
Advanced Accounting 11th Edition by Paul Fischer,William Tayler, Rita Cheng
النسخة 11الرقم المعياري الدولي: 978-0538480284
Advanced Accounting 11th Edition by Paul Fischer,William Tayler, Rita Cheng
النسخة 11الرقم المعياري الدولي: 978-0538480284 تمرين 4
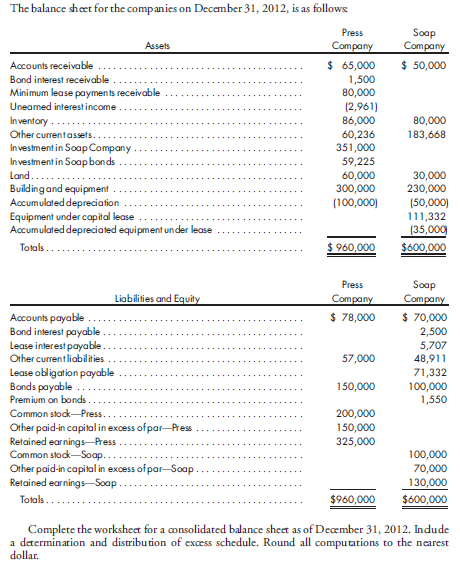
Balance sheet worksheet, intercompany inventory, bonds and capital lease. On January 1, 2011, Press Company acquires 90% of the common stock of Soap Company for $324,000. On this date, Soap has total owners' equity of $270,000, including retained earnings of $100,000.
On January 1, 2011, any excess of cost over book value is attributable to the undervaluation of land, building, and goodwill. Land is worth $20,000 more than cost. Building is worth $40,000 more than book value. It has a remaining useful life of 20 years and is depreciated using the straight-line method.
During 2011 and 2012, Press has appropriately accounted for its investment in Soap using the simple equity method.
During 2012, Soap sells merchandise to Press for $40,000, of which $15,000 is held by Press on December 31, 2012. Soap's usual gross profit on affiliated sales is 40%. On December 31, 2012, Press still owes Soap $8,000 for merchandise acquired in December.
On October 1, 2010, Soap sells $100,000 par value of 10-year, 10% bonds for $102,000. The bonds pay interest semiannually on April 1 and October 1. Straight-line amortization is used. On October 2, 2011, Press repurchases $60,000 par value of the bonds for $59,100. Straight-line amortization is used.
On January 1, 2012, Press purchases equipment for $111,332 and immediately leases the equipment to Soap on a 3-year lease. The minimum lease payments of $40,000 are to be made annually on January 1, beginning immediately, for a total of three payments. The implicit interest rate is 8%. The useful life of the equipment is three years. The lease has been capitalized by both companies. Soap is depreciating the equipment using the straight-line method and assuming a salvage value of $6,332. A lease amortization schedule, applicable to both companies, follows:
On January 1, 2011, any excess of cost over book value is attributable to the undervaluation of land, building, and goodwill. Land is worth $20,000 more than cost. Building is worth $40,000 more than book value. It has a remaining useful life of 20 years and is depreciated using the straight-line method.
During 2011 and 2012, Press has appropriately accounted for its investment in Soap using the simple equity method.
During 2012, Soap sells merchandise to Press for $40,000, of which $15,000 is held by Press on December 31, 2012. Soap's usual gross profit on affiliated sales is 40%. On December 31, 2012, Press still owes Soap $8,000 for merchandise acquired in December.
On October 1, 2010, Soap sells $100,000 par value of 10-year, 10% bonds for $102,000. The bonds pay interest semiannually on April 1 and October 1. Straight-line amortization is used. On October 2, 2011, Press repurchases $60,000 par value of the bonds for $59,100. Straight-line amortization is used.
On January 1, 2012, Press purchases equipment for $111,332 and immediately leases the equipment to Soap on a 3-year lease. The minimum lease payments of $40,000 are to be made annually on January 1, beginning immediately, for a total of three payments. The implicit interest rate is 8%. The useful life of the equipment is three years. The lease has been capitalized by both companies. Soap is depreciating the equipment using the straight-line method and assuming a salvage value of $6,332. A lease amortization schedule, applicable to both companies, follows:


التوضيح
Calculation of Investment
It is given th...
Advanced Accounting 11th Edition by Paul Fischer,William Tayler, Rita Cheng
لماذا لم يعجبك هذا التمرين؟
أخرى 8 أحرف كحد أدنى و 255 حرفاً كحد أقصى
حرف 255








