Passage
The Bloom syndrome helicase (BLM) transcript is catalytically inactive in Bloom syndrome (BS) , a genetic disorder that leads to genomic instability characterized by excessive somatic recombination events. Research studies have shown that BLM may be involved in DNA synthesis repair of stalled replication forks during replication stress (arrest) . To investigate this further, an experiment was conducted using cell lines derived from a patient with BS. One set of cells differed only by BLM status: PSNF5 (BLM+, vector with BLM cDNA transfected) and PSNG13 (BLM−, empty vector transfected) . Additional mutations, BLM-K695T and BLM-T99A, were studied in stable transfected cells.The nucleoside analogs iododeoxyuridine (IdU) and chlorodeoxyuridine (CldU) were used to label and track genomic regions of active replication. Cells were initially treated with IdU for 15 minutes. Subsequently, either 4 mM of hydroxyurea (HU) or 30 µM of aphidicolin (Aph) were used to induce replication stress for 4 hours, after which cells were treated with CldU for 85 minutes to assess replication recovery. Cells were mounted on microscope slides, lysed to isolate chromosome fibers, and then fixed on the slides. Sites of IdU and CldU incorporation into the growing DNA strand were then detected by immunostaining the isolated chromosome fibers with analog-specific, fluorescent-coupled antibodies. Replication activity was visualized via microscopy and measured.
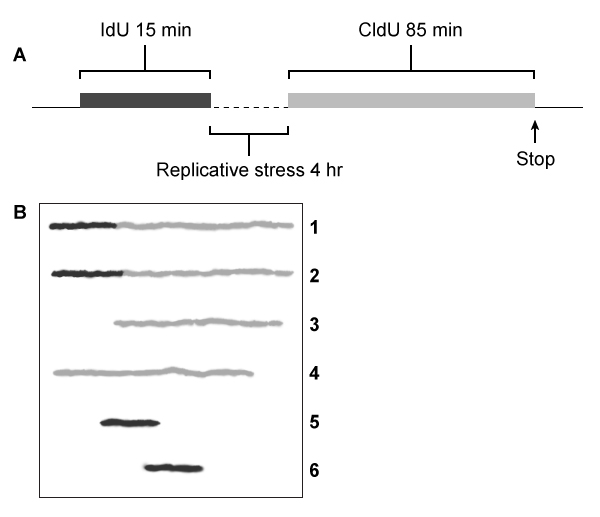 Figure 1 (A) Experimental protocol and (B) fluorescent imaging of a microscope slide showing incorporation of IdU (black lines) and CldU (gray lines) into DNA fibers isolated from a group of BLM+ and BLM− cells, with single fibers depicted in each row
Figure 1 (A) Experimental protocol and (B) fluorescent imaging of a microscope slide showing incorporation of IdU (black lines) and CldU (gray lines) into DNA fibers isolated from a group of BLM+ and BLM− cells, with single fibers depicted in each row
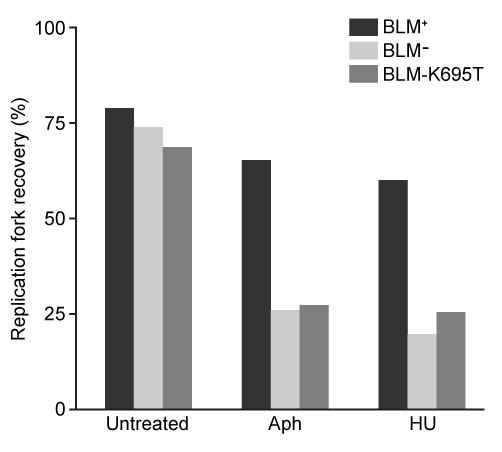 Figure 2 Replication fork recovery in cells expressing BLM+, BLM−, and the mutation BLM-K695T (antagonistic to wild-type)
Figure 2 Replication fork recovery in cells expressing BLM+, BLM−, and the mutation BLM-K695T (antagonistic to wild-type)
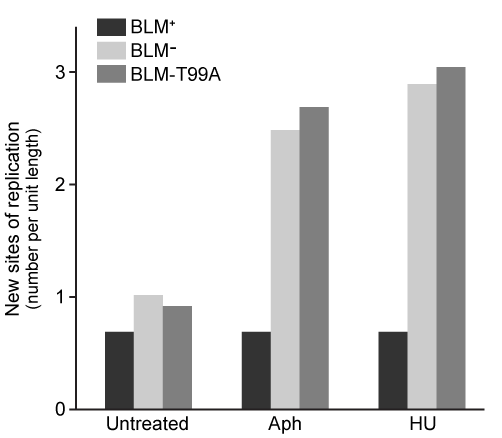 Figure 3 New sites of replication in cells expressing BLM+, BLM−, and the mutation BLM-T99A (T99 phosphorylated after replication arrest)
Figure 3 New sites of replication in cells expressing BLM+, BLM−, and the mutation BLM-T99A (T99 phosphorylated after replication arrest)
Adapted from Davies SL, North PS, Dart A, Lakin ND, Hickson ID. Mol Cell Biol. 2004;24(3) :1279-91.
-After Aph treatment, replication fork recovery in PSNF5 and PSNG13 cells was analyzed as a function of time. Which of the following conclusions explains the data shown in the graph below? 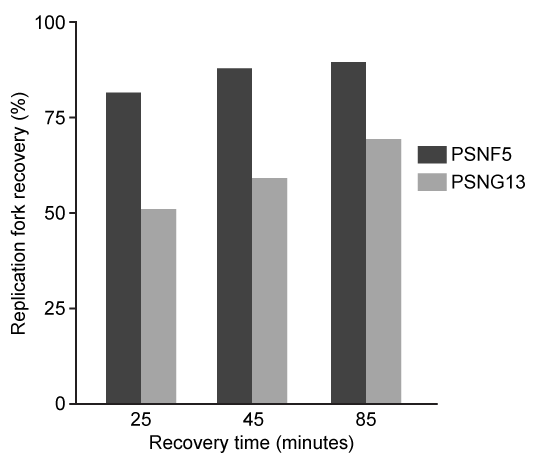
A) The time at which replication fork recovery was assessed serves to predict BLM expression levels in both cell types.
B) During replication fork recovery, the rates of DNA synthesis and somatic recombination differ in the two cell types.
C) PSNG13 cells are less sensitive to the effects of Aph than PSNF5 cells.
D) Recovery time is dependent on the percentage of replication forks that can be rescued.
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q30: Passage
Lipopolysaccharides (LPS) found in gram-negative bacterial cells
Q31: Passage
Quantitative fluorescence recovery after photobleaching (FRAP) is
Q32: Passage
Hematological anomalies have been observed in patients
Q33: Passage
Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC) O157:H7 is a
Q34: Passage
Hematological anomalies have been observed in patients
Q36: Passage
Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC) O157:H7 is a
Q37: Passage
Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC) O157:H7 is a
Q38: Passage
The lumen of the human gut is
Q39: Passage
Hematological anomalies have been observed in patients
Q40: Passage
Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC) O157:H7 is a
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents