On a frictionless horizontal surface, a 1.50-kg mass traveling at 3.50 m/s suddenly collides
with and sticks to a 3.00-kg mass that is initially at rest, as shown in the figure. This
system then runs into an ideal spring of force constant (spring constant) 50.0 N/cm.
(a) What will be the maximum compression distance of the spring?
(b) How much mechanical energy is lost during this process? During which parts of the
process (the collision and compression of the spring) is this energy lost? 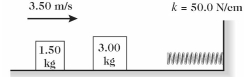
Correct Answer:
Verified
View Answer
Unlock this answer now
Get Access to more Verified Answers free of charge
Q118: In a police ballistics test, a 2.00-g
Q119: A 900-kg car traveling
Q120: A 900-kg car traveling east
Q121: Three masses are located in the
Q122: Three masses, 1.0 kg, 2.0 kg, and
Q124: A 30-kg child stands at one end
Q125: Three small masses are positioned at the
Q126: A 2.0-m rope is lying on a
Q127: Three balls are moving along a straight
Q128: An object initially at rest suddenly explodes
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents