
Financial & Managerial Accounting 17th Edition by Jan Williams ,Susan Haka,Mark Bettner,Joseph Carcello
النسخة 17الرقم المعياري الدولي: 978-0078025778
Financial & Managerial Accounting 17th Edition by Jan Williams ,Susan Haka,Mark Bettner,Joseph Carcello
النسخة 17الرقم المعياري الدولي: 978-0078025778 تمرين 1
Assume that you are the production manager of the Assembly Department illustrated on pages 817-822 of this chapter (Metal Products, Inc.). One of your responsibilities is to determine whether costs are remaining relatively stable from month to month. Assume that the $29,500 associated with the 1,000 units is process on March 1 (see Exhibit 18-5, page 820) is comprised of the following:
 The cost per equivalent unit of input resource used by the Assembly Department in March is as follows (see Exhibit 18-7, page 821):
The cost per equivalent unit of input resource used by the Assembly Department in March is as follows (see Exhibit 18-7, page 821):
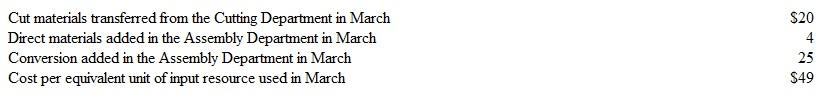 Instructions
Instructions
a. By how much did the cost per equivalent unit of cut material transferred in from the Cutting Department in February differ from the cost per equivalent unit of cut material transferred to the Assembly Department in March ?
b. By how much did the cost per equivalent unit of conversion for the Assembly Department in February differ front the cost per equivalent unit of conversion for the Assembly Department in March ?
c. Speculate as to why the cost per equivalent unit of input resource (cut materials and conversion) may have changed from February to March.
 The cost per equivalent unit of input resource used by the Assembly Department in March is as follows (see Exhibit 18-7, page 821):
The cost per equivalent unit of input resource used by the Assembly Department in March is as follows (see Exhibit 18-7, page 821):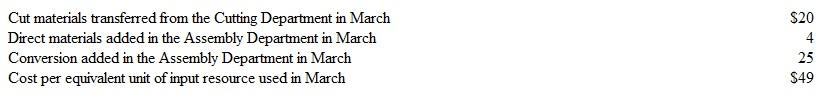 Instructions
Instructions a. By how much did the cost per equivalent unit of cut material transferred in from the Cutting Department in February differ from the cost per equivalent unit of cut material transferred to the Assembly Department in March ?
b. By how much did the cost per equivalent unit of conversion for the Assembly Department in February differ front the cost per equivalent unit of conversion for the Assembly Department in March ?
c. Speculate as to why the cost per equivalent unit of input resource (cut materials and conversion) may have changed from February to March.
التوضيح
a. The cost per equivalent unit of cut m...
Financial & Managerial Accounting 17th Edition by Jan Williams ,Susan Haka,Mark Bettner,Joseph Carcello
لماذا لم يعجبك هذا التمرين؟
أخرى 8 أحرف كحد أدنى و 255 حرفاً كحد أقصى
حرف 255








