
Accounting for Decision Making and Control 6th Edition by Jerold Zimmerman
النسخة 6الرقم المعياري الدولي: 9780071283700
Accounting for Decision Making and Control 6th Edition by Jerold Zimmerman
النسخة 6الرقم المعياري الدولي: 9780071283700 تمرين 19
Sunder manufactures hard rubber pet toys.The purple dog chewy has a variable cost of $3.00 per unit. It is produced on a machine that is leased.The three models of this machine have three different capacities.
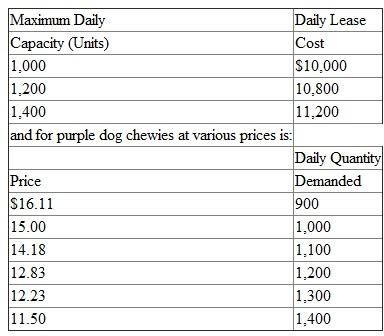 There is no uncertainty (daily variation) with respect to the daily demand for purple dog chewies.
There is no uncertainty (daily variation) with respect to the daily demand for purple dog chewies.
For example, if the price is set at $14.18, 1,100 chewies will be sold every day with certainty.
Required:
a. Given all the data, how many purple dog chewies should Sunder produce and sell (Show calculations, neatly labeled.)
b. Suppose Sunder has the policy of not charging fixed costs to products whenever excess capacity exists. The manager of purple dog chewies receives a bonus based on the accounting profits from purple dog chewies. This manager has private knowledge of machine capacities, lease fees, and the demand for purple dog chewies, as well as the decision rights over how large a machine to lease. How big a machine will the manager lease and how many chewies will be produced and sold (Show calculations, neatly labeled.)
c. Comment on Sunder's policy of not charging fixed costs to products whenever excess capacity exists.
 There is no uncertainty (daily variation) with respect to the daily demand for purple dog chewies.
There is no uncertainty (daily variation) with respect to the daily demand for purple dog chewies.For example, if the price is set at $14.18, 1,100 chewies will be sold every day with certainty.
Required:
a. Given all the data, how many purple dog chewies should Sunder produce and sell (Show calculations, neatly labeled.)
b. Suppose Sunder has the policy of not charging fixed costs to products whenever excess capacity exists. The manager of purple dog chewies receives a bonus based on the accounting profits from purple dog chewies. This manager has private knowledge of machine capacities, lease fees, and the demand for purple dog chewies, as well as the decision rights over how large a machine to lease. How big a machine will the manager lease and how many chewies will be produced and sold (Show calculations, neatly labeled.)
c. Comment on Sunder's policy of not charging fixed costs to products whenever excess capacity exists.
التوضيح
Capacity Cost
A limit cost is a cost ac...
Accounting for Decision Making and Control 6th Edition by Jerold Zimmerman
لماذا لم يعجبك هذا التمرين؟
أخرى 8 أحرف كحد أدنى و 255 حرفاً كحد أقصى
حرف 255








