
Biochemistry 4th Edition by Christopher Mathews,Kensal van Holde, Dean Appling, Spencer Anthony Cahill
النسخة 4الرقم المعياري الدولي: 978-0138004644
Biochemistry 4th Edition by Christopher Mathews,Kensal van Holde, Dean Appling, Spencer Anthony Cahill
النسخة 4الرقم المعياري الدولي: 978-0138004644 تمرين 17
For parts (a) and (b) of this problem use the following standard reduction potentials, free energies, and nonequilibrium concentrations of reactants and products: 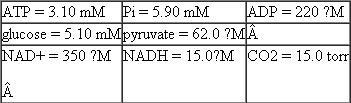
 pyruvate + NADH + 2H + ethanol + NAD + + CO2 AG° = 64.4kJ/mol
pyruvate + NADH + 2H + ethanol + NAD + + CO2 AG° = 64.4kJ/mol
ATP + H2 O ADP + P i + H+ G ° = 30.5kJ/mol
(a) Consider the last two steps in the alcoholic fermentation of glucose by brewer's yeast: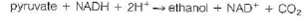
Calculate the nonequilibrium concentration of ethanol in yeast cells, if G = 38.3 kJ/mol for this reaction at pH = 7.4 and 37 °C when the reactants and products are at the concentrations given above.
(b) Consider the degradation of glucose to pyruvate by the glycolytic pathway: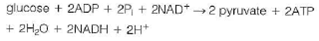
Calculate G for this reaction at pH = 7.4 and 37 °C.

 pyruvate + NADH + 2H + ethanol + NAD + + CO2 AG° = 64.4kJ/mol
pyruvate + NADH + 2H + ethanol + NAD + + CO2 AG° = 64.4kJ/molATP + H2 O ADP + P i + H+ G ° = 30.5kJ/mol
(a) Consider the last two steps in the alcoholic fermentation of glucose by brewer's yeast:
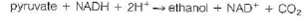
Calculate the nonequilibrium concentration of ethanol in yeast cells, if G = 38.3 kJ/mol for this reaction at pH = 7.4 and 37 °C when the reactants and products are at the concentrations given above.
(b) Consider the degradation of glucose to pyruvate by the glycolytic pathway:
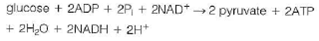
Calculate G for this reaction at pH = 7.4 and 37 °C.
التوضيح
Biochemistry 4th Edition by Christopher Mathews,Kensal van Holde, Dean Appling, Spencer Anthony Cahill
لماذا لم يعجبك هذا التمرين؟
أخرى 8 أحرف كحد أدنى و 255 حرفاً كحد أقصى
حرف 255








