
Introduction to Management Science 12th Edition by Bernard Taylor
النسخة 12الرقم المعياري الدولي: 978-0133778847
Introduction to Management Science 12th Edition by Bernard Taylor
النسخة 12الرقم المعياري الدولي: 978-0133778847 تمرين 57
Suppose that in Problem Easy Time can purchase all the baby food it needs from a New York City distributor at a price that will result in a profit of $9 per case at stores 1, 3, and 4; $8 per case at stores 2 and 6; and $7 per case at store 5. Should Easy Time purchase all, none, or some of its baby food from the distributor rather than purchase it at other stores and truck it in
Problem
The Easy Time Grocery chain operates in major metropolitan areas on the East Coast. The stores have a "no-frills" approach, with low overhead and high volume. They generally buy their stock in volume at low prices. However, in some cases they actually buy stock at stores in other areas and ship it in. They can do this because of high prices in the cities they operate in compared with costs in other locations. One example is baby food. Easy Time purchases baby food at stores in Albany, Binghamton, Claremont, Dover, and Edison and then trucks it to six stores in and around New York City. The stores in the outlying areas know what Easy Time is up to, so they limit the number of cases of baby food Easy Time can purchase. The following table shows the profit Easy Time makes per case of baby food, based on where the chain purchases it and at which store it is sold, plus the available baby food per week at purchase locations and the shelf space available at each Easy Time store per week:
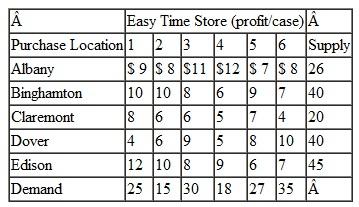 Determine where Easy Time should purchase baby food and how the food should be distributed to maximize profit.
Determine where Easy Time should purchase baby food and how the food should be distributed to maximize profit.
Problem
The Easy Time Grocery chain operates in major metropolitan areas on the East Coast. The stores have a "no-frills" approach, with low overhead and high volume. They generally buy their stock in volume at low prices. However, in some cases they actually buy stock at stores in other areas and ship it in. They can do this because of high prices in the cities they operate in compared with costs in other locations. One example is baby food. Easy Time purchases baby food at stores in Albany, Binghamton, Claremont, Dover, and Edison and then trucks it to six stores in and around New York City. The stores in the outlying areas know what Easy Time is up to, so they limit the number of cases of baby food Easy Time can purchase. The following table shows the profit Easy Time makes per case of baby food, based on where the chain purchases it and at which store it is sold, plus the available baby food per week at purchase locations and the shelf space available at each Easy Time store per week:
 Determine where Easy Time should purchase baby food and how the food should be distributed to maximize profit.
Determine where Easy Time should purchase baby food and how the food should be distributed to maximize profit.التوضيح
First, put together the linear programmi...
Introduction to Management Science 12th Edition by Bernard Taylor
لماذا لم يعجبك هذا التمرين؟
أخرى 8 أحرف كحد أدنى و 255 حرفاً كحد أقصى
حرف 255








