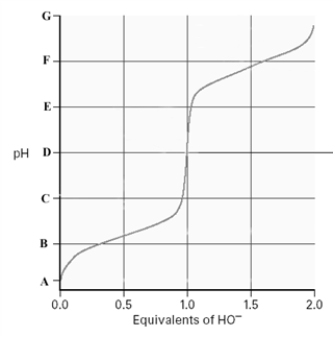 At which of the following "pH" values would the amino acid be fully deprotonated?
At which of the following "pH" values would the amino acid be fully deprotonated?
A)A
B)B
C)D
D)F
 At which of the following "pH" values would the amino acid be fully deprotonated?
At which of the following "pH" values would the amino acid be fully deprotonated?A)A
B)B
C)D
D)F

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 45 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
38
Exhibit 26-5
Refer to the data below to answer the following question(s):
The octapeptide saralasin is a specific antagonist of angiotensin II.A derivative of saralasin is used therapeutically as an antihypertensive.Amino acid analysis of saralasin show the presence of the following amino acids:
Ala,Arg,His,Pro,Sar,Tyr,Val,Val
Refer to Exhibit 26-5.N-Terminal analysis by the Edman method shows saralasin contains sarcosine at the N-terminus.Partial hydrolysis of saralasin with dilute hydrochloric acid yields the following fragments:
Tyr−Val−His
Sar−Arg−Val
His−Pro−Ala
Val−Tyr−Val
Arg−Val−Tyr
What is the structure of saralasin?
Refer to the data below to answer the following question(s):
The octapeptide saralasin is a specific antagonist of angiotensin II.A derivative of saralasin is used therapeutically as an antihypertensive.Amino acid analysis of saralasin show the presence of the following amino acids:
Ala,Arg,His,Pro,Sar,Tyr,Val,Val
Refer to Exhibit 26-5.N-Terminal analysis by the Edman method shows saralasin contains sarcosine at the N-terminus.Partial hydrolysis of saralasin with dilute hydrochloric acid yields the following fragments:
Tyr−Val−His
Sar−Arg−Val
His−Pro−Ala
Val−Tyr−Val
Arg−Val−Tyr
What is the structure of saralasin?

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 45 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
39
Which of the following is a correct representation of the amino acid below? Atoms other than carbon and hydrogen are labeled. 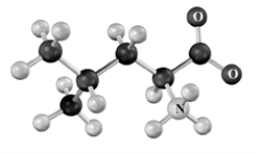
A)Isoleucine
B)ILe
C)I
D)None of these present this amino acid.
E)All of these represent this amino acid.

A)Isoleucine
B)ILe
C)I
D)None of these present this amino acid.
E)All of these represent this amino acid.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 45 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
40
On the titration curve for an amino acid.In terms of the letters on the graph,label the isoelectric point,the pKa of the amino group and the pKa of the carboxyl group. 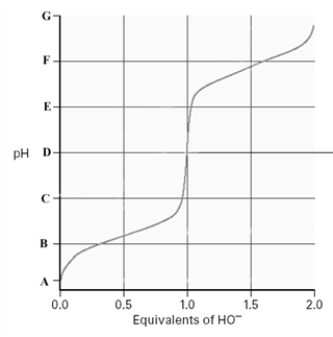


فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 45 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
41
The enzyme that would catalyze the following reaction 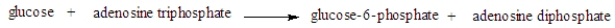 would belong in which classification?
would belong in which classification?
A)kinase
B)oxidase
C)protease
D)transaminase
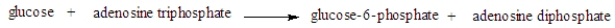 would belong in which classification?
would belong in which classification?A)kinase
B)oxidase
C)protease
D)transaminase

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 45 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
42
Consider the image below. 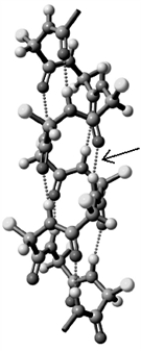 What type of interaction is indicated by the arrow?
What type of interaction is indicated by the arrow?
A)Salt bridges
B)Disulfide bonds
C)Hydrogen bonds
D)Dispersion forces
 What type of interaction is indicated by the arrow?
What type of interaction is indicated by the arrow?A)Salt bridges
B)Disulfide bonds
C)Hydrogen bonds
D)Dispersion forces

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 45 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
43
The coenzymes NAD+ and FAD are involved in:
A)acyl transfer.
B)methyl transfer.
C)decarboxylation.
D)oxidation/reduction.
A)acyl transfer.
B)methyl transfer.
C)decarboxylation.
D)oxidation/reduction.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 45 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
44
Which of the following contributes most substantially to rate acceleration produced by an enzyme?
A)Ability to bind the substrate
B)Ability to bind the transition state
C)Ability to bind the product
D)All of the above contribute equally.
A)Ability to bind the substrate
B)Ability to bind the transition state
C)Ability to bind the product
D)All of the above contribute equally.

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 45 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck
45
Which level of protein structure is disrupted upon mild heating or alteration in pH?
A)Primary
B)Secondary
C)Tertiary
A)Primary
B)Secondary
C)Tertiary

فتح الحزمة
افتح القفل للوصول البطاقات البالغ عددها 45 في هذه المجموعة.
فتح الحزمة
k this deck








