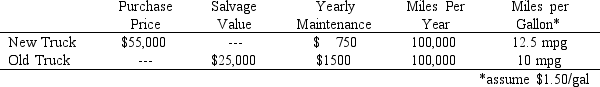
Kornfield Trucking handles private and commercial moves. They currently own 500 moving vans and employ 2000 full-time workers. Their trucks are used to pick-up and deliver office and household goods throughout the Eastern and Southeastern states. Kornfield mans each truck with three workers. This allows driver swaps providing increased miles-covered-per-hour ratio while staying within safety requirements for individual driving time. A 3-person crew also reduces company reliance on local help. Local distributors and warehouses provide a pool of laborers for loading and unloading the moving trucks. While in the past this arrangement has worked well, the arrangement has soured recently as the temporary workers have demanded higher wages while produced less work. Despite their pay and benefits package, Kornfield still finds that the nature of the work (lifting and time on the road) makes for a high rate of turnover. Thus, Kornfield maintains an excess of workers/drivers, but no more than 3.75 workers per truck at any time.The following information is available on the trucks in the Kornfield inventory and their options for new purchases.
 The following information applies to Kornfield personnel actions.
The following information applies to Kornfield personnel actions.
 Kornfield has an operating budget of $ 75M next year and wants to expand their operations. As a part of this expansion, they are considering options for their truck fleet and may purchase new trucks, sell old trucks to salvage or some combination of the two. Any salvage money received is rolled into the operating budget. Kornfield is also considering possible changes to their work force. Their current force has a fairly high average salary and their operating budget is not greatly affected by releasing current employees. On the other hand, newer employees carry a much lower average salary and do not tax the operating budget heavily in hiring and training costs.
Kornfield has an operating budget of $ 75M next year and wants to expand their operations. As a part of this expansion, they are considering options for their truck fleet and may purchase new trucks, sell old trucks to salvage or some combination of the two. Any salvage money received is rolled into the operating budget. Kornfield is also considering possible changes to their work force. Their current force has a fairly high average salary and their operating budget is not greatly affected by releasing current employees. On the other hand, newer employees carry a much lower average salary and do not tax the operating budget heavily in hiring and training costs.
The Cobb-Douglas production function is used to model the number of vehicle miles driven per year. This function represents the quantity Kornfield management would like to maximize as they expand their operations. The general form of the Cobb-Douglas production function is the following: 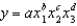 where y is the output, each Xi represents an input and the letters represent constants. This function generalizes to fewer or a greater number of parameters than the three depicted above. The constants for the Kornfield Trucking production function are (a, b, c, d) = (9.1, 0.05, 0.40, 0.50).
where y is the output, each Xi represents an input and the letters represent constants. This function generalizes to fewer or a greater number of parameters than the three depicted above. The constants for the Kornfield Trucking production function are (a, b, c, d) = (9.1, 0.05, 0.40, 0.50).
Formulate the Kornfield Trucking problem as a non-linear programming problem. Implement the problem in Excel and use Risk Solver Platform (RSP) generalized reduced gradient (GRG) routing to obtain a solution to the problem. What is a recommended solution for Kornfield Trucking?
Correct Answer:
Verified
View Answer
Unlock this answer now
Get Access to more Verified Answers free of charge
Q59: An investor is developing a portfolio of
Q61: A construction company just purchased a 300
Q63: Exhibit 8.2
The following questions pertain to the
Q63: How much must the objective function coefficient
Q64: How much are additional units of labor
Q68: Exhibit 8.2
The following questions pertain to the
Q69:
The following questions pertain to the problem
Q71: Exhibit 8.2
The following questions pertain to the
Q75: Exhibit 8.2
The following questions pertain to the
Q78: The Sweet Water beverage company is designing
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents