
Biology 1st Edition by Jerome Krueger, Kendra Hill, Robert Noyd
النسخة 1الرقم المعياري الدولي: 978-1305747852
Biology 1st Edition by Jerome Krueger, Kendra Hill, Robert Noyd
النسخة 1الرقم المعياري الدولي: 978-1305747852 تمرين 17
Plant and animal cells have structures and organelles that reflect their function. Consider three cells: a leaf mesophyll cell (see Fig. 1 ), a root parenchyma cell, and an animal stomach (epithelial) cell (see Fig. 2 ). Which of these cells has (a) mitochondria for ATP production respiration, (b) chloroplasts for photosynthesis, (c) leucoplasts to store starch, (d) ribosomes to make proteins, (e) Golgi complexes to secrete substances outside of the plasma membrane, (f) a nucleus containing chromosomes?
Figure 1 Parts of a plant cell. The main features of a plant cell are shown as they might appear in a photosynthetic cell of a coffee leaf. Photosynthetic cells have thin walls compared to the empty fiber cell shown in the upper left corner of the enlarged cell drawing. Notice that the cytoplasm of the cell is connected to other living cells around it through microscopic openings in their walls.
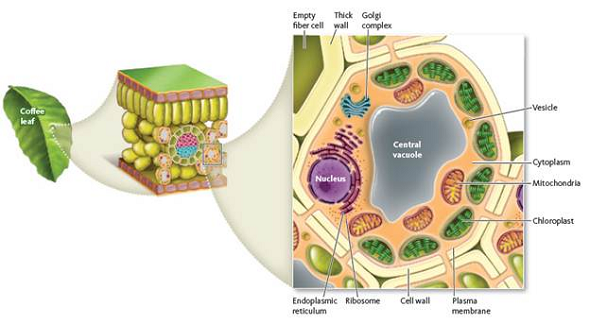
Figure 2 The leatherback's stomach. (a) The leatherback's stomach stores and digests food. (b) The stomach is lined with pits, which contain a variety of cells that secrete digestive enzymes and acids. (c) The photomicrograph shows the cells responsible for secreting acids to break down the prey. (b) The leatherback's stomach cells secrete a digestive enzyme that begins to break down the proteins in the turtle's jellyfish prey.
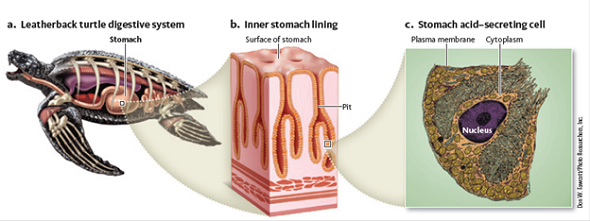
Figure 1 Parts of a plant cell. The main features of a plant cell are shown as they might appear in a photosynthetic cell of a coffee leaf. Photosynthetic cells have thin walls compared to the empty fiber cell shown in the upper left corner of the enlarged cell drawing. Notice that the cytoplasm of the cell is connected to other living cells around it through microscopic openings in their walls.

Figure 2 The leatherback's stomach. (a) The leatherback's stomach stores and digests food. (b) The stomach is lined with pits, which contain a variety of cells that secrete digestive enzymes and acids. (c) The photomicrograph shows the cells responsible for secreting acids to break down the prey. (b) The leatherback's stomach cells secrete a digestive enzyme that begins to break down the proteins in the turtle's jellyfish prey.

التوضيح
Following are the three cells considered...
Biology 1st Edition by Jerome Krueger, Kendra Hill, Robert Noyd
لماذا لم يعجبك هذا التمرين؟
أخرى 8 أحرف كحد أدنى و 255 حرفاً كحد أقصى
حرف 255








