
Molecular Biology of the Gene 7th Edition by Richard Losick, James Watson, Michael Levine, Tamara Baker, Alexander Gann
النسخة 7الرقم المعياري الدولي: 9780321762436
Molecular Biology of the Gene 7th Edition by Richard Losick, James Watson, Michael Levine, Tamara Baker, Alexander Gann
النسخة 7الرقم المعياري الدولي: 9780321762436 تمرين 5
The valyl-tRNA synthetase (ValRS) normally adenylylates and transfers valine to the tRNA Val. At some frequency, the ValRS mischarges tRNA Val with threonine. Researchers wanted to determine what amino acids in the editing pocket of the ValRS are important for editing mischarged Thr-tRNA Val.
A. Why does the ValRS mischarge the tRNA Val with threonine rather than another amino acid?
To study the critical residues in the editing pocket, the researchers made amino acid substitutions at different positions within the editing pocket. They measured the amount of Thr-tRNA Val synthesized or ATP consumed in an in vitro charging reaction that included a mutant or wild-type ValRS. The mutant labeled F264A means that the ValRS includes an alanine at the 264th position rather than phenylalanine. The data are shown below.
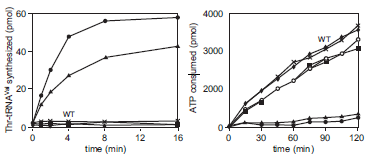
Enzyme activities of ValRS mutants. Wild type, ?; D279A,
 ; K270A, ?; other mutants shown as ?, ?× and *. (Adapted, with permission, from Fukunaga R. and Yokoyama S. 2005. J. Biol. Chem. 280 : 29937-29945, Fig. 5 B,C, p. 29943. © The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology.)
; K270A, ?; other mutants shown as ?, ?× and *. (Adapted, with permission, from Fukunaga R. and Yokoyama S. 2005. J. Biol. Chem. 280 : 29937-29945, Fig. 5 B,C, p. 29943. © The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology.)
B. Given the data on the left, which mutant(s) likely have the most significant loss of editing function relative to the wildtype ValRS? Why?
C. Explain why ATP consumption is higher for wild-type ValRS compared to the K270AValRS.
A. Why does the ValRS mischarge the tRNA Val with threonine rather than another amino acid?
To study the critical residues in the editing pocket, the researchers made amino acid substitutions at different positions within the editing pocket. They measured the amount of Thr-tRNA Val synthesized or ATP consumed in an in vitro charging reaction that included a mutant or wild-type ValRS. The mutant labeled F264A means that the ValRS includes an alanine at the 264th position rather than phenylalanine. The data are shown below.

Enzyme activities of ValRS mutants. Wild type, ?; D279A,
 ; K270A, ?; other mutants shown as ?, ?× and *. (Adapted, with permission, from Fukunaga R. and Yokoyama S. 2005. J. Biol. Chem. 280 : 29937-29945, Fig. 5 B,C, p. 29943. © The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology.)
; K270A, ?; other mutants shown as ?, ?× and *. (Adapted, with permission, from Fukunaga R. and Yokoyama S. 2005. J. Biol. Chem. 280 : 29937-29945, Fig. 5 B,C, p. 29943. © The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology.)B. Given the data on the left, which mutant(s) likely have the most significant loss of editing function relative to the wildtype ValRS? Why?
C. Explain why ATP consumption is higher for wild-type ValRS compared to the K270AValRS.
التوضيح
Threonine structure is similar in size t...
Molecular Biology of the Gene 7th Edition by Richard Losick, James Watson, Michael Levine, Tamara Baker, Alexander Gann
لماذا لم يعجبك هذا التمرين؟
أخرى 8 أحرف كحد أدنى و 255 حرفاً كحد أقصى
حرف 255








