
Introduction to Management Science 12th Edition by Bernard Taylor
النسخة 12الرقم المعياري الدولي: 978-0133778847
Introduction to Management Science 12th Edition by Bernard Taylor
النسخة 12الرقم المعياري الدولي: 978-0133778847 تمرين 23
In Chapter, the formula for the optimal order quantity of an item, Q , given its demand, D , ordering cost, C o, and the cost of holding, or carrying, an item in inventory, C c , is as follows:
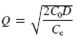
The total inventory cost formula is
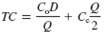
Ordering cost, C o , and carrying cost, C c , are generally values that the company is often able to determine with certainty because they are internal costs, whereas demand, D , is usually not known with certainty because it is external to the company. However, in the order quantity formula given here, demand is treated as if it were certain. To consider the uncertainty of demand, it must be simulated.
Using Crystal Ball, simulate the preceding formulas for Q and TC to determine their average values for an item, with C o = $150, C c = $0.75, and demand, D , that is normally distributed with a mean of 10,000 and a standard deviation of 4,000.
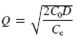
The total inventory cost formula is
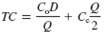
Ordering cost, C o , and carrying cost, C c , are generally values that the company is often able to determine with certainty because they are internal costs, whereas demand, D , is usually not known with certainty because it is external to the company. However, in the order quantity formula given here, demand is treated as if it were certain. To consider the uncertainty of demand, it must be simulated.
Using Crystal Ball, simulate the preceding formulas for Q and TC to determine their average values for an item, with C o = $150, C c = $0.75, and demand, D , that is normally distributed with a mean of 10,000 and a standard deviation of 4,000.
التوضيح
The formula to calculate optimal order q...
Introduction to Management Science 12th Edition by Bernard Taylor
لماذا لم يعجبك هذا التمرين؟
أخرى 8 أحرف كحد أدنى و 255 حرفاً كحد أقصى
حرف 255








