
Financial & Managerial Accounting 17th Edition by Jan Williams ,Susan Haka,Mark Bettner,Joseph Carcello
النسخة 17الرقم المعياري الدولي: 978-0078025778
Financial & Managerial Accounting 17th Edition by Jan Williams ,Susan Haka,Mark Bettner,Joseph Carcello
النسخة 17الرقم المعياري الدولي: 978-0078025778 تمرين 38
Smooth Corporation is a small producer of paint. During June, the company produced 10.000 cases of paint. Each case contains twelve quarts of paint. To achieve this level ol production. Smooth purchased and used 34.000 gallons of direct materials at a cost of. $43,520. It also incurred average direct labor costs of $14 per hour for the 8.300 hours worked in June by its production personnel. Manufacturing overhead for the month totaled $21,000. of which $4,500 was considered fixed. Smooth's standard cost information for each case of paint is as follows:
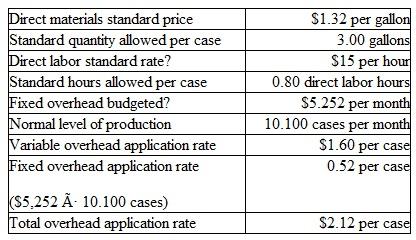 Instructions
Instructions
a. Compute the materials price and quantity variances.
b. Compute the labor rate and efficiency variances.
c. Compute the manufacturing overhead spending and volume variances.
d. Prepare the journal entries to:
1. Charge materials (at standard) to Work in Process.
2. Charge direct labor (at standard) to Work in Process.
3. Charge manufacturing overhead (at standard) to Work in Process.
4. Transfer the cost of the 10.000 cases of paint produced in June to Finished Goods.
5. Close any over- or underapplied overhead to Cost of Goods Sold.
 Instructions
Instructions a. Compute the materials price and quantity variances.
b. Compute the labor rate and efficiency variances.
c. Compute the manufacturing overhead spending and volume variances.
d. Prepare the journal entries to:
1. Charge materials (at standard) to Work in Process.
2. Charge direct labor (at standard) to Work in Process.
3. Charge manufacturing overhead (at standard) to Work in Process.
4. Transfer the cost of the 10.000 cases of paint produced in June to Finished Goods.
5. Close any over- or underapplied overhead to Cost of Goods Sold.
التوضيح
a.
Compute material price variance for u...
Financial & Managerial Accounting 17th Edition by Jan Williams ,Susan Haka,Mark Bettner,Joseph Carcello
لماذا لم يعجبك هذا التمرين؟
أخرى 8 أحرف كحد أدنى و 255 حرفاً كحد أقصى
حرف 255








