Passage
The β-lactam scaffold is an important feature in a class of broad-spectrum antibiotics that includes the penicillins, cephalosporins, and monobactams. These antibiotics are used to treat a variety of diseases caused by bacteria. The penicillins work by inhibiting a step in the synthesis of peptidoglycan. However, the development of antibiotic resistance in the form of enzymes such as β-lactamase is an ongoing problem.An aromatic ring linked to the β-lactam ring has been reported to participate in hydrophobic interactions with β-lactamase active sites, and an aromatic ring bonded to the nitrogen of the β-lactam has shown to be beneficial to biological activity. With this in mind, researchers synthesized a group of penicillanic acid analogues with substituted aromatic rings bonded to the β-lactam ring in an effort to overcome the challenge of antibiotic resistance. The substituents on the aromatic rings were varied, including -OCH3 and -NO2, to make several analogues. A key step in the synthesis of these analogues was the coupling of Compounds 1 and 2 to form a compound with two β-lactam rings (Reaction 1) .
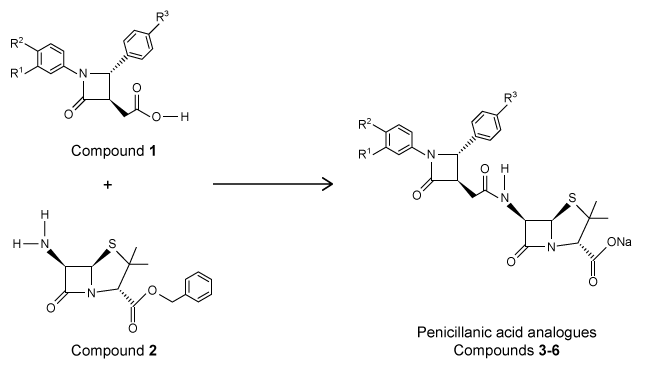 Reaction 1The researchers studied the analogues' structure-activity relationship and antimicrobial activity against the gram-negative bacteria Escherichia coli and the gram-positive bacteria Staphylococcus aureus. Ampicillin, a penicillin derivative used to treat illnesses brought about by gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, was used as a control. The minimal inhibitory concentrations are shown in Table 1.Table 1 Minimal Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)
Reaction 1The researchers studied the analogues' structure-activity relationship and antimicrobial activity against the gram-negative bacteria Escherichia coli and the gram-positive bacteria Staphylococcus aureus. Ampicillin, a penicillin derivative used to treat illnesses brought about by gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, was used as a control. The minimal inhibitory concentrations are shown in Table 1.Table 1 Minimal Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)
 The penicillanic acid analogues were tested for their effect on mammalian cell viability because toxicity to cells is also an important factor to consider for potential drug candidates. The general acceptable level of cell viability for a drug candidate is 70%. These results are shown in Figure 1.
The penicillanic acid analogues were tested for their effect on mammalian cell viability because toxicity to cells is also an important factor to consider for potential drug candidates. The general acceptable level of cell viability for a drug candidate is 70%. These results are shown in Figure 1.
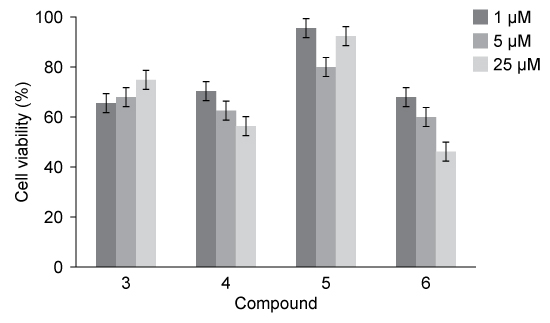 Figure 1 Cell viability assay results
Figure 1 Cell viability assay results
Adapted from De rosa M, Vigliotta G, Palma G, Saturnino C, Soriente A. Novel Penicillin-Type Analogues Bearing a Variable Substituted 2-Azetidinone Ring at Position 6: Synthesis and Biological Evaluation. Molecules. 2015.
-The synthesis of Compound 1 requires hydrolysis of an ester with LiOH and produces a carboxylate ion. The reaction is quenched in the next step by the addition of HCl. What is the expected result if blue litmus paper is immersed in the fully quenched solution? The blue litmus paper will:
A) turn red as the carboxylate becomes protonated.
B) turn red as the carboxylate becomes deprotonated.
C) remain blue as the solution becomes acidic.
D) remain blue as the solution becomes basic.
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q42: Passage
Ethanol is an important source of energy
Q43: Passage
Two key ingredients found in many soaps
Q44: Passage
The β-lactam scaffold is an important feature
Q45: Passage
Two key ingredients found in many soaps
Q46: Passage
Ethanol is an important source of energy
Q48: Passage
Two key ingredients found in many soaps
Q49: Passage
The β-lactam scaffold is an important feature
Q50: Passage
The β-lactam scaffold is an important feature
Q51: Passage
Two key ingredients found in many soaps
Q52: Passage
Ethanol is an important source of energy
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents