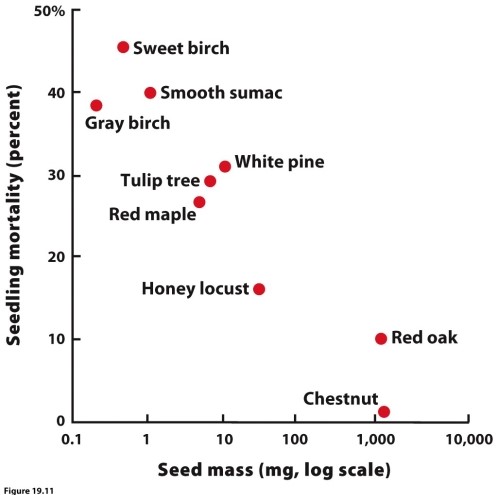
 (Figure 19.11) Given the results in the figure, what might prevent a tree with large seeds, like a chestnut, from establishing in a forest with high densities of sweet birch seeds, an early-succession species?
(Figure 19.11) Given the results in the figure, what might prevent a tree with large seeds, like a chestnut, from establishing in a forest with high densities of sweet birch seeds, an early-succession species?
A) The sweet birch seeds would germinate and grow faster, crowding out the chestnut saplings.
B) A chestnut seed would never be transported a large distance to the sweet birch forest.
C) Sweet birch seedlings exude chemicals that block the germination of chestnut seeds.
D) Chestnut seeds, being large, are more likely to be attacked by insects than sweet birch seeds.
Correct Answer:
Verified
Q32: Secondary succession takes place in habitats that
A)
Q42: What information about species is needed to
Q45: What characteristic shared by diatoms and cyanobacteria
Q47: How do herbivores affect the outcome of
Q48: Typical colonizers in primary succession are mosses
Q49: Topic succession in terrestrial environments
Level: medium
The assumptions
Q51: Jaccard's index quantifies
A) similarity between communities.
B) differences
Q57: Why do plants in early seral stages
Q58: Why are there no spruces in the
Q59: One of the traits common in late-succession
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents