Two chemical solutions, one containing N molecules of chemical A and another containing M molecules of chemical B, are mixed together at time t = 0. The molecules from the two chemicals combine to form another chemical solution containing y (AB) molecules. The rate at which the AB molecules are formed, 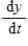 , is called the reaction rate and is jointly proportional to
, is called the reaction rate and is jointly proportional to 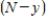 and
and 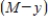 . Thus,
. Thus, 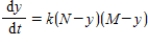 where k is a constant (we assume the temperature of the chemical mixture remains constant during the interaction). Solve this differential equation with the side condition
where k is a constant (we assume the temperature of the chemical mixture remains constant during the interaction). Solve this differential equation with the side condition 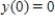 assuming that
assuming that 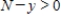 and
and 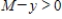
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q22: Find the general solution of the first-order
Q23: Find the general solution of the first-order
Q24: Find the solution of the initial value
Q25: An amount of money deposited in a
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents