Let 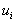 be distributed N(0,
be distributed N(0, 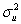 ),i.e. ,the errors are distributed normally with a constant variance (homoskedasticity).This results in
),i.e. ,the errors are distributed normally with a constant variance (homoskedasticity).This results in 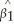 being distributed N(β1,
being distributed N(β1, 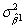 ),where
),where 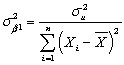 .Statistical inference would be straightforward if
.Statistical inference would be straightforward if 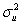 was known.One way to deal with this problem is to replace
was known.One way to deal with this problem is to replace 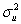 with an estimator
with an estimator 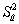 .Clearly since this introduces more uncertainty,you cannot expect
.Clearly since this introduces more uncertainty,you cannot expect 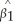 to be still normally distributed.Indeed,the t-statistic now follows Student's t distribution.Look at the table for the Student t-distribution and focus on the 5% two-sided significance level.List the critical values for 10 degrees of freedom,30 degrees of freedom,60 degrees of freedom,and finally ∞ degrees of freedom.Describe how the notion of uncertainty about
to be still normally distributed.Indeed,the t-statistic now follows Student's t distribution.Look at the table for the Student t-distribution and focus on the 5% two-sided significance level.List the critical values for 10 degrees of freedom,30 degrees of freedom,60 degrees of freedom,and finally ∞ degrees of freedom.Describe how the notion of uncertainty about 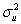 can be incorporated about the tails of the t-distribution as the degrees of freedom increase.
can be incorporated about the tails of the t-distribution as the degrees of freedom increase.
Correct Answer:
Verified
View Answer
Unlock this answer now
Get Access to more Verified Answers free of charge
Q45: Assume that the homoskedastic normal regression assumption
Q48: Using data from the Current Population Survey,you
Q49: Consider the following two models involving binary
Q50: (Requires Appendix material and Calculus)Equation (5.36)in your
Q51: Below you are asked to decide on
Q55: Using the California School data set from
Q56: The neoclassical growth model predicts that for
Q57: Your textbook discussed the regression model when
Q58: Your textbook discussed the regression model when
Q59: Your textbook states that under certain restrictive
Unlock this Answer For Free Now!
View this answer and more for free by performing one of the following actions

Scan the QR code to install the App and get 2 free unlocks

Unlock quizzes for free by uploading documents