
Basic Econometrics 5th Edition by Damodar Gujarati,Dawn Porter
النسخة 5الرقم المعياري الدولي: 978-0073375779
Basic Econometrics 5th Edition by Damodar Gujarati,Dawn Porter
النسخة 5الرقم المعياري الدولي: 978-0073375779 تمرين 1
State with reason whether the following statements are true, false, or uncertain. Be precise.
a. The t test of significance discussed in this chapter requires that the sampling distributions of estimators and
and 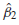 follow the normal distribution.
follow the normal distribution.
b. Even though the disturbance term in the CLRM is not normally distributed, the OLS estimators are still unbiased.
c. If there is no intercept in the regression model, the estimated u i (= û i ) will not sum to zero.
d. The p value and the size of a test statistic mean the same thing.
e. In a regression model that contains the intercept, the sum of the residuals is always zero.
f. If a null hypothesis is not rejected, it is true.
g. The higher the value of 2 , the larger is the variance of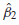 given in Eq. (3.3.1).
given in Eq. (3.3.1).
h. The conditional and unconditional means of a random variable are the same things.
i. In the two-variable PRF, if the slope coefficient 2 is zero, the intercept 1 is estimated by the sample mean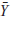 .
.
j. The conditional variance, var ( Y i | X i ) = 2 , and the unconditional variance of Y, var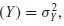 will be the same if X had no influence on Y.
will be the same if X had no influence on Y.
a. The t test of significance discussed in this chapter requires that the sampling distributions of estimators
 and
and 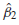 follow the normal distribution.
follow the normal distribution.b. Even though the disturbance term in the CLRM is not normally distributed, the OLS estimators are still unbiased.
c. If there is no intercept in the regression model, the estimated u i (= û i ) will not sum to zero.
d. The p value and the size of a test statistic mean the same thing.
e. In a regression model that contains the intercept, the sum of the residuals is always zero.
f. If a null hypothesis is not rejected, it is true.
g. The higher the value of 2 , the larger is the variance of
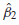 given in Eq. (3.3.1).
given in Eq. (3.3.1). h. The conditional and unconditional means of a random variable are the same things.
i. In the two-variable PRF, if the slope coefficient 2 is zero, the intercept 1 is estimated by the sample mean
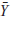 .
.j. The conditional variance, var ( Y i | X i ) = 2 , and the unconditional variance of Y, var
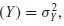 will be the same if X had no influence on Y.
will be the same if X had no influence on Y.التوضيح
In this exercise, the objective is to as...
Basic Econometrics 5th Edition by Damodar Gujarati,Dawn Porter
لماذا لم يعجبك هذا التمرين؟
أخرى 8 أحرف كحد أدنى و 255 حرفاً كحد أقصى
حرف 255








