A study examined the role of a humanized monoclonal antibody (mAb) that binds soluble forms of amyloid in treating Alzheimer disease. Patients were randomly assigned to a mAb injection or placebo group for 14 months. The outcomes included changes in cognitive performance assessed by different scores at week 72 compared to baseline. Higher scores indicate worse impairment. The following numbers were reported for patients with mild and moderate Alzheimer disease. 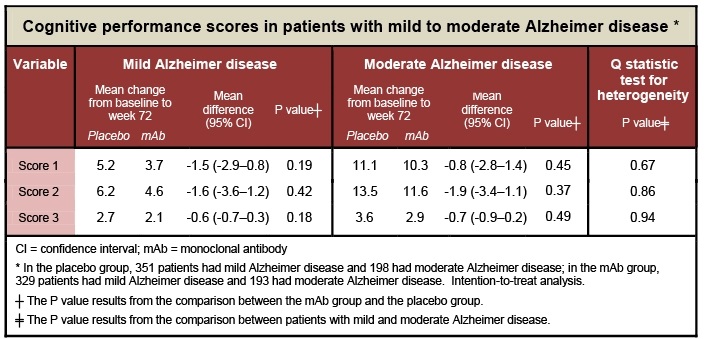 Which of the following is the most accurate interpretation of these study results?
Which of the following is the most accurate interpretation of these study results?
A) mAb therapy effectively slowed the process of mild and moderate Alzheimer disease
B) mAb therapy was more effective in patients with mild Alzheimer disease
C) mAb therapy was more effective in patients with moderate Alzheimer disease
D) Patients with mild Alzheimer disease had a sharper decline in all cognitive performance scores
E) There was no differential response to mAb therapy depending on Alzheimer disease severity
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q31: A 69-year-old man with chronic kidney disease
Q32: A randomized controlled trial is conducted to
Q33: A study evaluated predictors of adverse outcomes
Q34: A case-control study evaluated the association between
Q35: As part of a study on treatment
Q37: A group of cardiologists hypothesized that a
Q38: A study evaluated the accuracy of using
Q39: A 59-year-old man comes to the office
Q40: A study of patients with metastatic renal
Q41: A biomedical research company creates 2 similar
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents