A 4-year-old girl is brought to the emergency department due to a 1-week history of fever. Her family has also noticed that the patient is "much crankier than normal" and has decreased oral intake. She has had no cough, rhinorrhea, or emesis. She has no medical conditions, takes no daily medications, and has not received age-appropriate vaccines. Temperature is 39.4 C (102.9 F) , blood pressure is 90/60 mm Hg, and pulse is 135/min. On physical examination, the patient is irritable and has mild facial flushing. Bilateral conjunctivae are injected. A 1.7-cm, tender, mobile anterior cervical lymph node is palpated. Cardiac examination demonstrates a regular rhythm and no murmurs, rubs, or gallops. The trunk and extremities have a blanching maculopapular eruption; the hands and feet are erythematous and edematous. An image of the patient's mouth is shown below. 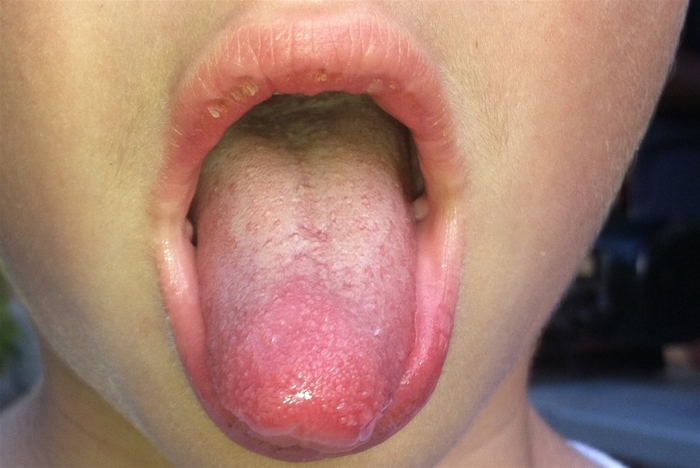 The posterior pharynx is mildly injected without exudates or tonsillar hypertrophy. Which of the following is the best next step in management of this patient?
The posterior pharynx is mildly injected without exudates or tonsillar hypertrophy. Which of the following is the best next step in management of this patient?
A) Echocardiogram
B) Oral penicillin therapy
C) Parvovirus serology
D) Reassurance and close follow-up
E) Serum measles IgM antibody
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q283: A 5-day-old neonate is brought to the
Q284: A 6-year-old boy with congenital deafness is
Q285: A 15-month-old boy is brought to the
Q286: A 1-day-old boy is brought to the
Q287: A 5-day-old girl is being evaluated for
Q289: A 6-month-old boy is brought to the
Q290: A 2-hour-old boy is admitted to the
Q291: A 15-year-old boy is found to have
Q292: A 1-hour-old boy is evaluated for respiratory
Q293: A 6-week-old boy is brought to the
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents